Abstract
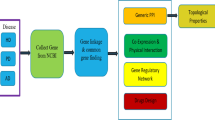
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), vascular dementia (VD), and Parkinson’s disease (PD) exert increasingly lethal or disabling effects on humans, but the associations among these diseases at the molecular level remain unclear. In our research, lists of genes related to these three diseases were acquired from public databases. We constructed gene–gene networks of the lists of disease-related genes using the STRING database and selected the plug-in MCODE as the most suitable method to divide the three disease-associated networks into modules through an entropy calculation. Notably, 1173 AD-related, 203 VD-related, and 722 PD-related genes as well as 72 overlapping genes were observed among the three diseases. By dividing the modules from the gene network, we divided the AD-related gene network into 27 modules, the VD-related gene network into 8 modules, and the PD-related gene network into 17 modules. After the enrichment analysis of each disease-related gene, 146 overlapping biological processes and 32 overlapping pathways were identified. Ultimately, through similarity analysis of the genes, biological processes, and pathways, we found that AD and VD were the most closely related at the biological process and pathway levels, with similarity coefficients of 0.2784 and 0.3626, respectively. After analyzing the overlapping gene network, we found that INS might play an important role in the network and that insulin and its signaling pathways may play a key role in these neurodegenerative diseases. Our research illustrates a new method for in-depth research on the three diseases, which may accelerate the progress of developing new therapeutics and may be applied to prevent neurodegenerative diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DAVID:
-
Database for annotation, visualization and integrated discovery
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- VD:
-
Vascular dementia
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Anang, J. B., Nomura, T., Romenets, S. R., Nakashima, K., Gagnon, J. F., & Postuma, R. B. (2017). Dementia predictors in parkinson disease: A validation study. Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, 7(1), 159–162. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-160925
Ashburner, M., Ball, C. A., Blake, J. A., Botstein, D., Butler, H., Cherry, J. M., Davis, A. P., Dolinski, K., Dwight, S. S., Eppig, J. T., Harris, M. A., Hill, D. P., Issel-Tarver, L., Kasarskis, A., Lewis, S., Matese, J. C., Richardson, J. E., Ringwald, M., Rubin, G. M., & Sherlock, G. (2000). Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene ontology consortium. Nature Genetics, 25(1), 25–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/75556
Ashraf, G. M., Chibber, S., Mohammad, Zaidi, S. K., Tabrez, S., Ahmad, A., Shakil, S., Mushtaq, G., Baeesa, S. S., & Kamal, M. A. (2016). Recent updates on the association between Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. Medicinal Chemistry (Shariqah (United Arab Emirates)), 12(3), 226–237. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573406411666151030111820
Bader, G. D., & Hogue, C. W. (2003). An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics, 4, 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-4-2
Barabási, A. L., Gulbahce, N., & Loscalzo, J. (2011). Network medicine: A network-based approach to human disease. Nature Reviews Genetics, 12(1), 56–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2918
Ben-Hamouda, I., Tougourti, M. N., & Hamza, M. (2002). Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a rare cause of vascular dementia. A case report. La Tunisie medicale, 80(7), 420–423.
