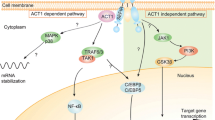
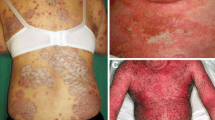
Abstract
In times of targeted therapies, innovative therapeutics become tools to further unravel the pathogenesis of the treated disease, thus influencing current pathogenetic concepts. Based on such paradigm shifts, the next generation of novel therapeutic targets might be identified. Psoriasis is a good example for the resulting most fruitful dialog between clinical and fundamental research. As a result of this, the key role of Th17 lymphocytes, some of their effector molecules, as well as mediators contributing to their maturation have been identified, many of these being targeted by some of the most effective drugs currently available to treat psoriasis. During this process, it became obvious that major parts of the puzzle remain yet to be uncovered or understood in much more detail. This review will therefore address the search for additional important effector cells other than Th17 lymphocytes, such as neutrophils, monocytes, and mast cells, mediators other than IL-17A, including some other IL-17 isoforms, and trigger factors such as potential autoantigens. This will lead to discussing the next generation of targeted therapies for psoriasis as well as treatment goals. These goals need to comprise both psoriasis as well as its comorbidities, as a comprehensive approach to manage the whole patient with all his health issues is urgently needed. Finally, given the substantial differences in resources available in different parts of the world, the global burden of psoriasis and options on how to care for patients outside developed countries will be assessed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boehncke WH, Schon MP (2015) Psoriasis. Lancet. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61909-7
WHO (2013) World psoriasis w—document EB133.R2, agenda item 6.2. http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/EB133/B133_R2-en.pdf
Capon F, Burden AD, Trembath RC, Barker JN (2012) Psoriasis and other complex trait dermatoses: from loci to functional pathways. J Invest Dermatol 132(3 Pt 2):915–922. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.395
Saurat JH, Stingl G, Dubertret L, Papp K, Langley RG, Ortonne JP, Unnebrink K, Kaul M, Camez A, Investigators CS (2008) Efficacy and safety results from the randomized controlled comparative study of adalimumab vs. methotrexate vs. placebo in patients with psoriasis (CHAMPION). Br J Dermatol 158(3):558–566. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08315.x
Thaci D, Blauvelt A, Reich K, Tsai TF, Vanaclocha F, Kingo K, Ziv M, Pinter A, Hugot S, You R, Milutinovic M (2015) Secukinumab is superior to ustekinumab in clearing skin of subjects with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: CLEAR, a randomized controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol 73(3):400–409. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.05.013
Lowes MA, Kikuchi T, Fuentes-Duculan J, Cardinale I, Zaba LC, Haider AS, Bowman EP, Krueger JG (2008) Psoriasis vulgaris lesions contain discrete populations of Th1 and Th17 T cells. J Invest Dermatol 128(5):1207–1211. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5701213
Steinman L (2007) A brief history of T(H)17, the first major revision in the T(H)1/T(H)2 hypothesis of T cell-mediated tissue damage. Nat Med 13(2):139–145. doi:10.1038/nm1551
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK (2009) IL-17 and Th17 cells. Annu Rev Immunol 27:485–517. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132710
Griffiths CE, Strober BE, van de Kerkhof P, Ho V, Fidelus-Gort R, Yeilding N, Guzzo C, Xia Y, Zhou B, Li S, Dooley LT, Goldstein NH, Menter A, Group AS (2010) Comparison of ustekinumab and etanercept for moderate-to-severe psoriasis. N Engl J Med 362(2):118–128. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0810652
Langley RG, Elewski BE, Lebwohl M, Reich K, Griffiths CE, Papp K, Puig L, Nakagawa H, Spelman L, Sigurgeirsson B, Rivas E, Tsai TF, Wasel N, Tyring S, Salko T, Hampele I, Notter M, Karpov A, Helou S, Papavassilis C, Group ES, Group FS (2014) Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis—results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med 371(4):326–338. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1314258
Lebwohl M, Strober B, Menter A, Gordon K, Weglowska J, Puig L, Papp K, Spelman L, Toth D, Kerdel F, Armstrong AW, Stingl G, Kimball AB, Bachelez H, Wu JJ, Crowley J, Langley RG, Blicharski T, Paul C, Lacour JP, Tyring S, Kircik L, Chimenti S, Callis Duffin K, Bagel J, Koo J, Aras G, Li J, Song W, Milmont CE, Shi Y, Erondu N, Klekotka P, Kotzin B, Nirula A (2015) Phase 3 studies comparing brodalumab with ustekinumab in psoriasis. N Engl J Med 373(14):1318–1328. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1503824
Reich K, Papp KA, Matheson RT, Tu JH, Bissonnette R, Bourcier M, Gratton D, Kunynetz RA, Poulin Y, Rosoph LA, Stingl G, Bauer WM, Salter JM, Falk TM, Blodorn-Schlicht NA, Hueber W, Sommer U, Schumacher MM, Peters T, Kriehuber E, Lee DM, Wieczorek GA, Kolbinger F, Bleul CC (2015) Evidence that a neutrophil-keratinocyte crosstalk is an early target of IL-17A inhibition in psoriasis. Exp Dermatol 24(7):529–535. doi:10.1111/exd.12710
