Abstract
Traumatic injuries are a leading cause of death and disability in both military and civilian populations. Given the complexity and diversity of traumatic injuries, novel and individualized treatment strategies are required to optimize outcomes. Cellular therapies have potential benefit for the treatment of acute or chronic injuries, and various cell-based pharmaceuticals are currently being tested in preclinical studies or in clinical trials. Cellular therapeutics may have the ability to complement existing therapies, especially in restoring organ function lost due to tissue disruption, prolonged hypoxia or inflammatory damage. In this article we highlight the current status and discuss future directions of cellular therapies for the treatment of traumatic injury. Both published research and ongoing clinical trials are discussed here.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Traumatic injuries are one of the leading causes of death in both civilian and military populations worldwide [1, 2]. More advanced methods of resuscitation have improved outcomes of severe traumatic injury associated with hemorrhage in all populations [2], however there are few if any effective therapies that mitigate the long-term consequences of traumatic injury which lead to organ failure and long-term morbidity and mortality. Specifically, in the military, the June 2009 Department of Defense (DoD) implementation of the “golden hour” policy mandating transport of injured service members to a medical treatment facility (MTF) within 60 min where possible has reduced the odds of Killed in Action (KIA) mortality by 39% for the patients transported within an hour in comparison to those who were not [3]. In contrast, civilian injury-related mortality has risen over the past several decades, with a 23% increase in trauma-related mortality in the United States between 2000 and 2010 [2]. In spite of the enormous societal and economic impacts of trauma, a relative lack of innovation in management of the physiological trauma response and disparities in care access for existing treatment strategies has led it to being referred to as the “neglected disease of modern society” [4, 5]. Addressing this need, the emergence of cell-based therapies for the treatment of both acute and chronic traumatic injuries affords a promising new opportunity for the future of critical care medicine.
Introduction
The 1966 U.S. National Academy of Sciences report “Accidental Death and Disability: The Neglected Disease of Modern Society” revealed trauma as the leading cause of death and disability among Americans, and with this revelation issued a plea to apply the lessons of combat injury management to civilian medicine [5]. In response, over the past 50 years the United States has witnessed the development of statewide and regional trauma centers, with 80% of Americans now able to access a Level I or Level II trauma center within 1 h by land or air. Throughout this period, during which active combat operations persisted, the U.S. military continued to improve their own management of traumatic injuries independent to civilian developments, with advances including aggressive tourniquet use, revised transfusion protocols, and an orchestrated sequence of stabilization and transport. Continuous re-evaluation of outcome data through the DoD trauma registry has informed further research for both the military and the civilian sector, and allowed for the centralization of evidence, leading to more standardized clinical practice guidelines [6].
In spite of these advances, an estimated 1000 American service members who perished in combat between 2001 and 2011 died of potentially survivable injuries. Civilian statistics are arguably even more sobering, owing in part to continued discrepancies between military and civilian treatment capabilities and access, with an estimated 1 in 5 trauma deaths considered to be preventable with better trauma care [6]. Thus, despite fifty years of admirable innovation, the urgency remains to develop novel and effective therapeutics for the treatment of the injured.
Cellular therapy (CT), which encompasses a number of different cell types of both autologous and non-autologous derivation is a relatively recent approach which shows potential in all phases of traumatic resuscitation (immediate, subacute, and chronic). Following the initial traumatic injury during which death from hemorrhage can occur rapidly and supportive resuscitation efforts play a key role, an interplay of infection, inflammation, vascular compromise, and dysfunctional coagulation can subsequently develop, leading to further systemic compromise. CT administered acutely after injury has the potential to modulate these systemic inflammatory processes, increasing survival in this vulnerable period until the acute provocation dissipates and hemodynamic stability is regained [2]. In the following review, we provide an overview of trauma pathophysiology, and the pre-clinical and clinical data available to date utilizing various cellular therapies.
Definition and Timeline of Traumatic Injury
A significant portion of trauma-related mortality is attributed to polytrauma [7]. The term “polytrauma” historically lacks a consensus definition. Previous authors have defined polytrauma as “>2 severe injuries, with at least one injury or the sum of all injuries being life threatening”, while others have defined it based on the Injury Severity Score (ISS), with discordant numerical values quantifying severity [8]. Studies have shown that providers have varying interpretations regarding the definition, even within the same institutions [9, 10]. In spite of this lack of formal definition, the ramifications of the injury time course are generally well-defined.
Trauma-related mortality was classically described as a trimodal model of distribution, characterized by three peaks: [1] immediate deaths from severe injuries, typically occurring within minutes of injury; [2] early deaths typically due to hemorrhage, defined as those occurring within 24 h of arrival to the trauma center; [3] late deaths due to multi-organ failure and sepsis, occurring days to weeks following the initial injury [11,12,13]. However, several large retrospective studies beginning in the early 2000s indicated a paradigm shift towards a more bimodal or unimodal distribution of trauma-related mortality, with up to 50–60% of deaths occurring in the first 24 h followed by an overall decrease in trauma-related mortality thereafter [14,15,16].
Trauma Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of trauma-induced injury is complex and depends on multiple factors, including severity and type of injury as well as factors related to the health and characteristics of the patient. Severe traumatic injury and the resulting systemic physiological responses challenge virtually all organ systems in the body. Some of these physiological responses to severe traumatic injury are shown in Fig. 1. Breaching the endothelial barrier exposes tissue factor and activates the coagulation cascade to halt bleeding. Additionally, trauma induces a series of innate and adaptive immune responses for the purpose of clearing damaged tissues and activating repair mechanisms [17]. Severe injury can prompt the release of endogenous damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs, including nucleic acids, histones, high-mobility group box 1 protein, and S100), from damaged, stressed or dying cells [18,19,20]. In addition, vulnerability to exogenous pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs, produced by infectious agents and pathogens) can be increased [21]. These molecules can cause activation of inflammatory systemic pathways, such as the complement cascade, as an initial defense [22]. In conjunction with this, a ‘cytokine storm’ may occur which stimulates the re-prioritization of leukocyte function unique to the pattern of injury. Under ideal circumstances, this results in balanced pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory protective effects that ultimately promote healing. However, if the initial injury is severe or associated with further exacerbating factors, e.g. hemorrhagic shock, generalized/overwhelming infection, or extended surgical intervention, the inflammatory effects can become dominant, leading to acute traumatic coagulopathy, vascular compromise and immune dysfunction — key factors which have been defined to encompass what is known as the endotheliopathy of trauma [23] (EOT). This, in turn, can cause endothelial dysfunction and cellular barrier breakdown, facilitating further release of PAMPs and DAMPs and, in a vicious cycle, amplifying the already disproportionate immune response [22].
In contrast, the adaptive immune response to trauma occurs later and is less defined. Accumulating evidence implicates interactions between the complement pathway and lymphocytes as a prominent feature in the acute setting. Severe trauma is associated with elevated levels of complement factors C3a, C4a, and C5a. The root cause of the complement factor elevation is unknown [24], whether by interaction with PAMPS or by consequence of activated thrombin in the coagulation cascade [17, 25, 26], however, histones released by C5a’s action on neutrophils were linked to induction of T cell apoptosis, suggesting that histone levels increased after trauma may contribute to T cell death through the indirect effect of C5a. In addition, C5aR activation was shown to enhance pro-inflammatory Th1 responses and to reduce anti-inflammatory Th2 responses, hereby shifting the balance toward a systemic inflammatory condition [24]. Collectively, these disparate immune responses can clinically manifest as multiple-organ-dysfunction syndrome in the acute setting, which can lead to persistent inflammation-immunosuppressive catabolism syndrome, both of which correlate with worse outcomes [26, 27].
Unpredictable physiological responses may also occur in response to severe trauma. Acute traumatic coagulopathy (ATC), also known as trauma induced coagulopathy, is one such complication further confounding trauma pathophysiology and management. ATC is multifactorial and highly variable between patients; it is clinically characterized by the initial onset of hemodynamic instability, with subsequent tissue hypoperfusion, and endothelial dysfunction with activation of the endothelium by factors such as catecholamines, cytokines and hypoxia following severe traumatic injury, leading to an early inflammatory and hypercoagulable state [28]. Excessive thrombin generation from the coagulation cascade leads to further hypocoagulation, characterized by fibrinolysis and platelet dysfunction [28,29,30,31]. This excessive thrombin generation can also further exacerbate activation of complement factors in the innate immune response [17, 24, 25].
Multi-organ dysfunction secondary to the aberrant systemic inflammatory response to trauma occurs in up to 30% of severely injured patients, and leads to poorer associated outcomes [32]. Both focal and multifocal injuries can lead to similar complications. For example, neurotrauma, such as traumatic brain injury (TBI) or spinal cord injury (SCI), is characterized by the initial injury which is subsequently followed by the inflammatory cascade, leading to fluid and electrolyte imbalance, cerebral edema, and neuronal cell death, all of which can continue for extended periods following the inciting event. Hemorrhagic shock can lead to pulmonary and renal injuries, including acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute renal failure. Marrow suppression due to ongoing inflammation can lead to persistent cytopenias, unrelated to the initial insult or ongoing hemorrhagic process [2]. In spite of the inter-related nature of their dysfunction, treatments to date have primarily focused on addressing each individual entity rather than the process as a whole.
Yet, given the complexity of trauma pathophysiology, it is not surprising that no single treatment has emerged to manage it. Cellular therapies utilize complex biological agents which comprise often living cells and are presumably able to actively respond to the variable environment in the injured patient. Thus, they have the potential to address multiple therapeutic targets of injury simultaneously that cannot be encompassed with other existing strategies [2].
Cellular Therapies
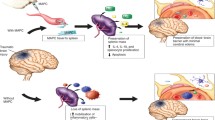
A number of different cell types are currently being investigated for use in CT, including intact live cells and cell-derived materials, such as extracellular vesicles (EVs) or conditioned media. A universal CT agent has not yet been identified, however it is likely that different cell types will be optimal depending on the patient indication and intended use. Figure 2 illustrates some of the more commonly used types of cellular therapy agents. The following is a summary of individual CT concepts and cell types, and their potential therapeutic application in trauma patients (Table 1).
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are multipotent adult stem-like cells [33] which may be involved in the physiologic response to regenerate damaged tissue following injury [34, 35]. When re-infused after ex vivo expansion, they can exert therapeutic effects such as immunomodulation and tissue regeneration. The term MSC itself encompasses cells which share some common characteristics derived from a broad range of tissue sources. The International Society of Cell and Gene Therapy has established minimal standardized criteria to define MSCs for the purposes of laboratory and pre-clinical research, which include adherence to plastic, specific surface antigen expression, and multipotent differentiation potential [36]. Originally, MSCs were isolated from the bone marrow, but more recently they have been derived from almost every tissue type within the body, with sources such as adipose tissue and placental-derived MSCs being tested for application in specific diseases. Despite overlapping properties of MSCs from different sources, it is recognized that they likely have a range of capabilities based upon cell source, donor, and variation in production and handling conditions [37].
MSCs respond to chemoattractant pathways and have the potential to target to the site of cellular damage via these pathways [38]. Based on our current understanding, they are presumed to exert therapeutic effects by secreting and/or releasing cytokines and other factors, possibly delivered by EVs, that affect inflammation, coagulation, vascular integrity and the immune response to trauma [39]. Yet, distinct mechanisms of action (MoA) pertaining to specific MSC preparations or clinical indications have not been identified to date. Their potential beneficial properties have informed a number of preclinical and clinical studies in various disease types, including sepsis, TBI, wound and fracture healing, cerebrovascular accident, graft versus host disease, renal disease, cardiovascular disease and pulmonary injury, among others [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. Interestingly, benefit in pre-clinical and clinical studies for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) [51,52,53] has led to a large number of preclinical studies and proposed clinical trials to investigate cellular therapies for COVID-19 [54,55,56]. However, pre-clinical evidence regarding MSC therapeutic efficacy in polytrauma remains limited.
Previous studies have indicated the presence of MSCs both sequestered within organ systems and in the peripheral blood of various animal models, as well as in instances of isolated tissue regeneration [43, 57, 58]. To date, little is known regarding the role or presence of endogenous MSCs in the setting of polytrauma. Wiegner et al. revealed in a monocenter, longitudinal observational clinical study of 11 patients that the relative numbers of MSC-like cells found in the peripheral blood were reduced following injury [59]. Whether this is due to lower mobilization of MSCs from the bone marrow or sequestration of MSCs to the sites of injury remains unclear at this time [59].
