Abstract
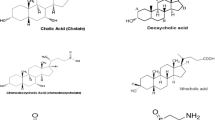
In the pursuit of developing new active ingredients for drug development, bile salts have emerged as promising substances that can enhance absorption. Their unique properties, characterized by being both hydrophilic and hydrophobic, provide numerous opportunities for modifying drugs across different categories. As naturally occurring surfactants within the body, bile salts have been extensively utilized to improve the absorption of drugs through various biological barriers, including the blood–brain barrier, skin, mucosa, cornea, buccal (oral cavity), nasal, pulmonary (lung), and intestinal membranes. By leveraging bile salts, researchers have discovered their significant potential in increasing drug permeability and bioavailability by facilitating transport through these barriers. Additionally, bile salts can be effectively combined with other commonly used materials in drug delivery, such as lipids and polymers, expanding their application as active ingredients. This comprehensive review aims to present the latest insights in this field by examining recent literature on the subject.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Debility S et al Jalinoos [Claudius Galen]–Galen of Pergamon
Macierzanka A, Torcello-Gómez A, Jungnickel C, Maldonado-Valderrama J (2019) Bile salts in digestion and transport of lipids. Adv Coll Interface Sci 274:102045
Sankhyan A, Pawar PK (2013) Metformin loaded non-ionic surfactant vesicles: optimization of formulation, effect of process variables and characterization. DARU J Pharm Sci 21:1–8
Kundu S, Kumar S, Bajaj A (2015) Cross-talk between bile acids and gastrointestinal tract for progression and development of cancer and its therapeutic implications. IUBMB Life 67(7):514–523
Ahmed M (2022) Functional, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of bile. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 105–120
Russell DW (2003) The enzymes, regulation, and genetics of bile acid synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem 72(1):137–174
Fini A, Feroci G, Roda A (2002) Acidity in bile acid systems. Polyhedron 21(14–15):1421–1427
Chang C-M, Bodmeier R (1997) Effect of dissolution media and additives on the drug release from cubic phase delivery systems. J Control Release 46(3):215–222
Moghimipour E, Ameri A, Handali S (2015) Absorption-enhancing effects of bile salts. Molecules 20(8):14451–14473
Quinn M et al (2014) Bile acids permeabilize the blood brain barrier after bile duct ligation in rats via Rac1-dependent mechanisms. Dig Liver Dis 46(6):527–534
Stojančević M, Pavlović N, Goločorbin-Kon S, Mikov M (2013) Application of bile acids in drug formulation and delivery. Front Life Sci 7(3–4):112–122
Arora G et al (2011) Formulation and evaluation of controlled release matrix mucoadhesive tablets of domperidone using Salvia plebeian gum. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2(3):163–169
Pavlović N et al (2018) Bile acids and their derivatives as potential modifiers of drug release and pharmacokinetic profiles. Front Pharmacol 9:1283
Shaikh M, Derle ND, Bhamber R (2012) Permeability enhancement techniques for poorly permeable drugs: a review. J Appl Pharm Sci 2(7):34–39
Aburahma MH (2016) Bile salts-containing vesicles: promising pharmaceutical carriers for oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs and peptide/protein-based therapeutics or vaccines. Drug Deliv 23(6):1847–1867
Thakur G, Singh A, Singh I (2016) Chitosan-montmorillonite polymer composites: formulation and evaluation of sustained release tablets of aceclofenac. Sci Pharm 84(4):603–618
Small DM (1968) Size and structure of bile salt micelles: influence of structure, concentration, counterion concentration, pH, and temperature, ACS Publications
Poša M, Pilipović A (2017) Self-association of C3 and C6 epimers of hyodeoxycholate anions in aqueous medium: hydrophobicity, critical micelle concentration and aggregation number. J Mol Liq 238:48–57
Naso JN, Bellesi FA, Ruiz-Henestrosa VMP, Pilosof AM (2019) Studies on the interactions between bile salts and food emulsifiers under in vitro duodenal digestion conditions to evaluate their bile salt binding potential. Colloids Surf, B 174:493–500