Lin AM, Rubin CJ, Khandpur R, Wang JY, Riblett M, Yalavarthi S, Villanueva EC, Shah P, Kaplan MJ, Bruce AT (2011) Mast cells and neutrophils release IL-17 through extracellular trap formation in psoriasis. J Immunol 187(1):490–500. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1100123
Senra L, Stalder R, Alvarez Martinez D, Chizzolini C, Boehncke WH, Brembilla NC (2016) Keratinocyte-derived IL-17E contributes to inflammation in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 136(10):1970–1980. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2016.06.009
Keijsers RR, Hendriks AG, van Erp PE, van Cranenbroek B, van de Kerkhof PC, Koenen HJ, Joosten I (2014) In vivo induction of cutaneous inflammation results in the accumulation of extracellular trap-forming neutrophils expressing RORgammat and IL-17. J Invest Dermatol 134(5):1276–1284. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.526
Taylor PR, Roy S, Leal SM Jr, Sun Y, Howell SJ, Cobb BA, Li X, Pearlman E (2014) Activation of neutrophils by autocrine IL-17A-IL-17RC interactions during fungal infection is regulated by IL-6, IL-23, RORgammat and dectin-2. Nat Immunol 15(2):143–151. doi:10.1038/ni.2797
Brembilla NC, Stalder R, Senra L, Bohencke WH (2017) IL-17A localizes in the exocytic compartment of mast cells in psoriatic skin. Br J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/bjd.15358
Mashiko S, Bouguermouh S, Rubio M, Baba N, Bissonnette R, Sarfati M (2015) Human mast cells are major IL-22 producers in patients with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 136(2):351–359 e351. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2015.01.033
Ikeda K, Nakajima H, Suzuki K, Kagami S, Hirose K, Suto A, Saito Y, Iwamoto I (2003) Mast cells produce interleukin-25 upon Fc epsilon RI-mediated activation. Blood 101(9):3594–3596. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-09-2817
Noordenbos T, Blijdorp I, Chen S, Stap J, Mul E, Canete JD, Lubberts E, Yeremenko N, Baeten D (2016) Human mast cells capture, store, and release bioactive, exogenous IL-17A. J Leukoc Biol. doi:10.1189/jlb.3HI1215-542R
Hueber AJ, Asquith DL, Miller AM, Reilly J, Kerr S, Leipe J, Melendez AJ, McInnes IB (2010) Mast cells express IL-17A in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. J Immunol 184(7):3336–3340. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0903566
Sibilano R, Frossi B, Calvaruso M, Danelli L, Betto E, Dall’Agnese A, Tripodo C, Colombo MP, Pucillo CE, Gri G (2012) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulates acute and late mast cell responses. J Immunol 189(1):120–127. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1200009
Dudeck A, Suender CA, Kostka SL, von Stebut E, Maurer M (2011) Mast cells promote Th1 and Th17 responses by modulating dendritic cell maturation and function. Eur J Immunol 41(7):1883–1893. doi:10.1002/eji.201040994
Piconese S, Gri G, Tripodo C, Musio S, Gorzanelli A, Frossi B, Pedotti R, Pucillo CE, Colombo MP (2009) Mast cells counteract regulatory T-cell suppression through interleukin-6 and OX40/OX40L axis toward Th17-cell differentiation. Blood 114(13):2639–2648. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-05-220004
Boyman O, Hefti HP, Conrad C, Nickoloff BJ, Suter M, Nestle FO (2004) Spontaneous development of psoriasis in a new animal model shows an essential role for resident T cells and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Exp Med 199(5):731–736. doi:10.1084/jem.20031482
Johnson-Huang LM, Suarez-Farinas M, Pierson KC, Fuentes-Duculan J, Cueto I, Lentini T, Sullivan-Whalen M, Gilleaudeau P, Krueger JG, Haider AS, Lowes MA (2012) A single intradermal injection of IFN-gamma induces an inflammatory state in both non-lesional psoriatic and healthy skin. J Invest Dermatol 132(4):1177–1187. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.458
Kryczek I, Bruce AT, Gudjonsson JE, Johnston A, Aphale A, Vatan L, Szeliga W, Wang Y, Liu Y, Welling TH, Elder JT, Zou W (2008) Induction of IL-17+ T cell trafficking and development by IFN-gamma: mechanism and pathological relevance in psoriasis. J Immunol 181(7):4733–4741
Zaba LC, Cardinale I, Gilleaudeau P, Sullivan-Whalen M, Suarez-Farinas M, Fuentes-Duculan J, Novitskaya I, Khatcherian A, Bluth MJ, Lowes MA, Krueger JG (2007) Amelioration of epidermal hyperplasia by TNF inhibition is associated with reduced Th17 responses. J Exp Med 204(13):3183–3194. doi:10.1084/jem.20071094
Nograles KE, Zaba LC, Guttman-Yassky E, Fuentes-Duculan J, Suarez-Farinas M, Cardinale I, Khatcherian A, Gonzalez J, Pierson KC, White TR, Pensabene C, Coats I, Novitskaya I, Lowes MA, Krueger JG (2008) Th17 cytokines interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-22 modulate distinct inflammatory and keratinocyte-response pathways. Br J Dermatol 159(5):1092–1102. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08769.x
Harden JL, Krueger JG, Bowcock AM (2015) The immunogenetics of psoriasis: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun 64:66–73. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2015.07.008