In spite of the well-established regenerative and immunomodulatory capacities of MSCs in experimental settings and their potential to migrate to areas of injury, evidence of overall clinical effectiveness of exogenous MSCs remains limited to certain specific conditions [60,61,62]. MSC use in trauma or trauma-associated conditions such as organ failure is still at an early stage of investigation, but preclinical studies show promise. Krumina et al. established MSCs´ therapeutic efficacy for rodent polytrauma in a study in which they injected rats with bone marrow MSCs at 36 h and 9 days following induced trauma. The animals who underwent experimental polytrauma with subsequent MSC infusion displayed improved rehabilitation scores in comparison to rats without the infusion. Interestingly, rats who received MSC infusions also displayed transient decreased red blood cell production with pathology remaining unclear [63]. Tanrivderi, et al. further substantiated this in a more recent study in which they injected rats with MSCs or normal saline intraperitoneally or intravenously 5 days following induced polytrauma vs. isolated liver injury. Rats injected with MSCs had statistically significant lower markers of inflammation (alanine aminotransferase, C-reactive protein) from peripheral samples and liver and bone tissue biopsies than untreated groups [64]. Yet, no study to date has replicated these therapeutic concepts in humans; most clinical studies examining MSC therapy for non-trauma settings are in the early stages of phase 1 and 2 trials [65,66,67]. Wilson, et al. completed a phase 1 safety clinical trial involving 9 patients with non-trauma induced ARDS divided into 3 cohorts with each given a different dose of MSCs. Those given the highest dose of MSCs displayed better scores on validated assessments of organ function and peripheral biomarker levels, although the results were statistically insignificant. A follow up phase 2a clinical trial was subsequently released with no differences in 28 day mortality noted between the treated and control groups. Notably, no adverse effects directly attributable to MSCs were found in either trial [51, 68]. A Phase 2b prospective randomized multi-center trial is currently underway for MSCs in trauma and non-trauma patients (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03818854). Phase 1 trials throughout Korea, China, and Brazil examining MSC use in acute and chronic spinal cord injuries have been completed with no data released to date (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT02152657, NCT02482194, NCT01393977).
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
In the adult, hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSCs) reside in the bone marrow and give rise to all blood cells throughout the body. They were among the first cell types that were applied clinically, with the first successful bone marrow transplant occurring in 1956 in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia [69]. Historically, HSCs were thought of as a homogeneous population of cells with similar abilities for self-renewal and differentiation. However, recent studies have identified HSC subtypes with distinctive functional properties, including self-renewal capacity and differentiation patterns [70]. Such operative diversity stimulates curiosity regarding unrealized treatment potential.
Previous studies have suggested a hypercatecholamine state with associated bone marrow dysfunction leading to prolonged peripheral HSC mobilization and suppressed erythroid progenitor cell maturation following severe trauma [69, 71, 72]. This HSC mobilization can persist for up to 14 days in humans, with trauma-associated anemia persisting thereafter, often for months [73]. Additionally, HSC apoptosis can occur due to the excessive induction of inflammatory cytokines that occurs in association with trauma [74].
Such functional suppression has led to questions about methods of marrow stimulation and replacement. While the clinical application of HSCs is well established in oncology, their use in trauma-associated injuries remains mostly unexplored. The most relevant example of their utility involves radiation exposure and its associated complications. Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) refers to multi-organ system dysfunction, including hematopoietic, gastrointestinal, neurovascular, and cutaneous, which occurs as a result of acute exposure to high doses of ionizing radiation, whether accidently or as a warfare tactic [75]. An estimated 50 patients with ARS have undergone allogeneic HSC transplantation (HSCT), with the most famous cases involving the victims of the 1986 Chernobyl and the 1999 Tokaimura nuclear plant accidents. Unfortunately, half of these patients died within 50 days of transplant, largely secondary to complications including burns, graft versus host disease, and infection [76, 77]. In 2018, the World Health Organization released their summary of recommendations regarding ARS management, with HSCT being recommended as second line therapy following the failure of colony-stimulating factors in the management of hematologic complications of radiation exposure [75].
Several studies have implied a benefit to HSC and MSC co-transplantation in an oncologic setting, with increased HSC engraftment due to bone marrow microenvironment modulation and hematopoietic support by MSCs [78, 79]. Such findings suggest a potential clinical benefit to combination CT in other disease processes. Additional trauma specific data is needed before more definitive utility can be determined.
Pluripotent Stem Cells
Human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the undifferentiated inner cell mass of a blastocyst [80], and differentiated cells can be re-programmed to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) featuring inner cell mass properties [81,82,83]. Although unmodified pluripotent cell use cannot be applied clinically due to their potential to form teratomas, their differentiation potential has prompted interest in use of ESC/iPSC derivatives—cells or cellular products of the pluripotent ESC/iPSC differentiation—as a therapy for a variety of disease types, including ophthalmologic and cardiovascular disorders [84, 85]. While data is relatively limited, ESC derivatives use in focal traumatic injuries—primarily neurologic—has been investigated with positive results.
Manley et al. corroborated the efficacy and safety profile of ESC-derived oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) in rats which underwent experimental spinal cord injury. Rats which received spinal injections of the OPCs displayed improved locomotor performance with increased sparing of myelinated axons at the injury site in comparison to controls [86]. Similar results were seen in several preceding studies [87,88,89,90]. There are currently more than 10 trials involving human ESC derivatives at various stages of completion listed on clinicaltrials.gov, primarily addressing cardiovascular, ophthalmologic, and neurodegenerative conditions. To our knowledge, no published pre-clinical or clinical studies investigating the application of ESC/iPSC derivatives in polytrauma are currently available.
Aside from this paucity of data restricting its therapeutic application, additional unique concerns related to ESC/iPSC based therapy have arisen throughout their investigation. These include the risk of potential tumorigenic contaminants in the ESC/iPSC-derived CT, as well as ethical and legal implications related to this cellular source [89, 91, 92]. Further information must be obtained prior to widespread utilization.
Neural Stem Cells
Historically, cells of the human central nervous system (CNS) were thought to have limited capacity for renewal and repair. However, the identification of neural stem cells (NSCs) in the 1960s led to extensive research that changed this central tenet from one of resignation to hope that at least some repair may be possible [93]. NSCs and their progenitors are multipotent cells located in the lateral ventricles and hippocampus in adults, and in the brain, umbilical cord, and bone marrow of fetuses, which have the ability to differentiate into both neurons and glial cells [94, 95]. The therapeutic potential of NSC transplantation in neurodegenerative diseases or in trauma (including spinal cord and traumatic brain injuries) was demonstrated in rat models [91, 96, 97]. Specifically, in a recent study, rats which underwent experimental TBI with subsequent injection of embryonic NSCs were found to have reduced neuroinflammation and increased neurogenesis via induction of neural progenitor proliferation at 1 and 4 weeks post-transplant in comparison to controls [90]. Given the global burden of neurologic injuries, with their associated acute and chronic effects, NSC cell therapies are a promising option for future research [95].
Similar to the CT discussed above, the mechanisms by which transplanted NSCs wield their neuroprotective effects are not yet fully understood, with recent animal studies suggesting contributions of various growth factors and anti-apoptotic proteins [96, 98]. However, several patterns have emerged [95]. First, the transplanted NSCs can proliferate, differentiate, and migrate in small numbers in vivo, which has been associated with some recovery of function. Second, NSCs display a comparatively prolonged tolerance to hypoxia allowing them to survive for longer periods in the hostile, injured tissue environment and exert their beneficial effects. Finally, transplanted NSCs participate in ‘internal crosstalk,’ in which they protect nearby cells from degeneration by secreting paracrine factors and modulating the immune response [95].
In addition to the aforementioned animal studies, several phase 2 clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of NSC transplantation in spinal cord injuries have been completed in Russia and Switzerland, although no results have yet been published (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT01321333, NCT02326662). A phase 1 clinical trial examining the efficacy of fetal-derived neural stem cell transplantation in multiple sclerosis patients is currently on-going (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03269071). A phase 1 trial of neural progenitor cells for SCI was conducted by Ciacci and colleagues in chronic SCI and demonstrated no adverse events [99]. A previous phase 1 clinical trial examining intraspinal injections of NSCs in patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) suggested a positive safety profile, however the study was insufficiently powered to suggest treatment efficacy [100]. A similar safety profile was noted at the 60 month follow up in a more recent phase 1 clinical trial of ALS patients [101].
In spite of the extensive research to date regarding NSC safety and utility, limited published data exists regarding their application in either animal or human models of trauma or polytrauma. Further research is needed, including safety, efficacy, and NSC behavior under systemic inflammatory conditions, prior to wider clinical application in the setting of traumatic injury.
Endothelial Progenitor Cells
The term “haemangioblast” was coined in 1932 to describe a cell type thought to be the precursor of both endothelial and hematopoietic cell lineages [102]. These cells, now termed endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), were only isolated from human peripheral blood in 1997 [103]. EPCs are a heterogeneous group of endothelial cell precursors comprised of both hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic lineages derived from bone marrow and peripheral blood sources, respectively. Unlike traditional progenitor cells lacking self-renewal capacity, EPCs are similar to stem cells in their ability to self-renew, form clones, and differentiate into endothelial cells [104,105,106]. Their role in vasculogenesis—previously thought to occur only via migration of existing endothelial cells or through induction of hematopoietic stem cells—has been well-established [107]. Several studies have shown a correlation between the presence of EPCs in blood to various disease processes, including neurologic and cardiovascular disease, sepsis, malignancy, and severe trauma, among others [108,109,110,111,112]. Given their ubiquitous nature and the importance of endothelial maintenance and neovascularization to wound healing, EPCs are an encouraging option for future trauma therapies.
Systemic mobilization of EPCs into the peripheral blood increases in the setting of either local or systemic organ dysfunction, prompting interest in their use as a potential biomarker for various disease processes [107]. Additionally, increased EPC recruitment to various organs, including the lung, liver, and kidney has shown physiologic benefit [112]. However, despite these correlations, their actual contribution to organ repair remains an area of contention. Some studies indicate that EPCs may migrate to areas of vascular damage, where they could subsequently increase vascularization, improving blood flow and tissue activity [113].
Early pre-clinical trials primarily focused on administered EPC contributions to re-vascularization in the setting of cardiovascular diseases. Kalka, et al. noted that rats injected with isolated EPCs had significantly improved perfusion in experimentally induced limb ischemia, with a 50% reduction of limb necrosis and auto-amputation compared to controls [114]. Positive outcomes were also noted with EPC infusion in the setting of myocardial infarction [115]. In regard to trauma, Guo, et al. noted that peripherally administered EPCs preferentially tracked to injured rather than normal brain tissue in rats with experimental TBI, with an overall improved functional recovery seen thereafter [113]. Other studies have also shown neuroprotection by EPCs [116]. Additionally, mice who underwent experimental femoral fractures followed by co-transplantation with bone marrow derived macrophages (BMMs) and EPCs had enhanced engraftment into the fracture site, increased neovascularization, and accelerated fracture healing compared to BMM monotherapy [117].
Clinical trial data involving EPC interventions is limited, especially for trauma. In non-trauma studies, a randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of autologous EPC infusion for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension suggested potential improvement in exercise capacity and pulmonary hemodynamic status [86]. Several other trials are currently underway, evaluating use of EPCs in chronic ischemic stroke, liver cirrhosis, and refractory angina (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT00694642, NCT02605707, NCT03109236). Further studies are needed to determine the potential utility and application of EPCs for various indications. Because beneficial effects on vascularization are expected to assist wound healing, it is of interest to evaluate EPCs for trauma. However, given the heterogeneity of the EPC population as a whole, a more defined and uniform cell type should be elucidated and characterized prior to widespread therapeutic application for trauma [118].
Fibroblasts
Many cell therapy agents are primary non-immortal cells with a finite lifespan. For stem cell clinical applications, large numbers of well-characterized cells will be needed, leading to the consideration of more easily accessible cell types. Fibroblasts are cells that encompass the main component of the connective tissue. They secrete collagens, which provide the structural integrity for many tissues, and play a vital role in wound healing, scar formation, and aging. Traditionally, fibroblasts were viewed as uniform cell types with equivalent functions despite originating in different tissues. However, recent literature has revealed significant phenotypic variance based upon tissue derivation and physiologic conditions to which they have been exposed [119, 120].
Fibroblasts generally proliferate rapidly during development and in disease, [121, 122] and they are relatively easy to expand in culture. Identification of fibroblast-specific cellular markers has proven elusive, further limiting study of fibroblasts in vivo and limiting our understanding of their potential clinical utility. However, preliminary studies indicate that human fibroblasts display similar morphology to MSCs with similar immunophenotypic capabilities [123, 124]. Similar immunomodulation capabilities to MSCs (at least in vitro) and greater relative abundance make primary fibroblasts attractive candidates for cell therapy. However, the safety profile of heterologous human fibroblast administration has been less studied and needs further analysis. Although they are thought to be less immune-privileged than MSCs, further work is needed on this issue [119, 120, 124, 125].
