Abstract
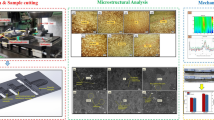
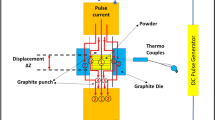
In this work, the effect of coal-fly ash (CFA) reinforcements on the physio-mechanical properties of iron metal matrix composites (IMMCs) are predicted and compared with the experimental results. The IMMCs were synthesized by reinforcing different amounts (0, 0.15, 0.28 and 0.38 vol. %) of CFA particulates to the iron matrix through powder metallurgy technique (P/M). The iron powder/CFA mixtures were compacted at a load of 10 ton followed by sintering in inert environment at 1150 ℃ for 90 min. Structural, morphological, and elemental characterisation of iron/CFA and IMMCs were performed using X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and Energy Dispersive X-Ray spectroscopy (EDS) respectively. Sufficient diffusion among the iron particles, uniform distribution of CFA particulates and clear interfaces between matrix and reinforcements have been observed in the FESEM micrographs. The trends of experimental results of sintered density and microhardness of the IMMCs has been found in line with the theoretical results predicted using rule of mixtures (ROM). Furthermore, the effects of increased vol.% of CFA inclusions on the elastic modulus \((E)\), yield strength \(({\sigma }_{y}\)) and ultimate tensile strength \({(\sigma }_{u})\) of the IMMCs have been conceived using Ramberg–Osgood (RO) model, under tensile loading. A significant reduction of 32% in sintered density and 42% increment in microhardness of the IMMCs have been observed. The RO model demonstrated significant enhancements of 51% in \(E\) and 42% in \({\sigma }_{y}\). On the other hand, whereas 44% reduction in ultimate tensile strength of IMMCs has been observed on increased amount of CFA (0–0.38 vol.%). The load transfer strengthening mechanism has been found dominating the Hall–Petch followed by Taylor’s strengthening mechanism. Further, the various specific properties of the IMMCs were compared with prevalent literature. The specific properties of IMMCs such as microhardness, \(E\), \({\sigma }_{y}\) and \({\sigma }_{u}\) are found comparable with the established aluminium based MMCs.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CFA:
-
Coal-fly ash
- MMC:
-
Metal matrix composite
- FMMC:
-
Ferrous metal matrix composite
- NFMMC:
-
Non-ferrous metal matrix composite
- IMMC:
-
Iron metal matrix composite
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- P/M:
-
Powder metallurgy
- ROM:
-
Rule of mixtures
- RO:
-
Ramberg–Osgood
- Wt. %:
-
Weight percentage
- Vol. %:
-
Volume percentage
- Hv:
-
Vickers’s microhardness
- \(\rho_{c}\) :
-
Density of composite
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Stress
- E :
-
Young’s modulus
- σ y :
-
Yield strength
References
Bajakke, P.A., Malik, V.R., Deshpande, A.S.: Particulate metal matrix composites and their fabrication via friction stir processing–a review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 34(8), 833–881 (2019)
Liu, G.R.: A step-by-step method of rule-of-mixture of fiber- and particle-reinforced composite materials. Compos. Struct. 40(3–4), 313–322 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-8223(98)00033-6
Tomoko Sano, P., Srivatsan, T.S., Michael, W.: Advanced Composites for aerospace, marine and land applications, 143rd ed. California: Springer International Publishers, Switzerland (2014).
Feng, K., Yang, Y., Shen, B., Guo, L.: In situ synthesis of TiC/Fe composites by reaction casting. Mater. Des. 26(1), 37–40 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2004.03.014
Vilakazi, A.Q., Ndlovu, S., Chipise, L., Shemi, A.: The recycling of coal fly ash: a review on sustainable developments and economic considerations. Sustainability (Switzerland). 14(4), 1–32 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14041958
Chen, G., Wan, J., He, N., Ming Zhang, H., Han, F., Min Zhang, Y.: Strengthening mechanisms based on reinforcement distribution uniformity for particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (English Edition) 28(12), 2395–2400 (2018)
Chen, J.K., Huang, I.S.: Thermal properties of aluminum-graphite composites by powder metallurgy. Compos. B Eng. 44(1), 698–703 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.01.083
Gupta, P., Kumar, D., Parkash, O., Jha, A. K.: Sintering and Hardness Behavior of Fe-Al2O3 Metal Matrix Nanocomposites Prepared by Powder Metallurgy. J. Compos. 1–10 (2014).
