Abstract
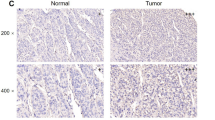
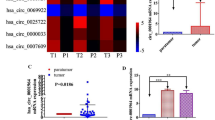
Ser/Thr protein phosphatase 5 (PPP5C) has been reported to participate in tumor progression. However, its functional role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unknown yet. In this study, we firstly evaluated the expression levels of PPP5C in six HCC cell lines by real-time PCR and found that PPP5C was widely expressed in HCC cells. To explore the role of PPP5C in HCC cell growth, lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNA (shRNA) was employed to silence PPP5C expression in HepG2 and Bel-7404 cells. The expression of PPP5C was significantly downregulated in PPP5C knockdown cells. Knockdown of PPP5C markedly suppressed the proliferation and colony formation ability of HCC cells. Moreover, cell cycle analysis showed that PPP5C depletion in HepG2 cells led to G0/G1 phase and G2/M phase arrest. We demonstrate for the first time that PPP5C is essential for growth of HCC cells, which suggests that inhibition of PPP5C by RNAi may be a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rahman, R., Hammoud, G. M., Almashhrawi, A. A., Ahmed, K. T., & Ibdah, J. A. (2013). Primary hepatocellular carcinoma and metabolic syndrome: an update. World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology, 5, 186–194.
Bosch, F. X., Ribes, J., Diaz, M., & Cleries, R. (2004). Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology, 127, S5–S16.
Wang, Z. G., Zhang, G. F., Wu, J. C., & Jia, M. K. (2013). Adjuvant therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current situation and prospect. Drug Discoveries and Therapeutics, 7, 137–143.
Agnello, F., Salvaggio, G., Cabibbo, G., Maida, M., Lagalla, R., Midiri, M., & Brancatelli, G. (2013). Imaging appearance of treated hepatocellular carcinoma. World Journal of Hepatology, 5, 417–424.
Mumby, M. C., & Walter, G. (1993). Protein serine/threonine phosphatases: structure, regulation, and functions in cell growth. Physiological Reviews, 73, 673–699.
Cohen, P. T., Brewis, N. D., Hughes, V., & Mann, D. J. (1990). Protein serine/threonine phosphatases; an expanding family. FEBS Letters, 268, 355–359.
Cohen, P. T. (1997). Novel protein serine/threonine phosphatases: variety is the spice of life. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 22, 245–251.
Zuo, Z., Dean, N. M., & Honkanen, R. E. (1998). Serine/threonine protein phosphatase type 5 acts upstream of p53 to regulate the induction of p21(WAF1/Cip1) and mediate growth arrest. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 12250–12258.
Golden, T., Swingle, M., & Honkanen, R. E. (2008). The role of serine/threonine protein phosphatase type 5 (PP5) in the regulation of stress-induced signaling networks and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Reviews, 27, 169–178.
Swingle, M. R., Honkanen, R. E., & Ciszak, E. M. (2004). Structural basis for the catalytic activity of human serine/threonine protein phosphatase-5. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 33992–33999.
Hinds, T. D., Jr., & Sanchez, E. R. (2008). Protein phosphatase 5. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 40, 2358–2362.
Yang, J., Roe, S. M., Cliff, M. J., Williams, M. A., Ladbury, J. E., Cohen, P. T., & Barford, D. (2005). Molecular basis for TPR domain-mediated regulation of protein phosphatase 5. EMBO Journal, 24, 1–10.
Golden, T., Aragon, I. V., Zhou, G., Cooper, S. R., Dean, N. M., & Honkanen, R. E. (2004). Constitutive over expression of serine/threonine protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) augments estrogen-dependent tumor growth in mice. Cancer Letters, 215, 95–100.
Golden, T., Aragon, I. V., Rutland, B., Tucker, J. A., Shevde, L. A., Samant, R. S., Zhou, G., Amable, L., Skarra, D., & Honkanen, R. E. (2008). Elevated levels of Ser/Thr protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) in human breast cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1782, 259–270.
Urban, G., Golden, T., Aragon, I. V., Cowsert, L., Cooper, S. R., Dean, N. M., & Honkanen, R. E. (2003). Identification of a functional link for the p53 tumor suppressor protein in dexamethasone-induced growth suppression. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 9747–9753.
Urban, G., Golden, T., Aragon, I. V., Scammell, J. G., Dean, N. M., & Honkanen, R. E. (2001). Identification of an estrogen-inducible phosphatase (PP5) that converts MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells into an estrogen-independent phenotype when expressed constitutively. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 27638–27646.
Morita, K., Saitoh, M., Tobiume, K., Matsuura, H., Enomoto, S., Nishitoh, H., & Ichijo, H. (2001). Negative feedback regulation of ASK1 by protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) in response to oxidative stress. EMBO Journal, 20, 6028–6036.
Wechsler, T., Chen, B. P., Harper, R., Morotomi-Yano, K., Huang, B. C., Meek, K., Cleaver, J. E., Chen, D. J., & Wabl, M. (2004). DNA-PKcs function regulated specifically by protein phosphatase 5. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 1247–1252.
Amable, L., Grankvist, N., Largen, J. W., Ortsater, H., Sjoholm, A., & Honkanen, R. E. (2011). Disruption of serine/threonine protein phosphatase 5 (PP5:PPP5c) in mice reveals a novel role for PP5 in the regulation of ultraviolet light-induced phosphorylation of serine/threonine protein kinase Chk1 (CHEK1). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286, 40413–40422.
Yamaguchi, Y., Katoh, H., Mori, K., & Negishi, M. (2002). Galpha(12) and Galpha(13) interact with Ser/Thr protein phosphatase type 5 and stimulate its phosphatase activity. Current Biology, 12, 1353–1358.
Chen, M. S., Silverstein, A. M., Pratt, W. B., & Chinkers, M. (1996). The tetratricopeptide repeat domain of protein phosphatase 5 mediates binding to glucocorticoid receptor heterocomplexes and acts as a dominant negative mutant. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 32315–32320.
Ali, A., Zhang, J., Bao, S., Liu, I., Otterness, D., Dean, N. M., Abraham, R. T., & Wang, X. F. (2004). Requirement of protein phosphatase 5 in DNA-damage-induced ATM activation. Genes and Development, 18, 249–254.
Zhang, J., Bao, S., Furumai, R., Kucera, K. S., Ali, A., Dean, N. M., & Wang, X. F. (2005). Protein phosphatase 5 is required for ATR-mediated checkpoint activation. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 25, 9910–9919.
Jeong, J. Y., Johns, J., Sinclair, C., Park, J. M., & Rossie, S. (2003). Characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein Ser/Thr phosphatase T1 and comparison to its mammalian homolog PP5. BMC Cell Biology, 4, 3.
Zhou, G., Golden, T., Aragon, I. V., & Honkanen, R. E. (2004). Ser/Thr protein phosphatase 5 inactivates hypoxia-induced activation of an apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1/MKK-4/JNK signaling cascade. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 46595–46605.
Chebotaev, D., Yemelyanov, A., & Budunova, I. (2007). The mechanisms of tumor suppressor effect of glucocorticoid receptor in skin. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 46, 732–740.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, L., Sun, P., Li, Z. et al. Knockdown of PPP5C Inhibits Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells In Vitro. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 526–534 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1281-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1281-8