To date, pre-clinical and clinical trials involving fibroblasts have primarily focused on their topical use in wound healing rather than systemic administration. A phase II randomized clinical trial using an intradermal allogeneic fibroblast suspension compared with vehicle alone injected into the chronic wounds of patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa revealed more rapid healing of wounds in those treated with fibroblasts [126]. Additionally, more recent pre-clinical trials have revealed a potential role for fibroblasts in nerve regeneration. In one study examining fibroblast use in murine models with induced peripheral nerve injury, co-transplantation of fibroblasts with Schwann cells revealed positive effects on peripheral nerve regeneration and functional recovery [127]. Clinical trials involving fibroblast transplantation for facial deformities and skin thickening at the surgical sites of amputees are currently on-going (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03947450, NCT0111563). A clinical trial involving the conversion of fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells for future therapeutic use is also active (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT00801372).
Natural Killer Cells
Natural killer (NK) cells are lymphocyte-like cells that are part of the innate immune system which historically recognize and respond to tumor and virally-infected cells by two mechanisms. First, they bind antibody-coated targets via immunoglobulin receptors leading to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Second, they bear natural cytotoxicity receptors that detect the altered expression of ligands on the surface of abnormal cells, ultimately triggering NK cell activation [128, 129]. Recent evidence has shown the complexity of their functionality, with their activity regulated by a series of activating and inhibitory cell receptors, in conjunction with a variety of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, activated NK cells modulate the behavior of other innate and adaptive immune cells through secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and TNF-α [130].
In relation to trauma, NK cells are thought to play a critical role in the development of systemic inflammation and multi-organ dysfunction by producing IFN-γ with subsequent activation of macrophages and increased inflammatory cascade activity. Depletion of NK cells in a rat model of polytrauma consisting of an induced femoral fracture and hemorrhagic shock, followed by sepsis resulted in a reduction in IL-6 mRNA in liver tissue with a 50% mortality reduction in comparison to controls [131]. Similar results were reproduced in rats who underwent experimental polytrauma with subsequent infusion of anti-NK1.1 antibody on the two consecutive days following injury [132]. Observational studies in humans revealed an increased presence of NK dim cells, considered to have a “cytotoxic phenotype, 2 h following traumatic injury, with concomitant development of multi-organ dysfunction and lymphopenia, although the clinical significance of this remains unclear [133]. This direct correlation has also been observed in other systemic illnesses, including sepsis [134]. Preliminary studies involving administration of NK cells for oncologic intervention have shown positive outcomes, with several clinical trials currently pending; however, at the time of this review, no trials involving their use in polytrauma have been completed and reported (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT02809092, NCT02409576, NCT03358849). Given the aforementioned findings, CT with NK cells may well focus on manipulation of their levels rather than their actual injection.
Extracellular Vesicles
‘Extracellular vesicles’ (EV) is a generic term used to describe secreted vesicles, commonly referred to as ectosomes, exosomes, microparticles, microvesicles, and oncosomes, based upon size [135, 136]. They are membrane-bound vesicles containing various molecular components, including RNA, proteins, and metabolites that are released from tissues to aid in intracellular molecular trafficking. Given this property, their potential use as disease markers and therapeutic targets remains an active topic of interest [137], with preliminary studies to date revealing promise for treating pulmonary injuries, acute kidney injuries, neurologic insults, and myocardial infarctions [138,139,140,141,142].
A number of studies have noted increased circulation of EVs following major physiologic insult. In trauma specifically, one observational study completed in 2015 of 22 patients revealed that platelet-derived and endothelial-derived microparticle concentrations increased significantly in patients with polytrauma compared to healthy patients or those with minor injuries, with EV concentrations correlated directly with injury severity [143]. Another study of 37 patients yielded comparable outcomes and also revealed EV counts to be negatively correlated with coagulation times, particularly within the first 3 days of injury, indicating a possible pro-coagulant effect of endogenous EVs in this setting [144]. Similar results have been found in patients with severe burn injuries, with leukocyte and granulocyte-derived EV levels on the initial day of injury directly correlated with mortality [145]. In spite of these observations, the effect of this increase is not well-described and is likely largely source dependent, with evidence to date suggesting a dual role of EVs in both tissue repair and damage [22].
Optimal sources of EVs to maximize treatment efficacy have yet to be defined. Initial studies using treatment with exogenous MSC-derived EVs have shown promise in a variety of disease processes, including systemic inflammatory responses [146]. In one study using a mouse model to examine ARDS after hemorrhagic shock, injured mice received MSCs, MSC-derived EVs, or normal saline following the initial injury. Subsequent lung biopsies revealed significantly decreased lung vascular permeability in both the MSC and MSC-derived EV treated groups compared to control animals [147]. Another pre-clinical trial examining the incidence of pneumonia in mice following burn injuries revealed improved bacterial clearance and overall survival in mice intra-nasally inoculated with EVs obtained via bronchoalveolar lavage versus controls [148]. Alam and colleagues have recently demonstrated in a swine model of TBI and hemorrhagic shock that early treatment with a single dose of MSC-derived exosomes significantly attenuated brain swelling, blood brain barrier permeability, lesion size and also decreased blood-based cerebral biomarkers [149]. In clinical studies, a safety study for the use of MSC-derived EVs in premature neonates at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia began enrollment in April 2019 (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03857841). Trials involving MSC-derived EVs for treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus, macular injury, and acute ischemic stroke are currently on-going (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03437759, NCT03384433, NCT02138331), as are several trials involving vesicle-based drug delivery (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT01854866, NCT02657460). Although preliminary, the use of EVs as therapeutic agents holds promise and has practical advantages over the use of live cells, especially in more austere treatment environments.
“Engineered” Therapies
Tissue engineering refers to the manipulation of cells and tissues. Historically, this research has focused on regaining tissue functionality, such as limb restoration in cases of traumatic amputation [150]. However, the expansion of “engineered therapy” use into medical sub-specialties such as oncology has introduced the possibility of wider application in all fields, including modulation of the immune system following trauma.
CAR-T cell therapy utilizes T lymphocytes obtained from individual patients that are genetically engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), a fusion protein combining an extracellular binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular signaling domain. The modified T cells are able to specifically recognize their target antigen via the binding domain, resulting in T cell activation upon their encounter [151]. T cell receptor (TCR) T cells represent a similar but distinctive T cell immunotherapy which help to combat the limitations of CAR-T cells related to extracellular antigen recognition. Following modification, TCRs are able to recognize and target antigen-derived peptides that are processed and presented on HLA molecules, thus allowing directed attack against intracellular antigens [152, 153]. Given their potential as an allogeneic therapeutic, the development of CAR-NK cells has also recently emerged with similar treatment goals [154]. To date, these therapies have shown promise in the treatment of various malignancies, but minimal data exists for their use outside of malignancy [155,156,157]. Recently Epstein and colleagues demonstrated that CAR-T cells could promote cardiac repair and inhibit fibrosis, which is one of the first studies demonstrating their potential outside of oncological applications and implies potentially broader utility [158]. Given our increasing understanding of trauma pathophysiology, including the previously described complement-mediated suppression of anti-inflammatory Th2 leading to increased inflammation, the potential use of lymphocyte immunotherapy to combat this cascade cannot be overlooked.
Aside from the aforementioned modifications of lymphocytes, genetic engineering of stem cells and progenitor cells has been studied with the intent of optimizing functionality and enhancing therapeutic efficacy [159]. Modification of EPCs resulting in overexpression of various growth factors has been shown to enhance vasculogenesis and neurogenesis in rats which underwent experimental vascular and neurologic injury, respectively [160, 161]. MSCs genetically engineered to overexpress IL-10—known to suppress secretion of pro-inflammatory markers—reduced inflammation and improved fine motor function in comparison to MSCs alone in rats who underwent experimental TBI [162]. One of the most publicly lauded and broadly applied engineered therapies to date, which was mentioned briefly above, involves induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). iPSCs—initially developed in 2006—are differentiated cells manipulated to dedifferentiate, and subsequently acquire properties similar to ESCs, including the ability to differentiate into any adult cell type [163]. Although initially heralded as the next great phenomenon of regenerative medicine due to the indefinite cell source and great variety of cellular re-programming capabilities, the challenging nature of their development as well as concerns for tumorogenicity [164,165,166,167] has shifted the focus for their use to replicating and researching human diseases [168]. However, in spite of this new focus, preclinical data regarding the use of iPSC derivatives in traumatic injuries has shown promise. A meta-analysis examining 6 randomized controlled trials involving iPSC derivatives that have been differentiated into neural precursors, oligodendrocyte progenitors or astrocytes in rat models of spinal cord injury concluded that rats which received therapy displayed improved locomotor function [169]. A recent meta-analysis which evaluated preclinical data involving a variety of rodent and monkey models for spinal cord injury also displayed hopeful results, with significant motor improvement after application of iPSC-derived neural cells noted in comparison to controls [170]. Current clinical trials involve the use of iPSCs in modeling various disease types, include ophthalmologic, cardiovascular, and neurologic (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03696628, NCT03971812, NCT02815072, NCT03853252). To our knowledge, no studies regarding their application in polytrauma currently exist. However, given their arduous development process and increased potential for tumorigenicity, the application of iPSC derivatives in acute polytrauma remains challenging.
Areas in Need of Further Study
Although this review highlights the enormous investigative efforts completed or ongoing to date, it demonstrates the significant amount of study still needed before widespread clinical application of CT for trauma indications is feasible. Two remaining issues, mentioned only briefly above, involve cellular product heterogeneity and the potential for tumorigenicity [164,165,166, 171,172,173,174]. CT, particularly MSCs and EPCs, can encompass a variety of cell types, each with distinctive properties based upon organ system and donor source [106, 175]. In short, the field lacks standardized cell identity and potency assays to evaluate product behavior and optimization . It is possible that a particular subset of CT may be optimal for a specific therapeutic application. This has yet to be determined. Additionally, given the potential for unbridled cellular proliferation with certain cell types (i.e. ESCs), further determination of ideal therapeutic half-life or requirement for engraftment must be determined in order to mitigate potential negative consequences such as tumor formation. For use in trauma patients, the ideal CT product may be one that only transiently remains in the body and has an acute effect.
The external factors that influence the behavior of the individual therapy types must also be identified. As no cell type exists naturally in isolation, one particularly vital consideration is how the interaction of various cell types effects treatment efficacy and safety. Interaction with immune cells in the trauma patient to modulate immune function and inflammation is an important function of CT. As an example, preliminary studies examining interaction of MSCs and NK cells have suggested a time-dependent component of regulation, during which both inhibition and activation of NK cells by MSCs may occur based upon secretory factor effects as well as cellular ratios [130, 176, 177]. While MSC infusion after HSCT has shown improved engraftment and decreased incidence of chronic GVHD, MSC infusion prior to HSCT displayed a tendency toward prolonged engraftment times along with an associated increase in relapse and death, again implying the importance of timing of delivery in the maximization of therapy [178]. More research is needed to determine the most effective cellular therapy regimens.
Relatively little is understood about how trauma pathophysiology may inform the application of therapies. Given the discordant immunologic response with resultant enzymatic dysfunction, trepidation exists regarding how the introduction of foreign cellular products may affect this stressed system. For example, increased circulation of tissue factor—the transmembrane protein responsible for initiation of the coagulation cascade—following traumatic injury leads to increased exposure to other coagulation factors, ultimately causing intravascular thrombosis [179]. The consequences of adding CT to this disordered state are largely unknown, but raise concerns regarding the potential risk of exacerbating the existing pro-coagulant state. MSCs express varying levels of tissue factor on their surface and may influence blood coagulation if administered intravenously [180,181,182,183]. Pre-clinical studies demonstrate that human MSCs are procoagulant when mixed with human blood or plasma [180, 181, 184]. Indeed, a wide range of tissue factor surface expression is observed in different CT agents, based on tissue of origin, donor variability, and cell preparation conditions. During in vitro experiments, the amount of surface tissue factor is inversely related to the clotting time observed upon mixing of cells with either whole blood or plasma. This relationship is also maintained with blood from patients with severe trauma, although the effect is less pronounced than that seen with blood from healthy donors [180]. Although numerous clinical trials using MSCs and other related products have indicated that administration of MSCs is relatively safe (at least at the doses tested), there have been some examples of adverse thrombotic events after administration, especially outside of tightly controlled clinical trials ( [185] and references therein, [186]). Because acute trauma patients may be coagulopathic, this issue should be addressed in preclinical models first to determine safety.
The use of CT or cell-derived biologicals such as EVs has been proposed as a means to mitigate this possible repercussion [187]. However, recent evidence indicates that EVs themselves contain tissue factor and pro-coagulant potential which varies between sources [188] and have procoagulant activity when mixed with whole blood or plasma [188, 189]. The conditions for expanding, maintaining, and harvesting cells may also affect tissue factor levels and procoagulant activity, [190] and should be further optimized to enhance safety. Alternatively, other methods of cell administration besides intravenous infusion may be preferred in some trauma patients. A number of methods are under investigation, including topical, intra-muscular, intra-arterial and direct injection into tissues ( [185] and references therein). These methods differ in their in their level of invasiveness and ease of performance in acute situations, but also in their effects on cell delivery, retention and probably cell efficacy. In the end, specific patient characteristics may dictate the choice of administration method, based on the type of injury and the invasiveness and risk of each method.
