Abstract
Microglia are resident macrophages within the central nervous system, serving as the first responders to neuroinflammation. Glucocorticoids (GCs) may cause damage to brain tissue, but the specific mechanism remains unclear. This study was divided into two parts: a glucocorticoid receptor (GR) mitochondrial translocation intervention experiment and a mitochondrial oxidative stress inhibition experiment. BV-2 microglia were stimulated with dexamethasone (DEX) and treated with either tubastatin-A or mitoquinone (MitoQ) for 24 h. Our results showed that DEX increased the translocation of GRs to mitochondria, and this effect was accompanied by decreases in the expression of mitochondrially encoded cytochrome c oxidase 1 (MT-CO1) and mitochondrially encoded cytochrome c oxidase 3 (MT-CO3) and increases in the expression of NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain–associated protein 3 (NLRP3), caspase-1, and Gasdermin D (GSDMD). The level of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex IV (MRCC IV) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) was decreased. An elevation in the level of mitochondrial oxidative stress and the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) was also observed. Mechanistically, tubastatin-A significantly suppressed the mitochondrial translocation of GRs, improved the expression of mitochondrial genes, promoted the restoration of mitochondrial function, and inhibited pyroptosis. MitoQ significantly prevented mitochondrial oxidative stress, improved mitochondrial function, and reduced apoptosis and pyroptosis. Both tubastatin-A and MitoQ suppressed DEX-induced pyroptosis. This study substantiates that the increase in the mitochondrial translocation of GRs mediated by GCs exacerbates oxidative stress and pyroptosis in microglia, which indicates that the regulation of mitochondrial pathways by GCs is pathogenic to microglia.
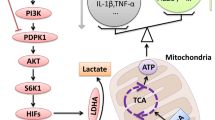
Graphical Abstract
The increase in mitochondrial translocation of GRs mediated by GCs aggravates mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, leading to pyroptosis in BV-2 microglia. Tubastatin-A and MitoQ can inhibit GR translocation and oxidative stress in mitochondria, respectively, and these effects can inhibit pyroptosis and other damage induced by GCs to microglia.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Akyuva Y, Nazıroğlu M, Yıldızhan K (2021) Selenium prevents interferon-gamma induced activation of TRPM2 channel and inhibits inflammation, mitochondrial oxidative stress, and apoptosis in microglia. Metab Brain Dis 36:285–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00624-0
Bhaskaran S, Kumar G, Thadathil N, Piekarz KM, Mohammed S, Lopez SD, Qaisar R, Walton D, Brown JL, Murphy A, Smith N, Saunders D, Beckstead MJ, Plafker S, Lewis TL Jr, Towner R, Deepa SS, Richardson A, Axtell RC, Van Remmen H (2023) Neuronal deletion of MnSOD in mice leads to demyelination, inflammation and progressive paralysis that mimics phenotypes associated with progressive multiple sclerosis. Redox Biol 59:102550–102550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2022.102550
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2038
Bolanos SH, Khan DA, Hanczyc M, Bauer MS, Dhanani N, Brown ES (2004) Assessment of mood states in patients receiving long-term corticosteroid therapy and in controls with patient-rated and clinician-rated scales. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 92:500–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1081-1206(10)61756-5
Bonora M, Giorgi C, Pinton P (2022) Molecular mechanisms and consequences of mitochondrial permeability transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 23(4):266–285. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-021-00433-y
Camm EJ, Tijsseling D, Richter HG, Adler A, Hansell JA, Derks JB, Cross CM, Giussani DA (2011) Oxidative stress in the developing brain: effects of postnatal glucocorticoid therapy and antioxidants in the rat. PLoS One 6:e21142. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0021142
Canet G, Zussy C, Hernandez C, Chevallier N, Marchi N, Desrumaux C, Givalois L (2022) Chronic glucocorticoids consumption triggers and worsens experimental Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology by detrimental immune modulations. Neuroendocrinology 112:982–997. https://doi.org/10.1159/000521559
Caruso G, Di Pietro L, Caraci F (2023) Gap junctions and connexins in microglia-related oxidative stress and neuroinflammation: perspectives for drug discovery. Biomolecules 13:505–505. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030505
Choi GE, Oh JY, Lee HJ, Chae CW, Kim JS, Jung YH, Han HJ (2018) Glucocorticoid-mediated ER-mitochondria contacts reduce AMPA receptor and mitochondria trafficking into cell terminus via microtubule destabilization. Cell Death Dis 9(11):1137. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1172-y
