Abstract
Background
Diabetes mellitus is a prevalent comorbidity in pancreatic cancer. Previous studies have mainly concentrated on the association between diabetes and pancreatic cancer outcomes. However, research on the impact of hyperglycemia on the prognosis of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer is limited.
Methods
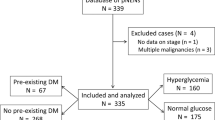
Information on patients with advanced pancreatic cancer was collected from a prospectively maintained database, and the patients were divided into the hyperglycemia group (fasting blood glucose ≥7.0 mmol/L) and the normoglycemia group (fasting blood glucose < 7.0 mmol/L). Patients with preexisting diabetes were not included in these groups. The associations between hyperglycemia and clinical variables or prognosis were analyzed.
Results
Among 697 patients with advanced pancreatic cancer and no prior history of diabetes, 25.3% were diagnosed with hyperglycemia. Patients older than 65 years had a higher risk of developing hyperglycemia (P = 0.044). Patients with hyperglycemia had a worse prognosis than those with normoglycemia (median survival, 7.5 vs. 8.8 months, P < 0.001). Hyperglycemia was associated with increased mortality (hazard ratio = 1.38; P = 0.003).
Conclusions
Hyperglycemia predicts worse overall survival in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.P. Klein, Pancreatic cancer epidemiology: understanding the role of lifestyle and inherited risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18(7), 493–502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-021-00457-x
T. Okusaka, M. Nakamura, M. Yoshida, M. Kitano, K. Uesaka, Y. Ito, J. Furuse, K. Hanada, S. K. Okazaki, Committee for Revision of Clinical Guidelines for Pancreatic Cancer of the Japan Pancreas, Clinical Practice Guidelines for Pancreatic Cancer 2019 From the Japan Pancreas Society: A Synopsis. Pancreas 49(3), 326–335 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000001513
R. Ranganath, Q. Chu, Global trends in pancreas cancer among Asia-Pacific population. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 12(Suppl 2), S374–S386 (2021). https://doi.org/10.21037/jgo-20-118
L. Rahib, B.D. Smith, R. Aizenberg, A.B. Rosenzweig, J.M. Fleshman, L.M. Matrisian, Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 74(11), 2913–2921 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0155
J.X. Hu, C.F. Zhao, W.B. Chen, Q.C. Liu, Q.W. Li, Y.Y. Lin, F. Gao, Pancreatic cancer: A review of epidemiology, trend, and risk factors. World J. Gastroenterol. 27(27), 4298–4321 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4298
T. Hackert, U. Klaiber, T. Pausch, A.L. Mihaljevic, M.W. Buchler, Fifty years of surgery for pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 49(8), 1005–1013 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000001634
W. Park, A. Chawla, E.M. O’Reilly, Pancreatic cancer: a review. JAMA 326(9), 851–862 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.13027
U. Walter, T. Kohlert, N.N. Rahbari, J. Weitz, T. Welsch, Impact of preoperative diabetes on long-term survival after curative resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 21(4), 1082–1089 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3415-6
C.K. Chu, A.E. Mazo, M. Goodman, V. Egnatashvili, J.M. Sarmiento, C.A. Staley, J.R. Galloway, N.V. Adsay, S. Jacobs, D.A. Kooby, Preoperative diabetes mellitus and long-term survival after resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surgical Oncol. 17(2), 502–513 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0789-6
S.J.S. Nagpal, H. Kandlakunta, T. Her, A. Sharma, S. Sannapaneni, T.C. Smyrk, P. Velamala, S.K. Garg, K. Rakshit, S. Majumder, S. Chari, A. Matveyenko, Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is associated with a unique endocrinopathy distinct from type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pancreatol.: Off. J. Int. Assoc. Pancreatol. 20(5), 929–935 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2020.05.010