Rizzo HL, Kagami S, Phillips KG, Kurtz SE, Jacques SL, Blauvelt A (2011) IL-23-mediated psoriasis-like epidermal hyperplasia is dependent on IL-17A. J Immunol 186(3):1495–1502. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1001001
Singh TP, Schon MP, Wallbrecht K, Michaelis K, Rinner B, Mayer G, Schmidbauer U, Strohmaier H, Wang XJ, Wolf P (2010) 8-Methoxypsoralen plus ultraviolet a therapy acts via inhibition of the IL-23/Th17 axis and induction of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells involving CTLA4 signaling in a psoriasis-like skin disorder. J Immunol 184(12):7257–7267. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0903719
Carrier Y, Ma HL, Ramon HE, Napierata L, Small C, O’Toole M, Young DA, Fouser LA, Nickerson-Nutter C, Collins M, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K, Medley QG (2011) Inter-regulation of Th17 cytokines and the IL-36 cytokines in vitro and in vivo: implications in psoriasis pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol 131(12):2428–2437. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.234
Harper EG, Guo C, Rizzo H, Lillis JV, Kurtz SE, Skorcheva I, Purdy D, Fitch E, Iordanov M, Blauvelt A (2009) Th17 cytokines stimulate CCL20 expression in keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo: implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol 129(9):2175–2183. doi:10.1038/jid.2009.65
Liang SC, Tan XY, Luxenberg DP, Karim R, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K, Collins M, Fouser LA (2006) Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. J Exp Med 203(10):2271–2279. doi:10.1084/jem.20061308
Zheng Y, Danilenko DM, Valdez P, Kasman I, Eastham-Anderson J, Wu J, Ouyang W (2007) Interleukin-22, a T(H)17 cytokine, mediates IL-23-induced dermal inflammation and acanthosis. Nature 445(7128):648–651. doi:10.1038/nature05505
Gaffen SL (2011) Recent advances in the IL-17 cytokine family. Curr Opin Immunol 23(5):613–619. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2011.07.006
Johansen C, Usher PA, Kjellerup RB, Lundsgaard D, Iversen L, Kragballe K (2009) Characterization of the interleukin-17 isoforms and receptors in lesional psoriatic skin. Br J Dermatol 160(2):319–324. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08902.x
Fujishima S, Watanabe H, Kawaguchi M, Suzuki T, Matsukura S, Homma T, Howell BG, Hizawa N, Mitsuya T, Huang SK, Iijima M (2010) Involvement of IL-17F via the induction of IL-6 in psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 302(7):499–505. doi:10.1007/s00403-010-1033-8
Watanabe H, Kawaguchi M, Fujishima S, Ogura M, Matsukura S, Takeuchi H, Ohba M, Sueki H, Kokubu F, Hizawa N, Adachi M, Huang SK, Iijima M (2009) Functional characterization of IL-17F as a selective neutrophil attractant in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 129(3):650–656. doi:10.1038/jid.2008.294
Glatt S, Helmer E, Haier B, Strimenopoulou F, Price G, Vajjah P, Harari OA, Lambert J, Shaw S (2017) First-in-human randomized study of bimekizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody and selective dual inhibitor of IL-17A and IL-17F, in mild psoriasis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 83(5):991–1001. doi:10.1111/bcp.13185
Johnston A, Fritz Y, Dawes SM, Diaconu D, Al-Attar PM, Guzman AM, Chen CS, Fu W, Gudjonsson JE, McCormick TS, Ward NL (2013) Keratinocyte overexpression of IL-17C promotes psoriasiform skin inflammation. J Immunol 190(5):2252–2262. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1201505
Johansen C, Vinter H, Soegaard-Madsen L, Olsen LR, Steiniche T, Iversen L, Kragballe K (2010) Preferential inhibition of the mRNA expression of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulated cytokines in psoriatic skin by anti-TNFalpha therapy. Br J Dermatol 163(6):1194–1204. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.10036.x
Ramirez-Carrozzi V, Sambandam A, Luis E, Lin Z, Jeet S, Lesch J, Hackney J, Kim J, Zhou M, Lai J, Modrusan Z, Sai T, Lee W, Xu M, Caplazi P, Diehl L, de Voss J, Balazs M, Gonzalez L Jr, Singh H, Ouyang W, Pappu R (2011) IL-17C regulates the innate immune function of epithelial cells in an autocrine manner. Nat Immunol 12(12):1159–1166. doi:10.1038/ni.2156
Iwakura Y, Ishigame H, Saijo S, Nakae S (2011) Functional specialization of interleukin-17 family members. Immunity 34(2):149–162. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.02.012
Angkasekwinai P, Park H, Wang YH, Wang YH, Chang SH, Corry DB, Liu YJ, Zhu Z, Dong C (2007) Interleukin 25 promotes the initiation of proallergic type 2 responses. J Exp Med 204(7):1509–1517. doi:10.1084/jem.20061675
Reynolds JM, Lee YH, Shi Y, Wang X, Angkasekwinai P, Nallaparaju KC, Flaherty S, Chang SH, Watarai H, Dong C (2015) Interleukin-17B antagonizes interleukin-25-mediated mucosal inflammation. Immunity 42(4):692–703. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2015.03.008
Deleuran M, Hvid M, Kemp K, Christensen GB, Deleuran B, Vestergaard C (2012) IL-25 induces both inflammation and skin barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis. Chem Immunol Allergy 96:45–49. doi:10.1159/000331871
Hvid M, Vestergaard C, Kemp K, Christensen GB, Deleuran B, Deleuran M (2011) IL-25 in atopic dermatitis: a possible link between inflammation and skin barrier dysfunction? J Invest Dermatol 131(1):150–157. doi:10.1038/jid.2010.277
