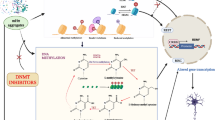
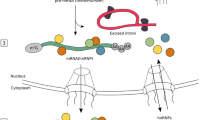
Abstract
Noncoding DNA undergoes widespread context-dependent transcription to produce noncoding RNAs. In recent decades, tremendous advances in genomics and transcriptomics have revealed important regulatory roles for noncoding DNA elements and the RNAs that they produce. Enhancers are one such element that are well-established drivers of gene expression changes in response to a variety of factors such as external stimuli, cellular responses, developmental cues, and disease states. They are known to act at long distances, interact with multiple target gene loci simultaneously, synergize with other enhancers, and associate with dynamic chromatin architectures to form a complex regulatory network. Recent advances in enhancer biology have revealed that upon activation, enhancers transcribe long noncoding RNAs, known as enhancer RNAs (eRNAs), that have been shown to play important roles in enhancer-mediated gene regulation and chromatin-modifying activities. In the brain, enhancer dysregulation and eRNA transcription has been reported in numerous disorders from acute injuries to chronic neurodegeneration. Because this is an emerging area, a comprehensive understanding of eRNA function has not yet been achieved in brain disorders; however, the findings to date have illuminated a role for eRNAs in activity-driven gene expression and phenotypic outcomes. In this review, we highlight the breadth of the current literature on eRNA biology in brain health and disease and discuss the challenges as well as focus areas and strategies for future in-depth research on eRNAs in brain health and disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Achour, M., Le Gras, S., Keime, C., Parmentier, F., Lejeune, F. X., Boutillier, A. L., & Merienne, K. (2015). Neuronal identity genes regulated by super-enhancers are preferentially down-regulated in the striatum of Huntington’s disease mice. Hum Mol Genet, 24(12), 3481–3496. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddv099
Adelman, K., & Lis, J. T. (2012). Promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II: Emerging roles in metazoans. Nature Reviews Genetics, 13(10), 720–731. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3293
Akins, P. T., Liu, P. K., & Hsu, C. Y. (1996). Immediate early gene expression in response to cerebral ischemia. Friend or foe? Stroke, 27(9), 1682–1687. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.27.9.1682
Andersson, R., Gebhard, C., Miguel-Escalada, I., Hoof, I., Bornholdt, J., Boyd, M., & Sandelin, A. (2014). An atlas of active enhancers across human cell types and tissues. Nature, 507(7493), 455–461. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12787
Aoi, Y., Smith, E. R., Shah, A. P., Rendleman, E. J., Marshall, S. A., Woodfin, A. R., & Shilatifard, A. (2020). NELF regulates a promoter-proximal step distinct from RNA Pol II pause-release. Molecular Cell, 78(2), 261-274 e265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2020.02.014
Arner, E., Daub, C. O., Vitting-Seerup, K., Andersson, R., Lilje, B., Drablos, F., & Hayashizaki, Y. (2015). Transcribed enhancers lead waves of coordinated transcription in transitioning mammalian cells. Science, 347(6225), 1010–1014. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1259418
Arnold, P. R., Wells, A. D., & Li, X. C. (2019). Diversity and emerging roles of enhancer RNA in regulation of gene expression and cell fate. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 7, 377. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2019.00377
Bharadwaj, R., Jiang, Y., Mao, W., Jakovcevski, M., Dincer, A., Krueger, W., & Akbarian, S. (2013). Conserved chromosome 2q31 conformations are associated with transcriptional regulation of GAD1 GABA synthesis enzyme and altered in prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(29), 11839–11851. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1252-13.2013
Bhattarai, S., Akella, A., Gandhi, A., & Dharap, A. (2021). Modulation of brain pathology by enhancer RNAs in cerebral ischemia. Molecular Neurobiology, 58(4), 1482–1490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02194-9
Bhattarai, S., Aly, A., Garcia, K., Ruiz, D., Pontarelli, F., & Dharap, A. (2019). Deep sequencing reveals uncharted isoform heterogeneity of the protein-coding transcriptome in cerebral ischemia. Molecular Neurobiology, 56(2), 1035–1043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1147-0
Bhattarai, S., Pontarelli, F., Prendergast, E., & Dharap, A. (2017). Discovery of novel stroke-responsive lncRNAs in the mouse cortex using genome-wide RNA-seq. Neurobiology of Diseases, 108, 204–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2017.08.016
