Abstract
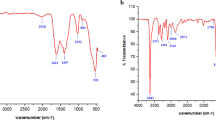
In recent years, researchers were attracted to nanomaterials components for their potential role in cancer treatment. This study aimed to develop a novel and biocompatible cobalt hydroxide (Co(OH)2) nano-flakes that is functionalized by glutamic acid (Glu) and conjugated to thiosemicarbazide (TSC) for anticancer activities against human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Physico-chemical properties of the Co(OH)2@Glu-TSC nanomaterial are characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive X–ray (EDX) analysis, and Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. MTT assay, flow cytometry, and caspase-3 activity analysis used for evaluating anticancer properties of the Co(OH)2@Glu-TSC nanomaterial. The MTT assay result showed cellular uptake of Co(OH)2@Glu-TSC and cell viability loss in a concentration-dependent. Results of flow cytometry and caspase-3 activity analysis indicated the stimulation of apoptosis through an increase in Caspase-3 and nucleus fragmentation. In general, our findings indicate the anticancer activities of Co(OH)2@Glu-TSC nanomaterial and so it can be considered as a new treatment for breast cancer. However, further in vivo studies are required to evaluate the accumulation of Co(OH)2@Glu-TSC nanomaterial in healthy organs, such as the liver, kidneys, brain, and testes, and potential toxic effects.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Bray F (2018) Global and regional estimates of the incidence and mortality for 38 cancers: GLOBOCAN. International Agency for Research on Cancer/World Health Organization, Lyon
Melo A, Amadeu MS, Lancellotti M, de Hollanda LM, Machado D (2015) The role of nanomaterials in cosmetics: national and international legislative aspects. Quim Nova 38(4):1–19
Schreiber HA, Prechl J, Jiang H, Zozulya A, Fabry Z, Denes F, Sandor M (2010) Using carbon magnetic nanoparticles to target, track, and manipulate dendritic cells. J Immunol Methods 356:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2010.02.009
Parveen S, Misra R, Sahoo SK (2012) Nanoparticles: a boon to drug delivery, therapeutics, diagnostics and imaging. Nanomedicine 8:147–166
Cheng J, Teply BA, Jeong SY, Yim CH, Ho D, Sherifi I, Jon S, Farokhzad OC, Khademhosseini A, Langer RS (2006) Magnetically responsive poltmeric microparticles for oral delivery of protein drugs. Pharm Res 23:557–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-9444-5
Asharani PV, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S (2009) Anti-proliferative activity of silver nanoparticles. BMC Cell Biol 10:65–79
Vinardell MP, Mitjans M (2015) Antitumor activities of metal oxide nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 5:1004–1021
Sharma A, Goyal AK, Rath G (2017) Recent advances in metal nanoparticles in cancer therapy. J Drug Target 26(8):617–632. https://doi.org/10.1080/1061186X.2017.1400553
Liu SH, Xing RM, Lu F, Rana RK, Zhu JJ (2009) One-pot template-free fabrication of hollow magnetite nanospheres and their application as potential drug carriers. J Phys Chem C 113:21042–21047
Azaria LH, Kirkpatrick CJ, Korenstein R, Marche PN, Maimon O, Ponti J, Romano R, Rossi F, Schindler UG, Sommer D, Uboldi C, Unger RE, Villiers C (2011) Predictive toxicology of cobalt nanoparticles and ions: com-parative in vitro study of different cellular models using methods of knowledge discovery from data. Toxicol Sci 122:489–501
Petrarca C, Perrone A, Verna N, Verginelli F, Ponti J, Sabbioni E, Di Giampaolo L, Dadorante V, Schiavone C, Boscolo P, Mariani Costantini R, Di Gioacchino M (2006) Cobalt nano-particles modulate cytokine in vitro release by human mononuclear cells mimicking autoimmune disease. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 19:11–14
Mo Y, Zhu X, Hu X, Tollerud DJ, Zhang Q (2008) Cytokine and NO release from peripheral blood neutrophils after exposure to metal nanoparticles: in vitro and ex vivo studies. Nanotoxicology 2:79–87
Ponti J, Sabbioni E, Munaro B, Broggi F, Marmorato P, Franchini F (2009) Genotoxicity and morphological transformation induced by cobalt nanoparticles and cobalt chloride: an in vitro study in Balb/3 T3 mouse fibroblasts. Mutagenesis 24:439–445
Papis E, Rossi F, Raspanti M, Isabella DD, Colombo G, Milzani A, Bernardini G, Gornati R (2009) Engineered cobalt oxide nanoparticles readily enter cells. Toxicol Lett 189:253–259
Uhrich KE, Cannizzaro SM, Langer RS, Shakesheff KM (1999) Polymeric system for controlled drug release. Chem Rev 99:3181–3198. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr940351u
Panyam J, Labhasetwar V (2003) Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55:329–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(02)00228-4
Marin RV, Ng CH, Wilke M, Tiersch B, Fratzl P, Peter MG (2005) Size controlled hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as self-organized organic–inorganic composite materials. Biomaterials 26:5414–5426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials
Marinakos SM, Anderson MF, Ryan JA, Martin LD, Feldheim DL (2001) Encapsulation, permeability, and cellular uptake characteristics of hollow nanometer-sized conductive polymer capsules. J Phys Chem B 105:8872–8876. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp010820d