Kim BE, Bin L, Ye YM, Ramamoorthy P, Leung DY (2013) IL-25 enhances HSV-1 replication by inhibiting filaggrin expression, and acts synergistically with Th2 cytokines to enhance HSV-1 replication. J Invest Dermatol 133(12):2678–2685. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.223
Lee J, Ho WH, Maruoka M, Corpuz RT, Baldwin DT, Foster JS, Goddard AD, Yansura DG, Vandlen RL, Wood WI, Gurney AL (2001) IL-17E, a novel proinflammatory ligand for the IL-17 receptor homolog IL-17Rh1. J Biol Chem 276(2):1660–1664. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008289200
Lonati PA, Brembilla NC, Montanari E, Fontao L, Gabrielli A, Vettori S, Valentini G, Laffitte E, Kaya G, Meroni PL, Chizzolini C (2014) High IL-17E and low IL-17C dermal expression identifies a fibrosis-specific motif common to morphea and systemic sclerosis. PLoS One 9(8):e105008. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0105008
Pan G, French D, Mao W, Maruoka M, Risser P, Lee J, Foster J, Aggarwal S, Nicholes K, Guillet S, Schow P, Gurney AL (2001) Forced expression of murine IL-17E induces growth retardation, jaundice, a Th2-biased response, and multiorgan inflammation in mice. J Immunol 167(11):6559–6567
Batalla A, Coto E, Gonzalez-Lara L, Gonzalez-Fernandez D, Gomez J, Aranguren TF, Queiro R, Santos-Juanes J, Lopez-Larrea C, Coto-Segura P (2015) Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms IL17RA rs4819554 and IL17E rs79877597 and psoriasis in a Spanish cohort. J Dermatol Sci 80(2):111–115. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2015.06.011
Otsuka A, Miyachi Y, Kabashima K (2012) Narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy decreased the serum IL-17E level in a patient with psoriasis vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 26(11):1455–1456. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04345.x
Hueber W, Sands BE, Lewitzky S, Vandemeulebroecke M, Reinisch W, Higgins PD, Wehkamp J, Feagan BG, Yao MD, Karczewski M, Karczewski J, Pezous N, Bek S, Bruin G, Mellgard B, Berger C, Londei M, Bertolino AP, Tougas G, Travis SP, Secukinumab in Crohn’s Disease Study G (2012) Secukinumab, a human anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody, for moderate to severe Crohn’s disease: unexpected results of a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Gut 61(12):1693–1700. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301668
Friedrich M, Tillack C, Wollenberg A, Schauber J, Brand S (2014) IL-36gamma sustains a proinflammatory self-amplifying loop with IL-17C in anti-TNF-induced psoriasiform skin lesions of patients with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 20(11):1891–1901. doi:10.1097/MIB.0000000000000198
Biancheri P, Pender SL, Ammoscato F, Giuffrida P, Sampietro G, Ardizzone S, Ghanbari A, Curciarello R, Pasini A, Monteleone G, Corazza GR, Macdonald TT, Di Sabatino A (2013) The role of interleukin 17 in Crohn’s disease-associated intestinal fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 6(1):13. doi:10.1186/1755-1536-6-13
Wolk K, Witte E, Wallace E, Docke WD, Kunz S, Asadullah K, Volk HD, Sterry W, Sabat R (2006) IL-22 regulates the expression of genes responsible for antimicrobial defense, cellular differentiation, and mobility in keratinocytes: a potential role in psoriasis. Eur J Immunol 36(5):1309–1323. doi:10.1002/eji.200535503
Pinto-Almeida T, Torres T (2014) Biologic therapy for psoriasis—still searching for the best target. An Bras Dermatol 89(2):365–367
Campa M, Mansouri B, Warren R, Menter A (2016) A review of biologic therapies targeting IL-23 and IL-17 for use in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Dermatol Ther 6(1):1–12. doi:10.1007/s13555-015-0092-3
Gaffen SL, Jain R, Garg AV, Cua DJ (2014) The IL-23-IL-17 immune axis: from mechanisms to therapeutic testing. Nat Rev Immunol 14(9):585–600. doi:10.1038/nri3707
Kaplan MH, Hufford MM, Olson MR (2015) The development and in vivo function of T helper 9 cells. Nat Rev Immunol 15(5):295–307. doi:10.1038/nri3824
Schlapbach C, Gehad A, Yang C, Watanabe R, Guenova E, Teague JE, Campbell L, Yawalkar N, Kupper TS, Clark RA (2014) Human TH9 cells are skin-tropic and have autocrine and paracrine proinflammatory capacity. Sci Transl Med 6(219):219ra218. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007828
Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ (2013) Psoriasis and metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Am Acad Dermatol 68(4):654–662. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.08.015
Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, Belloni Fortina A, Peserico A, Virgili AR, Bruni PL, Ingordo V, Lo Scocco G, Solaroli C, Schena D, Barba A, Di Landro A, Pezzarossa E, Arcangeli F, Gianni C, Betti R, Carli P, Farris A, Barabino GF, La Vecchia C (2005) Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case-control study. J Invest Dermatol 125(1):61–67. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23681.x
Boehncke WH, Boehncke S, Tobin AM, Kirby B (2011) The ‘psoriatic march’: a concept of how severe psoriasis may drive cardiovascular comorbidity. Exp Dermatol 20(4):303–307. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2011.01261.x