V. Morales-Oyarvide, M. Mino-Kenudson, C.R. Ferrone, D.V. Sahani, I. Pergolini, A.A. Negreros-Osuna, A.L. Warshaw, K.D. Lillemoe, C. Fernandez-Del Castillo, Diabetes mellitus in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas is associated with high-grade dysplasia and invasive carcinoma. Pancreatol.: Off. J. Int. Assoc. Pancreatol. 17(6), 920–926 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2017.08.073
C.M. Tseng, H.H. Wang, W.L. Wang, C.T. Lee, C.M. Tai, C.H. Tseng, C.C. Chen, Y.N. Tsai, M.S. Sun, Y.C. Hsu, Prognostic impact of diabetes mellitus on overall survival in a nationwide population-based cohort of patients with pancreatic cancer. Endocr. Pract.: Offic. J. Am. Coll. Endocrinol. Am. Assoc. Clin. Endocrinol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.4158/EP-2019-0565
J. Tan, Y. You, F. Guo, J. Xu, H. Dai, P. Bie, Association of elevated risk of pancreatic cancer in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncol. Lett. 13(3), 1247–1255 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.5586
S.T. Chari, C.L. Leibson, K.G. Rabe, L.J. Timmons, J. Ransom, M. de Andrade, G.M. Petersen, Pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus: prevalence and temporal association with diagnosis of cancer. Gastroenterology 134(1), 95–101 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.10.040
T. Hank, M. Sandini, M. Qadan, M. Weniger, D. Ciprani, A. Li, C.R. Ferrone, A.L. Warshaw, K.D. Lillemoe, C. Fernandez-Del Castillo, Diabetes mellitus is associated with unfavorable pathologic features, increased postoperative mortality, and worse long-term survival in resected pancreatic cancer. Pancreatol.: Off. J. Int. Assoc. Pancreatol. 20(1), 125–131 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2019.10.007
S. van Roessel, G.G. Kasumova, J. Verheij, R.M. Najarian, L. Maggino, M. de Pastena, G. Malleo, G. Marchegiani, R. Salvia, S.C. Ng, S.W. de Geus, S. Lof, F. Giovinazzo, J.L. van Dam, T.S. Kent, O.R. Busch, C.H. van Eijck, B.G. Koerkamp, M. Abu Hilal, C. Bassi, J.F. Tseng, M.G. Besselink, International Validation of the Eighth Edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM Staging System in Patients With Resected Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA Surg. 153(12), e183617 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2018.3617
K.A. Overbeek, N.C. Krak, I.C. Pieters, M.M. Smits, R.M. Bent, K.E.W. Vendrik, L. Tonneijck, M.H.A. Muskiet, D.H. van Raalte, M.J. Bruno, D.L. Cahen, High prevalence of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients. Pancreas 49(1), e5–e7 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000001444
A. Roy, J. Sahoo, S. Kamalanathan, D. Naik, P. Mohan, R. Kalayarasan, Diabetes and pancreatic cancer: Exploring the two-way traffic. World J. Gastroenterol. 27(30), 4939–4962 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.4939
S. Lee, H.K. Hwang, C.M. Kang, W.J. Lee, Adverse oncologic impact of new-onset diabetes mellitus on recurrence in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a comparison with long-standing and non-diabetes mellitus patients. Pancreas 47(7), 816–822 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000001099
D. Li, Y. Mao, P. Chang, C. Liu, M.M. Hassan, S.J. Yeung, J.L. Abbruzzese, Impacts of new-onset and long-term diabetes on clinical outcome of pancreatic cancer. American journal of cancer research 5(10),3260–3269 (2015)
J. Cho, R. Scragg, S.J. Pandol, M.O. Goodarzi, M.S. Petrov, Antidiabetic medications and mortality risk in individuals with pancreatic cancer-related diabetes and postpancreatitis diabetes: a nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Care 42(9), 1675–1683 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-0145
Y. Choi, T.Y. Kim, D.Y. Oh, K.H. Lee, S.W. Han, S.A. Im, T.Y. Kim, Y.J. Bang, The impact of diabetes mellitus and metformin treatment on survival of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Cancer Res. Treat. 48(1), 171–179 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.292
I. Alpertunga, R. Sadiq, D. Pandya, T. Lo, M. Dulgher, S. Evans, B. Bennett, N. Rennert, R.C. Frank, Glycemic control as an early prognostic marker in advanced pancreatic cancer. Front. Oncol. 11571855 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.571855