Swaan PW, Szoka FC Jr, Øie S (1996) Use of the intestinal and hepatic bile acid transporters for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 20(1):59–82
Azum N, Rub MA, Asiri AM (2019) Bile salt–bile salt interaction in mixed monolayer and mixed micelle formation. J Chem Thermodyn 128:406–414
Malik NA (2016) Solubilization and interaction studies of bile salts with surfactants and drugs: a review. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179:179–201
Gibaldi M, Feldman S (1970) Mechanisms of surfactant effects on drug absorption. J Pharm Sci 59(5):579–589
Hofmann A, Small DM (1967) Detergent properties of bile salts: correlation with physiological function. Annu Rev Med 18(1):333–376
Coreta-Gomes FM et al (2012) Quantification of cholesterol solubilized in bile salt micellar aqueous solutions using 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Anal Biochem 427(1):41–48
Mrestani Y, Bretschneider B, Härtl A, Neubert RH (2003) In-vitro and in-vivo studies of cefpirom using bile salts as absorption enhancers. J Pharm Pharmacol 55(12):1601–1606
Mudgil M et al (2012) Nanotechnology: a new approach for ocular drug delivery system. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4(2):105–12
Reis S et al (2004) Noninvasive methods to determine the critical micelle concentration of some bile acid salts. Anal Biochem 334(1):117–126
Roda A, Hofmann AF, Mysels KJ (1983) The influence of bile salt structure on self-association in aqueous solutions. J Biol Chem 258(10):6362–6370
Mooranian A et al (2020) Bile acid bio-nanoencapsulation improved drug targeted-delivery and pharmacological effects via cellular flux: 6-months diabetes preclinical study. Sci Rep 10(1):106
Ahmad J et al (2017) Bile salt stabilized vesicles (bilosomes): a novel nano-pharmaceutical design for oral delivery of proteins and peptides. Curr Pharm Des 23(11):1575–1588
Holm R, Müllertz A, Mu H (2013) Bile salts and their importance for drug absorption. Int J Pharm 453(1):44–55
Parekh PY, Patel VI, Khimani MR and Bahadur P (2023) Self-assembly of bile salts and their mixed aggregates as building blocks for smart aggregates. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 102846
Albalak A et al (1996) Effects of submicellar bile salt concentrations on biological membrane permeability to low molecular weight non-ionic solutes. Biochemistry 35(24):7936–7945
Attili A et al (1986) Bile acid-induced liver toxicity: relation to the hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance of bile acids. Med Hypotheses 19(1):57–69
Van Hasselt P et al (2009) The influence of bile acids on the oral bioavailability of vitamin K encapsulated in polymeric micelles. J Control Release 133(2):161–168
Van Hasselt P (2009). Vitamin K prophylaxis revisited: focus on risk factors, University Utrecht
Kabedev A et al (2021) Molecular dynamics simulations reveal membrane interactions for poorly water-soluble drugs: impact of bile solubilization and drug aggregation. J Pharm Sci 110(1):176–185
Alrefai WA, Gill RK (2007) Bile acid transporters: structure, function, regulation and pathophysiological implications. Pharm Res 24:1803–1823
Deng F, Bae YH (2020) Bile acid transporter-mediated oral drug delivery. J Control Release 327:100–116
Bashyal S, Seo J-E, Choi YW, Lee S (2021) Bile acid transporter-mediated oral absorption of insulin via hydrophobic ion-pairing approach. J Control Release 338:644–661
Kweon S et al (2023) Design of chimeric GLP-1A using oligomeric bile acids to utilize transporter-mediated endocytosis for oral delivery. Biomater Res 27(1):1–18
Murakami T, Bodor E, Bodor N (2021) Factors and dosage formulations affecting the solubility and bioavailability of P-glycoprotein substrate drugs. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 17(5):555–580
Zhang B et al (2016) Bile salt liposomes for enhanced lymphatic transport and oral bioavailability of paclitaxel. Die Pharmazie-An Int J Pharma Sci 71(6):320–326
Rupp C, Steckel H, Müller BW (2010) Mixed micelle formation with phosphatidylcholines: the influence of surfactants with different molecule structures. Int J Pharm 387(1–2):120–128
Guo Q et al (2016) Comparison of bile salt/phosphatidylcholine mixed micelles in solubilization to sterols and stability. Drug Des, Dev Therapy 3789–3798
