Abstract
Purpose
The four and a half LIM domain protein 1 (FHL1) has been found to act as a tumor suppressor in several cancers. However, the clinical and functional significance, as well as underlying molecular mechanisms of FHL1 in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) are largely unknown.
Methods
Bioinformatics analyses, qRT-PCR and Western blotting were used to investigate the expression of FHL1 in PTC. Cell proliferation was measured using CCK8, Edu, colony formation, and flow cytometry assays. Cell migration and invasion were examined by wound healing and Transwell assays. qRT-PCR, Western blot, immunofluorescence and Top/Fop reporter assays were performed to assess the underlying mechanisms.
Results
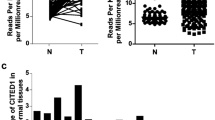
FHL1 expression was significantly downregulated in PTC. FHL1 downregulation negatively correlated with stage, T classification, and N classification of the patients. The downregulation of FHL1 is associated with poor prognosis. Overexpression of FHL1 inhibited PTC cells’ proliferation, invasion, migration and Wnt/β-catenin pathway activity. LiCl partially restored the inhibitory effects of FHL1 on aggressive phenotypes and Wnt/β-catenin pathway activity of PTC cells.
Conclusion
FHL1 is downregulated in PTC and its expression is associated with better clinical outcomes for patients with the disease. FHL1 acts as a tumor suppressor via, at least partially, suppressing Wnt/β-catenin pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The analyzed data sets generated during the study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
T. Shathasivam, T. Kislinger, A.O. Gramolini, Genes, proteins and complexes: the multifaceted nature of FHL family proteins in diverse tissues. J. Cell Mol. Med. 14, 2702–2720 (2010)
X. Cai, J. Wang, X. Huang, W. Fu, W. Xia, M. Zou et al. Identification and characterization of MT-1X as a novel FHL3-binding partner. PLoS One 9, e93723 (2014)
J. Lin, L. Ding, R. Jin, H. Zhang, L. Cheng, X. Qin et al. Four and a half LIM domains 1 (FHL1) and receptor interacting protein of 140kDa (RIP140) interact and cooperate in estrogen signaling. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41, 1613–1618 (2009)
B.S. Cowling, M.J. McGrath, M.A. Nguyen, D.L. Cottle, A.J. Kee, S. Brown et al. Identification of FHL1 as a regulator of skeletal muscle mass: implications for human myopathy. J. Cell Biol. 183, 1033–1048 (2008)
J. Schessl, S. Feldkirchner, C. Kubny, B. Schoser, Reducing body myopathy and other FHL1-related muscular disorders. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 18, 257–263 (2011)
Y. Liu, C. Wang, P. Cheng, S. Zhang, W. Zhou, Y. Xu et al. FHL1 inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Cancer 12, 5345–5354 (2021)
C. Niu, C. Liang, J. Guo, L. Cheng, H. Zhang, X. Qin et al. Downregulation and growth inhibitory role of FHL1 in lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 130, 2549–2556 (2012)
L. Ding, C. Niu, Y. Zheng, Z. Xiong, Y. Liu, J. Lin et al. FHL1 interacts with oestrogen receptors and regulates breast cancer cell growth. J. Cell Mol. Med. 15, 72–85 (2011)
Y. Xu, Z. Liu, K. Guo, Expression of FHL1 in gastric cancer tissue and its correlation with the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. Mol. Cell Biochem. 363, 93–99 (2012)
J. Wang, F. Huang, J. Huang, J. Kong, S. Liu, J. Jin, Epigenetic analysis of FHL1 tumor suppressor gene in human liver cancer. Oncol. Lett. 14, 6109–6116 (2017)
Y. Liu, H. Li, Y. Zhao, D. Li, Q. Zhang, J. Fu et al. Targeting FHL1 impairs cell proliferation and differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Biochem. Cell Biol. 100, 301–308 (2022)
C. Wang, X. Lv, C. He, J.S. Davis, C. Wang, G. Hua, Four and a Half LIM Domains 2 (FHL2) Contribute to the Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 7751 (2020)
W. Zhang, J. Wang, B. Zou, C. Sardet, J. Li, C.S. Lam et al. Four and a half LIM protein 2 (FHL2) negatively regulates the transcription of E-cadherin through interaction with Snail1. Eur. J. Cancer 47, 121–130 (2011)
E. Zienert, I. Eke, D. Aust, N. Cordes, LIM-only protein FHL2 critically determines survival and radioresistance of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 364, 17–24 (2015)
L. Qiao, Y. Wang, R. Pang, J. Wang, Y. Dai, J. Ma et al. Oncogene functions of FHL2 are independent from NF-kappaBIalpha in gastrointestinal cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 15, 31–36 (2009)
Y. Nouët, J. Dahan, C. Labalette, F. Levillayer, B. Julien, G. Jouvion et al. The four and a half LIM-only protein 2 regulates liver homeostasis and contributes to carcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 57, 1029–1036 (2012)
G. Cao, P. Li, X. He, M. Jin, M. Li, S. Chen et al. FHL3 contributes to EMT and chemotherapy resistance through up-regulation of slug and activation of TGFβ/Smad-independent pathways in gastric cancer. Front. Oncol. 11, 649029 (2021)