Bardhan, P.K., Patra, S., Sutradhar, G.: Analysis of density of sintered iron powder component using the response surface method. Mater. Sci. Appl. 01(03), 152–157 (2010)
Jagadeesh, G.V., Gangi Setti, S.: A review on micromechanical methods for evaluation of mechanical behavior of particulate reinforced metal matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 55(23), 9848–9882 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04715-2
Vignoli, L.L., Savi, M.A., Pacheco, P.M.C.L., Kalamkarov, A.L.: Comparative analysis of micromechanical models for the elastic composite laminae. Compos. Part B: Eng. 174, 106961 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106961
You, Y.J., Kim, J.H.J., Park, K.T., Seo, D.W., Lee, T.H.: Modification of rule of mixtures for tensile strength estimation of circular GFRP rebars. Polymers 9(12), 682 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120682
Dixit, S., Stefańska, A., Singh, P.: Manufacturing technology in terms of digital fabrication of contemporary biomimetic structures. Int. J. Construct. Manag. 1–9 (2021).
Dixit, S., et al.: Replacing E-waste with coarse aggregate in architectural engineering and construction industry. Mater. Today: Proc. (2021).
Dixit, S., Singh, S., Singh, S., Varghese, R. G., Pandey, A. K., Varshney, D.: Role of Solar energy and issues in its implementation in the Indian context. In: MATEC Web of Conferences, vol. 172, pp. 06001. EDP Sciences (2018).
Shen, Y.L., Williams, J.J., Piotrowski, G., Chawla, N., Guo, Y.L.: Correlation between tensile and indentation behavior of particle-reinforced metal matrix composites: an experimental and numerical study. Acta Mater. 49(16), 3219–3229 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(01)00226-9
Ramberg, W., Osgood, W.R.: Description of stress-strain curves by three parameters. Natl. Advis. Comm. Aeronaut. 902(July), 1–32 (1943)
Singh, A., Singh, J., Sinha, M.K., Kumar, R., Verma, V.: Investigations on microstructural and microhardness developments in sintered iron – coal fly ash composites. Sādhanā. 2020(45), 1–13 (2020)
Singh, A., Singh, J., Sinha, M.K., Kumar, R., Verma, V.: Compaction and densification characteristics of iron powder/coal fly ash mixtures processed by powder metallurgy technique. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30(2), 1207–1220 (2021)
Raj, R., Thakur, D.G.: Qualitative and quantitative assessment of microstructure in Al-B4C metal matrix composite processed by modified stir casting technique. Arch. Civil Mech. Eng. 16(4), 949–960 (2016)
Manimaran, R., Jayakumar, I., Giyahudeen, R.M., L.: Narayanan, Mechanical properties of fly ash composites—a review. Energy Sour., Part A: Recovery, Utilization, Environ. Effects 40(8), 887–893 (2018)
Igathinathane, C., Pordesimo, L.O., Columbus, E.P., Batchelor, W.D., Methuku, S.R.: Shape identification and particles size distribution from basic shape parameters using ImageJ. Comput. Electron. Agric. 63(2), 168–182 (2008)
Bai, S., Perevoshchikova, N., Sha, Y., Wu, X.: The effects of selective laser melting process parameters on relative density of the AlSi10Mg parts and suitable procedures of the archimedes method. Appl. Sci. (Switzerland). 9(3), 583 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030583
Melendez, N.M., McDonald, A.G.: Development of WC-based metal matrix composite coatings using low-pressure cold gas dynamic spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 214, 101–109 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.11.010
Srinivasanaik, A., Mallik, A.: Tractable synthesis of graphene oxide by electrochemical exfoliation method. In: Advances in Materials and Metallurgy, pp. 239-248. Springer, Singapore (2019).