Benn, M., Nordestgaard, B. G., Frikke-Schmidt, R., & Tybjærg-Hansen, A. (2017). Low LDL cholesterol, PCSK9 and HMGCR genetic variation, and risk of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: Mendelian randomisation study. BMJ (clinical Research Ed.), 357, j1648. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.j1648
Bisht, I., Ambasta, R. K., & Kumar, P. (2020). An integrated approach to unravel a putative crosstalk network in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Neuropeptides, 83, 102078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2020.102078
Brohée, S., & van Helden, J. (2006). Evaluation of clustering algorithms for protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics, 7, 488. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-7-488
Brown, G. R., Hem, V., Katz, K. S., Ovetsky, M., Wallin, C., Ermolaeva, O., Tolstoy, I., Tatusova, T., Pruitt, K. D., Maglott, D. R., & Murphy, T. D. (2015). Gene: a gene-centered information resource at NCBI. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(Database issue), D36–D42. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1055
Bubniene, U., Mazetyte, R., Ramanaviciene, A., Gulbinas, V., Ramanavicius, A., & Karpicz, R. (2018). Fluorescence quenching-based evaluation of glucose oxidase composite with conducting polymer, polypyrrole. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 122(17), 9491–9498. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b01610
Cenini, G., Lloret, A., & Cascella, R. (2019). Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases: From a mitochondrial point of view. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2019, 2105607. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2105607
Chen, Y. Y., Yu, Y. N., Zhang, Y. Y., Li, B., Liu, J., Li, D. F., Wu, P., Wang, J., Wang, Z., & Wang, Y. Y. (2016). Quantitative determination of flexible pharmacological mechanisms based on topological variation in mice anti-ischemic modular networks. PLoS ONE, 11(7), e0158379. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158379
Cheung, C., Chang, Y. C., Lin, T. Y., Cheng, S. M., & Leung, E. (2020). Anti-apoptotic proteins in the autophagic world: An update on functions of XIAP, Survivin, and BRUCE. Journal of Biomedical Science, 27(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-020-0627-5
Dennis, G., Jr., Sherman, B. T., Hosack, D. A., Yang, J., Gao, W., Lane, H. C., & Lempicki, R. A. (2003). DAVID: Database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biology, 4(5), P3.
Eckl-Dorna, J., Villazala-Merino, S., Campion, N. J., Byazrova, M., Filatov, A., Kudlay, D., Karsonova, A., Riabova, K., Khaitov, M., Karaulov, A., Niederberger-Leppin, V., & Valenta, R. (2019). Tracing IgE-producing cells in allergic patients. Cells, 8(9), 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8090994
Fischer, R., & Maier, O. (2015). Interrelation of oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease: Role of TNF. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2015, 610813. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/610813
Franco, R., Navarro, G., & Martínez-Pinilla, E. (2019). Lessons on differential neuronal-death-vulnerability from familial cases of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(13), 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133297
Ganguly, G., Chakrabarti, S., Chatterjee, U., & Saso, L. (2017). Proteinopathy, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction: Cross talk in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 11, 797–810. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S130514
Guzman-Martinez, L., Maccioni, R. B., Andrade, V., Navarrete, L. P., Pastor, M. G., & Ramos-Escobar, N. (2019). Neuroinflammation as a common feature of neurodegenerative disorders. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 10, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01008
Han, J. D., Bertin, N., Hao, T., Goldberg, D. S., Berriz, G. F., Zhang, L. V., Dupuy, D., Walhout, A. J., Cusick, M. E., Roth, F. P., & Vidal, M. (2004). Evidence for dynamically organized modularity in the yeast protein-protein interaction network. Nature, 430(6995), 88–93. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02555
Hou, Y., Dan, X., Babbar, M., Wei, Y., Hasselbalch, S. G., Croteau, D. L., & Bohr, V. A. (2019). Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nature Reviews Neurology, 15(10), 565–581. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0244-7
Jaccard, P. (1912). The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone.1. New Phytologist, 11, 37–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1912.tb05611.x
Jones, M. K., Nair, A., & Gupta, M. (2019). Mast cells in neurodegenerative disease. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 13, 171. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00171
Juul-Rasmussen, I., Tybjærg-Hansen, A., Rasmussen, K. L., Nordestgaard, B. G., & Frikke-Schmidt, R. (2019). Blood-brain barrier transcytosis genes, risk of dementia and stroke: A prospective cohort study of 74,754 individuals. European Journal of Epidemiology, 34(6), 579–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-019-00498-2