Bohnsack, J. P., Zhang, H., Wandling, G. M., He, D., Kyzar, E. J., Lasek, A. W., & Pandey, S. C. (2022). Targeted epigenomic editing ameliorates adult anxiety and excessive drinking after adolescent alcohol exposure. Science Advances, 8(18), eabn2748. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abn2748
Bose, D. A., Donahue, G., Reinberg, D., Shiekhattar, R., Bonasio, R., & Berger, S. L. (2017). RNA binding to CBP stimulates histone acetylation and transcription. Cell, 168(1–2), 135–149122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.020
Bullido, M. J., Artiga, M. J., Recuero, M., Sastre, I., Garcia, M. A., Aldudo, J., & Valdivieso, F. (1998). A polymorphism in the regulatory region of APOE associated with risk for Alzheimer’s dementia. Nature Genetics, 18(1), 69–71. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0198-69
Carullo, N. V. N., Phillips Iii, R. A., Simon, R. C., Soto, S. A. R., Hinds, J. E., Salisbury, A. J., & Day, J. J. (2020). Enhancer RNAs predict enhancer-gene regulatory links and are critical for enhancer function in neuronal systems. Nucleic Acids Research, 48(17), 9550–9570. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa671
Choi, J., Lysakovskaia, K., Stik, G., Demel, C., Soding, J., Tian, T. V., & Cramer, P. (2021). Evidence for additive and synergistic action of mammalian enhancers during cell fate determination. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.65381
Consortium, & E. P. (2012). An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature, 489(7414), 57–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11247
Corradin, O., & Scacheri, P. C. (2014). Enhancer variants: Evaluating functions in common disease. Genome Medicine, 6(10), 85. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-014-0085-3
Darmanis, S., Sloan, S. A., Zhang, Y., Enge, M., Caneda, C., Shuer, L. M., & Quake, S. R. (2015). A survey of human brain transcriptome diversity at the single cell level. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(23), 7285–7290. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1507125112
Davidson, S., Lear, M., Shanley, L., Hing, B., Baizan-Edge, A., Herwig, A., & MacKenzie, A. (2011). Differential activity by polymorphic variants of a remote enhancer that supports galanin expression in the hypothalamus and amygdala: Implications for obesity, depression and alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology, 36(11), 2211–2221. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2011.93
de la Torre-Ubieta, L., Stein, J. L., Won, H., Opland, C. K., Liang, D., Lu, D., & Geschwind, D. H. (2018). The dynamic landscape of open chromatin during human cortical neurogenesis. Cell, 172(1–2), 289–304218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.014
De Santa, F., Barozzi, I., Mietton, F., Ghisletti, S., Polletti, S., Tusi, B. K., & Natoli, G. (2010). A large fraction of extragenic RNA pol II transcription sites overlap enhancers. PLoS Biology, 8(5), e1000384. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000384
Dharap, A., Bowen, K., Place, R., Li, L. C., & Vemuganti, R. (2009). Transient focal ischemia induces extensive temporal changes in rat cerebral microRNAome. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 29(4), 675–687. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2008.157
Dharap, A., Nakka, V. P., & Vemuganti, R. (2011). Altered expression of PIWI RNA in the rat brain after transient focal ischemia. Stroke, 42(4), 1105–1109. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.598391
Dharap, A., Nakka, V. P., & Vemuganti, R. (2012). Effect of focal ischemia on long noncoding RNAs. Stroke, 43(10), 2800–2802. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.669465
Djebali, S., Davis, C. A., Merkel, A., Dobin, A., Lassmann, T., Mortazavi, A., & Gingeras, T. R. (2012). Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature, 489(7414), 101–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11233
Dong, X., Liao, Z., Gritsch, D., Hadzhiev, Y., Bai, Y., Locascio, J. J., & Scherzer, C. R. (2018). Enhancers active in dopamine neurons are a primary link between genetic variation and neuropsychiatric disease. Nature Neuroscience, 21(10), 1482–1492. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0223-0
Eckart, N., Song, Q., Yang, R., Wang, R., Zhu, H., McCallion, A. S., & Avramopoulos, D. (2016). Functional characterization of schizophrenia-associated variation in CACNA1C. PLoS ONE, 11(6), e0157086. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0157086
Flavell, S. W., & Greenberg, M. E. (2008). Signaling mechanisms linking neuronal activity to gene expression and plasticity of the nervous system. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 31, 563–590. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125631
Francelle, L., Lotz, C., Outeiro, T., Brouillet, E., & Merienne, K. (2017). Contribution of neuroepigenetics to Huntington’s disease. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11, 17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00017