Claros S, Gil A, Martinelli M, Valverde N, Lara E, Boraldi F, Pavia J, Martín-Montañez E, Garcia-Fernandez M (2021) Impact of glucocorticoid on a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease: oxidative stress and mitochondrial function. Brain Sci 11:1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11081106
Drakulić D, Stanojlović M, Nedeljković N, Grković I, Veličković N, Guševac I, Mitrović N, Buzadžić I, Horvat A (2015) Upregulation of nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 and ecto-5′-nucleotidase in rat hippocampus after repeated low-dose dexamethasone administration. J Mol Neurosci 55:959–967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0452-y
Du F, Qian Y, Swerdlow RH, Waites CL (2023) Glucocorticoid-driven mitochondrial damage stimulates Tau pathology. Brain 146:4378–4394. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awad127
Flores-Romero H, Dadsena Shashank, García-Sáez AJ (2023) Mitochondrial pores at the crossroad between cell death and inflammatory signaling. Mol Cell 83:843–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2023.02.021
Forman HJ, Zhang H (2021) Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 20:689–709. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-021-00233-1
Garrud TAC, Giussani DA (2019) Combined antioxidant and glucocorticoid therapy for safer treatment of preterm birth. Trends Endocrinol Metab 30:258–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2019.02.003
Garside H, Stevens A, Farrow S, Normand C, Houle B, Berry A, Maschera B, Ray D (2004) glucocorticoid ligands specify different interactions with NF-κB by allosteric effects on the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain. J Biol Chem 279:50050–50059. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m407309200
Grubman A, Kanninen KM, Malm T (2016) Multitasking microglia and Alzheimer’s disease: diversity, tools and therapeutic targets. J Mol Neurosci 60:390–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0825-5
Hanly JG, Kozora E, Beyea SD, Birnbaum J (2019) Nervous system disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: current status and future directions. Arthritis Rheumatol 71:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40591
Heitzer MD, Wolf IM, Sanchez ER, Witchel SF, DeFranco DB (2007) Glucocorticoid receptor physiology. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 8:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-007-9059-8
Henn A, Lund S, Hedtjärn M, Schrattenholz A, Pörzgen P, Leist M (2009) The suitability of BV2 cells as alternative model system for primary microglia cultures or for animal experiments examining brain inflammation. ALTEX 26(2):83–94. https://doi.org/10.14573/altex.2009.2.83
Kang L, Liu S, Li J, Tian Y, Xue Y, Liu X (2020) The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant MitoQ protects against intervertebral disc degeneration by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and redox imbalance. Cell Prolif 53(3):e12779. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12779
Kesavardhana S, Malireddi RKS, Kanneganti TD (2020) Caspases in cell death, inflammation, and pyroptosis. Annu Rev Immunol 38:567–595. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-073119-095439
Kirschke E, Goswami D, Southworth D, Griffin PR, Agard DA (2014) Glucocorticoid receptor function regulated by coordinated action of the Hsp90 and Hsp70 chaperone cycles. Cell 157:1685–1697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.038
Kokkinopoulou I, Moutsatsou P (2021) Mitochondrial glucocorticoid receptors and their actions. Int J Mol Sci 22:6054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22116054
Kovacs JJ, Murphy PJ, Gaillard S, Zhao X, Wu JT, Nicchitta CV, Yoshida M, Toft DO, Pratt WB, Yao TP (2005) HDAC6 regulates Hsp90 acetylation and chaperone-dependent activation of glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell 18:601–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2005.04.021
Kowalska M, Piekut T, Prendecki M, Sodel A, Kozubski W, Dorszewska J (2020) Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA oxidative damage in physiological and pathological aging. DNA Cell Biol 39(8):1410–1420. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2019.5347
Li ZY, Li QZ, Chen L, Chen BD, Zhang C, Wang X, Li WP (2016) HPOB, an HDAC6 inhibitor, attenuates corticosterone-induced injury in rat adrenal pheochromocytoma PC12 cells by inhibiting mitochondrial GR translocation and the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Neurochem Int 99:239–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2016.08.004
Liu Z, Yao X, Jiang W, Li W, Zhu S, Liao C, Zou L, Ding R, Chen J (2020) Advanced oxidation protein products induce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01751-2