Kanehisa, M., & Goto, S. (2000). KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 28(1), 27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Kelly, J., Moyeed, R., Carroll, C., Luo, S., & Li, X. (2020). Genetic networks in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease. Aging, 12(6):5221–5243. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102943
Kleinridders, A., Ferris, H. A., Cai, W., & Kahn, C. R. (2014). Insulin action in brain regulates systemic metabolism and brain function. Diabetes, 63(7), 2232–2243. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-0568
Laukens, K., Naulaerts, S., & Berghe, W. V. (2015). Bioinformatics approaches for the functional interpretation of protein lists: From ontology term enrichment to network analysis. Proteomics, 15(5–6), 981–996. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201400296
Leblhuber, F., Walli, J., Tilz, G. P., Wachter, H., & Fuchs, D. (1998). Systemic changes of the immune system in patients with Alzheimer's dementia. Deutsche medizinische Wochenschrift, 123(25–26), 787–791. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-1024069
Liu, Q., Zhang, Y., Wang, P., Liu, J., Li, B., Yu, Y., Wu, H., Kang, R., Zhang, X., & Wang, Z. (2019). Deciphering the scalene association among type-2 diabetes mellitus, prostate cancer, and chronic myeloid leukemia via enrichment analysis of disease-gene network. Cancer Medicine, 8(5), 2268–2277. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1845
Liu, C. C., Tseng, Y. T., Li, W., Wu, C. Y., Mayzus, I., Rzhetsky, A., Sun, F., Waterman, M., Chen, J. J., Chaudhary, P. M., Loscalzo, J., Crandall, E., & Zhou, X. J. (2014). DiseaseConnect: a comprehensive web server for mechanism-based disease-disease connections. Nucleic Acids Research, 42(Web Server issue), W137–W146. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku412
Lorenz, D. M., Jeng, A., & Deem, M. W. (2011). The emergence of modularity in biological systems. Physics of Life Reviews, 8(2), 129–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plrev.2011.02.003
Mata, I. F., Leverenz, J. B., Weintraub, D., Trojanowski, J. Q., Hurtig, H. I., Van Deerlin, V. M., Ritz, B., Rausch, R., Rhodes, S. L., Factor, S. A., Wood-Siverio, C., Quinn, J. F., Chung, K. A., Peterson, A. L., Espay, A. J., Revilla, F. J., Devoto, J., Hu, S. C., Cholerton, B. A., … Zabetian, C. P. (2014). APOE, MAPT, and SNCA genes and cognitive performance in Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurology, 71(11), 1405–1412. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.1455
Matsuzawa, A., & Ichijo, H. (2005). Stress-responsive protein kinases in redox-regulated apoptosis signaling. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 7(3–4), 472–481. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2005.7.472
Mazon, J. N., de Mello, A. H., Ferreira, G. K., & Rezin, G. T. (2017). The impact of obesity on neurodegenerative diseases. Life Sciences, 182, 22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.06.002
McKenzie, J. A., Spielman, L. J., Pointer, C. B., Lowry, J. R., Bajwa, E., Lee, C. W., & Klegeris, A. (2017). Neuroinflammation as a common mechanism associated with the modifiable risk factors for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Current Aging Science, 10(3), 158–176. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874609810666170315113244
Miryala, S. K., Anbarasu, A., & Ramaiah, S. (2018). Discerning molecular interactions: A comprehensive review on biomolecular interaction databases and network analysis tools. Gene, 642, 84–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.11.028
Morris, J. H., Apeltsin, L., Newman, A. M., Baumbach, J., Wittkop, T., Su, G., Bader, G. D., & Ferrin, T. E. (2011). clusterMaker: A multi-algorithm clustering plugin for Cytoscape. BMC Bioinformatics, 12, 436. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-436
O’Brien, J. T., & Thomas, A. (2015). Vascular dementia. Lancet (london, England), 386(10004), 1698–1706. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00463-8
Ozawa, T., Tanaka, M., Sugiyama, S., Ino, H., Ohno, K., Hattori, K., Ohbayashi, T., Ito, T., Deguchi, H., & Kawamura, K. (1991). Patients with idiopathic cardiomyopathy belong to the same mitochondrial DNA gene family of Parkinson’s disease and mitochondrial encephalomyopathy. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 177(1), 518–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(91)92014-b
Pandey, P., Pradhan, S., Modi, D. R., & Mittal, B. (2009). MTHFR and ACE gene polymorphisms and risk of vascular and degenerative dementias in the elderly. Brain and Cognition, 71(3), 295–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2009.07.007
Pereira, M. D., Ksiazek, K., & Menezes, R. (2012). Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases and ageing. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2012, 796360. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/796360
Petras, M., Tatarkova, Z., Kovalska, M., Mokra, D., Dobrota, D., Lehotsky, J., & Drgova, A. (2014). Hyperhomocysteinemia as a risk factor for the neuronal system disorders. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology : An Official Journal of the Polish Physiological Society, 65(1), 15–23.
