Abstract
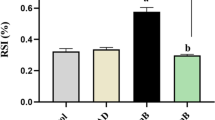
To explore the apoptosis mechanism in lymphocytes of rats induced by aluminum chloride (AlCl3) by activating cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)/protein kinase A (PKA) signaling pathway, the splenic lymphocytes of rats were cultured and exposed to different concentrations of AlCl3 for 24 h. The final concentrations of AlCl3 (AlCl3 · 6H2O) in supernatant were 0 (control group, CG), 0.3 mmol/L (low-dose group, LG), 0.6 mmol/L (mid-dose group, MG), and 1.2 mmol/L (high-dose group, HG), respectively. Lymphocytes Apoptosis rate, intracellular cAMP content, PKA, survivin, B cell lymphoma/leukemia-2 (Bcl-2) and Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) mRNA expressions, and the mRNA and protein expressions of nuclear factor-κ-gene binding (NF-κB, p65) were detected, respectively. The results showed that apoptosis index of lymphocytes, cAMP content in intracellular and PKA mRNA expression were significantly upregulated, whereas NF-κB and survivin mRNA expressions, nuclear NF-κB (p65) protein expression, and the ratio of Bcl-2 and Bax mRNA expression were downregulated in the AlCl3-treated groups compared with those in CG. The results indicated that the activated cAMP/PKA signaling pathway induces apoptosis by inhibited NF-κB in AlCl3-treated lymphocytes in vitro.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banasik A, Lankoff A, Piskulak A, Adamowska K, Lisowska H, Wojcik A (2005) Aluminum-induced micronuclei and apoptosis in human peripheral-blood lymphocytes treated during different phases of the cell cycle. Environ Toxicol 20:402–406
Willhite CC, Ball GL, McLellan CJ (2012) Total allowable concentrations of monomeric inorganic aluminum and hydrated aluminum silicates in drinking water. Crit Rev Toxicol 42:358–442
Bolitho P, Voskoboinik I, Trapani JA, Smyth MJ (2007) Apoptosis induced by the lymphocyte effector molecule perforin. Curr Opin Immunol 19:339–347
Dunkle A, He YW (2011) Apoptosis and autophagy in the regulation of T lymphocyte function. Immunol Res 49:70–86
Opferman JT (2008) Apoptosis in the development of the immune system. Cell Death Differ 15:234–242
Cesta MF (2006) Normal structure, function, and histology of the spleen. Toxicol Pathol 34:455–465
Tarantino G, Savastano S, Capone D, Colao A (2011) Spleen: a new role for an old player? World J Gastroenterol 17:3776–3784
Gao S, Wang Y, Zhang P, Dong Y, Li B (2008) Subacute oral exposure to dibromoacetic acid induced immunotoxicity and apoptosis in the spleen and thymus of the mice. Toxicol Sci 105:331–341
Fang XM, Feng YX, Wang JS, Dai JY (2010) Perfluorononanoic acid-induced apoptosis in rat spleen involves oxidative stress and the activation of caspase-independent death pathway. Toxicology 267:54–59
Coutant A, Lebeau J, Bidon-Wagner N, Levalois C, Lectard B, Chevillard S (2006) Cadmium-induced apoptosis in lymphoblastoid cell line: involvement of Caspase-dependent and-independent pathways. Biochimie 88:1815–1822
Ivanov VN, Lee RK, Podack ER, Malek TR (1997) Regulation of Fas-dependent activation-induced T cell apoptosis by cAMP signaling: a potential role for transcription factor NF-kappa B. Oncogene 14:2455–2464
Lomo J, Blomhoff HK, Beiske K, Stokke T, Smeland EB (1995) TGF-beta 1 and cyclic AMP promote apoptosis in resting human B lymphocytes. J Immunol 154:1634–1643
Li M, Song M, Ren LM, Xiu CY, Liu JY, Zhu YZ, Li YF (2014) AlCl3 induces lymphocyte apoptosis in rats through the mitochondria-caspase dependent pathway. Environ Toxicol. doi:10.1002/tox22051
Zhang JH, Hu CW, Zhu YZ, Liu SM, Bai CS, Han YF, Xia SL, Li YF (2013) Effects of norepinephrine on immune functions of cultured splenic lymphocytes exposed to aluminum trichloride. Biol Trace Elem Res 154:275–280
Liberman AC, Refojo D, Antunica-Noguerol M, Holsboer F, Arzt E (2012) Underlying mechanisms of cAMP-and glucocorticoid-mediated inhibition of FasL expression in activation-induced cell death. Mol Immunol 50:220–235
Parry GC, Mackman N (1997) Role of cyclic AMP response element-binding protein in cyclic AMP inhibition of NF-kappa B-mediated transcription. J Immunol 159:5450–5456