To mitigate risk, TF expression and the potency of the product should be considered in determining the choice of CT agent. If a product with high procoagulant activity is used, the administration of higher amounts of anticoagulant along with the cells may be able to reduce the risk of thrombosis. However, the clinical feasibility of this remains unclear, as this must be balanced with the risks of further anti-coagulation in actively bleeding patients. Thus, further investigation to determine the ideal CT agent, dose, timing and route of administration will be important to minimize the risk of thrombosis.
As no individual cell function is segregated from its surroundings, coinciding factors aside from cell-to-cell interaction must also be considered. For example, the immune responses triggered by interaction of adaptive and innate immune cells may in fact be central to the beneficial immune modulation and anti-inflammatory properties of MSCs. MSCs have the receptors for complement proteins C3a and Ca [191]. These complement proteins in the blood interact with MSCs and augment their phagocytosis, which may contribute to immune modulation but may also explain why MSCs are cleared from the bloodstream rapidly (Gavin 2019), in addition to being trapped in the lungs. MSC infusion causes a dramatic inflammatory response called the IBMIR (instant blood-mediated inflammatory reaction) [192]. All of these complex cellular interactions are likely to be important for potency, efficacy and adverse outcomes in trauma patients and require further preclinical study.
Besides the aforementioned coagulopathies, other factors commonly seen in severe traumatic injury include hypothermia and acidosis, with the three in combination collectively referred to as the ‘lethal triad’ [193]. Animal studies suggest that hypothermia serves to decrease tissue injury by exerting an anti-apoptotic and immunomodulatory effect. However, such compensation comes at a cost, with enzymatic dysregulation and an overall increase in mortality observed in even mild cases of trauma-associated hypothermia [194, 195]. Similarly, studies have shown that the degree of acidosis in trauma patients is directly correlated with the severity of hemostatic dysfunction, again demonstrating how small disruptions in homeostasis can lead to disastrous metabolic consequences [196]. Endogenous cell receptor conformational changes may occur in acidosis, subsequently affecting binding capabilities and overall functionality [197]. At this point, very little is understood about how exogenous cell-mediated therapies will engage with this process.
Many areas of study undoubtedly remain regarding the potential reciprocity of the cellular microenvironment and CT. A third element not yet addressed involves the factors external to the patient, particularly exposures sustained independent of the trauma itself. One example of this is how radiation exposure may affect all cell types, both endogenous and exogenous. As discussed above, HSCT has been applied in previous cases of massive radiation exposure with generally negative results. While part of these negative findings may be attributed to secondary complications of the radiation itself such as infection, some may be attributable to the currently not fully understood and, therefore, unpredictable cellular response. Given the non-uniformity of irradiation exposure in this setting, marrow recovery with resultant cellular production is feasible following an initial period of indolence. In the absence of complete myeloablation through established chemotherapy regimens, which sacrifice all tissue types, the consequence of autologous cell production in conjunction with exogenous therapies is unknown [77, 198].
Logistical Challenges of Cellular Therapy Application
While much regarding the physiologic aspects of CT remains to be determined, the logistical challenges of manufacture and application must also be acknowledged. As frequent public pleas for blood product donation indicate, CT sources apart from iPSCs do not exist in limitless supply, and ensuring consistent inventory with current isolation and growth practices will be difficult.
Additionally, while preservation techniques for use of cellular products in research are well-established, the consequences of this process for subsequent clinical application is not fully known. Transfusion of older stored packed red blood cells has been associated with increased complications, with pathophysiology incompletely understood. However, it is unclear if such issues will be as prominent with other CT [199]. Additionally, the storage methods for CT products have not been adequately defined. Many of the current storage techniques restrict mobility of these therapies, raising concerns for their use in resource-scarce settings such as occur in the event of natural disasters or military deployments. Challenges are also posed by the need for very low temperatures in the storage of CT products. Further investigation is needed to determine ideal storage and distribution conditions to maximize therapeutic viability, mobility, and utility.
Questions regarding appropriate dosing regimens also remain. As for all approved therapies, a standard potency assay must exist in order to ensure a particular response is achieved [200]. In order to do this, specific mechanisms of action (MoAs) and quantitative measures of biologic function would ideally be established for purposes of standardized manufacturing and reliable clinical efficacy. However, given the complexity of CT, likely featuring multiple, poorly understood MoAs that are largely batch dependent, such determinations are extremely difficult [201]. Consideration of meaningful and robust assays for batch characterization and release are essential in order to alleviate some of the known obstacles [201].
Finally, ideal candidates to receive these therapies must also be determined. Given the lack of a consensus definition for polytrauma, as discussed previously, clinical criteria would ideally be established to standardize this definition. Such formalization could then inform an evidence-based grading system that could be quickly referenced during an acute trauma resuscitation to determine who would most benefit from cellular therapy.
Conclusions
Preclinical and clinical studies of CT have shown significant capacity for their application in cases of both acute and chronic traumatic injury. However, much remains to be determined both physiologically and logistically before the widespread application of such treatments. Given the substantial morbidity and mortality associated with severe trauma in both military and civilian settings, and the comprehensive nature of the topic, it is imperative that the medical community collectively renews their efforts to seek further systemic therapy options, using the vast amount of knowledge that has already been built as their beacon. Focusing efforts on new therapies will ensure that traumatic injury will no longer be a neglected disease of modern society.
References
Prevention (2016) CfDCa, . Injury Prevention & Control. 10 Leading Causes of Death by Age Group United States-2016. [January 28, 2019]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/injury/wisqars/LeadingCauses.html.
Pati, S., Pilia, M., Grimsley, J. M., Karanikas, A. T., Oyeniyi, B., Holcomb, J. B., et al. (2015). Cellular therapies in trauma and critical care medicine: Forging new frontiers. Shock, 44(6), 505–523.
Howard, J. T., Kotwal, R. S., Santos-Lazada, A. R., Martin, M. J., & Stockinger, Z. T. (2018). Reexamination of a battlefield trauma golden hour policy. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 84(1), 11–18.
Sakran, J. V., Greer, S. E., Werlin, E., & McCunn, M. (2012). Care of the injured worldwide: trauma still the neglected disease of modern society. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine, 20, 64.
Committee on Trauma and Committee on Shock, Division of Medical Sciences, National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council. (1966). Accidental death and disability: the neglected disease of modern society. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US).
Committee on Military Trauma Care’s Learning Health System and Its Translation to the Civilian Sector, Board on Health Sciences Policy, Board on the Health of Select Populations, Health and Medicine Division, National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. (2016). In D. Berwick, A. Downey, F. Cornett (Eds.), A national trauma care system: integrating military and civilian trauma systems to achieve zero preventable deaths after injury. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US).
El Mestoui, Z., Jalalzadeh, H., Giannakopoulos, G. F., & Zuidema, W. P. (2017). Incidence and etiology of mortality in polytrauma patients in a Dutch level I trauma center. European Journal of Emergency Medicine, 24(1), 49–54.
Paffrath, T., Lefering, R., Flohe, S., & TraumaRegister DGU. (2014). How to define severely injured patients? -- an Injury Severity Score (ISS) based approach alone is not sufficient. Injury, 45(Suppl 3), S64–S69.
Butcher, N. E., Enninghorst, N., Sisak, K., & Balogh, Z. J. (2013). The definition of polytrauma: variable interrater versus intrarater agreement--a prospective international study among trauma surgeons. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 74(3), 884–889.
Butcher, N. E., & Balogh, Z. J. (2014). Update on the definition of polytrauma. European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery, 40(2), 107–111.
Trunkey, D. D. (1983). Trauma. Accidental and intentional injuries account for more years of life lost in the U.S. than cancer and heart disease. Among the prescribed remedies are improved preventive efforts, speedier surgery and further research. Scientific American, 249(2), 28–35.
Baker, C. C., Oppenheimer, L., Stephens, B., Lewis, F. R., & Trunkey, D. D. (1980). Epidemiology of trauma deaths. American Journal of Surgery, 140(1), 144–150.
Sobrino, J., & Shafi, S. (2013). Timing and causes of death after injuries. Proceedings (Baylor University Medical Center), 26(2), 120–123.
Rauf, R., von Matthey, F., Croenlein, M., Zyskowski, M., van Griensven, M., Biberthaler, P., et al. (2019). Changes in the temporal distribution of in-hospital mortality in severely injured patients-An analysis of the TraumaRegister DGU. PLoS One, 14(2), e0212095.
Bardes, J. M., Inaba, K., Schellenberg, M., Grabo, D., Strumwasser, A., Matsushima, K., et al. (2018). The contemporary timing of trauma deaths. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 84(6), 893–899.
McLaughlin, C., Zagory, J. A., Fenlon, M., Park, C., Lane, C. J., Meeker, D., et al. (2018). Timing of mortality in pediatric trauma patients: A National Trauma Data Bank analysis. Journal of Pediatric Surgery, 53(2), 344–351.
Satyam, A., Graef, E. R., Lapchak, P. H., Tsokos, M. G., Dalle Lucca, J. J., & Tsokos, G. C. (2019). Complement and coagulation cascades in trauma. Acute Med Surg, 6(4), 329–335.
Relja, B., & Land, W. G. (2020). Damage-associated molecular patterns in trauma. European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery, 6(4), 751–775.
Timmermans, K., Kox, M., Scheffer, G. J., & Pickkers, P. (2016). Danger in the Intensive Care Unit: Damps in Critically Ill Patients. Shock, 45(2), 108–116.
Hauser, C. J., & Otterbein, L. E. (2018). Danger signals from mitochondrial DAMPS in trauma and post-injury sepsis. European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery, 44(3), 317–324.
Bianchi, M. E. (2007). DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 81(1), 1–5.
Eppensteiner, J., Davis, R. P., Barbas, A. S., Kwun, J., & Lee, J. (2018). Immunothrombotic activity of damage-associated molecular patterns and extracellular vesicles in secondary organ failure induced by trauma and sterile insults. Frontiers in Immunology, 9, 190.
Naumann, D. N., Hazeldine, J., Midwinter, M. J., Hutchings, S. D., & Harrison, P. (2018). Poor microcirculatory flow dynamics are associated with endothelial cell damage and glycocalyx shedding after traumatic hemorrhagic shock. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 84(1), 81–88.
Chakraborty, S., Karasu, E., & Huber-Lang, M. (2018). Complement after trauma: suturing innate and adaptive immunity. Frontiers in Immunology, 9, 2050.
Huber-Lang, M. S., Ignatius, A., Kohl, J., Mannes, M., & Braun, C. K. (2020). Complement in trauma-traumatised complement? British Journal of Pharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15245.
Huber-Lang, M., Lambris, J. D., & Ward, P. A. (2018). Innate immune responses to trauma. Nature Immunology, 19(4), 41–327.
Lord, J. M., Midwinter, M. J., Chen, Y. F., Belli, A., Brohi, K., Kovacs, E. J., et al. (2014). The systemic immune response to trauma: an overview of pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet, 384(9952), 1455–1465.
Chang, R., Cardenas, J. C., Wade, C. E., & Holcomb, J. B. (2016). Advances in the understanding of trauma-induced coagulopathy. Blood, 128(8), 1043–1049.
Dobson, G. P., Letson, H. L., Sharma, R., Sheppard, F. R., & Cap, A. P. (2015). Mechanisms of early trauma-induced coagulopathy: The clot thickens or not? Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 79(2), 301–309.
Cap, A., & Hunt, B. (2014). Acute traumatic coagulopathy. Current Opinion in Critical Care, 20(6), 638–645.
White, N. J., Ward, K. R., Pati, S., Strandenes, G., & Cap, A. P. (2017). Hemorrhagic blood failure: Oxygen debt, coagulopathy, and endothelial damage. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 82(6S Suppl 1), S41–SS9.
Shepherd, J. M., Cole, E., & Brohi, K. (2017). Contemporary patterns of multiple organ dysfunction in trauma. Shock, 47(4), 429–435.
Murray, I. R., & Peault, B. (2015). Q&A: Mesenchymal stem cells - where do they come from and is it important? BMC Biology, 13, 99.
Schafer, R., & Northoff, H. (2008). Characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells - new stars in regenerative medicine or unrecognized old fellows in autologous regeneration? Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy, 35(3), 154–159.
Ratajczak, M. Z., Zuba-Surma, E. K., Machalinski, B., & Kucia, M. (2007). Bone-marrow-derived stem cells--our key to longevity? Journal of Applied Genetics, 48(4), 307–319.
Dominici, M., Le Blanc, K., Mueller, I., Slaper-Cortenbach, I., Marini, F., Krause, D., et al. (2006). Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy, 8(4), 315–317.
Via, A. G., Frizziero, A., & Oliva, F. (2012). Biological properties of mesenchymal Stem Cells from different sources. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J, 2(3), 154–162.