Mehta NN, Yu Y, Saboury B, Foroughi N, Krishnamoorthy P, Raper A, Baer A, Antigua J, Van Voorhees AS, Torigian DA, Alavi A, Gelfand JM (2011) Systemic and vascular inflammation in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis as measured by [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT): a pilot study. Arch Dermatol 147(9):1031–1039. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2011.119
Kruglikov IL, Scherer PE, Wollina U (2016) Are dermal adipocytes involved in psoriasis? Exp Dermatol. doi:10.1111/exd.12996
Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ, Walsh K (2011) Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11(2):85–97. doi:10.1038/nri2921
Brembilla NC, Boehncke WH (2016) Dermal adipocytes’ claim for fame in psoriasis. Exp Dermatol. doi:10.1111/exd.13074
Sprague AH, Khalil RA (2009) Inflammatory cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol 78(6):539–552. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.04.029
Steyers CM 3rd, Miller FJ Jr (2014) Endothelial dysfunction in chronic inflammatory diseases. Int J Mol Sci 15(7):11324–11349. doi:10.3390/ijms150711324
Vestweber D (2015) How leukocytes cross the vascular endothelium. Nat Rev Immunol 15(11):692–704. doi:10.1038/nri3908
Spah F (2008) Inflammation in atherosclerosis and psoriasis: common pathogenic mechanisms and the potential for an integrated treatment approach. Br J Dermatol 159(Suppl 2):10–17. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08780.x
Schluter K, Diehl S, Lang V, Kaufmann R, Boehncke WH, Burger C (2016) Insulin resistance may contribute to upregulation of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells in psoriatic plaques. Acta Derm Venereol 96(2):162–168. doi:10.2340/00015555-2227
Woth K, Prein C, Steinhorst K, Diehl S, Boehncke WH, Buerger C (2013) Endothelial cells are highly heterogeneous at the level of cytokine-induced insulin resistance. Exp Dermatol 22(11):714–718. doi:10.1111/exd.12235
Boehncke WH, Boehncke S (2012) Cardiovascular mortality in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: epidemiology, pathomechanisms, therapeutic implications, and perspectives. Curr Rheumatol Rep 14(4):343–348. doi:10.1007/s11926-012-0260-8
Elder JT (2006) PSORS1: linking genetics and immunology. J Invest Dermatol 126(6):1205–1206. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700357
Gudjonsson JE, Karason A, Antonsdottir A, Runarsdottir EH, Hauksson VB, Upmanyu R, Gulcher J, Stefansson K, Valdimarsson H (2003) Psoriasis patients who are homozygous for the HLA-Cw*0602 allele have a 2.5-fold increased risk of developing psoriasis compared with Cw6 heterozygotes. Br J Dermatol 148(2):233–235
Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis C, the Wellcome Trust Case Control C, Strange A, Capon F, Spencer CC, Knight J, Weale ME, Allen MH, Barton A, Band G, Bellenguez C, Bergboer JG, Blackwell JM, Bramon E, Bumpstead SJ, Casas JP, Cork MJ, Corvin A, Deloukas P, Dilthey A, Duncanson A, Edkins S, Estivill X, Fitzgerald O, Freeman C, Giardina E, Gray E, Hofer A, Huffmeier U, Hunt SE, Irvine AD, Jankowski J, Kirby B, Langford C, Lascorz J, Leman J, Leslie S, Mallbris L, Markus HS, Mathew CG, McLean WH, McManus R, Mossner R, Moutsianas L, Naluai AT, Nestle FO, Novelli G, Onoufriadis A, Palmer CN, Perricone C, Pirinen M, Plomin R, Potter SC, Pujol RM, Rautanen A, Riveira-Munoz E, Ryan AW, Salmhofer W, Samuelsson L, Sawcer SJ, Schalkwijk J, Smith CH, Stahle M, Su Z, Tazi-Ahnini R, Traupe H, Viswanathan AC, Warren RB, Weger W, Wolk K, Wood N, Worthington J, Young HS, Zeeuwen PL, Hayday A, Burden AD, Griffiths CE, Kere J, Reis A, McVean G, Evans DM, Brown MA, Barker JN, Peltonen L, Donnelly P, Trembath RC (2010) A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet 42(11):985–990. doi:10.1038/ng.694
Yin X, Low HQ, Wang L, Li Y, Ellinghaus E, Han J, Estivill X, Sun L, Zuo X, Shen C, Zhu C, Zhang A, Sanchez F, Padyukov L, Catanese JJ, Krueger GG, Duffin KC, Mucha S, Weichenthal M, Weidinger S, Lieb W, Foo JN, Li Y, Sim K, Liany H, Irwan I, Teo Y, Theng CT, Gupta R, Bowcock A, De Jager PL, Qureshi AA, de Bakker PI, Seielstad M, Liao W, Stahle M, Franke A, Zhang X, Liu J (2015) Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies multiple novel associations and ethnic heterogeneity of psoriasis susceptibility. Nat Commun 6:6916. doi:10.1038/ncomms7916
Conrad C, Boyman O, Tonel G, Tun-Kyi A, Laggner U, de Fougerolles A, Kotelianski V, Gardner H, Nestle FO (2007) Alpha1beta1 integrin is crucial for accumulation of epidermal T cells and the development of psoriasis. Nat Med 13(7):836–842. doi:10.1038/nm1605
Nishimoto S, Kotani H, Tsuruta S, Shimizu N, Ito M, Shichita T, Morita R, Takahashi H, Amagai M, Yoshimura A (2013) Th17 cells carrying TCR recognizing epidermal autoantigen induce psoriasis-like skin inflammation. J Immunol 191(6):3065–3072. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1300348
Boehncke WH (1996) Psoriasis and bacterial superantigens—formal or causal correlation? Trends Microbiol 4(12):485–489
