Abstract
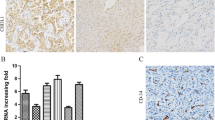
Vasohibin-1 (VASH1) is a newly discovered angiogenesis inhibitor that is specifically expressed in human vascular endothelial cells in response to vascular endothelial growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2. This study aimed to evaluate the expression of VASH1 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and correlates its expression with the clinicopathological parameters and prognosis of the disease. Immunohistochemical analysis was used to determine the expression of VASH1 in NSCLC tissue and adjacent normal tissue from 84 patients. The relationship between VASH1 expression and clinicopathological indicators was examined with the chi-squared test. Moreover, the survival rate was calculated with the Kaplan–Meier survivor curve. Finally, the correlation between the indicators and patient survival was estimated with Cox analysis. VASH1 was high expressed in 63.1 % of NSCLC tissues versus 21.4 % of adjacent tissues (P < 0.01). High VASH1 expression in NSCLC tissue was correlated with clinicopathological features including lymph node status (P = 0.024) and TNM stage (P = 0.036). The Kaplan–Meier curve indicated that the patients with high VASH1 expression had significantly shorter survival than those with low VASH1 expression. In the multivariate Cox regression model, high VASH1 expression was identified as an independent prognostic factor for patients with NSCLC. High VASH1 expression is predictive of poor prognosis of NSCLC, implying that VASH1 may be a promising new target for targeted therapies for NSCLC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(1):10–29.
Jema A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Powell CA, Halmos B, Nana-Sinkam SP. Update in lung cancer and mesothelioma 2012. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188(2):157–66.
Pirker R. Novel drugs against non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2014;26(2):145–51.
Cao Z, Bao M, Miele L, et al. Tumour vasculogenic mimicry is associated with poor prognosis of human cancer patients: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(18):3914–23.
Yazdani S, Miki Y, Tamaki K, et al. Proliferation and maturation of intratumoral blood vessels in non-small cell lung cancer. Hum Pathol. 2013;44(8):1586–96.
Aggarwal C, Somaiah N, Simon G. Antiangiogenic agents in the management of non-small cell lung cancer: where do we stand now and where are we headed? Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13(5):247–63.
Salgia R. Prognostic significance of angiogenesis and angiogenic growth factors in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2011;117(17):3889–99.
Quail DF, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. 2013;19(11):1423–37.
Fagiani E, Christofori G. Angiopoietins in angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2013;49(1):121–31.
Sato Y. The vasohibin family: novel regulators of angiogenesis. Vascul Pharmacol. 2012;56(5–6):262–6.
Sato Y. The vasohibin family: a novel family for angiogenesis regulation. J Biochem. 2013;153(1):5–11.
Wehland M, Bauer J, Magnusson NE, et al. Biomarkers for anti-angiogenic therapy in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(5):9338–64.
Cao R, Ji H, Feng N, et al. Collaborative interplay between FGF-2 and VEGF-C promotes lymphangiogenesis and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(39):15894–9.
Kubota Y. Tumor angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic therapy. Keio J Med. 2012;61(2):47–56.
Eklund L, Saharinen P. Angiopoietin signaling in the vasculature. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(9):1271–80.
Claesson-Welsh L, Welsh M. VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis. J Intern Med. 2013;273(2):114–27.
Tamaki K, Sasano H, Maruo Y, et al. Vasohibin-1 as a potential predictor of aggressive behavior of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(4):1051–8.
Wang Q, Tian X, Zhang C, et al. Upregulation of vasohibin-1 expression with angiogenesis and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative surgery. Med Oncol. 2012;29(4):2727–36.
Kanomata N, Sato Y, Miyaji Y, et al. Vasohibin-1 is a new predictor of disease-free survival in operated patients with renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2013;66(7):613–9.
Takahashi Y, Koyanagi T, Suzuki Y, et al. Vasohibin-2 expressed in human serous ovarian adenocarcinoma accelerates tumor growth by promoting angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 2012;10(9):1135–46.
Yan Y, Shen Z, Ye Y, et al. A novel molecular marker of prognosis in colorectal cancer: vasohibin-1. Med Oncol. 2014;31(2):816.
Zhao G, Yang Y, Tang Y, et al. Reduced expression of vasohibin-1 is associated with clinicopathological features in renal cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2012;29(5):3325–34.
Yoshinaga K, Ito K, Moriya T, et al. Roles of intrinsic angiogenesis inhibitor, vasohibin, in cervical carcinomas. Cancer Sci. 2011;102(2):446–51.
Shen Z, Kauttu T, Seppänen H, et al. Vasohibin-1 and vasohibin-2 expression in gastric cancer cells and TAMs. Med Oncol. 2012;29(4):2718–26.
Miyazaki Y, Kosaka T, Mikami S, et al. The prognostic significance of vasohibin-1 expression in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(15):4145–53.
Shirasuna K, Kobayashi A, Nitta A, et al. Possible action of vasohibin-1 as an inhibitor in the regulation of vascularization of the bovine corpus luteum. Reproduction. 2012;143(4):491–500.
Ito S, Miyashita H, Suzuki Y, et al. Enhanced cancer metastasis in mice deficient in vasohibin-1 gene. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e73931.
Xue X, Gao W, Sun B, et al. Vasohibin 2 is transcriptionally activated and promotes angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2013;32(13):1724–34.
Takahashi Y, Koyanagi T, Suzuki Y, et al. Vasohibin-2 expressed in human serous ovarian adenocarcinoma accelerates tumor growth by promoting angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 2012;10(9):1135–46.
Heishi T, Hosaka T, Suzuki Y, et al. Endogenous angiogenesis inhibitor vasohibin1 exhibits broad-spectrum antilymphangiogenic activity and suppresses lymph node metastasis. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(4):1950–8.
Li D, Zhou K, Wang S, et al. Recombinant adenovirus encoding vasohibin prevents tumor angiogenesis and inhibits tumor growth. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(2):448–52.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Tao Zhang and Ting-Ting Yu have contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Yu, TT., Zhang, DM. et al. Vasohibin-1 expression detected by immunohistochemistry correlates with prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol 31, 963 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0963-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0963-y