Prentice, H., Modi, J. P., & Wu, J. Y. (2015). Mechanisms of neuronal protection against excitotoxicity, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction in stroke and neurodegenerative diseases. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2015, 964518. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/964518
Prince, M. J. (2015). The global impact of dementia: an analysis of prevalence, incidence, cost and trends: Alzheimer's Disease International. World Alzheimer Report 2015.
Radi, E., Formichi, P., Battisti, C., & Federico, A. (2014). Apoptosis and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease: JAD, 42(Suppl 3), S125–S152. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-132738
Ramalingam, M., & Kim, S. J. (2014). Mechanisms of action of brain insulin against neurodegenerative diseases. Journal of Neural Transmission (Vienna, Austria: 1996), 121(6), 611–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1147-1
Rozycka, A., Jagodzinski, P. P., Kozubski, W., Lianeri, M., & Dorszewska, J. (2013). Homocysteine level and mechanisms of injury in Parkinson’s disease as related to MTHFR, MTR, and MTHFD1 genes polymorphisms and L-dopa treatment. Current Genomics, 14(8), 534–542. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202914666131210210559
Sajan, M., Hansen, B., Ivey, R., 3rd., Sajan, J., Ari, C., Song, S., Braun, U., Leitges, M., Farese-Higgs, M., & Farese, R. V. (2016). Brain insulin signaling is increased in insulin-resistant states and decreases in FOXOs and PGC-1α and increases in Aβ1-40/42 and phospho-tau may abet Alzheimer development. Diabetes, 65(7), 1892–1903. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-1428
Sanchez, P. E., Fares, R. P., Risso, J. J., Bonnet, C., Bouvard, S., Le-Cavorsin, M., Georges, B., Moulin, C., Belmeguenai, A., Bodennec, J., Morales, A., Pequignot, J. M., Baulieu, E. E., Levine, R. A., & Bezin, L. (2009). Optimal neuroprotection by erythropoietin requires elevated expression of its receptor in neurons. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(24), 9848–9853. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0901840106
Santiago, J., & Hallschmid, M. (2019). Outcomes and clinical implications of intranasal insulin administration to the central nervous system. Experimental Neurology, 317, 180–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.03.007
Selvaraji, S., Poh, L., Natarajan, V., Mallilankaraman, K., & Arumugam, T. V. (2019). Negative conditioning of mitochondrial dysfunction in age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Conditioning Medicine, 2(1), 30–39.
Seripa, D., Matera, M. G., D’Onofrio, G., Sancarlo, D., Bizzarro, A., Cascavilla, L., Paris, F., Gravina, C., Bonghi, L., Capurso, C., Solfrizzi, V., Daniele, A., Masullo, C., Panza, F., & Pilotto, A. (2010). Polymorphism C in the serotonin transporter gene in depression-free elderly patients with vascular dementia. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 29(5), 424–431. https://doi.org/10.1159/000275670
Shabir, O., Berwick, J., & Francis, S. E. (2018). Neurovascular dysfunction in vascular dementia, Alzheimer’s and atherosclerosis. BMC Neuroscience, 19(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-018-0465-5
Shefa, U., Jeong, N. Y., Song, I. O., Chung, H. J., Kim, D., Jung, J., & Huh, Y. (2019). Mitophagy links oxidative stress conditions and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regeneration Research, 14(5), 749–756. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.249218
Sheikh, S., Safia, H. E., & Mir, S. (2013). Neurodegenerative diseases: Multifactorial conformational diseases and their therapeutic interventions. Journal of Neurodegenerative Diseases, 2013, 563481. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/563481
Soul, J., Dunn, S. L., Hardingham, T. E., Boot-Handford, R. P., & Schwartz, J. M. (2016). PhenomeScape: A cytoscape app to identify differentially regulated sub-networks using known disease associations. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 32(24), 3847–3849. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw545
Srinivasan, V., Braidy, N., Chan, E. K., Xu, Y. H., & Chan, D. K. (2016). Genetic and environmental factors in vascular dementia: An update of blood brain barrier dysfunction. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology, 43(5), 515–521. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12558
Su, G., Kuchinsky, A., Morris, J. H., States, D. J., & Meng, F. (2010). GLay: Community structure analysis of biological networks. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 26(24), 3135–3137. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq596
