Abstract
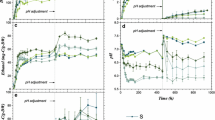
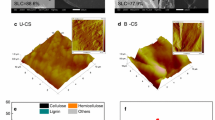
Lignocellulose-decaying fungal bioplatforms available are not commercially accessible and are limited to short-term use. In this study, those limitations were overcome by developing a platform using water-soaked rice straw (RS) biodegraded by irradiation-based fungal pretreatment (IBFP). This eco-friendly system increased the ability of RS to biodegrade and ferment without the generation of inhibitory compounds. When processed RS (i.e., with a water-soaking ratio of 81 % and irradiation dose of 80 kGy at 1 MeV and 0.12 mA) was pretreated with Dichomitus squalens for 9 days, the sugar yield was 58.5 % of the theoretical maximum. This sugar yield was comparable to that obtained with unirradiated RS for 15 days, which was 57.9 %. Furthermore, the ethanol concentration of 9.7 g L−1 provided a yield of 58.1 %; the theoretical maximum and productivity at 0.40 g L−1 h−1 were determined after simultaneous saccharification and fermentation for 24 h. In addition, microscopic images revealed that IBFP induced predominant ultrastructural modifications to the surface of cell wall fibers. The peroxidative profiles for different biosystems were analyzed in order to understand substrate-specific biocascades based on the differences in biomass components. The activation level of core lignocellulolysis-related factors was analogous under the optimized conditions of each system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanderson, K. (2011). Lignocellulose: a chewy problem. Nature, 474, S12–S14.
Jönsson, L. J., Alriksson, B., & Nilvebrant, N. O. (2013). Bioconversion of lignocellulose: inhibitors and detoxification. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 6, 16.
Saritha, M., Arora, A., & Lata. (2012). Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic substrates for enhanced delignification and enzymatic digestibility. Indian Journal of Microbiology, 52, 122–130.
Wan, C., & Li, Y. (2012). Fungal pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnology Advances, 30, 1447–1457.
Bak, J. S., Kim, M. D., Choi, I. G., & Kim, K. H. (2010). Biological pretreatment of rice straw by fermenting with Dichomitus squalens. New Biotechnology, 27, 424–434.
Bak, J. S., Ko, J. K., Choi, I. G., Park, Y. C., Seo, J. H., & Kim, K. H. (2009). Fungal pretreatment of lignocellulose by Phanerochaete chrysosporium to produce ethanol from rice straw. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 104, 471–482.
Bak, J. S. (2014). Electron beam irradiation enhances the digestibility and fermentation yield of water-soaked lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnology Reports, 4, 30–33.
Bak, J. S., Ko, J. K., Han, Y. H., Lee, B. C., Choi, I. G., & Kim, K. H. (2009). Improved enzymatic hydrolysis yield of rice straw using electron beam irradiation pretreatment. Bioresource Technology, 100, 1285–1290.
Perie, F., & Gold, M. (1991). Manganese regulation of manganese peroxidase expression and lignin degradation by the white rot fungus Dichomitus squalens. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 57, 2240–2245.
Teunissen, P. J. M., & Field, J. A. (1998). 2-Chloro-1,4-dimethoxybenzene as a novel catalytic cofactor for oxidation of anisyl alcohol by lignin peroxidase. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64, 830–835.
Bourbonnais, R., & Paice, M. G. (1988). Veratryl alcohol oxidases from the lignin-degrading basidiomycete Pleurotus sajor-caju. Biochemical Journal, 255, 445–450.
Muheim, A., Waldner, R., Leisola, M. S. A., & Fiechter, A. (1990). An extracellular aryl-alcohol oxidase from the white-rot fungus Bjerkendera adusta. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 12, 204–209.
Kersten, P. J., & Kirk, T. K. (1987). Involvement of a new enzyme, glyoxal oxidase, in extracellular H2O2 production by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Journal of Bacteriology, 169, 2195–2201.
Orth, A. B., Denny, M., & Tien, M. (1991). Overproduction of lignin-degrading enzymes by an isolate of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 57, 2591–2596.
Bao, W., Lymar, E., & Renganathan, V. (1994). Optimization of cellobiose dehydrogenase and β-glucosidase production by cellulose-degrading cultures of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 42, 642–646.
Bak, J. S. (2014). Complementary substrate-selectivity of metabolic adaptive convergence in the lignocellulolytic performance by Dichomitus squalens. Microbial Biotechnology, 7, 434–445.
Bak, J. S. (2015). Lignocellulose depolymerization occurs via an environmentally adapted metabolic cascades in the wood-rotting basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Microbiologyopen, 4, 151–166.
Znameroski, E. A., Coradetti, S. T., Roche, C. M., Tsai, J. C., Iavarone, A. T., Cate, J. H., & Glass, N. L. (2012). Induction of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes in Neurospora crassa by cellodextrins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109, 6012–6017.