Gudmundsdottir AS, Sigmundsdottir H, Sigurgeirsson B, Good MF, Valdimarsson H, Jonsdottir I (1999) Is an epitope on keratin 17 a major target for autoreactive T lymphocytes in psoriasis? Clin Exp Immunol 117(3):580–586
Jin L, Wang G (2014) Keratin 17: a critical player in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Med Res Rev 34(2):438–454. doi:10.1002/med.21291
Iversen OJ, Lysvand H, Slupphaug G (2017) Pso p27, a SERPINB3/B4-derived protein, is most likely a common autoantigen in chronic inflammatory diseases. Clin Immunol 174:10–17. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2016.11.006
Ganguly D, Chamilos G, Lande R, Gregorio J, Meller S, Facchinetti V, Homey B, Barrat FJ, Zal T, Gilliet M (2009) Self-RNA-antimicrobial peptide complexes activate human dendritic cells through TLR7 and TLR8. J Exp Med 206(9):1983–1994. doi:10.1084/jem.20090480
Lande R, Botti E, Jandus C, Dojcinovic D, Fanelli G, Conrad C, Chamilos G, Feldmeyer L, Marinari B, Chon S, Vence L, Riccieri V, Guillaume P, Navarini AA, Romero P, Costanzo A, Piccolella E, Gilliet M, Frasca L (2014) The antimicrobial peptide LL37 is a T-cell autoantigen in psoriasis. Nat Commun 5:5621. doi:10.1038/ncomms6621
Lande R, Gregorio J, Facchinetti V, Chatterjee B, Wang YH, Homey B, Cao W, Wang YH, Su B, Nestle FO, Zal T, Mellman I, Schroder JM, Liu YJ, Gilliet M (2007) Plasmacytoid dendritic cells sense self-DNA coupled with antimicrobial peptide. Nature 449(7162):564–569. doi:10.1038/nature06116
Arakawa A, Siewert K, Stohr J, Besgen P, Kim SM, Ruhl G, Nickel J, Vollmer S, Thomas P, Krebs S, Pinkert S, Spannagl M, Held K, Kammerbauer C, Besch R, Dornmair K, Prinz JC (2015) Melanocyte antigen triggers autoimmunity in human psoriasis. J Exp Med 212(13):2203–2212. doi:10.1084/jem.20151093
Capon F (2013) IL36RN mutations in generalized pustular psoriasis: just the tip of the iceberg? J Invest Dermatol 133(11):2503–2504. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.361
Thorleifsdottir RH, Sigurdardottir SL, Sigurgeirsson B, Olafsson JH, Petersen H, Sigurdsson MI, Gudjonsson JE, Johnston A, Valdimarsson H (2016) HLA-Cw6 homozygosity in plaque psoriasis is associated with streptococcal throat infections and pronounced improvement after tonsillectomy: a prospective case series. J Am Acad Dermatol 75(5):889–896. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.06.061
Spuls PI, Lecluse LL, Poulsen ML, Bos JD, Stern RS, Nijsten T (2010) How good are clinical severity and outcome measures for psoriasis?: quantitative evaluation in a systematic review. J Invest Dermatol 130(4):933–943. doi:10.1038/jid.2009.391
Strober B, Papp KA, Lebwohl M, Reich K, Paul C, Blauvelt A, Gordon KB, Milmont CE, Viswanathan HN, Li J, Pinto L, Harrison DJ, Kricorian G, Nirula A, Klekotka P (2016) Clinical meaningfulness of complete skin clearance in psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol 75(1):77–82 e77. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.03.026
McHorney CA, Spain CV (2011) Frequency of and reasons for medication non-fulfillment and non-persistence among American adults with chronic disease in 2008. Health Expect 14(3):307–320. doi:10.1111/j.1369-7625.2010.00619.x
Nast A, Boehncke WH, Mrowietz U, Ockenfels HM, Philipp S, Reich K, Rosenbach T, Sammain A, Schlaeger M, Sebastian M, Sterry W, Streit V, Augustin M, Erdmann R, Klaus J, Koza J, Muller S, Orzechowski HD, Rosumeck S, Schmid-Ott G, Weberschock T, Rzany B, Deutsche Dermatologische G, Berufsverband Deutscher D (2012) German S3-guidelines on the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris (short version). Arch Dermatol Res 304(2):87–113. doi:10.1007/s00403-012-1214-8
Blome C, Gosau R, Radtke MA, Reich K, Rustenbach SJ, Spehr C, Thaci D, Augustin M (2016) Patient-relevant treatment goals in psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 308(2):69–78. doi:10.1007/s00403-015-1613-8
Augustin M, Radtke MA, Zschocke I, Blome C, Behechtnejad J, Schafer I, Reusch M, Mielke V, Rustenbach SJ (2009) The patient benefit index: a novel approach in patient-defined outcomes measurement for skin diseases. Arch Dermatol Res 301(8):561–571. doi:10.1007/s00403-009-0928-8
Walsh JA, McFadden M, Woodcock J, Clegg DO, Helliwell P, Dommasch E, Gelfand JM, Krueger GG, Duffin KC (2013) Product of the Physician Global Assessment and body surface area: a simple static measure of psoriasis severity in a longitudinal cohort. J Am Acad Dermatol 69(6):931–937. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.07.040
Chiesa Fuxench ZC, Callis Duffin K, Siegel M, Van Voorhees AS, Gelfand JM (2015) Validity of the Simple-Measure for Assessing Psoriasis Activity (S-MAPA) for objectively evaluating disease severity in patients with plaque psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol 73(5):868–870. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.001
Tugwell P, Boers M, Brooks P, Simon L, Strand V, Idzerda L (2007) OMERACT: an international initiative to improve outcome measurement in rheumatology. Trials 8:38. doi:10.1186/1745-6215-8-38
Boers M, Kirwan JR, Wells G, Beaton D, Gossec L, d’Agostino MA, Conaghan PG, Bingham CO 3rd, Brooks P, Landewe R, March L, Simon LS, Singh JA, Strand V, Tugwell P (2014) Developing core outcome measurement sets for clinical trials: OMERACT filter 2.0. J Clin Epidemiol 67(7):745–753. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.11.013