Yu X et al (2015) Ginsenoside Rg3 bile salt-phosphatidylcholine-based mixed micelles: design, characterization, and evaluation. Chem Pharm Bull 63(5):361–368
Hammad MA, Müller BW (1999) Solubility and stability of lorazepam in bile salt/soya phosphatidylcholine–mixed micelles. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 25(4):409–417
Cautela J et al (2017) Wormlike reverse micelles in lecithin/bile salt/water mixtures in oil. Colloids Surf, A 532:411–419
Fornasier M et al (2021) Tuning lipid structure by bile salts: hexosomes for topical administration of catechin. Colloids Surf, B 199:111564
Dening TJ, Douglas JT, Hageman MJ (2021) Do macrocyclic peptide drugs interact with bile salts under simulated gastrointestinal conditions? Mol Pharm 18(8):3086–3098
Matheson AB et al (2017) The development of phytosterol-lecithin mixed micelles and organogels. Food Funct 8(12):4547–4554
Jain S, Reddy CSK, Swami R, Kushwah V (2018) Amphotericin B loaded chitosan nanoparticles: implication of bile salt stabilization on gastrointestinal stability, permeability and oral bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 19:3152–3164
Liu X, Clifford A, Zhao Q, Zhitomirsky I (2020) Biomimetic strategies in colloidal-electrochemical deposition of functional materials and composites using chenodeoxycholic acid. Colloids Surf, A 603:125189
Mathavan S, Chen-Tan N, Arfuso F, Al-Salami H (2016) The role of the bile acid chenodeoxycholic acid in the targeted oral delivery of the anti-diabetic drug gliclazide, and its applications in type 1 diabetes. Artif Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol 44(6):1508–1519
Mooranian A et al (2021) Chenodeoxycholic acid pharmacology in biotechnology and transplantable pharmaceutical applications for tissue delivery: an acute preclinical study. Cells 10(9):2437
Qian M et al (2022) Discovery of novel cholic acid derivatives as highly potent agonists for G protein-coupled bile acid receptor. Bioorg Chem 120:105588
Salminen S et al (1998) Functional food science and gastrointestinal physiology and function. Br J Nutr 80(S1):S147–S171
Chan OH, Stewart BH (1996) Physicochemical and drug-delivery considerations for oral drug bioavailability. Drug Discov Today 1(11):461–473
Jeon OC et al (2013) Oral delivery of ionic complex of ceftriaxone with bile acid derivative in non-human primates. Pharm Res 30(4):959–967
Lillienau J, Schteingart CD, Hofmann AF (1992) Physicochemical and physiological properties of cholylsarcosine. A potential replacement detergent for bile acid deficiency states in the small intestine. J Clin Invest 89(2):420–431
Michael S et al (2000) Improvement of intestinal peptide absorption by a synthetic bile acid derivative, cholylsarcosine. Eur J Pharm Sci 10(2):133–140
Yang L, Zhang H, Mikov M, Tucker IG (2009) Physicochemical and biological characterization of monoketocholic acid, a novel permeability enhancer. Mol Pharm 6(2):448–456
Chen G et al (2012) Effect of ketocholate derivatives on methotrexate uptake in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Int J Pharm 433(1–2):89–93
Chen G, Fawcett JP, Mikov M, Tucker IG (2009) Monoketocholate can decrease transcellular permeation of methotrexate across Caco-2 cell monolayers and reduce its intestinal absorption in rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 61(7):953–959
Leuenberger M et al (2021) Characterization of novel fluorescent bile salt derivatives for studying human bile salt and organic anion transporters. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 377(3):346–357
Schneider S et al (1991) Fluorescent derivatives of bile salts. I. Synthesis and properties of NBD-amino derivatives of bile salts. J Lipid Res 32(11):1755–1767
Schramm U et al (1991) Fluorescent derivatives of bile salts. II. Suitability of NBD-amino derivatives of bile salts for the study of biological transport. J Lipid Res 32(11):1769–1779
Lalić-Popović M et al (2013) Deoxycholic acid as a modifier of the permeation of gliclazide through the blood brain barrier of a rat. J Diabetes Res
Greenwood J et al (1991) The effect of bile salts on the permeability and ultrastructure of the perfused, energy-depleted, rat blood-brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11(4):644–654
Watanabe A, Fujiwara M, Tominaga S, Nagashima H (1987) Bile acid and ammonia-induced brain edema in rats. Hiroshima J Med Sci 36(2):257–259