TEG, K., DLJ, T., Denmeade, S. R., Isaacs, J. T., & Brennen, W. N. (2018). Concise review: mesenchymal stem cell-based drug delivery: the good, the bad, the ugly, and the promise. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 7(9), 651–663.
Huber-Lang, M., Wiegner, R., Lampl, L., & Brenner, R. E. (2016). Mesenchymal stem cells after polytrauma: Actor and target. Stem Cells International, 2016, 6289825.
Laroye, C., Gibot, S., Reppel, L., & Bensoussan, D. (2017). Concise review: mesenchymal stromal/stem cells: A new treatment for sepsis and septic shock? Stem Cells, 35(12), 2331–2339.
Qi, L., Xue, X., Sun, J., Wu, Q., Wang, H., Guo, Y., et al. (2018). The promising effects of transplanted umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on the treatment in traumatic brain injury. The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 29(7), 1689–1692.
Kebriaei, P., Hayes, J., Daly, A., Uberti, J., Marks, D. I., Soiffer, R., et al. (2019). A Phase 3 randomized study of Remestemcel-L versus placebo added to second line therapy in patients with steroid refractory acute graft versus host disease. Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, 26(5), 835–844.
Li, S., Huang, K. J., Wu, J. C., Hu, M. S., Sanyal, M., Hu, M., et al. (2015). Peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells: candidate cells responsible for healing critical-sized calvarial bone defects. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 4(4), 359–368.
Martinello, T., Gomiero, C., Perazzi, A., Iacopetti, I., Gemignani, F., GM, D. B., et al. (2018). Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells improve the wound healing process of sheep skin. BMC Veterinary Research, 14(1), 202.
Gregoire, C., Ritacco, C., Hannon, M., Seidel, L., Delens, L., Belle, L., et al. (2019). Comparison of mesenchymal stromal cells from different origins for the treatment of graft-vs.-host-disease in a humanized mouse model. Frontiers in Immunology, 10, 619.
Mahdavi Gorabi, A., Banach, M., Reiner, Z., Pirro, M., Hajighasemi, S., Johnston, T. P., et al (2019). The role of mesenchymal stem cells in atherosclerosis: prospects for therapy via the modulation of inflammatory milieu. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(9), 1413.
Cho, J. W., Park, K. S., & Bae, J. Y. (2019). Effects of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Regen Ther, 11, 207–211.
Lopes-Pacheco, M., Robba, C., Rocco, P. R. M., & Pelosi, P. (2020). Current understanding of the therapeutic benefits of mesenchymal stem cells in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Cell Biology and Toxicology, 36(1), 83–102.
Dabrowska, S., Andrzejewska, A., Lukomska, B., & Janowski, M. (2019). Neuroinflammation as a target for treatment of stroke using mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 16(1), 178.
Rota, C., Morigi, M., & Imberti, B. (2019). Stem cell therapies in kidney diseases: progress and challenges. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(11), 2790.
Matthay, M. A., Calfee, C. S., Zhuo, H., Thompson, B. T., Wilson, J. G., Levitt, J. E., et al. (2019). Treatment with allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells for moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (START study): a randomised phase 2a safety trial. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, 7(2), 154–162.
Yen, B. L., Yen, M. L., Wang, L. T., Liu, K. J., & Sytwu, H. K. (2020). Current status of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for immune/inflammatory lung disorders: gleaning insights for possible use in COVID-19. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 9(10), 1163–1173.
Amann, E. M., Rojewski, M. T., Rodi, S., Furst, D., Fiedler, J., Palmer, A., et al. (2018). Systemic recovery and therapeutic effects of transplanted allogenic and xenogenic mesenchymal stromal cells in a rat blunt chest trauma model. Cytotherapy, 20(2), 218–231.
Moll, G., Drzeniek, N., Kamhieh-Milz, J., Geissler, S., Volk, H. D., & Reinke, P. (2020). MSC therapies for COVID-19: Importance of patient coagulopathy, thromboprophylaxis, cell product quality and mode of delivery for treatment safety and efficacy. Frontiers in Immunology, 11, 1091.
Golchin, A. (2020). Cell-based therapy for severe COVID-19 patients: clinical trials and cost-utility. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-020-10046-1.
Schafer, R., Spohn, G., Bechtel, M., Bojkova, D., Baer, P. C., Kuci, S., et al. (2020). Human mesenchymal stromal cells are resistant to sars-cov-2 infection under steady-state, inflammatory conditions and in the presence of SARS-CoV-2-infected cells. Stem Cell Reports. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.09.003.
Wan, C., He, Q., & Li, G. (2006). Allogenic peripheral blood derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) enhance bone regeneration in rabbit ulna critical-sized bone defect model. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 24(4), 610–618.
ALF, L., Salazar, T. E., Vieira, C., Trinh, T., Duan, Y., Pay, L. M., et al. (2019). Peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells demonstrate immunomodulatory potential for therapeutic use in horses. PLoS One, 14(3), e0212642.
Wiegner, R., Rudhart, N. E., Barth, E., Gebhard, F., Lampl, L., Huber-Lang, M. S., et al. (2018). Mesenchymal stem cells in peripheral blood of severely injured patients. European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery, 44(4), 627–636.
Galleu, A,, Riffo-Vasquez, Y., Trento, C., Lomas, C., Dolcetti, L., Cheung, T. S., et al. (2017). Apoptosis in mesenchymal stromal cells induces in vivo recipient-mediated immunomodulation. Science Translational Medicine, 9(416), eaam7828.
Galleu, A., Milojkovic, D., Deplano, S., Szydlo, R., Loaiza, S., Wynn, R., et al. (2019). Mesenchymal stromal cells for acute graft-versus-host disease: response at 1 week predicts probability of survival. British Journal of Haematology, 185(1), 89–92.
Mohty, M., Duarte, R. F., Kuball, J., Bader, P., Basak, G. W., Bonini, C., et al. (2018). Recommendations from the European society for blood and marrow transplantation (EBMT) for a curriculum in hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplantation, 53(12), 1548–1552.
Krumina, G., Babarykin, D., Krumina, Z., Paegle, I., Suhorukov, O., Vanags, D., et al. (2013). Effects of systemically transplanted allogeneic bone marrow multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells on rats’ recovery after experimental polytrauma. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 74(3), 785–791.
Tanriverdi, A. K., Polat, O., Elcin, A. E., Ahlat, O., Gurman, G., Gunalp, M., et al. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in polytrauma: evaluation of bone and liver healing response in an experimental rat model. European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery, 46(1), 53–64.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01206179.
clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02152657.
Bhansali, A., Asokumar, P., Walia, R., Bhansali, S., Gupta, V., Jain, A., et al. (2014). Efficacy and safety of autologous bone marrow-derived stem cell transplantation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized placebo-controlled study. Cell Transplantation, 23(9), 1075–1085.
Wilson, J. G., Liu, K. D., Zhuo, H., Caballero, L., McMillan, M., Fang, X., et al. (2015). Mesenchymal stem (stromal) cells for treatment of ARDS: a phase 1 clinical trial. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, 3(1), 24–32.
Juric, M. K., Ghimire, S., Ogonek, J., Weissinger, E. M., Holler, E., van Rood, J. J., et al. (2016). Milestones of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation - From First Human Studies to Current Developments. Frontiers in Immunology, 7, 470.
Crisan, M., & Dzierzak, E. (2016). The many faces of hematopoietic stem cell heterogeneity. Dev, 143(24), 4571–4581.
Fonseca, R. B., Mohr, A. M., Wang, L., Sifri, Z. C., Rameshwar, P., & Livingston, D. H. (2005). The impact of a hypercatecholamine state on erythropoiesis following severe injury and the role of IL-6. The Journal of Trauma, 59(4), 884–889 discussion 9–90.
Fonseca, R. B., Mohr, A. M., Wang, L., Clinton, E., Sifri, Z. C., Rameshwar, P., et al. (2004). Adrenergic modulation of erythropoiesis following severe injury is mediated through bone marrow stroma. Surgical Infections, 5(4), 385–393.
Alamo, I. G., Kannan, K. B., Loftus, T. J., Ramos, H., Efron, P. A., & Mohr, A. M. (2017). Severe trauma and chronic stress activates extramedullary erythropoiesis. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 83(1), 144–150.
Kumar, M., Bhoi, S., & Galwankar, S. (2016). Hematopoietic stem cells: Can it be a therapeutic option for the hematopoietic failure in patients with trauma-hemorrhagic shock? Journal of Emergencies, Trauma, and Shock, 9(2), 51–52.
Dainiak, N. (2018). Medical management of acute radiation syndrome and associated infections in a high-casualty incident. Journal of Radiation Research, 59(suppl_2), ii54–ii64.
Gurudutta, G. U., Satija, N. K., Singh, V. K., Verma, Y. K., Gupta, P., & Tripathi, R. P. (2012). Stem cell therapy: a novel & futuristic treatment modality for disaster injuries. The Indian Journal of Medical Research, 135, 15–25.
Asano, S. (2012). Current status of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute radiation syndromes. International Journal of Hematology, 95(3), 227–231.
Zhao, K., & Liu, Q. (2016). The clinical application of mesenchymal stromal cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 9(1), 46.
Maitra, B., Szekely, E., Gjini, K., Laughlin, M. J., Dennis, J., Haynesworth, S. E., et al. (2004). Human mesenchymal stem cells support unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cells and suppress T-cell activation. Bone Marrow Transplantation, 33(6), 597–604.
Lukovic, D., Moreno Manzano, V., Stojkovic, M., Bhattacharya, S. S., & Erceg, S. (2012). Concise review: human pluripotent stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury. Stem Cells, 30(9), 1787–1792.
Cherry, A. B., & Daley, G. Q. (2013). Reprogrammed cells for disease modeling and regenerative medicine. Annual Review of Medicine, 64, 277–290.
Yamanaka, S. (2007). Strategies and new developments in the generation of patient-specific pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell, 1(1), 39–49.
Takahashi, K., Tanabe, K., Ohnuki, M., Narita, M., Ichisaka, T., Tomoda, K., et al. (2007). Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell, 131(5), 861–872.
Menasche, P., Vanneaux, V., Hagege, A., Bel, A., Cholley, B., Parouchev, A., et al. (2018). Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiovascular progenitors for severe ischemic left ventricular dysfunction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 71(4), 429–438.
Schwartz, S. D., Regillo, C. D., Lam, B. L., Eliott, D., Rosenfeld, P. J., Gregori, N. Z., et al. (2015). Human embryonic stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium in patients with age-related macular degeneration and Stargardt’s macular dystrophy: follow-up of two open-label phase 1/2 studies. Lancet, 385(9967), 509–516.
Manley, N. C., Priest, C. A., Denham, J., Wirth 3rd, E. D., & Lebkowski, J. S. (2017). Human embryonic stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte progenitor cells: preclinical efficacy and safety in cervical spinal cord injury. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, (6, 10), 1917–1929.
Keirstead, H. S., Nistor, G., Bernal, G., Totoiu, M., Cloutier, F., Sharp, K., et al. (2005). Human embryonic stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte progenitor cell transplants remyelinate and restore locomotion after spinal cord injury. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25(19), 4694–4705.
Cloutier, F., Siegenthaler, M. M., Nistor, G., & Keirstead, H. S. (2006). Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte progenitors into rat spinal cord injuries does not cause harm. Regenerative Medicine, 1(4), 469–479.
Gazdic, M., Volarevic, V., Harrell, C. R., Fellabaum, C., Jovicic, N., Arsenijevic, N., et al. (2018). Stem cells therapy for spinal cord injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4).
Nasser, M., Ballout, N., Mantash, S., Bejjani, F., Najdi, F., Ramadan, N., et al. (2018). Transplantation of embryonic neural stem cells and differentiated cells in a controlled cortical Impact (CCI) model of adult mouse somatosensory cortex. Frontiers in Neurology, 9, 895.
Beretta, S., Cunningham, K. M., Haus, D. L., Gold, E. M., Perez, H., Lopez-Velazquez, L., et al. (2017). Effects of human ES-derived neural stem cell transplantation and kindling in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Cell Transplantation, 26(7), 1247–1261.
Poulos, J. (2018). The limited application of stem cells in medicine: a review. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 9(1), 1.
Takagi, Y. (2016). History of neural stem cell research and its clinical application. Neurologia Medico-Chirurgica (Tokyo), 56(3), 110–124.
Weston, N. M., & Sun, D. (2018). The potential of stem cells in treatment of traumatic brain injury. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports, 18(1), 1.
Gincberg, G., Arien-Zakay, H., Lazarovici, P., & Lelkes, P. I. (2012). Neural stem cells: therapeutic potential for neurodegenerative diseases. British Medical Bulletin, 104, 7–19.
Pang, A. L., Xiong, L. L., Xia, Q. J., Liu, F., Wang, Y. C., Liu, F., et al. (2017). Neural stem cell transplantation is associated with inhibition of apoptosis, Bcl-xL upregulation, and recovery of neurological function in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Cell Transplantation, 26(7), 1262–1275.