Takahashi N, Tetsuka T, Uranishi H, Okamoto T (2002) Inhibition of the NF-kappaB transcriptional activity by protein kinase A. Eur J Biochem 269:4559–4565
Sen R (2006) Control of B lymphocyte apoptosis by the transcription factor NF-kappaB. Immunity 25:871–883
Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M (2009) Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 27:693–733
Zatta P, Zambenedetti P, Pizzuiti A, Perazzolo M (1995) Different effects of aluminum upon carbonic anhydrases and Na+/K+-ATPase activities in rat. Neurosci Lett 197:65–68
She Y, Wang N, Chen C, Zhu YZ, Xia SL, Hu CW, Li YF (2012) Effects of aluminum on immune functions of cultured splenic T and B lymphocytes in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 147:246–250
Amirmajdi MM, Sankian M, Eftekharzadeh M, Varasteh A, Vahedi F, Sadrizadeh A, Spotin (2011) Apoptosis of human lymphocytes after exposure to hydatid fluid. Iran J Parasitol 6:9–16
Schmidt SM, Schag K, Müller MR, Weck MM, Appel S, Kanz L, Grünebach F, Brossart P (2003) Survivin is a shared tumor-associated antigen expressed in a broad variety of malignancies and recognized by specific cytotoxic T cells. Blood 102:571–576
Nizamutdinova IT (2013) Retinoic acid protects cardiomyocytes from high glucose-induced apoptosis via inhibition of sustained activation of NF-κB signaling. J Cell Physiol 228
Ishida M, Mitsui T, Yamakawa K, Sugiyama N, Takahashi W, Shimura H, Endo T, Kobayashi T, Arita J (2007) Involvement of cAMP response element-binding protein in the regulation of cell proliferation and the prolactin promoter of lactotrophs in primary culture. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E1529–E1537
Moore AR, Willoughby DA (1995) The role of cAMP regulation in controlling inflammation. Clin Exp Immunol 101:387–389
Mosenden R, Taskén K (2011) Cyclic AMP-mediated immune regulation-overview of mechanisms of action in T cells. Cell Signal 23:1009–1016
Insel PA, Zhang L, Murray F, Yokouchi H, Zambon AC (2012) Cyclic AMP is both a pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic second messenger. Acta Physiol 204:277–287
Zhang L, Murray F, Zahno A, Kanter JR, Chou D, Suda R, Fenlon M, Rassenti L, Cottam H, Kipps TJ, Insel PA (2008) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase profiling reveals increased expression of phosphodiesterase 7B in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:19532–19537
Zambon AC, Zhang L, Minovitsky S, Kanter JR, Prabhakar S, Salomonis N, Vranizan K, Dubchak I, Conklin BR, Insel PA (2005) Gene expression patterns define key transcriptional events in cell-cycle regulation by cAMP and protein kinase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:8561–8566
Zhang L, Zambon AC, Vranizan K, Pothula K, Conklin BR, Insel PA (2008) Gene expression signatures of cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA)-promoted, mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. J Biophys Chem 283:4304–4313
Gupta S (2003) Molecular signaling in death receptor and mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. (Rev) Int J Oncol 22:15–20
Si MS, Reitz BA, Borie DC (2005) Effects of the kinase inhibitor CGP41251 (PKC 412) on lymphocyte activation and TNF-alpha production. Int Immunopharmacol 5:1141–1149
Zhang A, Chen D, Wei H, Du L, Zhao T, Wang X, Zhou H (2012) Functional characterization of TNF-alpha in grass carp head kidney leukocytes: induction and involvement in the regulation of NF-kappaB signaling. Fish Shellfish Immunol 33:1123–1132
Zhang L, Yun H, Murray F, Lu R, Wang L, Hook V, Insel PA (2011) Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-2 alpha induces apoptosis of murine T-lymphoma cells and cardiac fibroblasts and is regulated by cAMP/PKA. Cell Signal 23:1611–1616
Altieri DC (2008) New wirings in the survivin networks. Oncogene 27:6276–6284
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC (1997) A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 3:917–921
Liu N, Zheng Y, Zhu Y, Xiong S, Chu Y (2011) Selective impairment of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by paclitaxel is explained by Bcl-2/Bax mediated apoptosis. Int Immunopharmacol 11:212–219