Jain S et al (2019) Mechanistic insights into high permeation vesicle-mediated synergistic enhancement of transdermal drug permeation. Nanomedicine 14(16):2227–2241
Khafagy E-S, Almutairy BK, Abu Lila AS (2023) Tailoring of novel bile salt stabilized vesicles for enhanced transdermal delivery of simvastatin: a new therapeutic approach against inflammation. Polymers 15(3):677
Lohan S et al (2021) QbD-steered development of mixed nanomicelles of galantamine: Demonstration of enhanced brain uptake, prolonged systemic retention and improved biopharmaceutical attributes. Int J Pharm 600:120482
Fetih G, Ibrahim M, Amin M (2011) Design and characterization of transdermal films containing ketorolac tromethamine. Int J PharmTech Res 3(1):449–458
Alvarez-Figueroa MJ, Muggli-Galaz C, González PM (2019) Effect of the aggregation state of bile salts on their transdermal absorption enhancing properties. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 54:101333
Salem HF et al (2022) Evaluation of metformin hydrochloride tailoring bilosomes as an effective transdermal nanocarrier. Int J Nanomedicine 1185–1201
Ahmed S, Kassem MA and Sayed S (2020) Bilosomes as promising nanovesicular carriers for improved transdermal delivery: construction, in vitro optimization, ex vivo permeation and in vivo evaluation. Int J Nanomedicine 9783–9798
Sasaki H et al (1995) Ocular permeability of FITC-dextran with absorption promoter for ocular delivery of peptide drug. J Drug Target 3(2):129–135
Hayakawa E et al (1992) Conjunctival penetration of insulin and peptide drugs in the albino rabbit. Pharm Res 9(6):769–775
Dai Y et al (2013) Liposomes containing bile salts as novel ocular delivery systems for tacrolimus (FK506): in vitro characterization and improved corneal permeation. Int J Nanomedicine 8:1921–1933
Dalpiaz A et al (2019) Bile salt-coating modulates the macrophage uptake of nanocores constituted by a zidovudine prodrug and enhances its nose-to-brain delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 144:91–100
Johansson F et al (2002) Mechanisms for absorption enhancement of inhaled insulin by sodium taurocholate. Eur J Pharm Sci 17(1–2):63–71
Miyake M et al (2021) Spermine with sodium taurocholate enhances pulmonary absorption of macromolecules in rats. J Pharm Sci 110(10):3464–3470
Natalini PM et al (2019) The influence of surfactant on the properties of albendazole-bile salts particles designed for lung delivery. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 53:101162
Pilcer G, Amighi K (2010) Formulation strategy and use of excipients in pulmonary drug delivery. Int J Pharm 392(1–2):1–19
Sørli JB et al (2018) Bile salt enhancers for inhalation: correlation between in vitro and in vivo lung effects. Int J Pharm 550(1–2):114–122
Yamamoto A et al (1992) A mechanistic study on enhancement of rectal permeability to insulin in the albino rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263(1):25–31
Dolai J, Mandal K, Jana NR (2021) Nanoparticle size effects in biomedical applications. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4(7):6471–6496
Heiligtag FJ, Niederberger M (2013) The fascinating world of nanoparticle research. Mater Today 16(7–8):262–271
Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem 12(7):908–931
Miyajima K, Yokoi M, Komatsu H, Nakagaki M (1986) Interaction of β-cyclodextrin with bile salts in aqueous solutions. Chem Pharm Bull 34(3):1395–1398
Olesen NE, Westh P, Holm R (2016) Displacement of drugs from cyclodextrin complexes by bile salts: a suggestion of an intestinal drug-solubilizing capacity from an in vitro model. J Pharm Sci 105(9):2640–2647
Camilleri M (2022) Bile acid detergency:permeability, inflammation, and effects of sulfation. Am J Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol 322(5):480–488
Zhao D, Hirst BH (1990) Bile salt-induced increases in duodenal brush-border membrane proton permeability, fluidity, and fragility. Dig Dis Sci 35:589–595
Wu S et al (2019) A delivery system for oral administration of proteins/peptides through bile acid transport channels. J Pharm Sci 108(6):2143–2152
Yang G et al (2019) Formulation design, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of nanostructured lipid carriers containing a bile salt for oral delivery of gypenosides. Int J Nanomedicine 14:2267–2280
