Abstract
Purpose
Lipid parameters have been shown to have significant predictive value for cardiovascular disease, but few studies have evaluated their correlation with erectile dysfunction (ED) in young men.
Methods
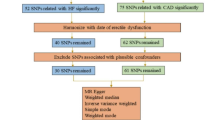
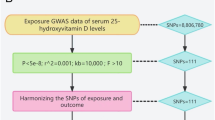
The case-control study encompassed 186 young ED patients (ages 20–40) and 186 healthy controls. Lipid parameters, including total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), TC/HDL ratio, TG/HDL ratio, and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio, were assessed in all participants. The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) scores were collected for all participants to evaluate erectile status. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was utilized to appraise the association of lipid-related parameters with ED. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) significantly correlated with lipid parameters (TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C) were selected from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) as instrumental variables (IV) (P < 5.0 × 10−8). Summary data for ED was gathered from a GWAS with a sample size of (n = 17,353 cases/28,210 controls). The inverse variance weighted (IVW) method was employed as the primary mendelian randomization (MR) analysis method to assess causal effects. Causal estimates were represented as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results
Results from the case-control study revealed that, when compared with the control group, levels of LDL-C, TG, UA, LDL-C/HDL-C, TG/HDL-C, and TC/HDL-C in the ED group were significantly elevated (P < 0.01), while HDL-C was significantly decreased (P < 0.01) in the ED group. Multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated LDL-C/HDL-C as a risk factor for both the incidence and severity of ED (P < 0.001). Two-sample MR analysis demonstrated no significant causal correlation between lipid parameters—LDL-C (OR, 0.98, 95% CI, 0.88–1.08, P = 0.616), HDL-C (OR, 1.07, 95% CI: 0.96–1.19, P = 0.249), TC (OR, 1.07, 95% CI, 0.96–1.18, P = 0.208), TG (OR, 0.98, 95% CI, 0.80–1.13, P = 0.579) —and an increased risk of ED (all P > 0.05).
Conclusions
The case-control analysis ascertained a significant association between LDL-C, HDL-C, LDL-C/HDL-C, and ED and its severity. However, results from the MR study do not support a causal role of lipid parameters in ED.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.B. Najari, J.A. Kashanian, Erectile dysfunction. JAMA 316, 1838 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.12284
R. Shamloul, H. Ghanem, Erectile dysfunction. Lancet 381, 153–165 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(12)60520-0
L. Antonio L., F.C.W. Wu, H. Moors, C. Matheï, I.T. Huhtaniemi, G. Rastrelli, M. Dejaeger, T.W. O’Neill, S.R. Pye, G. Forti et al. Erectile dysfunction predicts mortality in middle-aged and older men independent of their sex steroid status. Age Ageing 51, (2022), https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afac094
P. Capogrosso, M. Colicchia, E. Ventimiglia, G. Castagna, M.C. Clementi, N. Suardi, F. Castiglione, A. Briganti, F. Cantiello, R. Damiano et al. One patient out of four with newly diagnosed erectile dysfunction is a young man–worrisome picture from the everyday clinical practice. J. Sex. Med. 10, 1833–1841 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12179
O.A. Orimoloye, D.I. Feldman, M.J. Blaha, Erectile dysfunction links to cardiovascular disease-defining the clinical value. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 29, 458–465 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2019.01.002
D. Terentes-Printzios, N. Ioakeimidis, K. Rokkas, C. Vlachopoulos, Interactions between erectile dysfunction, cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular drugs. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 19, 59–74 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-021-00593-6
Â. Castela, C. Costa, Molecular mechanisms associated with diabetic endothelial-erectile dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Urol. 13, 266–274 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2016.23
A.W. Pastuszak, D.A. Hyman, N. Yadav, G. Godoy, L.I. Lipshultz, A.B. Araujo, M. Khera, Erectile dysfunction as a marker for cardiovascular disease diagnosis and intervention: a cost analysis. J. Sex. Med. 12, 975–984 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12848
X. Cai, Y. Tian, T. Wu, C.X. Cao, S.Y. Bu, K.J. Wang, The role of statins in erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian J. Androl. 16, 461–466, (2014). https://doi.org/10.4103/1008-682x.123678
W.J. Ma, M. Qin, T.W. Cui, X.P. Zhang, Z.H. Ke, Z.K. Pan, Y.X. Gao, B.X. Liu, Relationship between the risk factors of cardiovascular disease by testing biochemical markers and young men with erectile dysfunction: a case-control study. Transl. Androl. Urol. 10, 724–733 (2021). https://doi.org/10.21037/tau-20-1056