Frank, C. L., Liu, F., Wijayatunge, R., Song, L., Biegler, M. T., Yang, M. G., & West, A. E. (2015). Regulation of chromatin accessibility and Zic binding at enhancers in the developing cerebellum. Nature Neuroscience, 18(5), 647–656. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3995
Gallitano, A. L. (2020). Editorial: The role of immediate early genes in neuropsychiatric illness. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 14, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2020.00016
Gayen, S., & Kalantry, S. (2017). Chromatin-enriched lncRNAs: A novel class of enhancer RNAs. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 24(7), 556–557. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3430
Gorbovytska, V., Kim, S. K., Kuybu, F., Gotze, M., Um, D., Kang, K., & Kuhn, C. D. (2022). Enhancer RNAs stimulate Pol II pause release by harnessing multivalent interactions to NELF. Nature Communications, 13(1), 2429. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29934-w
Han, Z., & Li, W. (2022). Enhancer RNA: What we know and what we can achieve. Cell Proliferation, 55(4), e13202. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.13202
Hauberg, M. E., Fullard, J. F., Zhu, L., Cohain, A. T., Giambartolomei, C., Misir, R., & CommonMind, C. (2019). Differential activity of transcribed enhancers in the prefrontal cortex of 537 cases with schizophrenia and controls. Molecular Psychiatry, 24(11), 1685–1695. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0059-8
Heintzman, N. D., Hon, G. C., Hawkins, R. D., Kheradpour, P., Stark, A., Harp, L. F., & Ren, B. (2009). Histone modifications at human enhancers reflect global cell-type-specific gene expression. Nature, 459(7243), 108–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07829
Heinz, S., Romanoski, C. E., Benner, C., & Glass, C. K. (2015). The selection and function of cell type-specific enhancers. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 16(3), 144–154. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3949
Hendrickx, A., Pierrot, N., Tasiaux, B., Schakman, O., Kienlen-Campard, P., De Smet, C., & Octave, J. N. (2014). Epigenetic regulations of immediate early genes expression involved in memory formation by the amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer disease. PLoS ONE, 9(6), e99467. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099467
Hsieh, C. L., Fei, T., Chen, Y., Li, T., Gao, Y., Wang, X., & Kantoff, P. W. (2014). Enhancer RNAs participate in androgen receptor-driven looping that selectively enhances gene activation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(20), 7319–7324. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1324151111
Inoue, Y. U., & Inoue, T. (2016). Brain enhancer activities at the gene-poor 5p141 autism-associated locus. Scientific Reports, 6, 31227. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31227
Jin, F., Li, Y., Dixon, J. R., Selvaraj, S., Ye, Z., Lee, A. Y., & Ren, B. (2013). A high-resolution map of the three-dimensional chromatin interactome in human cells. Nature, 503(7475), 290–294. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12644
Kikuchi, M., Hara, N., Hasegawa, M., Miyashita, A., Kuwano, R., Ikeuchi, T., & Nakaya, A. (2019). Enhancer variants associated with Alzheimer’s disease affect gene expression via chromatin looping. BMC Medical Genomics, 12(1), 128. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-019-0574-8
Kim, T. K., Hemberg, M., Gray, J. M., Costa, A. M., Bear, D. M., Wu, J., & Greenberg, M. E. (2010). Widespread transcription at neuronal activity-regulated enhancers. Nature, 465(7295), 182–187. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09033
Kim, Y. W., Lee, S., Yun, J., & Kim, A. (2015). Chromatin looping and eRNA transcription precede the transcriptional activation of gene in the beta-globin locus. Bioscience Reports. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20140126
Kyzar, E. J., Zhang, H., & Pandey, S. C. (2019). Adolescent alcohol exposure epigenetically suppresses Amygdala Arc enhancer RNA expression to confer adult anxiety susceptibility. Biological Psychiatry, 85(11), 904–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.12.021
Le Gras, S., Keime, C., Anthony, A., Lotz, C., De Longprez, L., Brouillet, E., & Merienne, K. (2017). Altered enhancer transcription underlies Huntington’s disease striatal transcriptional signature. Scientific Reports, 7, 42875. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42875
Li, P., Marshall, L., Oh, G., Jakubowski, J. L., Groot, D., He, Y., & Labrie, V. (2019). Epigenetic dysregulation of enhancers in neurons is associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology and cognitive symptoms. Nature Communications, 10(1), 2246. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10101-7