Kim KS, Suzuki K, Cho H, Bae YH (2020) Selected factors affecting oral bioavailability of nanoparticles surface-conjugated with glycocholic acid via intestinal lymphatic pathway. Mol Pharm 17(11):4346–4353
Singh I, Swami R, Khan W, Sistla R (2014) Lymphatic system: a prospective area for advanced targeting of particulate drug carriers. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 11(2):211–229
Mutlu-Agardan NB, Han S (2021) In vitro and in vivo evaluations on nanoparticle and phospholipid hybrid nanoparticles with absorption enhancers for oral insulin delivery. Pharm Dev Technol 26(2):157–166
Bao X et al (2023) Intestinal epithelium penetration of liraglutide via cholic acid pre-complexation and zein/rhamnolipids nanocomposite delivery. J Nanobiotechnology 21(1):16
Bao X, Qian K, Yao P (2021) Insulin-and cholic acid-loaded zein/casein–dextran nanoparticles enhance the oral absorption and hypoglycemic effect of insulin. J Mater Chem B 9(31):6234–6245
Jeong JH et al (2019) Protective effect of cholic acid-coated poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) nanoparticles loaded with erythropoietin on experimental stroke. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 19(10):6524–6533
Lu X et al (2021) Redox-responsive prodrug for improving oral bioavailability of paclitaxel through bile acid transporter-mediated pathway. Int J Pharm 600:120496
Wang L et al (2022) Enhanced oral absorption and liver distribution of polymeric nanoparticles through traveling the enterohepatic circulation pathways of bile acid. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14(37):41712–41725
Yan C et al (2019) 5β-cholanic acid/glycol chitosan self-assembled nanoparticles (5β-CHA/GC-NPs) for enhancing the absorption of FDs and insulin by rat intestinal membranes. AAPS PharmSciTech 20:1–8
Yang S et al (2023) TPGS and Doca dual-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers enhance the efficient delivery and in vivo absorption of Coenzyme Q10. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 81:104243
Deng F, Bae YH (2022) Lipid raft-mediated and upregulated coordination pathways assist transport of glycocholic acid-modified nanoparticle in a human breast cancer cell line of SK-BR-3. Int J Pharm 617:121589
Cunningham AJ, Zhu X (2016) Polymers made of bile acids: from soft to hard biomaterials. Can J Chem 94(8):659–666
Raei H, Jahanshahi M, Morad H (2022) Three-layer sandwich-like drug-loaded nanofibers of insulin, titanium oxide nanotubes and nitroglycerin as a promising wound healing candidate. Mater Chem Phys 292:126767
Altinkok C, Karabulut HF, Tasdelen MA, Acik G (2020) Bile acid bearing poly (vinyl chloride) nanofibers by combination of CuAAC click chemistry and electrospinning process. Mater Today Commun 25:101425
Hadinejad F, Jahanshahi M, Morad H (2021) Microwave-assisted and ultrasonic phyto-synthesis of copper nanoparticles: a comparison study. Nano Biomedicine Eng 13(1):6–19
Morad H et al (2021) Formulation, optimization and evaluation of nanofiber based fast dissolving drug delivery system of colchicine for pediatrics. Int J Pediatr 9(3):13213–13224
Wenseleers W et al (2004) Efficient isolation and solubilization of pristine single-walled nanotubes in bile salt micelles. Adv Func Mater 14(11):1105–1112
Palekar-Shanbhag P, Lande S, Chandra R, Rane D (2020) Bilosomes: superior vesicular carriers. Curr Drug Therapy 15(4):312–320
Uddin MN, Allon A, Roni MA, Kouzi S (2019) Overview and future potential of fast dissolving buccal films as drug delivery system for vaccines. J Pharm Pharm Sci 22:388–406
Soliman MO et al (2023) Lactoferrin decorated bilosomes for the oral delivery of quercetin in type 2 diabetes: in vitro and in vivo appraisal. Int J Pharm 647:123551
Liu C, Guo Y, Cheng Y, Qian H (2023) Torularhodin-Loaded bilosomes ameliorate lipid accumulation and amino acid metabolism in hypercholesterolemic mice. J Agric Food Chem 71(7):3250–3260
Youness RA et al (2023) Oral delivery of psoralidin by mucoadhesive surface-modified bilosomes showed boosted apoptotic and necrotic effects against breast and lung cancer cells. Polymers 15(6):1464
Salem HF et al (2023) Budesonide-loaded bilosomes as a targeted delivery therapeutic approach against acute lung injury in rats. J Pharm Sci 112(3):760–770
