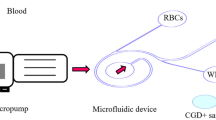
Abstract
Breast cancer cell-derived exosomes have high potential as biomarkers for continuous biopsies and longitudinal monitoring in breast cancer. However, it is extremely difficult to separate exosomes with high recovery and high purity from complex media, such as urine, plasma, saliva and cell culture supernatants. Here, we designed a flexible and simple microfluidic chip for exosome separation. The capture zone of the chip is a three-dimensional structure of interlaced cylinders doped with nickel powder. Exosomes were separated from cell culture supernatant by the immunomagnetic separation method in continuous flow mode and were detected by fluorescence imaging with high sensitivity. The chip achieved a high exosome recovery rate (> 74%) and purity (> 67%) at an injection rate of 3.6 mL/h. Thus, this chip was demonstrated to be a cutting-edge platform for the separation and detection of exosomes. It could also be applied to separate and detect other types of exosomes, microbubbles and cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Fuchs, H. E., & Jemal, A. (2022). Cancer statistics, 2022. CA:A Cancer Journal for Clinician, 72, 7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21708.
Paskeh, M. D. A., Entezari, M., Mirzaei, S., Zabolian, A., Saleki, H., Naghdi, M. J., Sabet, S., Khoshbakht, M. A., Hashemi, M., Hushmandi, K., Sethi, G., Zarrabi, A., Kumar, A. P., Tan, S. C., Papadakis, M., Alexiou, A., Islam, M. A., Mostafavi, E., & Ashrafizadeh, M. (2022). Emerging role of exosomes in cancer progression and tumor microenvironment remodeling. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 15, 83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-022-01305-4.
Zhang, X., Yuan, X., Shi, H., Wu, L., Qian, H., & Xu, W. (2015). Exosomes in cancer: small particle, big player. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 8, 83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-015-0181-x.
Kalluri, R., & LeBleu, V. S. (2020). The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science, 367, eaau6977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977.
Kumar, D. N., Chaudhuri, A., Aqil, F., Dehari, D., Munagala, R., Singh, S., Gupta, R. C., & Agrawal, A. K. (2022). Exosomes as Emerging Drug Delivery and Diagnostic modality for breast Cancer: recent advances in isolation and application. Cancers (Basel), 14, 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061435.
Hu, C., Jiang, W., Lv, M., Fan, S., Lu, Y., Wu, Q., & Pi, J. (2022). Potentiality of Exosomal Proteins as Novel Cancer biomarkers for Liquid Biopsy. Frontiers in Immunology, 13, 792046. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.792046.
Shao, Y., Shen, Y., Chen, T., Xu, F., Chen, X., & Zheng, S. (2016). The functions and clinical applications of tumor⁃derived exosomes. Oncotarget, 7, 60736–60751. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11177.
Lin, S., Yu, Z., Chen, D., Wang, Z., Miao, J., Li, Q., Zhang, D., Song, J., & Cui, D. (2020). Progress in Microfluidics-Based exosome separation and Detection Technologies for diagnostic applications. Small (Weinheim An Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 16, e1903916. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201903916.
Li, P., Kaslan, M., Lee, S. H., Yao, J., & Gao, Z. (2017). Progress in Exosome isolation techniques. Theranostics, 7, 789–804. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.18133.
Jiang, Z., Liu, G., & Li, J. (2020). Recent progress on the isolation and detection methods of Exosomes. Chemistry-An Asian Journal, 15, 3973–3982. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.202000873.
Lane, R. E., Korbie, D., Trau, M., & Hill, M. M. (2019). Optimizing size exclusion chromatography for Extracellular Vesicle Enrichment and Proteomic Analysis from clinically relevant samples. Proteomics, 19, e1800156. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201800156.
Abramowicz, A., Widlak, P., & Pietrowska, M. (2016). Proteomic analysis of exosomal cargo: the challenge of high purity vesicle isolation. Molecular BioSystems, 12, 1407–1419. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mb00082g.