Shinagawa A, Yoshida Y, Kurokawa T, Horiuchi Y, Tsuyoshi H, Orisaka M, Sawamura Y, Kleinman HK, Kotsuji F (2011) The potent peptide antagonist to angiogenesis, C16Y, and cisplatin act synergistically in the down-regulation of the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and the induction of apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells. Int J Oncol 39:1359–1364
Lu HF, Chie YJ, Yang MS, Lee CS, Fu JJ, Yang JS, Tan TW, Wu SH, Ma YS, Ip SW, Chung JG (2010) Apigenin induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human lung cancer A549 cells through Bax-and Bcl-2-triggered mitochondrial pathway. Int J Oncol 36:1477–1484
Dohi T, Beltrami E, Wall NR, Plescia J, Altieri DC (2004) Mitochondrial survivin inhibits apoptosis and promotes tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest 114:1117–1127
Al-Maghrebi M, Kehinde EO, Anim JT (2010) Long term testicular ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced apoptosis: involvement of survivin down-regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 395:342–347
Ogura A, Oowada S, Kon Y, Hirayama A, Yasui H, Meike S, Kobayashi S, Kuwabara M, Inanami O (2009) Redox regulation in radiation-induced cytochrome c release from mitochondria of human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Cancer Lett 277:64–71
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-kappa B regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2:725–734
Villela D, de Sa LL, Peres R, Peliciari-Garcia RA, do Amaral FG, Cipolla-Neto J, Scavone C, Afeche SC (2014) Norepinephrine activates NF-kappaB transcription factor in cultured rat pineal gland. Life Sci 94:122–129
Vang T, Torgersen KM, Sundvold V, Saxena M, Levy FO, Skålhegg BS, Hansson V, Mustelin TTaskén K (2001) Activation of the COOH-terminal Src kinase (Csk) by cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits signaling through the T cell receptor. J Exp Med 193:497–508
Skålhegg B, Landmark B, Døskeland S, Hansson V, Lea T, Jahnsen T (1992) Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase type I mediates the inhibitory effects of 3′, 5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate on cell replication in human T lymphocytes. J Biophys Chem 267:15707–15714
Aandahl EM, Aukrust P, Skalhegg BS, Muller F, Froland SS, Hansson V, Tasken K (1998) Protein kinase A type I antagonist restores immune responses of T cells from HIV-infected patients. FASEB J 12:855–862
Betz M, Fox BS (1991) Prostaglandin E2 inhibits production of Th1 lymphokines but not of Th2 lymphokines. J Immunol 146:108–113
Haraguchi S, Good RA, Day NK (1995) Immunosuppressive retroviral peptides: cAMP and cytokine patterns. Immunol Today 16:595–603
Hilkens CM, Snijders A, Snijdewint FG, Wierenga EA, Kapsenberg ML (1996) Modulation of T-cell cytokine secretion by accessory cell-derived products. Eur Respir J Suppl 22:90s–94s
Snijdewint FG, Kalinski P, Wierenga EA, Bos JD, Kapsenberg ML (1993) Prostaglandin E2 differentially modulates cytokine secretion profiles of human T helper lymphocytes. J Immunol 150:5321–5329
Balistreri CR, Candore G, Accardi G, Colonna-Romano G, Lio D (2013) NF-κB pathway activators as potential ageing biomarkers: targets for new therapeutic strategies. Immun Ageing 10:24
Espinosa L, Cathelin S, D’Altri T, Trimarchi T, Statnikov A, Guiu J, Rodilla V, Inglés-Esteve J, Nomdedeu J, Bellosillo B (2010) The Notch/Hes1 pathway sustains NF-κB activation through CYLD repression in T cell leukemia. Cancer Cell 18:268–281
Lopez-Guerra M, Colomer D (2010) NF-κB as a therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Expert Opin Ther Targets 14:275–288
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the National Science Foundation Project of China (31172375, 31302147).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Feibo Xu and Jing Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Wang, J., Cao, Z. et al. cAMP/PKA Signaling Pathway Induces Apoptosis by Inhibited NF-κB in Aluminum Chloride-Treated Lymphocytes In Vitro. Biol Trace Elem Res 170, 424–431 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0461-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0461-x