Su, G., Morris, J. H., Demchak, B., & Bader, G. D. (2014). Biological network exploration with Cytoscape 3. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics, 47, 8.13.1-8.13.24. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi0813s47
Sun, M. K. (2018). Potential therapeutics for vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Current Neuropharmacology, 16(7), 1036–1044. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X15666171016164734
Szklarczyk, D., Morris, J. H., Cook, H., Kuhn, M., Wyder, S., Simonovic, M., Santos, A., Doncheva, N. T., Roth, A., Bork, P., Jensen, L. J., & von Mering, C. (2017). The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Research, 45(D1), D362–D368. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw937
Tisher, A., & Salardini, A. (2019). A comprehensive update on treatment of dementia. Seminars in Neurology, 39(2), 167–178. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1683408
Tumminia, A., Vinciguerra, F., Parisi, M., & Frittitta, L. (2018). Type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease: role of insulin signalling and therapeutic implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113306
Ullah, R., Khan, M., Shah, S. A., Saeed, K., & Kim, M. O. (2019). Natural antioxidant anthocyanins-a hidden therapeutic candidate in metabolic disorders with major focus in neurodegeneration. Nutrients, 11(6), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061195
Uttara, B., Singh, A. V., Zamboni, P., & Mahajan, R. T. (2009). Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Current Neuropharmacology, 7(1), 65–74. https://doi.org/10.2174/157015909787602823
Valko, M., Leibfritz, D., Moncol, J., Cronin, M. T., Mazur, M., & Telser, J. (2007). Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 39(1), 44–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001
Xie, A., Gao, J., Xu, L., & Meng, D. (2014). Shared mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. BioMed Research International, 2014, 648740. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/648740
Zhang, Y., Kong, P., Chen, Y., Yu, Y., Liu, J., Yang, L., Zhao, T., Nan, J., & Wang, Z. (2014). Significant overlapping modules and biological processes between stroke and coronary heart disease. CNS & Neurological Disorders Drug Targets, 13(4), 652–660. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527312666131223115112
Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Yu, Y., Liu, J., Yuan, Y., Zhao, Y., Li, H., Wang, J., & Wang, Z. (2015). Convergence and divergence of genetic and modular networks between diabetes and breast cancer. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 19(5), 1094–1102. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12504
Funding
Our research was supported by the National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for “Significant New Drug Development” [2017ZX09301-059].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The authors certify that the manuscript has not been submitted to more than one journal for simultaneous consideration.
The submitted work is original and has not been published elsewhere in any form or language (partially or in full), unless the new work concerns an expansion of previous work.
The authors also certify that results are presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification.
No data, text, or theories by others are presented as if they were the author’s own (‘plagiarism’). Proper acknowledgements to other works must be given (this includes material that is closely copied (near verbatim), summarized and/or paraphrased), quotation marks (to indicate words taken from another source) are used for verbatim copying of material, and permissions secured for material that is copyrighted
Our research articles cite appropriate and relevant literature in support of the claims made.
The authors also certify that our article has no untrue statements about an entity (who can be an individual person or a company) or descriptions of their behavior or actions.
Our research has not posed a threat to public health or national security.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Chen Yafei and Liu Qiong have contributed equally to this work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Liu, Q., Liu, J. et al. Revealing the Modular Similarities and Differences Among Alzheimer’s Disease, Vascular Dementia, and Parkinson’s Disease in Genomic Networks. Neuromol Med 24, 125–138 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-021-08670-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-021-08670-2