K. Sato, H. Hikita, Y. Myojin, K. Fukumoto, K. Murai, S. Sakane, T. Tamura, T. Yamai, Y. Nozaki, T. Yoshioka, T. Kodama, M. Shigekawa, R. Sakamori, T. Tatsumi, T. Takehara, Hyperglycemia enhances pancreatic cancer progression accompanied by elevations in phosphorylated STAT3 and MYC levels. PloS One 15(7), e0235573 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0235573
A. Sharma, T.C. Smyrk, M.J. Levy, M.A. Topazian, S.T. Chari, Fasting blood glucose levels provide estimate of duration and progression of pancreatic cancer before diagnosis. Gastroenterology 155(2), 490–500 e2 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.04.025
N. Keum, K.H. Ha, Y. Bao, M.J. Chung, H.C. Kim, E.L. Giovannucci, Long-term patterns of fasting blood glucose levels and pancreatic cancer incidence. Cancer Causes Control.: CCC 29(1), 135–142 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-017-0988-6
M. Gallo, V. Adinolfi, L. Morviducci, S. Acquati, E. Tuveri, P. Ferrari, M.C. Zatelli, A. Faggiano, A. Argentiero, A. Natalicchio, S. D’Oronzo, R. Danesi, S. Gori, A. Russo, M. Montagnani, G.D. Beretta, P. Di Bartolo, N. Silvestris, F. Giorgino, Early prediction of pancreatic cancer from new-onset diabetes: an Associazione Italiana Oncologia Medica (AIOM)/Associazione Medici Diabetologi (AMD)/Societa Italiana Endocrinologia (SIE)/Societa Italiana Farmacologia (SIF) multidisciplinary consensus position paper. ESMO Open 6(3), 100155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100155
G. Luo, K. Jin, S. Deng, H. Cheng, Z. Fan, Y. Gong, Y. Qian, Q. Huang, Q. Ni, C. Liu, X. Yu, Roles of CA19-9 in pancreatic cancer: Biomarker, predictor, and promoter. Biochimica et. Biophysica Acta Rev. Cancer 1875(2), 188409 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188409
G. Luo, C. Liu, M. Guo, H. Cheng, Y. Lu, K. Jin, L. Liu, J. Long, J. Xu, R. Lu, Q. Ni, X. Yu, Potential biomarkers in Lewis negative patients with pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. 265(4), 800–805 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000001741.
D.D. Engle, H. Tiriac, K.D. Rivera, A. Pommier, S. Whalen, T.E. Oni, B. Alagesan, E.J. Lee, M.A. Yao, M.S. Lucito, B. Spielman, B. Da Silva, C. Schoepfer, K. Wright, B. Creighton, L. Afinowicz, K.H. Yu, R. Grutzmann, D. Aust, P.A. Gimotty, K.S. Pollard, R.H. Hruban, M.G. Goggins, C. Pilarsky, Y. Park, D.J. Pappin, M.A. Hollingsworth, D.A. Tuveson, The glycan CA19-9 promotes pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in mice. Science 364(6446), 1156–1162 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw3145
A. Sharma, S.T. Chari, Pancreatic cancer and diabetes mellitus. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 16(4), 466–478 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11938-018-0197-8
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank American Journal Experts (www.aje.com) for English language editing.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. G.L. and X.Y.: conceptualization and funding acquisition. Z.X., X.Z., and H.X.: resources and investigation and data curation. G.L. and X.Y.: project administration. G.L. and Q.N.: review and editing. Z.X., X.Z., and H.X.: formal analysis and software and writing—original draft. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82072693, 81625016, 81871940, 81902417, 82172625), the Scientific Innovation Project of Shanghai Education Committee (2019-01-07-00-07-E00057), Clinical and Scientific Innovation Project of Shanghai Hospital Development Center (SHDC12018109, SHDC2020CR1006A), the Shanghai Cancer Center Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (grant number YJJQ201803), Shanghai Charity Foundation (HYXH2021042), and the Fudan University Personalized Project for “Double Top” Original Research (grant number XM03190633).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Centre.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Xinzhe Zhu, Huaxiang Xu, Zhiwen Xiao
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Xu, H., Xiao, Z. et al. Hyperglycemia predicts adverse prognosis in advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Endocrine 79, 296–303 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-022-03196-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-022-03196-4