Abstract
With the progress and advancement in discovery of novel antimicrobial drugs, efficient solubility plays an important component for a drug to express its out-turn effectively. A biocompatible neutral/non-ionic surfactant, Triton X-100 (Tx-100), was successfully employed to solubilize an antibiotic drug, sulfamethazine (SMZ), through micellization process. The association process of Tx-100 toward SMZ was confirmed through the characteristic spectral change in absorption and emission spectroscopy. The morphological behavior of the complex was studied from small angle neutron scattering (SANS). Changes in size(s) and charge(s) of the micelles were monitored using zeta (z) potential technique. This present study emphasized the molecular mechanism and characteristics of Tx-100 as an effective drug solubilizing and carrier agent. Thus, the drug-loaded micellar system can enhance cellular uptake and increase the antibacterial effects of drugs in the biological system(s).
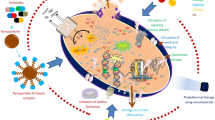
Graphical Abstract
Schematic illustration of drug-surfactant micelle formation and target release of drug at the targeted site







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data are available from the authors and can be shared upon reasonable request.
References
Meseli, T., Dogan, S. D., Gunduz, M. G., Kokbudak, Z., Skaro Bogojevic, S., & Noonan, T. (2021). Design, synthesis, antibacterial activity evaluation and molecular modeling studies of new sulfonamides containing a sulfathiazole moiety. New Journal of Chemistry, 45(18), 8166–8177.
Trussell, J., Goldman, N., Kuziemko, I., & Mueller, U. (1930). Evidence on the impact of sulfa drugs. Journal of Applied Economics, 2, 118–146.
Kołaczek, A., Fusiarz, I., Lawecka, J., & Branowska, D. (2014). Biological activity and synthesis of sulfonamide derivatives: A brief review. Chemik., 68(7), 620–628.
Fotouhi, L., & Zabeti, M. (2016). Photochemically induced fluorimetry, UV–Vis spectroscopy, and voltammetry on the DNA/MWCNT/GCE to investigate the interaction of sulfamethazine with DNA : Determination of DNA. Monatshefte für Chemie - Chem Mon., 147(4), 837–844.
Perez, P., Eichhorn, P., & Diana, S. A. (2005). Evaluating the biodegradability of sulfamethazine, sulfamethoxazole, sulfathiazole, and trimethoprim at different stages of sewage treatment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24(6), 1361–1367.
Mavani, A., Ovung, A., Luikham, S., Ray, D., Aswal, V. K., Chatterjee, S., et al. (2021). In vitro solubilization of antibiotic drug sulfamethazine: An investigation on drug–micelle aggregate formation by spectroscopic and scattering techniques. Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 25, 331–339.
Luo, J., Zhang, Y., Matios, E., Wang, P., Wang, C., Xu, Y., et al. (2022). Stabilizing sodium metal anodes with surfactant-based electrolytes and unraveling the atomic structure of interfaces by cryo-TEM. Nano Letters, 22(3), 1382–1390.
Chatterjee, S., & Suresh Kumar, G. (2016). Visualization of stepwise drug-micelle aggregate formation and correlation with spectroscopic and calorimetric results. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 120(45), 11751–11760.
Seedher, N., Kanojia, M. (2008). Brief/technical note micellar solubilization of some poorly soluble antidiabetic drugs : A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech, 9(2), 431–436.
Rangel-yagui, C. O., Pessoa-jr, A., Tavares, L. C. (2005). Micellar solubilization of drugs. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Science, 8(2):147–65.
Bahri, M. A., Hoebeke, M., Grammenos, A., Delanaye, L., Vandewalle, N., & Seret, A. (2006). Investigation of SDS, DTAB and CTAB micelle microviscosities by electron spin resonance. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp., 290(1–3), 206–212.
Bhat, P. A., Dar, A. A., Rather, G. M. (2008). Solubilization capabilities of some cationic, anionic, and nonionic surfactants toward the poorly water-soluble antibiotic drug erythromycin. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data. 53, 1271–77.