Lee, J. Y., Acosta, S., Tuazon, J. P., Xu, K., Nguyen, H., Lippert, T., et al. (2019). Human parthenogenetic neural stem cell grafts promote multiple regenerative processes in a traumatic brain injury model. Theranostics, 9(4), 1029–1046.
Xiong, L. L., Hu, Y., Zhang, P., Zhang, Z., Li, L. H., Gao, G. D., et al. (2018). Neural stem cell transplantation promotes functional recovery from traumatic brain injury via brain derived neurotrophic factor-mediated neuroplasticity. Molecular Neurobiology, 55(3), 2696–2711.
Curtis, E., Martin, J. R., Gabel, B., Sidhu, N., Rzesiewicz, T. K., Mandeville, R., et al. (2018). A first-in-human, phase i study of neural stem cell transplantation for chronic spinal cord injury. Cell Stem Cell, 22(6), 941–950 e6.
Glass, J. D., Boulis, N. M., Johe, K., Rutkove, S. B., Federici, T., Polak, M., et al. (2012). Lumbar intraspinal injection of neural stem cells in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: results of a phase I trial in 12 patients. Stem Cells, 30(6), 1144–1151.
Mazzini, L., Gelati, M., Profico, D. C., Soraru, G., Ferrari, D., Copetti, M., et al. (2019). Results from phase i clinical trial with intraspinal injection of neural stem cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A long-term outcome. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 8(9), 887–897.
Murray, P. D. F. (1932). The development in vitro of the blood of the early chick embryo. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 111(773), 497–521.
Asahara, T., Murohara, T., Sullivan, A., Silver, M., van der Zee, R., Li, T., et al. (1997). Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science., 275(5302), 964–967.
Chopra, H., Hung, M. K., Kwong, D. L., Zhang, C. F., & Pow, E. H. N. (2018). Insights into endothelial progenitor cells: origin, classification, potentials, and prospects. Stem Cells International, 2018, 9847015.
Wang, X., Zhao, Z., Zhang, H., Hou, J., Feng, W., Zhang, M., et al. (2018). Simultaneous isolation of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells derived from murine bone marrow. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 16(6), 5171–5177.
Asahara, T., Kawamoto, A., & Masuda, H. (2011). Concise review: Circulating endothelial progenitor cells for vascular medicine. Stem Cells, 29(11), 1650–1655.
Banyard, D. A., Adnani, B. O., Melkumyan, S., Araniego, C. A., & Widgerow, A. D. (2016). Endothelial progenitor cells and burn injury - exploring the relationship. Burns Trauma., 4, 4.
Huang, X., Wan, D., Lin, Y., Xue, N., Hao, J., Ma, N., et al. (2017). Endothelial progenitor cells correlated with oxidative stress after mild traumatic brain injury. Yonsei Medical Journal, 58(5), 1012–1017.
Grisar, J. C., Haddad, F., Gomari, F. A., & Wu, J. C. (2011). Endothelial progenitor cells in cardiovascular disease and chronic inflammation: from biomarker to therapeutic agent. Biomarkers in Medicine, 5(6), 731–744.
Ritz, U., Spies, V., Mehling, I., Gruszka, D., Rommens, P. M., & Hofmann, A. (2014). Mobilization of CD34+-progenitor cells in patients with severe trauma. PLoS One, 9(5), e97369.
de la Puente, P., Muz, B., Azab, F., & Azab, A. K. (2013). Cell trafficking of endothelial progenitor cells in tumor progression. Clinical Cancer Research, 19(13), 3360–3368.
Mao, S. Z., Ye, X., Liu, G., Song, D., & Liu, S. F. (2014). An obligatory role of NF-kappaB in mediating bone marrow derived endothelial progenitor cell recruitment and proliferation following endotoxemic multiple organ injury in mice. PLoS One, 9(10), e111087.
Guo, X. B., Deng, X., & Wei, Y. (2017). Homing of cultured endothelial progenitor cells and their effect on traumatic brain injury in rat model. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 4164.
Kalka, C., Masuda, H., Takahashi, T., Kalka-Moll, W. M., Silver, M., Kearney, M., et al. (2000). Transplantation of ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cells for therapeutic neovascularization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(7), 3422–3427.
Cheng, Y., Jiang, S., Hu, R., & Lv, L. (2013). Potential mechanism for endothelial progenitor cell therapy in acute myocardial infarction: Activation of VEGF- PI3K/Akte-NOS pathway. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science, 43(4), 395–401.
Wang, T., Fang, X., & Yin, Z. S. (2018). Endothelial progenitor cell-conditioned medium promotes angiogenesis and is neuroprotective after spinal cord injury. Neural Regeneration Research, 13(5), 887–895.
Cui, Y., Fu, S., Hou, T., & Wu, X. (2018). Endothelial progenitor cells enhance the migration and osteoclastic differentiation of bone marrow-derived macrophages in vitro and in a mouse femur fracture model through talin-1. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 49(2), 555–564.
Keighron, C., Lyons, C. J., Creane, M., O'Brien, T., & Liew, A. (2018). Recent advances in endothelial progenitor cells toward their use in clinical translation. Front Med (Lausanne), 5, 354.
Ichim, T. E., O'Heeron, P., & Kesari, S. (2018). Fibroblasts as a practical alternative to mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Translational Medicine, 16(1), 212.
Chang, Y., Li, H., & Guo, Z. (2014). Mesenchymal stem cell-like properties in fibroblasts. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 34(3), 703–714.
Wynn, T. A. (2008). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. The Journal of Pathology, 214(2), 199–210.
Wynn, T. A. (2007). Common and unique mechanisms regulate fibrosis in various fibroproliferative diseases. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 117(3), 524–529.
Denu, R. A., Nemcek, S., Bloom, D. D., Goodrich, A. D., Kim, J., Mosher, D. F., et al. (2016). Fibroblasts and Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Are Phenotypically Indistinguishable. Acta Haematologica, 136(2), 85–97.
Christy, B. A., Herzig, M. C., Delavan, C., Cantu, C., Salgado, C., Bynum, J. A., et al. (2019). Human primary fibroblasts perform similarly to MSCs in assays used to evaluate MSC safety and potency. Transfusion, 59(S2), 1593–1600.
Alt, E., Yan, Y., Gehmert, S., Song, Y. H., Altman, A., Gehmert, S., et al. (2011). Fibroblasts share mesenchymal phenotypes with stem cells, but lack their differentiation and colony-forming potential. Biology of the Cell, 103(4), 197–208.
Venugopal, S. S., Yan, W., Frew, J. W., Cohn, H. I., Rhodes, L. M., Tran, K., et al. (2013). A phase II randomized vehicle-controlled trial of intradermal allogeneic fibroblasts for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 69(6), 898–908 e7.
Wang, Y., Li, D., Wang, G., Chen, L., Chen, J., Liu, Z., et al. (2017). The effect of co-transplantation of nerve fibroblasts and Schwann cells on peripheral nerve repair. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 13(12), 1507–1519.
Parkin, J., & Cohen, B. (2001). An overview of the immune system. Lancet, 357(9270), 1777–1789.
Dahlberg, C. I., Sarhan, D., Chrobok, M., Duru, A. D., & Alici, E. (2015). Natural killer cell-based therapies targeting cancer: possible strategies to gain and sustain anti-tumor activity. Frontiers in Immunology, 6, 605.
Najar, M., Fayyad-Kazan, M., Merimi, M., Burny, A., Bron, D., Fayyad-Kazan, H., et al. (2019). Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Natural Killer Cells: A Complex Story of Love and Hate. Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 14(1), 14–21.
Barkhausen, T., Frerker, C., Putz, C., Pape, H. C., Krettek, C., & van Griensven, M. (2008). Depletion of NK cells in a murine polytrauma model is associated with improved outcome and a modulation of the inflammatory response. Shock., 30(4), 401–410.
Chen, S., Hoffman, R. A., Scott, M., Manson, J., Loughran, P., Ramadan, M., et al. (2017). NK1.1(+) cells promote sustained tissue injury and inflammation after trauma with hemorrhagic shock. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 102(1), 127–134.
Manson, J., Cole, E., De'Ath, H. D., Vulliamy, P., Meier, U., Pennington, D., et al. (2016). Early changes within the lymphocyte population are associated with the development of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in trauma patients. Critical Care, 20(1), 176.
Andaluz-Ojeda, D., Iglesias, V., Bobillo, F., Almansa, R., Rico, L., Gandia, F., et al. (2011). Early natural killer cell counts in blood predict mortality in severe sepsis. Critical Care, 15(5), R243.
van Niel, G., D'Angelo, G., & Raposo, G. (2018). Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 19(4), 213–228.
Raposo, G., & Stoorvogel, W. (2013). Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. The Journal of Cell Biology, 200(4), 373–383.
Shah, R., Patel, T., & Freedman, J. E. (2018). Circulating extracellular vesicles in human disease. The New England Journal of Medicine, 379(10), 958–966.
Lai, R. C., Arslan, F., Lee, M. M., Sze, N. S., Choo, A., Chen, T. S., et al. (2010). Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Research, 4(3), 214–222.
Arslan, F., Lai, R. C., Smeets, M. B., Akeroyd, L., Choo, A., Aguor, E. N., et al. (2013). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Research, 10(3), 301–312.
Reis, L. A., Borges, F. T., Simoes, M. J., Borges, A. A., Sinigaglia-Coimbra, R., & Schor, N. (2012). Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells repaired but did not prevent gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury through paracrine effects in rats. PLoS One, 7(9), e44092.
Xin, H., Katakowski, M., Wang, F., Qian, J. Y., Liu, X. S., Ali, M. M., et al. (2017). MicroRNA cluster miR-17-92 Cluster in Exosomes Enhance Neuroplasticity and Functional Recovery After Stroke in Rats. Stroke., 48(3), 747–753.
Willis, G. R., Mitsialis, S. A., & Kourembanas, S. (2018). “Good things come in small packages”: application of exosome-based therapeutics in neonatal lung injury. Pediatric Research, 83(1–2), 298–307.
Frohlich, M., Schafer, N., Caspers, M., Bohm, J. K., Sturmer, E. K., Bouillon, B., et al. (2018). Temporal phenotyping of circulating microparticles after trauma: a prospective cohort study. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine, 26(1), 33.
Kuravi, S. J., Yates, C. M., Foster, M., Harrison, P., Hazeldine, J., Hampson, P., et al. (2017). Changes in the pattern of plasma extracellular vesicles after severe trauma. PLoS One, 12(8), e0183640.
O'Dea, K. P., Porter, J. R., Tirlapur, N., Katbeh, U., Singh, S., Handy, J. M., et al. (2016). Circulating microvesicles are elevated acutely following major burns injury and associated with clinical severity. PLoS One, 11(12), e0167801.
Yu, B., Zhang, X., & Li, X. (2014). Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(3), 4142–4157.
Potter, D. R., Miyazawa, B. Y., Gibb, S. L., Deng, X., Togaratti, P. P., Croze, R. H., et al. (2018). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate pulmonary vascular permeability and lung injury induced by hemorrhagic shock and trauma. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 84(2), 245–256.
Rice, T. C., Pugh, A. M., Xia, B. T., Seitz, A. P., Whitacre, B. E., Gulbins, E., et al. (2017). Bronchoalveolar lavage microvesicles protect burn-injured mice from pulmonary infection. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 225(4), 538–547.
Williams, A. M., Bhatti, U. F., Brown, J. F., Biesterveld, B. E., Kathawate, R. G., Graham, N. J., et al. (2020). Early single-dose treatment with exosomes provides neuroprotection and improves blood-brain barrier integrity in swine model of traumatic brain injury and hemorrhagic shock. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 88(2), 207–218.
Dlaska, C. E., Andersson, G., Brittberg, M., Suedkamp, N. P., Raschke, M. J., & Schuetz, M. A. (2015). Clinical translation in tissue engineering—the surgeon’s view. Current Molecular Biology Reports., 1(2), 61–70.
Wang, Z., Wu, Z., Liu, Y., & Han, W. (2017). New development in CAR-T cell therapy. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 10(1), 53.
Bonini, C. (2016). Engineering t-cells beyond chimeric antigen receptor. Blood, 128(22), SCI-13.
Martinez, M., & Moon, E. K. (2019). CAR T cells for solid tumors: new strategies for finding, infiltrating, and surviving in the tumor microenvironment. Frontiers in Immunology, 10, 128.
(2019). Natural killer cells for cancer immunotherapy: a new CAR is catching up. EBioMedicine, 39, 1–2.
Subklewe, M., von Bergwelt-Baildon, M., & Humpe, A. (2019). Chimeric antigen receptor T cells: A race to revolutionize cancer therapy. Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy, 46(1), 15–24.
Ping, Y., Liu, C., & Zhang, Y. (2018). T-cell receptor-engineered T cells for cancer treatment: current status and future directions. Protein & Cell, 9(3), 254–266.