Madore C, Yin Z, Leibowitz J, Butovsky O (2020) Microglia, lifestyle stress, and neurodegeneration. Immunity 52:222–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2019.12.003
Mehl LC, Manjally AV, Bouadi O, Gibson EM, Tay TL (2022) Microglia in brain development and regeneration. Development 149: dev200425. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.200425
Morán M, Moreno-Lastres D, Marín-Buera L, Arenas J, Martín MA, Ugalde C (2012) Mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction: implications in neurodegeneration. Free Radic Biol Med 53:595–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.05.009
Noddings CM, Wang RY-R, Johnson JL, Agard DA (2022) Structure of Hsp90–p23–GR reveals the Hsp90 client-remodelling mechanism. Nature 601:465–469. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04236-1
Oh S, Yang J, Park C, Son K, Byun K (2021) Dieckol attenuated glucocorticoid-induced muscle atrophy by decreasing NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis. Int J Mol Sci 22:8057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158057
Oray M, Abu Samra K, Ebrahimiadib N, Meese H, Foster CS (2016) Long-term side effects of glucocorticoids. Expert Opin Drug Saf 15:457–465. https://doi.org/10.1517/14740338.2016.1140743
Panettieri RA, Schaafsma D, Amrani Y, Koziol-White C, Ostrom R, Tliba O (2019) Non-genomic effects of glucocorticoids: an updated view. Trends Pharmacol Sci 40:38–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2018.11.002
Pedrazzoli M, Losurdo M, Paolone G, Medelin M, Jaupaj L, Cisterna B, Slanzi A, Malatesta M, Coco S, Buffelli M (2019) Glucocorticoid receptors modulate dendritic spine plasticity and microglia activity in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 132:104568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104568
Psarra A-MG, Sekeris CE (2009) Glucocorticoid receptors and other nuclear transcription factors in mitochondria and possible functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1787:431–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.11.011
Qiu Y, Huang Y, Chen M, Yang Y, Li X, Zhang W (2022) Mitochondrial DNA in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int Immunopharmacol 108:108719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108719
Rehman MU, Sehar N, Dar NJ, Khan A, Arafah A, Rashid S, Rashid SM, Ganaie MA (2023) Mitochondrial dysfunctions, oxidative stress and neuroinflammation as therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative diseases: an update on current advances and impediments. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 144:104961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104961
Rostami A, Taleahmad F, Haddadzadeh-Niri N, Joneidi E, Afshin-Majd S, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Roghani M (2022) Sinomenine attenuates trimethyltin-induced cognitive decline via targeting hippocampal oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. J Mol Neurosci 72(8):1609–1621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02021-x
Salim S (2017) Oxidative stress and the central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 360:201–205. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.116.237503
Shen S, Svoboda M, Zhang G, Cavasin MA, Motlova L, McKinsey TA, Eubanks JH, Bařinka C, Kozikowski AP (2020) Structural and in vivo characterization of tubastatin A, a widely used histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 11:706–712. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00560
Shimojo M, Hiroi N, Yakushiji F, Ueshiba H, Yamaguchi N, Miyachi Y (1995) Differences in down-regulation of glucocorticoid receptor mRNA by cortisol, prednisolone and dexamethasone in HeLa cells. Endocr J 42:629–636. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.42.629
Tarr T, Papp G, Nagy N, Cserép E, Zeher M (2017) Chronic high-dose glucocorticoid therapy triggers the development of chronic organ damage and worsens disease outcome in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 36:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3492-6
Tayanloo-Beik A, Kiasalari Z, Roghani M (2022) Paeonol ameliorates cognitive deficits in streptozotocin murine model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Mol Neurosci 72(2):336–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01936-1
Teleanu DM, Niculescu AG, Lungu II, Radu CI, Vladâcenco O, Roza E, Costăchescu B, Grumezescu AM, Teleanu RI (2022) An overview of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci 23:5938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23115938
Trigo D, Avelar C, Fernandes M, Sá J, da Cruz E, Silva O (2022) Mitochondria, energy, and metabolism in neuronal health and disease. FEBS Lett 596:1095–1110. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.14298
Vandewalle J, Luypaert A, De Bosscher K, Libert C (2018) Therapeutic mechanisms of glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol Metab 29:42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2017.10.010
