Abstract
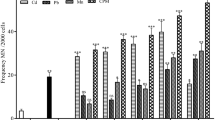
The primary aim of the current study was to recognize the biomarker approach as the finest tool to identify the geno-toxicological effects of copper, chromium, and lead inside the blood of grass carp using micronucleus test and comet assay. The induced micronuclei frequency in response to the administered concentrations of LC50 metals was discovered in the erythrocytes of metal-exposed fish at four-time intervals. The genotoxic effect of these metals with respect to the formation of micronuclei was ranked as chromium > lead > copper. Percentages of other cellular and nuclear abnormalities were also determined in the exposed blood films. Equally, the genotoxic studies in terms of comet assay in fish blood revealed significant deviations p < 0.05 against each of the studied metal at their respective time interval as compared with the healthy fish group. However, induced frequency of micronuclei and the calculated DNA damage were not found to be duration dependent. Consequently, copper, chromium, and lead have been explored as cytotoxic elements that can be responsible for inducing genotoxic effects in fish existing aquatic habitats.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oropesa A-L, García-Cambero JP, Soler F (2009) Glutathione and malondialdehyde levels in common carp after exposure to simazine. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 27(1):30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2008.08.003
Vinodhini R, St. Xavier’s College, Aquatic Biodiversity Research Centre, Palayamkottai (India), Narayanan M, St. Xavier’s College, Aquatic Biodiversity Research Centre, Palayamkottai (India) (2009) Ağır metallere maruz bırakılan Pullu Sazanlarda (Cyprinus carpio L.) antioksidan enzimlerdeki biyokimyasal değişiklikler. v. 33
Su C, Jiang L, Zhang W (2014) A review on heavy metal contamination in the soil worldwide: situation, impact and remediation techniques. Environ Sci 3(2):24–38
Paul MS, Varun M, D’Souza R, Favas PJC, Pratas J (2014) Metal contamination of soils and prospects of phytoremediation in and around River Yamuna: a case study from North-Central India. In: Hernandez-Soriano MC (ed) Environmental risk assessment of soil contamination. InTech, Rijeka. https://doi.org/10.5772/57239
Mohammed AS, Kapri A, Goel R (2011) Heavy metal pollution: source, impact, and remedies. In: Biomanagement of metal-contaminated soils. Springer, pp 1–28
Nwabunike M (2016) The effects of bioaccumulation of heavy metals on fish fin over two years. J Fisheries Livest Prod :1–7
Awoyemi OM, Bawa-Allah KA, Otitoloju AA (2014) Accumulation and anti-oxidant enzymes as biomarkers of heavy metal exposure in Clarias gariepinus and Oreochromis niloticus. Appl Ecol Environ Sci 2(5):114–122
Singha Roy U, Chattopadhyay B, Datta S, Mukhopadhyay SK (2011) Metallothionein as a biomarker to assess the effects of pollution on Indian major carp species from wastewater-fed fishponds of East Calcutta Wetlands (a Ramsar site). Environ Res Eng Manag 58(4). https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.erem.58.4.660
Bauvais C, Zirah S, Piette L, Chaspoul F, Domart-Coulon I, Chapon V, Gallice P, Rebuffat S, Perez T, Bourguet-Kondracki ML (2015) Sponging up metals: bacteria associated with the marine sponge Spongia officinalis. Mar Environ Res 104:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2014.12.005
He ZL, Yang XE, Stoffella PJ (2005) Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. J Trace Elem Med Biol 19(2–3):125–140
Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ, Tchounwou PB (2012) Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. Published in final edited form as: EXS 3:133–164
Arruti A, Fernandez-Olmo I, Irabien A (2010) Evaluation of the contribution of local sources to trace metals levels in urban PM2.5 and PM10 in the Cantabria region (Northern Spain). J Environ Monit 12(7):1451–1458. https://doi.org/10.1039/b926740a
Wagner A, Boman J (2003) Biomonitoring of trace elements in muscle and liver tissue of freshwater fish. Spectrochim Acta B At Spectrosc 58(12):2215–2226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2003.05.003
Ardeshir RA, Movahedinia A-A, Rastgar S (2017) Fish liver biomarkers for heavy metal pollution: a review article. Am J Toxicol 2(1):1–8
Sabullah MK, Ahmad SA, Shukor MY, Shamaan NA (2015) Heavy metal biomarker: fish behavior, cellular alteration, enzymatic reaction and proteomics approaches. Int Food Res J 22(2):435–454
Liney KE, Hagger JA, Tyler CR, Depledge MH, Galloway TS, Jobling S (2006) Health effects in fish of long-term exposure to effluents from wastewater treatment works. Environ Health Perspect 114(Suppl 1):81–89. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8058
Frenzilli G, Nigro M, Lyons BP (2009) The Comet assay for the evaluation of genotoxic impact in aquatic environments. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 681(1):80–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2008.03.001
Bagdonas E, Vosylienė M (2006) A study of toxicity and genotoxicity of copper, zinc and their mixture to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Biologija (1)
Gabbianelli R, Lupidi G, Villarini M, Falcioni G (2003) DNA damage induced by copper on erythrocytes of gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata and mollusk Scapharca inaequivalvis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45(3):350–356
Goodale BC, Walter R, Pelsue SR, Thompson WD, Wise SS, Winn RN, Mitani H, Wise JP Sr (2008) The cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of hexavalent chromium in medaka (Oryzias latipes) cells. Aquat Toxicol 87(1):60–67