Shih IL, Van YT, Shen MH (2004) Biomedical applications of chemically and microbiologically synthesized poly (glutamic acid) and poly (lysine). Mini Rev Med Chem 4(2):179–188
Tiperciuc B, Pârvu A, Tamaian R, Nastasă C, Ionuţ I, Oniga O (2013) New anti-inflammatory thiazolyl-carbonyl-thiosemicarbazides and thiazolyl-azoles with antioxidant properties as potential iNOS inhibitors. Arch Pharm Res 36(6):702–714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0083-9
Cihan-Üstündağ G, Gürsoy E, Naesens L, Ulusoy-Güzeldemirci N, Çapan G (2016) Synthesis and antiviral properties of novel indole-based thiosemicarbazides and 4-thiazolidinones. Bioorg Med Chem 24(2):240–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2015.12.008
Siwek A, Stefańska J, Dzitko K, Ruszczak A (2012) Antifungal effect of 4-arylthiosemicarbazides against Candida species. Search for molecular basis of antifungal activity of thiosemicarbazide derivatives. J Mol Model 18(9):4159–4170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1420-5
Kalhor M, Shabani M, Nikokar I, Reyhaneh Banisaeed S (2015) Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of some novel thiosemicarbazides, 1,2,4-triazol-3-thiols and their S-substituted derivatives. Iran J Pharm Res 14(1):67–75
Unsal Tan O, Ozadali K, Yogeeswari P, Sriram D, Balkan A (2012) Synthesis and antimycobacterial activities of some new N-acylhydrazone and thiosemicarbazide derivatives of 6-methyl-4,5-dihydropyridazin-3(2H)-one. Med Chem Res 21:2388–2394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-011-9770-6
Arora S, Agarwal S, Singhal S (2014) Anticancer activities of thiosemicarbazides/thiosemicarbazones: a review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 6(9):34–41
Li J, Yang M, Wei J, Zhou Z (2012) Preparation and electrochemical performances of doughnut-like Ni (OH)2–Co (OH)2 composites as pseudocapacitor materials. Nanoscale 4:4498–4503. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr30936j
Navarrete JTL, Hernández V, Ramírez FJ (1995) Vibrational study of aspartic acid and glutamic acid dipeptides. J Mol Struct 348:249–252
Foldbjerg R, Olesen P, Hougaard M, Dang DA, Hoffmann HJ, Autrup H (2009) PVP-coated silver nanoparticles and silver ions induce reactive oxygen species, apoptosis, and necrosis in THP-1 monocytes. Toxicol Lett 190(2):156–162
Ma DD, Yang WX (2016) Engineered nanoparticles induce cell apoptosis: potential for cancer therapy. Oncotarget 7(26):40882–40903. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8553
Shafagh M, Rahmani F, Delirezh N (2015) CuO nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human K562 cancer cell line via mitochondrial pathway, through reactive oxygen species and P53. Iran J Basic Med Sci 18(10):993–1000
Nuñez G, Benedict MA, Hu Y (1998) Inohara N, caspases: the proteases of the apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 17:3237–3245
Abudayyak M, Gurkaynak TA, Özhan G (2017) In vitro evaluation of cobalt oxide nanoparticle-induced toxicity. Toxicol Ind Health 33(8):646–654. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233717706633
Alarifi S, Ali D, AO Y, Ahamed M, Siddiqui MA, Al-Khedhairy AA (2013) Oxidative stress contributes to cobalt oxide nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity and DNA damage in human hepatocarcinoma cells. Int J Nanomedicine 8:189–199. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S37924
Chattopadhyay S, Chakraborty SP, Laha D, Baral R, Pramanik P (2012) Roy S surface-modified cobalt oxide nanoparticles: new opportunities for anti-cancer drug development. Cancer Nanotechnol 3(1–6):13–23
Shao J, Ma ZY, Li A, Liu YH, Xie CZ, Qiang ZY, Xu JY (2014) Thiosemicarbazone Cu (II) and Zn (II) complexes as potential anticancer agents: syntheses, crystal structure, DNA cleavage, cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction activity. J Inorg Biochem 136:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.03.004
Eckle VS, Buchmann A, Bursch W, Schulte-Hermann R, Schwarz M (2004) Immunohistochemical detection of activated caspases in apoptotic hepatocytes in rat liver. Toxicol Pathol 32(1):9–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230490260673
Krishnan P, Rajan M, Kumari S, Sakinash S, Priya SP, Amira F, Danjuma L, Pooi Ling M, Fakurazi S, Arulselvan P, Higuchi A, Arumugam R, Alarfaj AA, Munusamy MA, Hamat RA, Benelli G, Murugan K, Kumar SS (2017) Efficiency of newly formulated camptothecin with β-cyclodextrin-EDTA-Fe3O4 nanoparticle-conjugated nanocarriers as an anti-colon cancer (HT29) drug. Sci Rep 7(1):10962. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09140-1
Chattopadhyay S, Dash SK, Ghosh T, Das D, Pramanik P, Roy S (2013) Surface modification of cobalt oxide nanoparticles using phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid followed by folic acid: a biocompatible vehicle for targeted anticancer drug delivery. Cancer Nanotechnol 4(4–5):103–116
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bejarbaneh, M., Moradi-Shoeili, Z., Jalali, A. et al. Synthesis of Cobalt Hydroxide Nano-flakes Functionalized with Glutamic Acid and Conjugated with Thiosemicarbazide for Anticancer Activities Against Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 198, 98–108 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02049-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02049-3