Wang L, Jiao XF, Wu C, Li XQ, Sun HX, Shen XY, Zhang KZ, Zhao C, Liu L, Wang M, Bu YL, Li JW, Xu F, Chang CL, Lu X, Gao W (2021) Trimetazidine attenuates dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy via inhibiting NLRP3/GSDMD pathway-mediated pyroptosis. Cell Death Discov 7(1):251. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00648-0
Wu T, Liang X, Liu X, Li Y, Wang Y, Kong L, Tang M (2020) Induction of ferroptosis in response to graphene quantum dots through mitochondrial oxidative stress in microglia. Part Fibre Toxicol 17(1):30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12989-020-00363-1
Xian H, Watari K, Sanchez-Lopez E, Offenberger J, Onyuru J, Sampath H, Ying W, Hoffman HM, Shadel GS, Karin M (2022) Oxidized DNA fragments exit mitochondria via mPTP- and VDAC-dependent channels to activate NLRP3 inflammasome and interferon signaling. Immunity 55:1370-1385.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2022.06.007
Xiao L, Xu X, Zhang F, Wang M, Xu Y, Tang D, Wang J, Qin Y, Liu Y, Tang C, He L, Greka A, Zhou Z, Liu F, Dong Z, Sun L (2017) The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ ameliorated tubular injury mediated by mitophagy in diabetic kidney disease via Nrf2/PINK1. Redox Biol 11:297–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.022
Yang L, Zhou H, Huang L, Su Y, Kong L, Ji P, Sun R, Wang C, Li W, Li W (2022) Stress level of glucocorticoid exacerbates neuronal damage and Aβ production through activating NLRP1 inflammasome in primary cultured hippocampal neurons of APP-PS1 mice. Int Immunopharmacol 110:108972–108972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108972
Yıldızhan K, Nazıroğlu M (2019) Microglia and its role in neurodegenerative diseases. J Cell Neurosci Oxid Stress 11:861–873. https://doi.org/10.37212/jcnos.683407
Yıldızhan K, Nazıroğlu M (2020) Glutathione depletion and parkinsonian neurotoxin MPP+-induced TRPM2 channel activation play central roles in oxidative cytotoxicity and inflammation in microglia. Mol Neurobiol 57:3508–3525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-01974-7
Yıldızhan K, Nazıroğlu M (2023) NMDA receptor activation stimulates hypoxia-induced TRPM2 channel activation, mitochondrial oxidative stress, and apoptosis in neuronal cell line: modular role of memantine. Brain Res 1803:148232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2023.148232
Zelko IN, Mariani TJ, Folz RJ (2002) Superoxide dismutase multigene family: a comparison of the CuZn-SOD (SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures, evolution, and expression. Free Radic Biol Med 33:337–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-5849(02)00905-x
Zhao Y, Liu B, Xu L, Yu S, Fu J, Wang J, Yan X, Su J (2021) ROS-induced mtDNA release: the emerging messenger for communication between neurons and innate immune cells during neurodegenerative disorder progression. Antioxidants 10:1917–1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10121917
Zhao X, Dang R, Cheng X, Song X, Huang X, Huang C, Liu S, Wang X, Yan P, Yang Y, Fan P, Zhou Y, Zhang S (2022) Effects of compound Ziyin Qingre prescription, NAC and mitoQ on abnormal renal mitochondrial function in dexamethasone-induced MRL/lpr mice. Int J Immunol 45(6):564–574. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4394.2022.06.002
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge all members of the State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease at Guangzhou Medical University for their invaluable support and stimulating discussions.
Funding
Guangzhou City's Construction Project for Tier-Three Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinics, 3208203801, Zhongnanshan Medical Foundation of Guangdong Province, ZNSA-2020013, National Natural Science Foundation of China, 81673983, 82074172, Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, 02820005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DRN, HXY, HXL, CXP, and XXH designed the experiments. DRN, HXY, and HXL performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. HCF, ZXQ, WXR, ZN, and YYQ provided experimental technical support and assisted in completing the study. LN, LS, and YP analyzed the data. ZSY and DYQ participated in the review and coordination. FP, SXH, CXP, and XXH provided the resources. CXP and XXH supervised the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Informed Consent
Not applicable
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, R., Hou, X., Huang, X. et al. Effects of the Glucocorticoid-Mediated Mitochondrial Translocation of Glucocorticoid Receptors on Oxidative Stress and Pyroptosis in BV-2 Microglia. J Mol Neurosci 74, 30 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-024-02192-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-024-02192-9