Li, W., Notani, D., Ma, Q., Tanasa, B., Nunez, E., Chen, A. Y., & Rosenfeld, M. G. (2013). Functional roles of enhancer RNAs for oestrogen-dependent transcriptional activation. Nature, 498(7455), 516–520. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12210
Liu, D. Z., Tian, Y., Ander, B. P., Xu, H., Stamova, B. S., Zhan, X., & Sharp, F. R. (2010). Brain and blood microRNA expression profiling of ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and kainate seizures. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 30(1), 92–101. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2009.186
Lusardi, T. A., Murphy, S. J., Phillips, J. I., Chen, Y., Davis, C. M., Young, J. M., & Saugstad, J. A. (2014). MicroRNA responses to focal cerebral ischemia in male and female mouse brain. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 7, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2014.00011
Marballi, K. K., & Gallitano, A. L. (2018). Immediate early genes anchor a biological pathway of proteins required for memory formation, long-term depression and risk for schizophrenia. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 12, 23. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00023
McClymont, S. A., Hook, P. W., Soto, A. I., Reed, X., Law, W. D., Kerans, S. J., & McCallion, A. S. (2018). Parkinson-associated SNCA enhancer variants revealed by open chromatin in mouse dopamine neurons. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 103(6), 874–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.10.018
Mifsud, B., Tavares-Cadete, F., Young, A. N., Sugar, R., Schoenfelder, S., Ferreira, L., & Osborne, C. S. (2015). Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C. Nature Genetics, 47(6), 598–606. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3286
Minatohara, K., Akiyoshi, M., & Okuno, H. (2015). Role of immediate-early genes in synaptic plasticity and neuronal ensembles underlying the memory trace. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 8, 78. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2015.00078
Mousavi, K., Zare, H., Dell’orso, S., Grontved, L., Gutierrez-Cruz, G., Derfoul, A., & Sartorelli, V. (2013). eRNAs promote transcription by establishing chromatin accessibility at defined genomic loci. Molecular Cell, 51(5), 606–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2013.07.022
Nord, A. S., Blow, M. J., Attanasio, C., Akiyama, J. A., Holt, A., Hosseini, R., & Visel, A. (2013). Rapid and pervasive changes in genome-wide enhancer usage during mammalian development. Cell, 155(7), 1521–1531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.033
Raghavendra Rao, V. L., Bowen, K. K., Dhodda, V. K., Song, G., Franklin, J. L., Gavva, N. R., & Dempsey, R. J. (2002). Gene expression analysis of spontaneously hypertensive rat cerebral cortex following transient focal cerebral ischemia. Journal of Neurochemistry, 83(5), 1072–1086. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.01208.x
Ramirez, M., Badayeva, Y., Yeung, J., Wu, J., Abdalla-Wyse, A., Yang, E., & Goldowitz, D. (2022). Temporal analysis of enhancers during mouse cerebellar development reveals dynamic and novel regulatory functions. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.74207
Ramirez, M., Robert, R., Yeung, J., Wu, J., Abdalla-Wyse, A., Consortium, F., & Goldowitz, D. (2023). Identification and characterization of transcribed enhancers during cerebellar development through enhancer RNA analysis. BMC Genomics, 24(1), 351. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-023-09368-4
Ruiz, D., Bhattarai, S., & Dharap, A. (2021). Sex-based eRNA expression and function in ischemic stroke. Neurochemistry International, 150, 105149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105149
Sanyal, A., Lajoie, B. R., Jain, G., & Dekker, J. (2012). The long-range interaction landscape of gene promoters. Nature, 489(7414), 109–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11279
Schaukowitch, K., Joo, J. Y., Liu, X., Watts, J. K., Martinez, C., & Kim, T. K. (2014). Enhancer RNA facilitates NELF release from immediate early genes. Molecular Cell, 56(1), 29–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.023
Schmidt-Kastner, R., Zhang, B., Belayev, L., Khoutorova, L., Amin, R., Busto, R., & Ginsberg, M. D. (2002). DNA microarray analysis of cortical gene expression during early recirculation after focal brain ischemia in rat. Molecular Brain Research, 108(1–2), 81–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-328x(02)00516-8
Shechner, D. M., Hacisuleyman, E., Younger, S. T., & Rinn, J. L. (2015). Multiplexable, locus-specific targeting of long RNAs with CRISPR-display. Nature Methods, 12(7), 664–670. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3433