Kloess, S., Kretschmer, A., Stahl, L., Fricke, S., & Koehl, U. (2019). CAR-Expressing natural killer cells for cancer retargeting. Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy, 46(1), 4–13.
Hampton, T. (2019). Exploring the potential of CAR-T therapy for heart failure. JAMA., 322(21), 2066–2067.
Phillips, M. I., & Tang, Y. L. (2008). Genetic modification of stem cells for transplantation. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 60(2), 160–172.
Wang, H., Yin, Y. G., Huang, H., Zhao, X. H., Yu, J., Wang, Q., et al. (2016). Transplantation of EPCs overexpressing PDGFR-beta promotes vascular repair in the early phase after vascular injury. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders, 16(1), 179.
Li, Y., Chang, S., Li, W., Tang, G., Ma, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2018). cxcl12-engineered endothelial progenitor cells enhance neurogenesis and angiogenesis after ischemic brain injury in mice. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 9(1), 139.
Peruzzaro, S. T., Andrews, M. M. M., Al-Gharaibeh, A., Pupiec, O., Resk, M., Story, D., et al. (2019). Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells genetically engineered to overexpress interleukin-10 promotes alternative inflammatory response in rat model of traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 16(1), 2.
Braganca, J., Lopes, J. A., Mendes-Silva, L., & Almeida Santos, J. M. (2019). Induced pluripotent stem cells, a giant leap for mankind therapeutic applications. World J Stem Cells., 11(7), 421–430.
Kanemura, H., Go, M. J., Shikamura, M., Nishishita, N., Sakai, N., Kamao, H., et al. (2014). Tumorigenicity studies of induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration. PLoS One, 9(1), e85336.
Nori, S., Okada, Y., Nishimura, S., Sasaki, T., Itakura, G., Kobayashi, Y., et al. (2015). Long-term safety issues of iPSC-based cell therapy in a spinal cord injury model: oncogenic transformation with epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Stem Cell Reports, 4(3), 360–373.
Nagoshi, N., & Okano, H. (2018). iPSC-derived neural precursor cells: potential for cell transplantation therapy in spinal cord injury. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 75(6), 989–1000.
Itakura, G., Kawabata, S., Ando, M., Nishiyama, Y., Sugai, K., Ozaki, M., et al. (2017). Fail-Safe System against Potential Tumorigenicity after Transplantation of iPSC Derivatives. Stem Cell Reports, 8(3), 673–684.
Scudellari, M. (2016). How iPS cells changed the world. Nature., 534(7607), 310–312.
Qin, C., Guo, Y., Yang, D. G., Yang, M. L., Du, L. J., & Li, J. J. (2018). Induced pluripotent stem cell transplantation improves locomotor recovery in rat models of spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 47(5), 1835–1852.
Ramotowski, C., Qu, X., & Villa-Diaz, L. G. (2019). Progress in the use of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural cells for traumatic spinal cord injuries in animal populations: meta-analysis and review. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 8(7), 681–693.
Zong, C., Zhang, H., Yang, X., Gao, L., Hou, J., Ye, F., et al. (2018). The distinct roles of mesenchymal stem cells in the initial and progressive stage of hepatocarcinoma. Cell Death & Disease, 9(3), 345.
Yang, J., Ren, Z., Du, X., Hao, M., & Zhou, W. (2014). The role of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in sarcoma: update and dispute. Stem Cell Investig, 1, 18.
Vakhshiteh, F., Atyabi, F., & Ostad, S. N. (2019). Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: a two-edged sword in cancer therapy. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 14, 2847–2859.
Torsvik, A., & Bjerkvig, R. (2013). Mesenchymal stem cell signaling in cancer progression. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 39(2), 180–188.
Kang, I., Lee, B. C., Choi, S. W., Lee, J. Y., Kim, J. J., Kim, B. E., et al. (2018). Donor-dependent variation of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in response to hypoxic preconditioning and amelioration of limb ischemia. Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 50(4), 35.
Petri, R. M., Hackel, A., Hahnel, K., Dumitru, C. A., Bruderek, K., Flohe, S. B., et al. (2017). Activated Tissue-Resident Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Regulate Natural Killer Cell Immune and Tissue-Regenerative Function. Stem Cell Reports, 9(3), 985–998.
Cui, R., Rekasi, H., Hepner-Schefczyk, M., Fessmann, K., Petri, R. M., Bruderek, K., et al. (2016). Human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells acquire immunostimulatory capacity upon cross-talk with natural killer cells and might improve the NK cell function of immunocompromised patients. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 7(1), 88.
Zhao, L., Chen, S., Yang, P., Cao, H., & Li, L. (2019). The role of mesenchymal stem cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: prevention and treatment of graft-versus-host disease. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 10(1), 182.
Cimmino, G., & Cirillo, P. (2018). Tissue factor: newer concepts in thrombosis and its role beyond thrombosis and hemostasis. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther, 8(5), 581–593.
George, M. J., Prabhakara, K., Toledano-Furman, N. E., Gill, B. S., Wade, C. E., Cotton, B. A., et al. (2020). Procoagulant in vitro effects of clinical cellular therapeutics in a severely injured trauma population. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 9(4), 491–498.
Christy, B. A., Herzig, M. C., Montgomery, R. K., Delavan, C., Bynum, J. A., Reddoch, K. M., et al. (2017). Procoagulant activity of human mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 83(1 Suppl 1), S164–S1S9.
Li, C. Y., Wu, X. Y., Tong, J. B., Yang, X. X., Zhao, J. L., Zheng, Q. F., et al. (2015). Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue under xeno-free conditions for cell therapy. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 6, 55.
Gleeson, B. M., Martin, K., Ali, M. T., Kumar, A. H., Pillai, M. G., Kumar, S. P., et al. (2015). Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells have innate procoagulant activity and cause microvascular obstruction following intracoronary delivery: Amelioration by antithrombin therapy. Stem Cells, 33(9), 2726–2737.
George, M. J., Prabhakara, K., Toledano-Furman, N. E., Wang, Y. W., Gill, B. S., Wade, C. E., et al. (2018). Clinical cellular therapeutics accelerate clot formation. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 7(10), 731–739.
Caplan, H., Olson, S. D., Kumar, A., George, M., Prabhakara, K. S., Wenzel, P., et al. (2019). Mesenchymal stromal cell therapeutic delivery: translational challenges to clinical application. Frontiers in Immunology, 10, 1645.
Bauer, G., Elsallab, M., & Abou-El-Enein, M. (2018). Concise Review: A Comprehensive Analysis of Reported Adverse Events in Patients Receiving Unproven Stem Cell-Based Interventions. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 7(9), 676–685.
Zhao, T., Sun, F., Liu, J., Ding, T., She, J., Mao, F., et al. (2019). Emerging Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Exosomes in Regenerative Medicine. Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 14(6), 482–494.
Chance, T. C., Rathbone, C. R., Kamucheka, R. M., Peltier, G. C., Cap, A. P., & Bynum, J. A. (2019). The effects of cell type and culture condition on the procoagulant activity of human mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 87(1S Suppl 1), S74–S82.
Silachev, D. N., Goryunov, K. V., Shpilyuk, M. A., Beznoschenko, O. S., Morozova, N. Y., Kraevaya, E. E., et al. (2019). Effect of MSCs and MSC-derived extracellular vesicles on human blood coagulation. Cells, 8(3), 258.
Mangum, L. H., Natesan, S., Stone 2nd, R., Wrice, N. L., Larson, D. A., Florell, K. F., et al. (2017). Tissue source and cell expansion condition influence phenotypic changes of adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells International, 2017, 7108458.
Schraufstatter, I. U., Discipio, R. G., Zhao, M., & Khaldoyanidi, S. K. (2009). C3a and C5a are chemotactic factors for human mesenchymal stem cells, which cause prolonged ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Journal of Immunology, 182(6), 3827–3836.
Moll, G., Rasmusson-Duprez, I., von Bahr, L., Connolly-Andersen, A. M., Elgue, G., Funke, L., et al. (2012). Are therapeutic human mesenchymal stromal cells compatible with human blood? Stem Cells, 30(7), 1565–1574.
Muthukumar, V., Karki, D., & Jatin, B. (2019). Concept of lethal triad in critical care of severe burn injury. Indian J Crit Care Med, 23(5), 206–209.
Frink, M., Flohe, S., van Griensven, M., Mommsen, P., & Hildebrand, F. (2012). Facts and fiction: the impact of hypothermia on molecular mechanisms following major challenge. Mediators of Inflammation, 2012, 762840.
Gerecht, R. (2014). The lethal triad. Hypothermia, acidosis & coagulopathy create a deadly cycle for trauma patients. JEMS, 39(4), 56–60.
Lv, X., Mao, Y., & Qin, Z. (2018). Evaluation for effects of severe acidosis on hemostasis in trauma patients using thrombelastography analyzer. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine, 36(8), 1332–1340.
Cao, T. M., Mitchell, M. J., Liesveld, J., & King, M. R. (2013). Stem cell enrichment with selectin receptors: mimicking the pH environment of trauma. Sensors (Basel), 13(9), 12516–12526.
DiCarlo, A. L., Tamarat, R., Rios, C. I., Benderitter, M., Czarniecki, C. W., Allio, T. C., et al. (2017). Cellular Therapies for Treatment of Radiation Injury: Report from a NIH/NIAID and IRSN Workshop. Radiation Research, 188(2), e54–e75.
Belizaire, R. M., Prakash, P. S., Richter, J. R., Robinson, B. R., Edwards, M. J., Caldwell, C. C., et al. (2012). Microparticles from stored red blood cells activate neutrophils and cause lung injury after hemorrhage and resuscitation. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 214(4), 648–655 discussion 56–7.
Bieback, K., Kuci, S., & Schafer, R. (2019). Production and quality testing of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell therapeutics for clinical use. Transfusion, 59(6), 2164–2173.
Bravery, C. A., Carmen, J., Fong, T., Oprea, W., Hoogendoorn, K. H., Woda, J., et al. (2013). Potency assay development for cellular therapy products: an ISCT review of the requirements and experiences in the industry. Cytotherapy, 15(1), 9–19.
McIntyre, L. A., Stewart, D. J., Mei, S. H. J., Courtman, D., Watpool, I., Granton, J., et al. (2018). Cellular immunotherapy for septic shock. A phase i clinical trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 197(3), 337–347.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02482194.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01393977.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03015623.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02195323.
Makhlough, A., Shekarchian, S., Moghadasali, R., Einollahi, B., Hosseini, S. E., Jaroughi, N., et al. (2017). Safety and tolerability of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells in ADPKD patients. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 8(1), 116.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01222039.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02824653.
Cohen, J. A., Imrey, P. B., Planchon, S. M., Bermel, R. A., Fisher, E., Fox, R. J., et al. (2018). Pilot trial of intravenous autologous culture-expanded mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis, 24(4), 501–511.
Karussis, D., Karageorgiou, C., Vaknin-Dembinsky, A., Gowda-Kurkalli, B., Gomori, J. M., Kassis, I., et al. (2010). Safety and immunological effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Archives of Neurology, 67(10), 1187–1194.
Nabavi, S. M., Arab, L., Jarooghi, N., Bolurieh, T., Abbasi, F., Mardpour, S., et al. (2019). Safety, feasibility of intravenous and intrathecal injection of autologous bone marrow derived mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: An open label phase i clinical trial. Cell Journal, 20(4), 592–598.
Sykova, E., Rychmach, P., Drahoradova, I., Konradova, S., Ruzickova, K., Vorisek, I., et al. (2017). Transplantation of mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: results of phase I/IIa clinical trial. Cell Transplantation, 26(4), 647–658.
Petrou, P., Gothelf, Y., Argov, Z., Gotkine, M., Levy, Y. S., Kassis, I., et al. (2016). Safety and clinical effects of mesenchymal stem cells secreting neurotrophic factor transplantation in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Results of Phase 1/2 and 2a clinical trials. JAMA Neurology, 73(3), 337–344.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03550183.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02611167.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03684122.
Diez-Tejedor, E., Gutierrez-Fernandez, M., Martinez-Sanchez, P., Rodriguez-Frutos, B., Ruiz-Ares, G., Lara, M. L., et al. (2014). Reparative therapy for acute ischemic stroke with allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue: a safety assessment: a phase II randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-center, pilot clinical trial. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 23(10), 2694–2700.
Levy, M. L., Crawford, J. R., Dib, N., Verkh, L., Tankovich, N., & Cramer, S. C. (2019). Phase I/II study of safety and preliminary efficacy of intravenous allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells in chronic stroke. Stroke, 50(10), 2835–2841.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01828957.
Powell, S. B., & Silvestri, J. M. (2019). Safety of intratracheal administration of human umbilical cord blood derived mesenchymal stromal cells in extremely low birth weight preterm infants. The Journal of Pediatrics, 210, 209–213 e2.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02804945.
