Abstract
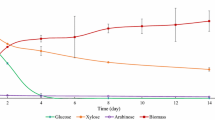
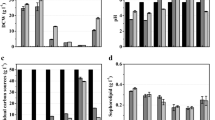
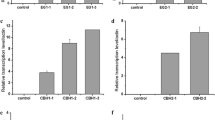
Although extensive research has been conducted on producing sophorolipids using Candida (Starmerella) bombicola from pure sugars and various oil sources, production of this biosurfactant has not been evaluated when cells are cultivated in lignocellulosic hydrolysates. Here, we report for the first time that C. bombicola is capable of producing sophorolipids on hydrolysates derived from sweet sorghum bagasse and corn fiber. Without oil supplementation, a sophorolipid concentration of 3.6 and 1.0 g/L was detected from cultures with bagasse and corn fiber hydrolysates, respectively. With the addition of soybean oil at 100 g/L, the yield of sophorolipids from these two hydrolysates in the same order was 84.6 and 15.6 g/L. Surprisingly, C. bombicola consumed all monomeric sugars and nonsugar compounds in the hydrolysates, and cultures with bagasse hydrolysates had higher yield of sophorolipids than those from a standard medium which contained pure glucose at the same concentration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashby, R. D., & Solaiman, D. K. (2010). The influence of increasing media methanol concentration on sophorolipid biosynthesis from glycerol-based feedstocks. Biotechnology Letters, 32, 1429–1437.
Borzeix, C. F. (1999). Use of sophorolipids comprising diacetyl lactones as agent for stimulating skin fibroblast metabolism. World patent 99/62479.
Casas, J., & García-Ochoa, F. (1999). Sophorolipid production by Candida bombicola: medium composition and culture methods. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 88, 488–494.
Choudhary, R., Umagiliyage, A. L., Liang, Y., Siddaramu, T., Haddock, J., & Markevicius, G. (2012). Microwave pretreatment for enzymatic saccharification of sweet sorghum bagasse. Biomass and Bioenergy, 39, 218–226.
Ciesielska, K., Li, B., Groeneboer, S., Van Bogaert, I., Lin, Y. C., Soetaert, W., Van de Peer, Y., & Devreese, B. (2013). SILAC-based proteome analysis of Starmerella bombicola sophorolipid production. Journal of Proteome Research, 12, 4376–4392.
Ciesielska, K., Van Bogaert, I. N., Chevineau, S., Li, B., Groeneboer, S., Soetaert, W., Van de Peer, Y., & Devreese, B. (2014). Exoproteome analysis of Starmerella bombicola results in the discovery of an esterase required for lactonization of sophorolipids. Journal of Proteomics, 98, 159–174.
Daniel, H.-J., Reuss, M., & Syldatk, C. (1998). Production of sophorolipids in high concentration from deproteinized whey and rapeseed oil in a two stage fed batch process using Candida bombicola ATCC 22214 and Cryptococcus curvatus ATCC 20509. Biotechnology Letters, 20, 1153–1156.
Daverey, A., & Pakshirajan, K. (2010). Kinetics of growth and enhanced sophorolipids production by Candida bombicola using a low-cost fermentative medium. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 2090–2101.
Davila, A.-M., Marchal, R., & Vandecasteele, J.-P. (1992). Kinetics and balance of a fermentation free from product inhibition: sophorose lipid production by Candida bombicola. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 38, 6–11.
Davila, A.-M., Marchal, R., & Vandecasteele, J.-P. (1997). Sophorose lipid fermentation with differentiated substrate supply for growth and production phases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 47, 496–501.
Davila, A. M., Marchal, R., Monin, N., & Vandecasteele, J. P. (1993). Identification and determination of individual sophorolipids in fermentation products by gradient elution high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light-scattering detection. Journal of Chromatography, 648, 139–149.
Gao, R., Falkeborg, M., Xu, X., & Guo, Z. (2013). Production of sophorolipids with enhanced volumetric productivity by means of high cell density fermentation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 1103–1111.
Gupta, R., & Prabhune, A. A. (2012). Structural determination and chemical esterification of the sophorolipids produced by Candida bombicola grown on glucose and α-linolenic acid. Biotechnology Letters, 34, 701–707.
Hillion, G., Marchal, R., Stoltz, C. and Borzeix, F. (1998). Use of a sophorolipid to provide free radical formation inhibiting activity or elastase inhibiting activity. US patent 5756471.