Soldner, F., Stelzer, Y., Shivalila, C. S., Abraham, B. J., Latourelle, J. C., Barrasa, M. I., & Jaenisch, R. (2016). Parkinson-associated risk variant in distal enhancer of alpha-synuclein modulates target gene expression. Nature, 533(7601), 95–99. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17939
Tan, K. S., Armugam, A., Sepramaniam, S., Lim, K. Y., Setyowati, K. D., Wang, C. W., & Jeyaseelan, K. (2009). Expression profile of MicroRNAs in young stroke patients. PLoS ONE, 4(11), e7689. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007689
Tang, Y., Lu, A., Aronow, B. J., Wagner, K. R., & Sharp, F. R. (2002). Genomic responses of the brain to ischemic stroke, intracerebral haemorrhage, kainate seizures, hypoglycemia, and hypoxia. European Journal of Neuroscience, 15(12), 1937–1952. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02030.x
Tischmeyer, W., & Grimm, R. (1999). Activation of immediate early genes and memory formation. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 55(4), 564–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050315
Tsai, P. F., Dell’Orso, S., Rodriguez, J., Vivanco, K. O., Ko, K. D., Jiang, K., & Sartorelli, V. (2018). A muscle-specific enhancer RNA mediates cohesin recruitment and regulates transcription in trans. Molecular Cell, 71(1), 129–141128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.008
Wang, J. C., Kwon, J. M., Shah, P., Morris, J. C., & Goate, A. (2000). Effect of APOE genotype and promoter polymorphism on risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 55(11), 1644–1649. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.55.11.1644
Watts, J. A., Grunseich, C., Rodriguez, Y., Liu, Y., Li, D., Burdick, J. T., & Cheung, V. G. (2022). A common transcriptional mechanism involving R-loop and RNA abasic site regulates an enhancer RNA of APOE. Nucleic Acids Research, 50(21), 12497–12514. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1107
Wei, D., Chen, J., Chen, X., Wu, S., Chen, Z., Huang, Y., & He, W. (2021). Screening for differentially expressed circRNAs in ischemic stroke by RNA sequencing. BMC Neurology, 21(1), 370. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-021-02397-0
Werner, M. S., Sullivan, M. A., Shah, R. N., Nadadur, R. D., Grzybowski, A. T., Galat, V., & Ruthenburg, A. J. (2017). Chromatin-enriched lncRNAs can act as cell-type specific activators of proximal gene transcription. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 24(7), 596–603. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3424
Wu, C. H., Yamaguchi, Y., Benjamin, L. R., Horvat-Gordon, M., Washinsky, J., Enerly, E., & Gilmour, D. (2003). NELF and DSIF cause promoter proximal pausing on the hsp70 promoter in Drosophila. Genes Development, 17(11), 1402–1414. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1091403
Xiang, J. F., Yin, Q. F., Chen, T., Zhang, Y., Zhang, X. O., Wu, Z., & Chen, L. L. (2014). Human colorectal cancer-specific CCAT1-L lncRNA regulates long-range chromatin interactions at the MYC locus. Cell Research, 24(5), 513–531. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2014.35
Yamaguchi, Y., Inukai, N., Narita, T., Wada, T., & Handa, H. (2002). Evidence that negative elongation factor represses transcription elongation through binding to a DRB sensitivity-inducing factor/RNA polymerase II complex and RNA. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 22(9), 2918–2927. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.22.9.2918-2927.2002
Yao, P., Lin, P., Gokoolparsadh, A., Assareh, A., Thang, M. W., & Voineagu, I. (2015). Coexpression networks identify brain region-specific enhancer RNAs in the human brain. Nature Neuroscience, 18(8), 1168–1174. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4063
Zhao, Y., Wang, L., Ren, S., Wang, L., Blackburn, P. R., McNulty, M. S., & Huang, H. (2016). Activation of P-TEFb by androgen receptor-regulated enhancer RNAs in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cell Reports, 15(3), 599–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.038
Zheng, K., Lin, L., Jiang, W., Chen, L., Zhang, X., Zhang, Q., & Hao, J. (2022). Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the transcriptional landscape in ischemic stroke. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 42(1), 56–73. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X211026770
Acknowledgements
Figure 1 was created with BioRender.com.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R01NS115835 to Ashutosh Dharap.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AP and AD wrote the main manuscript text. AP prepared Figure 1. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, A., Dharap, A. An Emerging Role for Enhancer RNAs in Brain Disorders. Neuromol Med 26, 7 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-024-08776-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-024-08776-3