G. Corona, D.M. Lee, G. Forti, D.B. O’Connor, M. Maggi, T.W. O’Neill, N. Pendleton, G. Bartfai, S. Boonen, F.F. Casanueva et al. Age-related changes in general and sexual health in middle-aged and older men: results from the European Male Ageing Study (EMAS). J. Sex. Med. 7, 1362–1380 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01601.x
G. Jackson, Prediction of coronary artery disease by erectile function status: evidence-based data. Sex. Med. Rev. 1, 104–107 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/smrj.12
E.O. Laumann, S. West, D. Glasser, C. Carson, R. Rosen, J.H. Kang, Prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction by race and ethnicity among men aged 40 or older in the United States: from the male attitudes regarding sexual health survey. J. Sex. Med. 4, 57–65 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00340.x
M.K. Kim, K. Han, H.S. Kim, K.H. Yoon, S.H. Lee, Lipid cutoffs for increased cardiovascular disease risk in non-diabetic young people. Eur. J. preventive Cardiol. 29, 1866–1877 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1093/eurjpc/zwac139
Z. Zhong, J. Hou, Q. Zhang, W. Zhong, B. Li, C. Li, Z. Liu, M. Yang, P. Zhao, Assessment of the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio as a predictor of one year clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes after percutaneous coronary intervention and drug-eluting stent implantation. Lipids health Dis. 18, 40 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-019-0979-6
M. Nayor, R.S. Vasan, Recent Update to the US Cholesterol Treatment Guidelines: A Comparison With International Guidelines. Circulation 133, 1795–1806 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.116.021407
J. Huang, B. Su, V. Karhunen, D. Gill, V. Zuber, A. Ahola-Olli, S. Palaniswamy, J. Auvinen, K.H. Herzig, S. Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi et al. Inflammatory diseases, inflammatory biomarkers, and alzheimer disease: an observational analysis and Mendelian randomization. Neurology 100, e568–e581 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000201489
E. Sanderson, M.M. Glymour, M.V. Holmes, H. Kang, J. Morrison, M.R. Munafò, T. Palmer, C.M. Schooling, C. Wallace, Q. Zhao et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-021-00092-5
R. Aleksandra, S. Aleksandra, R. Iwona, Erectile dysfunction in relation to metabolic disorders and the concentration of sex hormones in aging men. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19, (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137576
V.W. Skrivankova, R.C. Richmond, B.A.R. Woolf, J. Yarmolinsky, N.M. Davies, S.A. Swanson, T.J. VanderWeele, J.P.T. Higgins, N.J. Timpson, N. Dimou et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization: the STROBE-MR statement. JAMA 326, 1614–1621, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.18236
J. Bovijn, L. Jackson, J. Censin, C.Y. Chen, T. Laisk, S. Laber, T. Ferreira, S.L. Pulit, C.A. Glastonbury, J.W. Smoller et al. GWAS identifies risk locus for erectile dysfunction and implicates hypothalamic neurobiology and diabetes in etiology. Am. J. Hum. Genet 104, 157–163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.11.004
B. Bao, J. Guo, L. Zhang, Z. Pan, H. Huang, Z. Qin, L. Chen, X. Zhou, B. Liu. Effects of obesity-related anthropometric indices and body composition on erectile dysfunction mediated by coronary artery disease: a Mendelian randomization study. Andrology (2023), https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.13443
C. de Leeuw, J. Savage, I.G. Bucur, T. Heskes, D. Posthuma, Understanding the assumptions underlying Mendelian randomization. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. : EJHG 30, 653–660 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-022-01038-5
Q. Zhang, X. Zhang, J. Zhang, M. Jiang, Y. Zhang, D. Zheng, L. Wu, W. Wang, B. Wang, Y. Wang, Genetic association and causal inference between lung function and venous thromboembolism. Respiratory Res. 24, 36 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-023-02335-3
G. Chen, Q. Wang, R. Xue, X. Liu, H. Yu, Examining the causal inference of leptin and soluble plasma leptin receptor levels on schizophrenia: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Psychiatry 12, 753224 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.753224
J. Bowden, G. Davey Smith, S. Burgess, Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 44, 512–525 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv080
J. Bowden, G. Davey Smith, P.C. Haycock, S. Burgess, Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 40, 304–314 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.21965
F.P. Hartwig, G. Davey Smith, J. Bowden, Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 46, 1985–1998 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyx102
S. Burgess, S.G. Thompson, Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 32, 377–389 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-017-0255-x
X. Wu, G. Liu, Y. Zhang, W. Zhang, Y. Dai, H. Jiang, X. Zhang, The association between uric acid and erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Andrologia 54, e14319 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1111/and.14319