P. Li, G. Cao, Y. Zhang, J. Shi, K. Cai, L. Zhen et al. FHL3 promotes pancreatic cancer invasion and metastasis through preventing the ubiquitination degradation of EMT associated transcription factors. Aging (Albany NY) 12, 53–69 (2020)
C. Niu, Z. Yan, L. Cheng, J. Zhu, H. Zhang, X. Xu et al. Downregulation and antiproliferative role of FHL3 in breast cancer. IUBMB Life 63, 764–771 (2011)
C.M. Kitahara, J.A. Sosa, The changing incidence of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 12, 646–653 (2016)
S.R. Chung, J.H. Baek, Y.J. Choi, J.H. Lee, Longer-term outcomes of radiofrequency ablation for locally recurrent papillary thyroid cancer. Eur. Radio. 29, 4897–4903 (2019)
S. Ulisse, E. Baldini, A. Lauro, D. Pironi, D. Tripodi, E. Lori et al. Papillary thyroid cancer prognosis: an evolving field. Cancers (Basel) 13, 5567 (2021)
M.A. Adam, J. Pura, L. Gu, M.A. Dinan, D.S. Tyler, S.D. Reed et al. Extent of surgery for papillary thyroid cancer is not associated with survival: an analysis of 61,775 patients. Ann. Surg. 260, 601–605 (2014).
J.S. Radowsky, R.S. Howard, H.B. Burch, A. Stojadinovic, Impact of degree of extrathyroidal extension of disease on papillary thyroid cancer outcome. Thyroid 24, 241–244 (2014)
R. Nusse, H. Clevers, Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 169, 985–999 (2017)
Y. Zhang, X. Wang, Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 13, 165 (2020)
T. Valenta, G. Hausmann, K. Basler, The many faces and functions of β-catenin. Embo J. 31, 2714–2736 (2012)
M.T. Veeman, J.D. Axelrod, R.T. Moon, A second canon. Functions and mechanisms of beta-catenin-independent Wnt signaling. Dev. Cell 5, 367–377 (2003)
B. Das, D. Sinha, Diallyl disulphide suppresses the cannonical Wnt signaling pathway and reverses the fibronectin-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition of A549 lung cancer cells. Food Funct. 10, 191–202 (2019)
N. Aguilera-Montilla, E. Bailón, R. Uceda-Castro, E. Ugarte-Berzal, A. Santos, A. Gutiérrez-González et al. MMP-9 affects gene expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia revealing CD99 as an MMP-9 target and a novel partner in malignant cell migration/arrest. Oncogene 38, 4605–4619 (2019)
M.K. Shi, Y.L. Xuan, X.F. He, FHL1 overexpression as a inhibitor of lung cancer cell invasion via increasing RhoGDIß mRNA expression. Cell J. 24, 239–244 (2022)
X. Li, Z. Jia, Y. Shen, H. Ichikawa, J. Jarvik, R.G. Nagele et al. Coordinate suppression of Sdpr and Fhl1 expression in tumors of the breast, kidney, and prostate. Cancer Sci. 99, 1326–1333 (2008)
A. Sebio, M. Kahn, H.J. Lenz, The potential of targeting Wnt/β-catenin in colon cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 18, 611–615 (2014)
R. Dahmani, P.A. Just, C. Perret, The Wnt/β-catenin pathway as a therapeutic target in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Res Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 35, 709–713 (2011)
T. Hu, C. Li, Convergence between Wnt-β-catenin and EGFR signaling in cancer. Mol. Cancer 9, 236 (2010)
L. Chen, F. Qin, X. Deng, J. Avruch, D. Zhou, Hippo pathway in intestinal homeostasis and tumorigenesis. Protein Cell 3, 305–310 (2012)
W. Zheng, M. Yao, M. Wu, J. Yang, D. Yao, L. Wang, Secretory clusterin promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by facilitating cancer stem cell properties via AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin axis. J. Transl. Med. 18, 81 (2020)
T. Liu, Q. Wei, J. Jin, Q. Luo, Y. Liu, Y. Yang et al. The m6A reader YTHDF1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via augmenting EIF3C translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, 3816–3831 (2020)
Funding
The funding for this project was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82073050 and No. 82201551); Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 2019A1515012046 and No. 2019A1515010275); Guangzhou Technology Project (No. 202102080311).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.H.Y. and L.Y.B. contributed to the conception and the design of the work. J.J.W. and Z.P.Y. offered administrative support. Z.Y.L. and Z.H.R. provided materials for the study. C.J.X., Z.C.M. and Z.Y.L. contributed to implementation of the experiment and analysis of data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Research Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. The samples were obtained with informed consent from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Zeng, C., Jin, J. et al. Overexpression of FHL1 suppresses papillary thyroid cancer proliferation and progression via inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Endocrine (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-023-03675-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-023-03675-2