Heldman, A. W., DiFede, D. L., Fishman, J. E., Zambrano, J. P., Trachtenberg, B. H., Karantalis, V., et al. (2014). Transendocardial mesenchymal stem cells and mononuclear bone marrow cells for ischemic cardiomyopathy: the TAC-HFT randomized trial. JAMA, 311(1), 62–73.
Hare, J. M., DiFede, D. L., Rieger, A. C., Florea, V., Landin, A. M., El-Khorazaty, J., et al. (2017). Randomized comparison of allogeneic versus autologous mesenchymal stem cells for nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy: POSEIDON-DCM trial. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 69(5), 526–537.
Gupta, P. K., Chullikana, A., Parakh, R., Desai, S., Das, A., Gottipamula, S., et al. (2013). A double blind randomized placebo controlled phase I/II study assessing the safety and efficacy of allogeneic bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cell in critical limb ischemia. Journal of Translational Medicine, 11, 143.
Lee, H. C., An, S. G., Lee, H. W., Park, J. S., Cha, K. S., Hong, T. J., et al. (2012). Safety and effect of adipose tissue-derived stem cell implantation in patients with critical limb ischemia: a pilot study. Circulation Journal, 76(7), 1750–1760.
Emadedin, M., Ghorbani Liastani, M., Fazeli, R., Mohseni, F., Moghadasali, R., Mardpour, S., et al. (2015). Long-term follow-up of intra-articular injection of autologous mesenchymal stem cells in patients with knee, ankle, or hip osteoarthritis. Archives of Iranian Medicine, 18(6), 336–344.
Vega, A., Martin-Ferrero, M. A., Del Canto, F., Alberca, M., Garcia, V., Munar, A., et al. (2015). Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: a randomized controlled trial. Transplantation., 99(8), 1681–1690.
Carlsson, P. O., Schwarcz, E., Korsgren, O., & Le Blanc, K. (2015). Preserved beta-cell function in type 1 diabetes by mesenchymal stromal cells. Diabetes., 64(2), 587–592.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03333681.
Alvaro-Gracia, J. M., Jover, J. A., Garcia-Vicuna, R., Carreno, L., Alonso, A., Marsal, S., et al. (2017). Intravenous administration of expanded allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in refractory rheumatoid arthritis (Cx611): results of a multicentre, dose escalation, randomised, single-blind, placebo-controlled phase Ib/IIa clinical trial. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 76(1), 196–202.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03171194.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02633163.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT00294112.
Garcia-Olmo, D., Garcia-Arranz, M., Herreros, D., Pascual, I., Peiro, C., & Rodriguez-Montes, J. A. (2005). A phase I clinical trial of the treatment of Crohn's fistula by adipose mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Diseases of the Colon and Rectum, 48(7), 1416–1423.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01842477.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03257098.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02330978.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03265808.
Barnes, D. W., & Loutit, J. F. (1957). Treatment of murine leukaemia with x-rays and homologous bone marrow. II. Br J Haematol, 3(3), 241–252.
Passweg, J. R., Halter, J., Bucher, C., Gerull, S., Heim, D., Rovo, A., et al. (2012). Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a review and recommendations for follow-up care for the general practitioner. Swiss Medical Weekly, 142, w13696.
Shenoy, S. (2013). Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for sickle cell disease: current evidence and opinions. Ther Adv Hematol, 4(5), 335–344.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT00730314.
Nash, R. A., Hutton, G. J., Racke, M. K., Popat, U., Devine, S. M., Griffith, L. M., et al. (2015). High-dose immunosuppressive therapy and autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (HALT-MS): a 3-year interim report. JAMA Neurology, 72(2), 159–169.
Atkins, H. L., Bowman, M., Allan, D., Anstee, G., Arnold, D. L., Bar-Or, A., et al. (2016). Immunoablation and autologous haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation for aggressive multiple sclerosis: a multicentre single-group phase 2 trial. Lancet, 388(10044), 576–585.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT00730561.
Cantu-Rodriguez, O. G., Lavalle-Gonzalez, F., Herrera-Rojas, M. A., Jaime-Perez, J. C., Hawing-Zarate, J. A., Gutierrez-Aguirre, C. H., et al. (2016). Long-term insulin independence in type 1 diabetes mellitus using a simplified autologous stem cell transplant. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 101(5), 2141–2148.
Li, L., Shen, S., Ouyang, J., Hu, Y., Hu, L., Cui, W., et al. (2012). Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation modulates immunocompetent cells and improves beta-cell function in Chinese patients with new onset of type 1 diabetes. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 97(5), 1729–1736.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT00278551.
Burt, R. K., Traynor, A., Statkute, L., Barr, W. G., Rosa, R., Schroeder, J., et al. (2006). Nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for systemic lupus erythematosus. JAMA., 295(5), 527–535.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT00278564.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03000296.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03219359.
Aharonowiz, M., Einstein, O., Fainstein, N., Lassmann, H., Reubinoff, B., & Ben-Hur, T. (2008). Neuroprotective effect of transplanted human embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. PLoS One, 3(9), e3145.
Soria, B., Roche, E., Berna, G., Leon-Quinto, T., Reig, J. A., & Martin, F. (2000). Insulin-secreting cells derived from embryonic stem cells normalize glycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Diabetes., 49(2), 157–162.
Kaufman, D. S., & Thomson, J. A. (2002). Human ES cells--haematopoiesis and transplantation strategies. Journal of Anatomy, 200(Pt 3), 243–248.
Sadahiro, T. (2019). Cardiac regeneration with pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes and direct cardiac reprogramming. Regen Ther., 11, 95–100.
Min, J. Y., Yang, Y., Converso, K. L., Liu, L., Huang, Q., Morgan, J. P., et al. (2002). Transplantation of embryonic stem cells improves cardiac function in postinfarcted rats. Journal of Applied Physiology (Bethesda, MD: 1985), 92(1), 288–296.
Hedlund, E., Pruszak, J., Lardaro, T., Ludwig, W., Vinuela, A., Kim, K. S., et al. (2008). Embryonic stem cell-derived Pitx3-enhanced green fluorescent protein midbrain dopamine neurons survive enrichment by fluorescence-activated cell sorting and function in an animal model of Parkinson's disease. Stem Cells, 26(6), 1526–1536.
Yoon, D., Yoon, D., Sim, H., Hwang, I., Lee, J. S., & Chun, W. (2018). Accelerated wound healing by fibroblasts differentiated from human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a pressure ulcer animal model. Stem Cells International, 2018, 4789568.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03482050.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03119636.
Mitsuzawa, S., Ikeguchi, R., Aoyama, T., Ando, M., Takeuchi, H., Yurie, H., et al. (2019). Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells prolong hind limb survival in a rat vascularized composite allotransplantation model. Microsurgery, 39(8), 737–747.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03763136.
Tang, Y., Yu, P., & Cheng, L. (2017). Current progress in the derivation and therapeutic application of neural stem cells. Cell Death & Disease, 8(10), e3108.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01321333.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01772810.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03282760.
Mazzini, L., Gelati, M., Profico, D. C., Sgaravizzi, G., Projetti Pensi, M., Muzi, G., et al. (2015). Human neural stem cell transplantation in ALS: initial results from a phase I trial. Journal of Translational Medicine, 13, 17.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02452723.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03815071.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03128450.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02117635.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03725865.
Kalladka, D., Sinden, J., Pollock, K., Haig, C., McLean, J., Smith, W., et al. (2016). Human neural stem cells in patients with chronic ischaemic stroke (PISCES): a phase 1, first-in-man study. Lancet, 388(10046), 787–796.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01172964.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03072134.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01632527.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03005249.
Liao, S., Luo, C., Cao, B., Hu, H., Wang, S., Yue, H., et al. (2017). Endothelial progenitor cells for ischemic stroke: Update on basic research and application. Stem Cells International, 2017, 2193432.
Yang, J. X., Pan, Y. Y., Zhao, Y. Y., & Wang, X. X. (2013). Endothelial progenitor cell-based therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Cell Transplantation, 22(8), 1325–1336.
Chade, A. R., Zhu, X., Lavi, R., Krier, J. D., Pislaru, S., Simari, R. D., et al. (2009). Endothelial progenitor cells restore renal function in chronic experimental renovascular disease. Circulation., 119(4), 547–557.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02605707.
Fang, J., Guo, Y., Tan, S., Li, Z., Xie, H., Chen, P., et al. (2019). Autologous endothelial progenitor cells transplantation for acute ischemic stroke: A 4-year follow-up study. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 8(1), 14–21.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03109236.
D'Avola, D., Fernandez-Ruiz, V., Carmona-Torre, F., Mendez, M., Perez-Calvo, J., Prosper, F., et al. (2017). Phase 1–2 pilot clinical trial in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis treated with bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells. Translational Research, 188, 80–91 e2.
Wang, X. X., Zhang, F. R., Shang, Y. P., Zhu, J. H., Xie, X. D., Tao, Q. M., et al. (2007). Transplantation of autologous endothelial progenitor cells may be beneficial in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 49(14), 1566–1571.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT00694642.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02474381.
Arici, V., Perotti, C., Fabrizio, C., Del Fante, C., Ragni, F., Alessandrino, F., et al. (2015). Autologous immuno magnetically selected CD133+ stem cells in the treatment of no-option critical limb ischemia: clinical and contrast enhanced ultrasound assessed results in eight patients. Journal of Translational Medicine, 13, 342.
Woodley, D. T., Remington, J., Huang, Y., Hou, Y., Li, W., Keene, D. R., et al. (2007). Intravenously injected human fibroblasts home to skin wounds, deliver type VII collagen, and promote wound healing. Molecular Therapy, 15(3), 628–635.
Jalili, R. B., Zhang, Y., Hosseini-Tabatabaei, A., Kilani, R. T., Khosravi Maharlooei, M., Li, Y., et al. (2016). Fibroblast cell-based therapy for experimental autoimmune diabetes. PLoS One, 11(1), e0146970.
Jalili, R. B., Kilani, R. T., Li, Y., Khosravi-Maharlooie, M., Nabai, L., Wang, E. H. C., et al. (2018). Fibroblast cell-based therapy prevents induction of alopecia areata in an experimental model. Cell Transplantation, 27(6), 994–1004.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01359735.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01737762.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT00642642.
Chhetri, D. K., & Berke, G. S. (2011). Injection of cultured autologous fibroblasts for human vocal fold scars. Laryngoscope, 121(4), 785–792.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT00655356.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT00649428.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT00654654.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01874015.
Hu, S., Yang, J., Shangguan, J., Eresen, A., Li, Y., Ma, Q., et al. (2019). Natural killer cell-based adoptive transfer immunotherapy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in a Kras(LSL-G12D) p53(LSL-R172H) Pdx1-Cre mouse model. American Journal of Cancer Research, 9(8), 1757–1765.
Mehta, R. S., Randolph, B., Daher, M., & Rezvani, K. (2018). NK cell therapy for hematologic malignancies. International Journal of Hematology, 107(3), 262–270.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03358849.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01884688.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03346499.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03899480.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03948828.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03894579.
Dai, H., Zhou, Y., Tong, C., Guo, Y., Shi, F., Wang, Y., et al. (2018). Restoration of CD3(+)CD56(+) cell level improves skin lesions in severe psoriasis: A pilot clinical study of adoptive immunotherapy for patients with psoriasis using autologous cytokine-induced killer cells. Cytotherapy, 20(9), 1155–1163.
Hong, P., Yang, H., Wu, Y., Li, K., & Tang, Z. (2019). The functions and clinical application potential of exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 10(1), 242.
Shologu, N., Scully, M., Laffey, J. G., O’Toole, D. (2018). Human mesenchymal stem cell secretome from bone marrow or adipose-derived tissue sources for treatment of hypoxia-induced pulmonary epithelial injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 2996.
Allan, D. S., Tieu, A., Lalu, M., Burger, D. (2020). Concise review: mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles for regenerative therapy and immune modulation: progress and challenges toward clinical application. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 9(1), 39–46.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03857841.
Xie, Y. J., Dougan, M., Jailkhani, N., Ingram, J., Fang, T., Kummer, L., et al. (2019). Nanobody-based CAR T cells that target the tumor microenvironment inhibit the growth of solid tumors in immunocompetent mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116(16), 7624–7631.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02203825.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01454596.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02030847.
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT03197025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
The work presented here was funded by the US Army Medical Research and Development Command, Combat Casualty Care Research Program. Captain Lowry (US Air Force) was supported under an Internal Medicine Residency Research & Scholarly Activity Curriculum Individualized Research Elective program.
Dr. Lowry performed the literature searches and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript, and all authors contributed to critical revisions of the work and approved the final submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclaimer
The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors and are not to be construed as official or as reflecting the views of the Department of the Army or the Department of Defense.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lowry, L.E., Herzig, M.C., Christy, B.A. et al. Neglected No More: Emerging Cellular Therapies in Traumatic Injury. Stem Cell Rev and Rep 17, 1194–1214 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-020-10086-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-020-10086-7