Chakrabarty, A., Das, P., Mallick, A., & Chattopadhyay, N. (2008). Effect of surfactant chain length on the binding interaction of a biological photosensitizer with cationic micelles. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 112(12), 3684–3692.
Chakrabarty, A., Mallick, A., Haldar, B., Purkayastha, P., Das, P., & Chattopadhyay, N. (2007). Surfactant chain-length-dependent modulation of the prototropic transformation of a biological photosensitizer: Norharmane in anionic micelles. Langmuir, 23(9), 4842–4848.
Dey, S., Patel, A., Raina, K., Pradhan, N., Biswas, O., Thummer, R. P., et al. (2020). A stimuli-responsive anticancer drug delivery system with inherent antibacterial activities. Chemical Communications, 56(11), 1661–1664.
Tennouga, L., Mansri, A., & Kouider, M. (2015). The micelle formation of cationic and anionic surfactants in aqueous medium : Determination of CMC and thermodynamic parameters at different temperatures. Journal of Materials and Environmental Science, 6(10), 2711–2716.
Kumar, D., Parray, M., Wani, F. A., Dohare, N., Ali, M., Patel, R., et al. (2022). Deciphering the role of alkyl chain length on interaction study of antidepressant drug-cationic surfactants in imidazolium based ionic liquid. Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 19(6), 2449–57.
Lalthlengliani, J., Gurung, J., & Pulikkal, A. K. (2022). Solubilization of aqueous-insoluble phenothiazine drug in TX-100 micellar solution and interactions of cationic/anionic surfactants with phenothiazine–TX-100 system. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 354, 118823.
Gul, J., Ullah, S., Ali, I., Rao, K., Iqbal, K. M., Jabri, T., et al. (2021). Synthesis, characterization and drug delivery application of dapsone based double tailed biocompatible nonionic surfactant. Chemistry and Physcis of Lipids, 239, 105115.
Masjedi, M., Montahaei, T. (2021). An illustrated review on nonionic surfactant vesicles (niosomes) as an approach in modern drug delivery: Fabrication, characterization, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic applications. Journal of Biomedical Sciences. 10(2).
Ruhul Amin, M., Abdul Rub, M., Hosaain Shah, A., Kumar, D., Majibur Rahman, M., Anamul Hoque, M., et al. (2022). Phase separation and conductivity studies on the interaction of promethazine hydrochloride drug with cationic and nonionic surfactants: Influences of salts and temperature. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 359, 119325.
Dharaiya, N., Bahadur, P., Singh, K., Marangoni, G. G. D., & Bahadur, P. (2013). Light scattering and NMR studies of Triton X-100 micelles in the presence of short chain alcohols and ethoxylates. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp., 436, 252–259.
Maiti, S., & Chatterji, P. R. (2000). Transition from normal to flowerlike micelles. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 104(44), 10253–10257.
Aswal, V. K., & Goyal, P. S. (2000). Small-angle neutron scattering diffractometer at Dhruva reactor. Current Science, 79(7), 947–953.
Thakkar, K., Bharatiya, B., Shah, D. O., Ray, D., Aswal, V. K., & Bahadur, P. (2015). Interaction of ionic liquid type cationic surfactants with Triton X-100 nonionic micelles. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp., 484, 547–557.
Pathan, H., Patil, R., Ray, D., Aswal, V. K., Bahadur, P., Tiwari, S. (2019). PT NU SC. Journal of Molecular Liquids 111235.
Hayter, J. B., & Penfold, J. (1983). Determination of micelle structure and charge by neutron small-angle scattering. Colloid and Polymer Science, 261(12), 1022–1030.
Ray, D., Aswal, V. K., & Kohlbrecher, J. (2011). Synthesis and characterization of high concentration block copolymer-mediated gold nanoparticles. Langmuir, 27(7), 4048–4056.
Hayter, J. B., & Penfold, J. (1981). An analytic structure factor for macroion solutions. Molecular Physics, 42(1), 109–118.