Chacko IA, Ghate VM, Dsouza L, Lewis SA (2020) Lipid vesicles: a versatile drug delivery platform for dermal and transdermal applications. Colloids Surf, B 195:111262
Abdel-moneum R and Abdel-Rashid RS (2022) Bile salt stabilized nanovesicles as a promising drug delivery technology: a general overview and future perspectives. J Drug Deliv SciTechnol 104057
Gupta DK et al (2022) Bilosomes: a novel platform for drug delivery. Elsevier, Systems of Nanovesicular Drug Delivery, pp 293–309
Mondal D, Mandal RP, De S (2022) Addressing the superior drug delivery performance of bilosomes─ a microscopy and fluorescence study. ACS Appl Bio Mater 5(8):3896–3911
AbuBakr A-H et al (2023) Therapeutic potential of cationic bilosomes in the treatment of carrageenan-induced rat arthritis via fluticasone propionate gel. Int J Pharm 635:122776
Elkomy MH et al (2022) Surface-modified bilosomes nanogel bearing a natural plant alkaloid for safe management of rheumatoid arthritis inflammation. Pharmaceutics 14(3):563
Sultan AA, Saad GA, El Maghraby GM (2023) Permeation enhancers loaded bilosomes for improved intestinal absorption and cytotoxic activity of doxorubicin. Int J Pharm 630:122427
Hegazy H, Amin MM, Fayad W, Zakaria MY (2022) TPGS surface modified bilosomes as boosting cytotoxic oral delivery systems of curcumin against doxorubicin resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int J Pharm 619:121717
Balakrishnan A, Polli JE (2006) Apical sodium dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT, SLC10A2): a potential prodrug target. Mol Pharm 3(3):223–230
Dawson PA, Karpen SJ (2015) Intestinal transport and metabolism of bile acids. J Lipid Res 56(6):1085–1099
Waglewska E, Pucek-Kaczmarek A and Bazylińska U (2020) Novel surface-modified bilosomes as functional and biocompatible nanocarriers of hybrid compounds. Nanomaterials (Basel) 10(12)
Guan P, Lu Y, Qi J, Wu W (2016) Readily restoring freeze-dried probilosomes as potential nanocarriers for enhancing oral delivery of cyclosporine A. Colloids Surf, B 144:143–151
Haritha P and Lakshmi P (2020) Probilosomes: a novel bile salt containing nanocarrier for enhancing oral bioavailability. Int J Pharm Investig 10(1)
Hao F et al (2016) Improvement of oral availability of ginseng fruit saponins by a proliposome delivery system containing sodium deoxycholate. Saudi J Biol Sci 23(1):S113–S125
Pigliacelli C et al (2023) Interaction of polymers with bile salts–impact on solubilisation and absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs. Colloids Surf, B 222:113044
Liu C, Guo Y, Cheng Y, Qian H (2022) Bilosomes: a controlled delivery system for the sustained release of torularhodin during digestion in the small intestine both in vitro and in vivo. Colloids Surf, A 654:130055
Mohsen AM, Salama A, Kassem AA (2020) Development of acetazolamide loaded bilosomes for improved ocular delivery: preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 59:101910
Elnaggar YS, Omran S, Hazzah HA, Abdallah OY (2019) Anionic versus cationic bilosomes as oral nanocarriers for enhanced delivery of the hydrophilic drug risedronate. Int J Pharm 564:410–425
Salama A, El-Hashemy HA, Darwish AB (2022) Formulation and optimization of lornoxicam-loaded bilosomes using 23 full factorial design for the management of osteoarthritis in rats: modulation of MAPK/Erk1 signaling pathway. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 69:103175
El-Nabarawi MA, Shamma RN, Farouk F, Nasralla SM (2020) Bilosomes as a novel carrier for the cutaneous delivery for dapsone as a potential treatment of acne: preparation, characterization and in vivo skin deposition assay. J Liposome Res 30(1):1–11
Abbas H, Gad HA, Khattab MA, Mansour M (2021) The tragedy of Alzheimer’s disease: towards better management via resveratrol-loaded oral bilosomes. Pharmaceutics 13(10):1635
Waglewska E, Pucek-Kaczmarek A, Bazylińska U (2022) Self-assembled bilosomes with stimuli-responsive properties as bioinspired dual-tunable nanoplatform for pH/temperature-triggered release of hybrid cargo. Colloids Surf, B 215:112524
Durník R, Šindlerová L, Babica P, Jurček O (2022) Bile acids transporters of enterohepatic circulation for targeted drug delivery. Molecules 27(9):2961