J. Xu, Z. Xu, H. Pan, Z. Zhou, Association between erectile dysfunction and Helicobacter pylori, folic acid, vitamin B12, and homocysteine: a cross-sectional study. Sex. Med. 11, qfac018 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1093/sexmed/qfac018
D.J. Hawksworth, A.L. Burnett, Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, male sexual dysfunction, and infertility: common links, common problems. Sex. Med. Rev. 8, 274–285 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sxmr.2019.01.002
M. Nikoobakht, M. Pourkasmaee, H. Nasseh, The relationship between lipid profile and erectile dysfunction. Urol. J. 2, 40–44 (2005)
S.C. Kim, Hyperlipidemia and erectile dysfunction. Asian J. Androl. 2, 161–166 (2000)
A. Ghosh, L. Gao, A. Thakur, P.M. Siu, C.W.K. Lai, Role of free fatty acids in endothelial dysfunction. J. Biomed. Sci. 24, 50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-017-0357-5
F. Yao, Y. Huang, Y. Zhang, Y. Dong, H. Ma, C. Deng, H. Lin, D. Liu, K. Lu, Subclinical endothelial dysfunction and low-grade inflammation play roles in the development of erectile dysfunction in young men with low risk of coronary heart disease. Int. J. Androl. 35, 653–659 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2605.2012.01273.x
D.I. Feldman, M. Cainzos-Achirica, K.L. Billups, A.P. DeFilippis, K. Chitaley, P. Greenland, J.H. Stein, M.J. Budoff, Z. Dardari, M. Miner et al. Subclinical vascular disease and subsequent erectile dysfunction: the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). Clin. Cardiol. 39, 291–298 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.22530
G. Rastrelli, M. Maggi, Erectile dysfunction in fit and healthy young men: psychological or pathological? Transl. Androl. Urol. 6, 79–90 (2017). https://doi.org/10.21037/tau.2016.09.06
Y. Lou, X. Li, L. Cao, P. Qin, J. Shi, Y. Zhang, C. Wang, J. Ma, L. Wang, X. Peng et al. LDL-cholesterol to HDL-cholesterol ratio discordance with lipid parameters and carotid intima-media thickness: a cohort study in China. Lipids health Dis. 19, 141 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-020-01324-5
M. Li, Z. Ma, X.L. Zhang, L.Q. Guo, M.Z. Yuan, Significance of blood lipid parameters as effective markers for arteriogenic erectile dysfunction. Andrology 8, 1086–1094 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12776
D.R. Kaiser, K. Billups, C. Mason, R. Wetterling, J.L. Lundberg, A.J. Bank, Impaired brachial artery endothelium-dependent and -independent vasodilation in men with erectile dysfunction and no other clinical cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 43, 179–184 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2003.07.042
P. Montorsi, P.M. Ravagnani, S. Galli, F. Rotatori, A. Briganti, A. Salonia, P. Rigatti, F. Montorsi, The artery size hypothesis: a macrovascular link between erectile dysfunction and coronary artery disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 96, 19m–23m (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.07.006
J.Y. Dong, Y.H. Zhang, L.Q. Qin, Erectile dysfunction and risk of cardiovascular disease: meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 58, 1378–1385 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2011.06.024
G. Davey Smith, G. Hemani, Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 23, R89–98, (2014). https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu328
B.A. Ference, M.V. Holmes, G.D. Smith, Using Mendelian randomization to improve the design of randomized trials. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Med. 11, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a040980
D.A. Lawlor, R.M. Harbord, J.A. Sterne, N. Timpson, G. Davey Smith, Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat. Med. 27, 1133–1163 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.3034
R.E. Peterson, K. Kuchenbaecker, R.K. Walters, C.Y. Chen, A.B. Popejoy, S. Periyasamy, M. Lam, C. Iyegbe, R.J. Strawbridge, L. Brick et al. Genome-wide association studies in ancestrally diverse populations: opportunities, methods, pitfalls, and recommendations. Cell 179, 589–603 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.051
R. Mägi, M. Horikoshi, T. Sofer, A. Mahajan, H. Kitajima, N. Franceschini, M.I. McCarthy, A.P. Morris, Trans-ethnic meta-regression of genome-wide association studies accounting for ancestry increases power for discovery and improves fine-mapping resolution. Hum. Mol. Genet. 26, 3639–3650 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx280
R.C. Rosen, J.C. Cappelleri, M.D. Smith, J. Lipsky, B.M. Peña, Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 11, 319–326 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900472
Author contributions
M.K. and B.B. conceived the study and wrote and revised the report. Z.K., W.M., and L.Z. analyzed the data. J.G., H.W. assisted in the study’s implementation. B.L., G.F., and L.M. modified the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ke, M., Bao, B., Ke, Z. et al. The association between lipid parameters and erectile dysfunction: a two-sample Mendelian randomization and case-control study. Endocrine (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-023-03653-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-023-03653-8