Pedersen, J. S. (1997). Analysis of small-angle scattering data from colloids and polymer solutions: Modeling and least-squares fitting. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 70(1–3), 171–210.
Salopek, B., Krasic, D., & Filipovic, S. (1992). Measurement and application of zeta-potential. Rudarsko-geolosko-naftnis Zbornik, 4, 147–151.
Gupta, V., Trivedi, P. (2018). In vitro and in vivo characterization of pharmaceutical topical nanocarriers containing anticancer drugs for skin cancer treatment. Lipid Nanocarriers for Drug Targeting. 563–627.
Carvalho, P. M., Felício, M. R., Santos, N. C., Gonçalves, S., Domingues, M. M.(2018). Application of light scattering techniques to nanoparticle characterization and development. Frontiers Chemistry. 1–17.
Karimi, M. A., Mozaheb, M. A., Hatefi-Mehrjardi, A., Tavallali, H., Attaran, A. M., & Shamsi, R. (2015). A new simple method for determining the critical micelle concentration of surfactants using surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 6(1), 4–11.
Kalyanasundaram, K., & Thomas, J. K. (1977). Environmental effects on vibronic band intensities in pyrene monomer fluorescence and their application in studies of micellar systems. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 99(7), 2039–2044.
Haldar, B., Mallick, A., & Chattopadhyay, N. (2004). Photophysics of pyrene-end-capped poly(ethyleneoxide) in aqueous micellar environments. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 115(2–3), 113–120.
Mallick, A., Mandal, M. C., Haldar, B., Chakrabarty, A., Das, P., & Chattopadhyay, N. (2006). Surfactant-induced modulation of fluorosensor activity: A simple way to maximize the sensor efficiency. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 128(10), 3126–3127.
Das, P., Mallick, A., Sarkar, D., & Chattopadhyay, N. (2008). Application of anionic micelle for dramatic enhancement in the quenching-based metal ion fluorosensing. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 320(1), 9–14.
Aguiar, J., Carpena, P., Molina-Bolívar, J. A., & Carnero Ruiz, C. (2003). On the determination of the critical micelle concentration by the pyrene 1:3 ratio method. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 258(1), 116–122.
Basu Ray, G., Chakraborty, I., & Moulik, S. P. (2006). Pyrene absorption can be a convenient method for probing critical micellar concentration (cmc) and indexing micellar polarity. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 294(1), 248–254.
Patel, V., Ray, D., Aswal, V. K., & Bahadur, P. (2014). Triton X-100 micelles modulated by solubilized cinnamic acid analogues: The pH dependant micellar growth. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp., 450(1), 106–114.
Funding
This work was supported by the DST Women Scientist Award Grant (DST/WOS-A/CS-83/2019), GOI (recipient: Ms. A. Mavani), UGC-DAE, Mumbai Center, BARC, Mumbai (CRS-266), DBT Twinning Research Scheme (BT/PR25026/NER/95/963/2017), DRDO (through North East Science & Technology Centre, Mizoram University, project no. DFTM/07/3603/NESTC/EWM/P-04), and GOI (recipient: Dr. Jhimli Bhattacharyya).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Mavani performed the experiment, collected the data, and wrote the paper. Debes Ray helped in performing the SANS, zeta potential experiment, and critical reviewing of the paper. Vinod K. Aswal contributed in the analysis tool (SANS and zeta potential instrument) and critical reviewing of the paper. Jhimli Bhattacharyya conceived and designed the experiment, and did critical reviewing and revision of the manuscript. All the authors contributed to the discussion of the results and writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The study requires no ethical approval. The manuscript is in compliance with ethical standards.
Consent for Publication
Consent to publish has been received from all authors.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests r.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mavani, A., Ray, D., Aswal, V.K. et al. Application of Drug Aggregation to Solubilize Antimicrobial Compound and Enhancing its Bioavailability. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 3206–3216 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04298-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04298-5