Merino, S., & Cherry, J. (2007). Progress and challenges in enzyme development for biomass utilization. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 108, 95–120.
Kim, T. H., Taylor, F., & Hicks, K. B. (2008). Bioethanol production from barley hull using SAA (soaking in aqueous ammonia) pretreatment. Bioresource Technology, 99, 5694–5702.
Noureddini, H., & Byun, J. (2010). Dilute-acid pretreatment of distillers’ grains and corn fiber. Bioresource Technology, 101, 1060–1067.
Sharma, R., Palled, V., Sharma-Shivappa, R. R., & Osborne, J. (2012). Potential of potassium hydroxide pretreatment of switchgrass for fermentable sugar production. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 169, 761–772.
Zhao, Y., Wang, Y., Zhu, J. Y., Ragauskas, A., & Deng, Y. (2008). Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of spruce by alkaline pretreatment at low temperature. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 99, 1320–1328.
Kim, T. H., Lee, Y. Y., Sunwoo, C., & Kim, J. S. (2006). Pretreatment of corn stover by low-liquid ammonia recycle percolation process. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 133, 41–57.
Shi, J., Sharma-Shivappa, R. R., Chinn, M., & Howell, N. (2009). Effect of microbial pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of cotton stalks for ethanol production. Biomass & Bioenergy, 33, 88–96.
Shrestha, P., Rasmussen, M., Khanal, S. K., Pometto, A. L., 3rd, & van Leeuwen, J. H. (2008). Solid-substrate fermentation of corn fiber by Phanerochaete chrysosporium and subsequent fermentation of hydrolysate into ethanol. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56, 3918–3924.
Dias, A. A., Freitas, G. S., Marque, G. S. M., Sampaio, A., Fraga, I. S., Rodrigue, M. A. M., Evtuguin, D. V., & Bezerra, R. M. F. (2010). Enzymatic saccharification of biologically pre-treated wheat straw with white-rot fungi. Bioresource Technology, 101, 6045–6050.
Mesa, L., González, E., Cara, C., González, M., Castro, E., & Mussatto, S. I. (2011). The effect of organosolv pretreatment variables on enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168, 1157–1162.
Wan, C., & Li, Y. (2011). Effectiveness of microbial pretreatment by Ceriporiopsis subvermispora on different biomass feedstocks. Bioresource Technology, 102, 7507–7512.
Cullen, D., & Kersten, P. J. (2004). Enzymology and molecular biology of lignin degradtion. In R. Brambl & G. A. Marzluf (Eds.), The mycota III: biochemistry and molecular biology. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Fernandez-Fueyo, E., Ruiz-Dueñas, F. J., Ferreira, P., Ferreira, P., Floudas, D., Hibbett, D. S., Canessa, P., Larrondo, L. F., James, T. Y., Seelenfreund, D., Lobos, S., Polanco, R., Tello, M., Honda, Y., Watanabe, T., Watanabe, T., Ryu, J. S., Kubicek, C. P., Schmoll, M., Gaskell, J., Hammel, K. E., St John, F. J., Vanden Wymelenberg, A., Sabat, G., Splinter BonDurant, S., Syed, K., Yadav, J. S., Doddapaneni, H., Subramanian, V., Lavín, J. L., Oguiza, J. A., Perez, G., Pisabarro, A. G., Ramirez, L., Santoyo, F., Master, E., Coutinho, P. M., Henrissat, B., Lombard, V., Magnuson, J. K., Kües, U., Hori, C., Igarashi, K., Samejima, M., Held, B. W., Barry, K. W., LaButti, K. M., Lapidus, A., Lindquist, E. A., Lucas, S. M., Riley, R., Salamov, A. A., Hoffmeister, D., Schwenk, D., Hadar, Y., Yarden, O., de Vries, R. P., Wiebenga, A., Stenlid, J., Eastwood, D., Grigoriev, I. V., Berka, R. M., Blanchette, R. A., Kersten, P., Martinez, A. T., Vicuna, R., & Cullen, D. (2012). Comparative genomics of Ceriporiopsis subvermispora and Phanerochaete chrysosporium provide insight into selective ligninolysis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109, 5458–5463.
Vanden Wymelenberg, A., Gaskell, J., Mozuch, M., Sabat, G., Ralph, J., Skyba, O., Mansfield, S. D., Blanchette, R. A., Martinez, D., Grigoriev, I., Kersten, P. J., & Cullen, D. (2010). Comparative transcriptome and secretome analysis of wood decay fungi Postia placenta and Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 3599–3610.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bak, J.S. Bioprocess-Technological Potential of Irradiation-Based Fungal Pretreatment Platform Relevant to Lignocellulolytic Biocascade. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177, 1654–1664 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1843-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1843-4