de Lemos CT, Rödel PM, Terra NR, Erdtmann B (2001) Evaluation of basal micronucleus frequency and hexavalent chromium effects in fish erythrocytes. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(6):1320–1324
Sunjog K, Gačić Z, Kolarević S, Višnjić-Jeftić Ž, Jarić I, Knežević-Vukčević J, Vuković-Gačić B, Lenhardt M (2012) Heavy metal accumulation and the genotoxicity in barbel (Barbus barbus) as indicators of the Danube River pollution. Sci World J 2012:1–6
Maccubbin AE (1994) DNA adduct analysis in fish: laboratory and field studies. Aquat. Toxicol: Molecular, Biochemical, and Cellular Perspectives:267–294
Shugart LR (2000) DNA damage as a biomarker of exposure. Ecotoxicology 9(5):329–340
Laboratory Animal Science A, Universities Federation for Animal W (1990) Guidelines on the care of laboratory animals and their use for scientific purposes. 4, 4. Laboratory Animals Science Association; Universities Federation for Animal Welfare, London; Potters Bar
APHA (2018) 2020 QUALITY ASSURANCE/QUALITY CONTROL (2017). In: Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Am Public Health Assoc. https://doi.org/10.2105/SMWW.2882.015
Imanpoor MR, Bagheri T, Hedayati SAA (2010) The anesthetic effects of clove essence in Persian sturgeon, Acipenser persicus. WJFMS 2(1):29–36
Fenech M (1993) The cytokinesis-block micronucleus technique: a detailed description of the method and its application to genotoxicity studies in human populations. Mutat Res 285(1):35–44
Khan MS, Qureshi NA, Jabeen F (2017) Assessment of toxicity in fresh water fish Labeo rohita treated with silver nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci 7(5):167–179
Mohammed DS, El Haliem NGA (2013) Histological study on the possible protective role of parsley oil on prednisolone-induced liver and lung injury in adult male albino rats. EJH 36(2):439–448. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.EHX.0000429317.64942.2b
Fenech M, Chang WP, Kirsch-Volders M, Holland N, Bonassi S, Zeiger E (2003) HUMN project: detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat Res 534(1–2):65–75
Shah AI (2017) Heavy metal impact on aquatic life and human health–an over view. In: IAIA17 Conference Proceedings| IA’s Contribution in Addressing Climate Change 37th Annual Conference of the International Association for Impact Assessment, pp 4–7
Anbumani S, Mohankumar MN (2012) Gamma radiation induced micronuclei and erythrocyte cellular abnormalities in the fish Catla catla. Aquat Toxicol 122:125–132
da Silva ST, Fontanetti CS (2006) Micronucleus test and observation of nuclear alterations in erythrocytes of Nile tilapia exposed to waters affected by refinery effluent. Mutat Res 605(1–2):87–93
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175(1):184–191
Osipov A, Arkhangelskaya E, Vinokurov A, Smetaninа N, Zhavoronkov A, Klokov D (2014) DNA comet Giemsa staining for conventional bright-field microscopy. Int J Mol Sci 15(4):6086–6095
Gyori BM, Venkatachalam G, Thiagarajan PS, Hsu D, Clement M-V (2014) OpenComet: an automated tool for comet assay image analysis. Redox Biol 2:457–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2013.12.020
Kašuba V, Rozgaj R, Sarić MM, Blanuša M (2002) Evaluation of genotoxic damage of cadmium chloride in peripheral blood of suckling Wistar rats. J Appl Toxicol 22(4):271–277
Rozgaj R, Kašuba V, Fučić A (2002) Genotoxicity of cadmium chloride in human lymphocytes evaluated by the comet assay and cytogenetic tests. J Trace Elem Med Biol 16(3):187–192
Jiraungkoorskul W, Kosai P, Sahaphong S, Kirtputra P, Chawlab J, Charucharoen S (2007) Evaluation of micronucleus test’s sensitivity in freshwater fish species. Res J Environ Sci 1(2):56–63
Hussain B, Sultana T, Sultana S, Masoud MS, Ahmed Z, Mahboob S (2018) Fish eco-genotoxicology: comet and micronucleus assay in fish erythrocytes as in situ biomarker of freshwater pollution. Saudi J Biol Sci 25(2):393–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.11.048
Serrano-García L, Montero-Montoya R (2001) Micronuclei and chromatid buds are the result of related genotoxic events. Environ Mol Mutagen 38(1):38–45
Pietrapiana D, Modena M, Guidetti P, Falugi C, Vacchi M (2002) Evaluating the genotoxic damage and hepatic tissue alterations in demersal fish species: a case study in the Ligurian Sea (NW-Mediterranean). Mar Pollut Bull 44(3):238–243
Çavaş T, Ergene-Gözükara S (2003) Micronuclei, nuclear lesions and interphase silver-stained nucleolar organizer regions (AgNORs) as cyto-genotoxicity indicators in Oreochromis niloticus exposed to textile mill effluent. Mutat Res 538(1–2):81–91
Matsumoto ST, Mantovani MS, Malaguttii MIA, Dias AL, Fonseca IC, Marin-Morales MA (2006) Genotoxicity and mutagenicity of water contaminated with tannery effluents, as evaluated by the micronucleus test and comet assay using the fish Oreochromis niloticus and chromosome aberrations in onion root-tips. Genet Mol Biol 29(1):148–158
Scalon MC, Rechenmacher C, Siebel AM, Kayser ML, Rodrigues MT, Maluf SW, Rodrigues MA, Silva LB (2010) Evaluation of Sinos River water genotoxicity using the comet assay in fish. Braz J Biol 70(4):1217–1222
Kousar S, Javed M (2015) Diagnosis of metals induced DNA damage in fish using comet assay. Pak Vet J 35(2):168–172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval for the study was taken from the Ethical Committee, University of Peshawar.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, N., Khan, A., Habib Khan, N. et al. Genotoxic Consequences in Common Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella Valenciennes, 1844) Exposed to Selected Toxic Metals. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 305–314 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02122-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02122-x