Imura, T., Kawamura, D., Morita, T., Sato, S., Fukuoka, T., Yamagata, Y., Takahashi, M., Wada, K., & Kitamoto, D. (2013). Production of sophorolipids from non-edible jatropha oil by Stamerella bombicola NBRC 10243 and evaluation of their interfacial properties. Journal of Oleo Science, 62, 857–864.
Isoda, H., Kitamoto, D., Shinmoto, H., Matsumura, M., & Nakahara, T. (1997). Microbial extracellular glycolipid induction of differentiation and inhibition of the protein kinase C activity of human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL60. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 61, 609–614.
Kim, Y. B., Yun, H. S., & Kim, E. K. (2009). Enhanced sophorolipid production by feeding-rate-controlled fed-batch culture. Bioresource Technology, 100, 6028–6032.
Kitamoto, D., Isoda, H., & Nakahara, T. (2002). Functions and potential applications of glycolipid biosurfactants—from energy-saving materials to gene delivery carriers. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 94, 187–201.
Klinke, H. B., Thomsen, A., & Ahring, B. K. (2004). Inhibition of ethanol-producing yeast and bacteria by degradation products produced during pre-treatment of biomass. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 66, 10–26.
Li, H., Ma, X. J., Wang, S., & Song, X. (2013). Production of sophorolipids with eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid from Wickerhamiella domercqiae var. sophorolipid using fish oil as a hydrophobic carbon source. Biotechnology Letters, 35, 901–908.
Liang, Y., Jarosz, K., Wardlow, A. T., Zhang, J., & Cui, Y. (2014). Lipid Production by Cryptococcus curvatus on hydrolysates derived from corn fiber and sweet sorghum bagasse following dilute acid pretreatment. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 173, 2086–2098.
Liang, Y., Perez, I., Goetzelmann, K., & Trupia, S. (2014). Microbial lipid production from pretreated and hydrolyzed corn fiber. Biotechnology Progress, 30, 367–375.
Liang, Y., Tang, T., Siddaramu, T., Choudhary, R., & Umagiliyage, A. L. (2012). Lipid production from sweet sorghum bagasse through yeast fermentation. Renewable Energy, 40, 130–136.
Liang, Y., Tang, T., Umagiliyage, A. L., Siddaramu, T., McCarroll, M., & Choudhary, R. (2012). Utilization of sorghum bagasse hydrolysates for producing microbial lipids. Applied Energy, 91, 451–458.
Mager, H., Röthlisberger, R., Wzgner, F. (1987). Use of sophorolse-lipid lactone for the treatment of dandruffs and body odour. European patent 0209783.
Maingault, M. (1999). Utilization of sophorolipids as therapeutically active substances or cosmetic products, in particular for the treatment of the skin. US patent 5981497.
Otto, R. T., Daniel, H. J., Pekin, G., Müller-Decker, K., Fürstenberger, G., Reuss, M., & Syldatk, C. (1999). Production of sophorolipids from whey: II. Product composition, surface active properties, cytotoxicity and stability against hydrolases by enzymatic treatment. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 52, 495–501.
Palmqvist, E., & Hahn-Hägerdal, B. R. (2000). Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. I: inhibition and detoxification. Bioresource Technology, 74, 17–24.
Palmqvist, E., & Hahn-Hägerdal, B. (2000). Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. II: inhibitors and mechanisms of inhibition. Bioresource Technology, 74, 25–33.
Parawira, W., & Tekere, M. (2011). Biotechnological strategies to overcome inhibitors in lignocellulose hydrolysates for ethanol production: review. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 31, 20–31.
Pekin, G., Vardar-Sukan, F., & Kosaric, N. (2005). Production of sophorolipids from Candida bombicola ATCC 22214 using Turkish corn oil and honey. Engineering in Life Sciences, 5, 357–362.
Rau, U., Hammen, S., Heckmann, R., Wray, V., & Lang, S. (2001). Sophorolipids: a source for novel compounds. Industrial Crops and Products, 13, 85–92.
Sluiter, A., Hames, B., Ruiz, R., Scarlata, C., Sluiter, J., Templeton, D. and Crocker, D. (2004). Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. NREL, Golden, CO.
Van Bogaert, I. N. A., Saerens, K., De Muynck, C., Develter, D., Soetaert, W., & Vandamme, E. J. (2007). Microbial production and application of sophorolipids. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 76, 23–34.
Yesuf, J. N., & Liang, Y. (2014). Optimization of sugar release from sweet sorghum bagasse following solvation of cellulose and enzymatic hydrolysis using response surface methodology. Biotechnology Progress, 30, 367–375.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samad, A., Zhang, J., Chen, D. et al. Sophorolipid Production from Biomass Hydrolysates. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 2246–2257 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1425-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1425-x