Mishra R, Mishra S (2020) Updates in bile acid-bioactive molecule conjugates and their applications. Steroids 159:108639
Jha SK et al (2020) Enhanced antitumor efficacy of bile acid-lipid complex-anchored docetaxel nanoemulsion via oral metronomic scheduling. J Control Release 328:368–394
Lei K et al (2021) Research progress in the application of bile acid-drug conjugates: a “trojan horse″ strategy. Steroids 173:108879
Xiao L et al (2019) Transporter-targeted bile acid-camptothecin conjugate for improved oral absorption. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 67(10):1082–1087
Zou X et al (2021) Study on the structure-activity relationship of dihydroartemisinin derivatives: discovery, synthesis, and biological evaluation of dihydroartemisinin-bile acid conjugates as potential anticancer agents. Eur J Med Chem 225:113754
Sreekanth V, Bajaj A (2019) Recent advances in engineering of lipid drug conjugates for cancer therapy. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 5(9):4148–4166
Sreekanth V et al (2021) Self-assembled supramolecular nanomicelles from a bile acid–docetaxel conjugate are highly tolerable with improved therapeutic efficacy. Biomater Sci 9(16):5626–5639
Sreekanth V et al (2021) Bile acid tethered docetaxel-based nanomicelles mitigate tumor progression through epigenetic changes. Angew Chem Int Ed 60(10):5394–5399
Chen D-q et al (2011) Novel liver-specific cholic acid-cytarabine conjugates with potent antitumor activities: synthesis and biological characterization. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32(5):664–672
Zhang D et al (2016) Transporter-targeted cholic acid-cytarabine conjugates for improved oral absorption. Int J Pharm 511(1):161–169
Gao Y et al (2021) Zwitterion-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhancing oral delivery of protein drugs by overcoming multiple gastrointestinal barriers. J Colloid Interface Sci 582:364–375
Lin C et al (2021) Recent progress in bile acid-based antimicrobials. Bioconjug Chem 32(3):395–410
Thareja A et al (2021) Penetration enhancers for topical drug delivery to the ocular posterior segment—a systematic review. Pharmaceutics 13(2):276
Kim D et al (2019) A novel transdermal delivery system based on a bile acid-conjugated nanoparticle model for cosmetics. Asian J Beauty Cosmetology 17(1):81–91
Kumar S et al (2021) Nonimmunogenic hydrogel-mediated delivery of antibiotics outperforms clinically used formulations in mitigating wound infections. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(37):44041–44053
Wang SY et al (2020) Development of microRNA-21 mimic nanocarriers for the treatment of cutaneous wounds. Theranostics 10(7):3240
Mann JF et al (2004) Optimisation of a lipid based oral delivery system containing A/Panama influenza haemagglutinin. Vaccine 22(19):2425–2429
Mann JF et al (2006) Oral delivery of tetanus toxoid using vesicles containing bile salts (bilosomes) induces significant systemic and mucosal immunity. Methods 38(2):90–95
Shukla A et al (2008) Oral immunization against hepatitis B using bile salt stabilized vesicles (bilosomes). J Pharm Pharm Sci 11(1):59–66
Langley KE, Bitter GA, Sachdev RK and Fieschko JC (1993). A hepatitis b vaccine formulation incorporating a bile acid salt, Google Patents
Sachdev GABCFELK (1995) Hepatitis B vaccine with bile salt adjuvant. Australia. AU657168B2
Azuar A et al (2019) Cholic acid-based delivery system for vaccine candidates against group A streptococcus. ACS Med Chem Lett 10(9):1253–1259
FDA U GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database
Samareh Fekri M et al (2013) Pulmonary complications of gastric fluid and bile salts aspiration, an experimental study in rat. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(6):790–796
Aldhahrani A, Verdon B, Ward C and Pearson J (2017) Effects of bile acids on human airway epithelial cells: implications for aerodigestive diseases. ERJ Open Res 3(1)
Kirby J, Heaton K, Burton J (1974) Pruritic effect of bile salts. Br Med J 4(5946):693–695
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chakravarthy, P.S.A., Popli, P., Challa, R.R. et al. Bile salts: unlocking the potential as bio-surfactant for enhanced drug absorption. J Nanopart Res 26, 76 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-024-05985-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-024-05985-6