Williamson PR, Altman DG, Blazeby JM, Clarke M, Devane D, Gargon E, Tugwell P (2012) Developing core outcome sets for clinical trials: issues to consider. Trials 13:132. doi:10.1186/1745-6215-13-132
Elman SA, Merola JF, Armstrong AW, Duffin KC, Latella J, Garg A, Gottlieb AB (2017) The International Dermatology Outcome Measures (IDEOM) initiative: a review and update. J Drugs Dermatol 16(2):119–124
Puig L (2015) PASI90 response: the new standard in therapeutic efficacy for psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 29(4):645–648. doi:10.1111/jdv.12817
Puig L, Thom H, Mollon P, Tian H, Ramakrishna GS (2017) Clear or almost clear skin improves the quality of life in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 31(2):213–220. doi:10.1111/jdv.14007
Coates LC, Fransen J, Helliwell PS (2010) Defining minimal disease activity in psoriatic arthritis: a proposed objective target for treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 69(1):48–53. doi:10.1136/ard.2008.102053
Coates LC, Helliwell PS (2016) Defining low disease activity states in psoriatic arthritis using novel composite disease instruments. J Rheumatol 43(2):371–375. doi:10.3899/jrheum.150826
Mrowietz U, Kragballe K, Reich K, Spuls P, Griffiths CE, Nast A, Franke J, Antoniou C, Arenberger P, Balieva F, Bylaite M, Correia O, Dauden E, Gisondi P, Iversen L, Kemeny L, Lahfa M, Nijsten T, Rantanen T, Reich A, Rosenbach T, Segaert S, Smith C, Talme T, Volc-Platzer B, Yawalkar N (2011) Definition of treatment goals for moderate to severe psoriasis: a European consensus. Arch Dermatol Res 303(1):1–10. doi:10.1007/s00403-010-1080-1
Kolios AG, Yawalkar N, Anliker M, Boehncke WH, Borradori L, Conrad C, Gilliet M, Hausermann P, Itin P, Laffitte E, Mainetti C, French LE, Navarini AA (2016) Swiss S1 guidelines on the systemic treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. Dermatology 232(4):385–406. doi:10.1159/000445681
Nast A, Gisondi P, Ormerod AD, Saiag P, Smith C, Spuls PI, Arenberger P, Bachelez H, Barker J, Dauden E, de Jong EM, Feist E, Jacobs A, Jobling R, Kemeny L, Maccarone M, Mrowietz U, Papp KA, Paul C, Reich K, Rosumeck S, Talme T, Thio HB, van de Kerkhof P, Werner RN, Yawalkar N (2015) European S3-guidelines on the systemic treatment of psoriasis vulgaris—update 2015—short version—EDF in cooperation with EADV and IPC. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 29(12):2277–2294. doi:10.1111/jdv.13354
Coates LC, Moverley AR, McParland L, Brown S, Navarro-Coy N, O’Dwyer JL, Meads DM, Emery P, Conaghan PG, Helliwell PS (2015) Effect of tight control of inflammation in early psoriatic arthritis (TICOPA): a UK multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 386(10012):2489–2498. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00347-5
Grigor C, Capell H, Stirling A, McMahon AD, Lock P, Vallance R, Kincaid W, Porter D (2004) Effect of a treatment strategy of tight control for rheumatoid arthritis (the TICORA study): a single-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 364(9430):263–269. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16676-2
Kimball AB, Gieler U, Linder D, Sampogna F, Warren RB, Augustin M (2010) Psoriasis: is the impairment to a patient’s life cumulative? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 24(9):989–1004. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03705.x
Warren RB, Kleyn CE, Gulliver WP (2011) Cumulative life course impairment in psoriasis: patient perception of disease-related impairment throughout the life course. Br J Dermatol 164(Suppl 1):1–14. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10280.x
Elder GHGJ (2009) The craft of life course research. The Guilford Press, New York
Linder MD, Piaserico S, Augustin M, Fortina AB, Cohen AD, Gieler U, Jemec GB, Kimball AB, Peserico A, Sampogna F, Warren RB, de Korte J (2016) Psoriasis—the life course approach. Acta Derm Venereol 96(217):102–108. doi:10.2340/00015555-2430
Boehncke S, Thaci D, Beschmann H, Ludwig RJ, Ackermann H, Badenhoop K, Boehncke WH (2007) Psoriasis patients show signs of insulin resistance. Br J Dermatol 157(6):1249–1251. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08190.x
Boehncke S, Fichtlscherer S, Salgo R, Garbaraviciene J, Beschmann H, Diehl S, Hardt K, Thaci D, Boehncke WH (2011) Systemic therapy of plaque-type psoriasis ameliorates endothelial cell function: results of a prospective longitudinal pilot trial. Arch Dermatol Res 303(6):381–388. doi:10.1007/s00403-010-1108-6
Boehncke S, Salgo R, Garbaraviciene J, Beschmann H, Hardt K, Diehl S, Fichtlscherer S, Thaci D, Boehncke WH (2011) Effective continuous systemic therapy of severe plaque-type psoriasis is accompanied by amelioration of biomarkers of cardiovascular risk: results of a prospective longitudinal observational study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 25(10):1187–1193. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03947.x
Wu JJ, Guerin A, Sundaram M, Dea K, Cloutier M, Mulani P (2017) Cardiovascular event risk assessment in psoriasis patients treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors versus methotrexate. J Am Acad Dermatol 76(1):81–90. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.07.042
Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, Mehta NN, Ogdie A, Van Voorhees AS, Gelfand JM (2017) Psoriasis and comorbid diseases: epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol 76(3):377–390. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.07.064
Gupta Y, Moller S, Zillikens D, Boehncke WH, Ibrahim SM, Ludwig RJ (2013) Genetic control of psoriasis is relatively distinct from that of metabolic syndrome and coronary artery disease. Exp Dermatol 22(8):552–553. doi:10.1111/exd.12192
Coates LC, Kavanaugh A, Mease PJ, Soriano ER, Laura Acosta-Felquer M, Armstrong AW, Bautista-Molano W, Boehncke WH, Campbell W, Cauli A, Espinoza LR, FitzGerald O, Gladman DD, Gottlieb A, Helliwell PS, Husni ME, Love TJ, Lubrano E, McHugh N, Nash P, Ogdie A, Orbai AM, Parkinson A, O’Sullivan D, Rosen CF, Schwartzman S, Siegel EL, Toloza S, Tuong W, Ritchlin CT (2016) Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis 2015 Treatment Recommendations for Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68(5):1060–1071. doi:10.1002/art.39573
Dauden E, Castaneda S, Suarez C, Garcia-Campayo J, Blasco AJ, Aguilar MD, Ferrandiz C, Puig L, Sanchez-Carazo JL, Working Group on Comorbidity in P (2013) Clinical practice guideline for an integrated approach to comorbidity in patients with psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 27(11):1387–1404. doi:10.1111/jdv.12024
Boehncke WH, Boehncke S, Schon MP (2010) Managing comorbid disease in patients with psoriasis. BMJ 340:b5666. doi:10.1136/bmj.b5666
Mrowietz U, Steinz K, Gerdes S (2014) Psoriasis: to treat or to manage? Exp Dermatol 23(10):705–709. doi:10.1111/exd.12437
Smolen JS, Schoels M, Aletaha D (2015) Disease activity and response assessment in psoriatic arthritis using the Disease Activity Index for PSoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA). A brief review. Clin Exp Rheumatol 33(5 Suppl 93):S48–S50
FitzGerald O, Helliwell P, Mease P, Mumtaz A, Coates L, Pedersen R, Nab H, Molta C (2012) Application of composite disease activity scores in psoriatic arthritis to the PRESTA data set. Ann Rheum Dis 71(3):358–362. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200093
Jarraya F (2016) Treatment of hypertension: which goal for which patient? Adv Exp Med Biol. doi:10.1007/5584_2016_97
Mease P (2015) A short history of biological therapy for psoriatic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 33(5 Suppl 93):S104–S108
Puig L (2017) The role of IL 23 in the treatment of psoriasis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 1–10. doi:10.1080/1744666X.2017.1292137
Papp KA, Blauvelt A, Bukhalo M, Gooderham M, Krueger JG, Lacour JP, Menter A, Philipp S, Sofen H, Tyring S, Berner BR, Visvanathan S, Pamulapati C, Bennett N, Flack M, Scholl P, Padula SJ (2017) Risankizumab versus ustekinumab for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med 376(16):1551–1560. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1607017
de Mora F (2015) Biosimilar: what it is not. Br J Clin Pharmacol 80(5):949–956. doi:10.1111/bcp.12656
Kurki P, Ekman N (2015) Biosimilar regulation in the EU. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 8(5):649–659. doi:10.1586/17512433.2015.1071188
Reich K, Thaci D, Mrowietz U, Kamps A, Neureither M, Luger T (2009) Efficacy and safety of fumaric acid esters in the long-term treatment of psoriasis—a retrospective study (FUTURE). J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 7(7):603–611. doi:10.1111/j.1610-0387.2009.07120.x
Al Hammadi A, Al-Sheikh A, Ammoury A, Ghosn S, Gisondi P, Hamadah I, Kibbi AG, Shirazy K (2017) Experience and challenges for biologic use in the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis in Africa and the Middle East region. J Dermatolog Treat 28(2):129–135. doi:10.1080/09546634.2016.1183763
Svendsen MT, Jeyabalan J, Andersen KE, Andersen F, Johannessen H (2016) Worldwide utilization of topical remedies in treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review. J Dermatolog Treat:1–10. doi:10.1080/09546634.2016.1254331
Ammar-Khodja A, Benkaidali I, Bouadjar B, Serradj A, Titi A, Benchikhi H, Amal S, Hassam B, Sekkat A, Mernissi FZ, Mokhtar I, Dahoui R, Denguezli M, Doss N, Turki H (2015) EPIMAG: international cross-sectional epidemiological psoriasis study in the Maghreb. Dermatology 231(2):134–144. doi:10.1159/000382123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
WHB has received honoraria as an advisor or speaker on the occasion of company-sponsored symposia from the following companies: Abbvie, Almirall, Biogen, Celgene, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. NB states no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was supported by grant 310030_152680 from the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Ethical Approval and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boehncke, WH., Brembilla, N.C. Unmet Needs in the Field of Psoriasis: Pathogenesis and Treatment. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 55, 295–311 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-017-8634-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-017-8634-3