Abstract
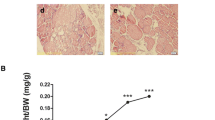
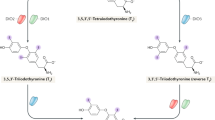
In mammals, iodothyronine deiodinase and iodotyrosine deiodinase (IYD) are known to catalyze the reductive dehalogenation. IYD is a critical enzyme in maintaining iodine homeostasis. Advances in the study of iodothyronine deiodinase have been published steadily; research on IYD has been slow on its function and regulation. We studied the expression of IYD in thyroid, liver, and kidney in conditions such as iodine deficiency and excess to determine its regulation and role in iodine recycling. Sixty 4-week-old female Wistar rats were randomly divided into two groups, with each group containing three subgroups. The rats were fed with different iodine intake for 3 months. After 3 months, all the rats were sacrificed, and the expression of IYD in thyroid, liver, and kidney of the rats were determined. We found that the expression of thyroidal IYD in 0.3-fold-iodine intake group was significantly higher as compared with the low-iodine feed control group (p < 0.01), whereas the expression in 6-fold-iodine intake group was significantly decreased as compared with normal-iodine feed control group (p < 0.01). However, the variation of IYD expression in thyroid was not similar to liver and kidney. In conclusion, iodine deficiency results in an increased expression of IYD in thyroid, whereas excess iodine decreases the expression of thyroidal IYD. In humans, daily iodine intake of <75 or >500 μg can affect the expression of thyroidal IYD. The safety range of iodine intake is narrow. In addition, further investigations are required to study the expression and regulation of IYD in various organs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delange F (2001) Iodine deficiency as a cause of brain damage. Postgrad Med J 77:217–220
Zimmermann MB (2011) The role of iodine in human growth and development. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22:645–652
Zimmermann MB (2009) Iodine deficiency. Endocr Rev 30:376–408
Kopp PA (2008) Reduce, recycle, reuse—iodotyrosine deiodinase in thyroid iodide metabolism. N Engl J Med 358:1856–1859
Roche J, Michel R, Michel O, Lissitzky S (1952) Sur la déshalogénation enzymatique des iodotyrosines par le corps thyroïde et sur son rôle physiologique. Biochim Biophys Acta 9:161–169
Rosenberg IN, Goswami A (1979) Purification and characterization of a flavoprotein from bovine thyroid with iodotyrosine deiodinase activity. J Biol Chem 254:12318–12325
Moreno JC, Pauws E, van Kampen AH, Jedlickova M, de Vijlder JJ, Ris-Stalpers C (2001) Cloning of tissue-specific genes using serial analysis of gene expression and a novel computational substraction approach. Genomics 75:70–76
Moreno JC (2003) Identification of novel genes involved in congenital hypothyroidism using serial analysis of gene expression. Horm Res 60(Suppl 3):96–102
Gnidehou S, Lacroix L, Sezan A, Ohayon R, Noel-Hudson MS, Morand S, Francon J, Courtin F, Virion A, Dupuy C (2006) Cloning and characterization of a novel isoform of iodotyrosine dehalogenase 1 (DEHAL1) DEHAL1C from human thyroid: comparisons with DEHAL1 and DEHAL1B. Thyroid 16:715–724
Maayan ML, Rosenberg IN (1963) Effect of injection of thyrotropin upon deiodination of diiodotyrosine by rat thyroid and liver. Endocrinology 73:38–44
Gnidehou S, Caillou B, Talbot M, Ohayon R, Kaniewski J, Noel-Hudson MS, Morand S, Agnangji D, Sezan A, Courtin F, Virion A, Dupuy C (2004) Iodotyrosine dehalogenase 1 (DEHAL1) is a transmembrane protein involved in the recycling of iodide close to the thyroglobulin iodination site. FASEB J 18:1574–1576
Moreno JC, Klootwijk W, van Toor H, Pinto G, D'Alessandro M, Leger A, Goudie D, Polak M, Gruters A, Visser TJ (2008) Mutations in the iodotyrosine deiodinase gene and hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 358:1811–1818
Macours P, Aubry JC, Hauquier B, Boeynaems JM, Goldman S, Moreno-Reyes R (2008) Determination of urinary iodine by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Trace Elem Med Biol 22:162–165
Rokita SE, Adler JM, McTamney PM, Watson JJ (2010) Efficient use and recycling of the micronutrient iodide in mammals. Biochimie 92:1227–1235
Solis-S JC, Villalobos P, Orozco A, Delgado G, Quintanar-Stephano A, Garcia-Solis P, Hernandez-Montiel HL, Robles-Osorio L, Valverde-R C (2011) Inhibition of intrathyroidal dehalogenation by iodide. J Endocrinol 208:89–96
Shimizu R, Yamaguchi M, Uramaru N, Kuroki H, Ohta S, Kitamura S, Sugihara K (2013) Structure–activity relationships of 44 halogenated compounds for iodotyrosine deiodinase-inhibitory activity. Toxicology 314:22–29
Delange F, Burgi H, Chen ZP, Dunn JT (2002) World status of monitoring iodine deficiency disorders control programs. Thyroid 12:915–924
WHO, UNICEF, ICCIDD (2001) Assessment of iodine deficiency disorders and monitoring their elimination. Geneva, World Health Organization (WHO/NHD/01.1)
de Benoist B, McLean E, Andersson M, Rogers L (2008) Iodine deficiency in 2007: global progress since 2003. Food Nutr Bull 29:195–202
Teng W, Shan Z, Teng X, Guan H, Li Y, Teng D, Jin Y, Yu X, Fan C, Chong W, Yang F, Dai H, Yu Y, Li J, Chen Y, Zhao D, Shi X, Hu F, Mao J, Gu X, Yang R, Tong Y, Wang W, Gao T, Li C (2006) Effect of iodine intake on thyroid diseases in China. N Engl J Med 354:2783–2793
Trumbo P, Yates AA, Schlicker S, Poos M (2001) Dietary reference intakes: vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc. J Am Diet Assoc 101:294–301
European Commission HCPD-GSCF (2002) Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the tolerable upper level of intake of iodine. European Commission, Brussels
Kohrle J, Jakob F, Contempre B, Dumont JE (2005) Selenium, the thyroid, and the endocrine system. Endocr Rev 26:944–984
Lavado-Autric R, Calvo RM, de Mena RM, de Escobar GM, Obregon MJ (2013) Deiodinase activities in thyroids and tissues of iodine-deficient female rats. Endocrinology 154:529–536
Acknowledgments
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xin Sun and Xiaowen Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Zhang, X., Jiang, Y. et al. Expression of Iodotyrosine Deiodinase in Thyroid and Other Organs in Iodine-Deficient and Iodine-Excess Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 167, 272–279 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0328-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0328-1