Hassanpour, Tamrin, S., Sanati, Nezhad, A., & Sen, A. (2021). Label-free isolation of Exosomes using Microfluidic Technologies. Acs Nano, 15, 17047–17079. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c03469.
Woo, H. K., Sunkara, V., Park, J., Kim, T. H., Han, J. R., Kim, C. J., Choi, H. I., Kim, Y. K., & Cho, Y. K. (2017). Exodisc for Rapid, Size-Selective, and efficient isolation and analysis of Nanoscale Extracellular vesicles from Biological samples. Acs Nano, 11, 1360–1370. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b06131.
Lee, K., Shao, H., Weissleder, R., & Lee, H. (2015). Acoustic purification of extracellular microvesicles. Acs Nano, 9, 2321–2327. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn506538f.
Zhao, Z., Yang, Y., Zeng, Y., & He, M. (2016). A microfluidic ExoSearch chip for multiplexed exosome detection towards blood-based ovarian cancer diagnosis. Lab on a Chip, 16, 489–496. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5lc01117e.
Moura, S. L., Pallarès-Rusiñol, A., Sappia, L., Martí, M., & Pividori, M. I. (2022). The activity of alkaline phosphatase in breast cancer exosomes simplifies the biosensing design. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 198, 113826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113826.
Théry, C., Witwer, K. W., Aikawa, E., Alcaraz, M. J., Anderson, J. D., Andriantsitohaina, R., Antoniou, A., Arab, T., Archer, F., Atkin-Smith, G. K., et al. (2018). Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 7, 1535750. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750.
Yu, Z., Lin, S., Xia, F., Liu, Y., Zhang, D., Wang, F., Wang, Y., Li, Q., Niu, J., Cao, C., Cui, D., Sheng, N., Ren, J., Wang, Z., & Chen, D. (2021). ExoSD chips for high-purity immunomagnetic separation and high-sensitivity detection of gastric cancer cell-derived exosomes. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 194, 113594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113594.
Malic, L., Zhang, X., Brassard, D., Clime, L., Daoud, J., Luebbert, C., Barrere, V., Boutin, A., Bidawid, S., Farber, J., Corneau, N., & Veres, T. (2015). Polymer-based microfluidic chip for rapid and efficient immunomagnetic capture and release of Listeria monocytogenes. Lab on a Chip, 15, 3994–4007. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5lc00852b.
Liu, C., Guo, J., Tian, F., Yang, N., Yan, F., Ding, Y., Wei, J., Hu, G., Nie, G., & Sun, J. (2017). Field-free isolation of Exosomes from Extracellular vesicles by Microfluidic Viscoelastic flows. Acs Nano, 11, 6968–6976. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b02277.
Wunsch, B. H., Smith, J. T., Gifford, S. M., Wang, C., Brink, M., Bruce, R. L., Austin, R. H., Stolovitzky, G., & Astier, Y. (2016). Nanoscale lateral displacement arrays for the separation of exosomes and colloids down to 20 nm. Nature Nanotechnology, 11, 936–940. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2016.134.
Momen-Heravi, F., Balaj, L., Alian, S., Mantel, P. Y., Halleck, A. E., Trachtenberg, A. J., Soria, C. E., Oquin, S., Bonebreak, C. M., Saracoglu, E., Skog, J., & Kuo, W. P. (2013). Current methods for the isolation of extracellular vesicles.Biological Chemistry, 394, 1253–1262. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2013-0141.
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (No. cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0367) and the Chongqing Medical Scientific Research Project (Joint Project of Chongqing Health Commission and Science and Technology Bureau, No. 2022MSXM136).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huiying Fang and Mei Liu contributed equally to this work. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Huiying Fang and Mei Liu. The manuscript was written by Wei Jiang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Huiying Fang and Mei Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, H., Liu, M. & Jiang, W. Nickel-Doped Microfluidic Chip for Rapid and Efficient Immunomagnetic Separation and Detection of Breast Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 3109–3121 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04272-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04272-1