Olawuni, E.O., Durowoju, M.O., Asafa, T.B.: Correlation between theoretical and experimental hardness, elastic modulus of discarded aluminium piston reinforced with zirconium diboride and snail shells. SN Appl. Sci. 2(3), 1–12 (2020)
Gadamchetty, G., Pandey, A., Gawture, M.: On Practical Implementation of the Ramberg-Osgood Model for FE Simulation. SAE Int. J. Mater. Manuf. 9(1), 200–205 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4271/2015-01-9086
Hight, T.K., Brandeau, J.F.: Mathematical modeling of the stress strain-strain rate behavior of bone using the Ramberg-Osgood equation. J. Biomech. 16(6), 445–450 (1983)
Anatolyevich, B.P., Yakovlevna, G.N.: Generalization of the Ramberg-Osgood model for elastoplastic materials. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 28(12), 7342–7346 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04422-3
Biswas, P., Mandal, D., Mondal, M.K.: Failures analysis of in-situ Al–Mg2Si composites using actual microstructure based model. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 797, 140155 (2020)
Qiu, Z., Fan, H.: Nonlinear modeling of bamboo fiber reinforced composite materials. Compos. Struct. 238(January), 1–12 (2020)
Saba, F., Zhang, F., Liu, S., Liu, T.: Reinforcement size dependence of mechanical properties and strengthening mechanisms in diamond reinforced titanium metal matrix composites. Compos. Part B: Eng. 167, 7–19 (2019)
Sahoo, S., Jha, B.B., Sahoo, T.K., Mandal, A.: Influence of reinforcement and processing on steel-based composites: Microstructure and mechanical response. Mater. Manuf. Process. 33(5), 564–571 (2018)
Li, C.L., Mei, Q.S., Li, J.Y., Chen, F., Ma, Y., Mei, X.M.: Hall-Petch relations and strengthening of Al-ZnO composites in view of grain size relative to interparticle spacing. Scripta Mater. 153(April), 27–30 (2018)
Ferguson, J.B., Schultz, B.F., Venugopalan, D., Lopez, H.F., Rohatgi, P.K., Cho, K., Kim, C.S.: On the superposition of strengthening mechanisms in dispersion strengthened alloys and metal-matrix nanocomposites: Considerations of stress and energy. Met. Mater. Int. 20(2), 375–388 (2014)
Dixit, S., Stefańska, A.: Digitisation of contemporary fabrication processes in the AEC sector. Mater. Today: Proc. 56, 1882–1885 (2022)
Singh, S., Dixit, S., Sahai, S., Sao, A., Kalonia, Y., Kumar, R. S. Key benefits of adopting lean manufacturing principles in Indian construction industry. In: MATEC Web of Conferences, vol. 172, pp. 05002. EDP Sciences (2018).
Kumar, K., Arora, R., Khan, S., Dixit, S.: Characterization of fly ash for potential utilization in green concrete. Mater. Today: Proc. 56, 1886–1890 (2021)
Dixit, S., Singh, P.: Investigating the disposal of E-Waste as in architectural engineering and construction industry. Mater. Today: Proc. 56, 1891–1895 (2021)
Dixit, S., Stefańska, A., Musiuk, A.: Architectural form finding in arboreal supporting structure optimisation. Ain Shams Eng. J. 12(2), 2321–2329 (2021)
Mishra, D.P., Das, S.K., Prasad, D., Kumar, S.: A study of physico-chemical and mineralogical properties of Talcher coal fly ash for stowing in underground coal mines. Mater. Charact. 61(11), 1252–1259 (2010)
Singh, J., Verma, V., Kumar, R., Kumar, R.: Influence of Mg2+-substitution on the optical band gap energy of Cr2− xMgxO3 nanoparticles. Results Phys. 13, 102106 (2019)
William, J., Callister, D.: Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering, Fifth. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York (2001)
Enginsoy, H.M., Bayraktar, E., Katundi, D., Gatamorta, F., Miskioglu, I.: Comprehensive analysis and manufacture of recycled aluminum based hybrid metal matrix composites through the combined method; sintering and sintering + forging. Compos. B Eng. 194(April), 1–14 (2020)
Sim, J., Kang, Y., Kim, B.J., Park, Y.H., Lee, Y.C.: Preparation of fly ash/epoxy composites and its effects on mechanical properties. Polymers 12(1), 1–12 (2020)
Rohatgi, P.K., Gupta, N., Alaraj, S.: Thermal expansion of aluminum-fly ash cenosphere composites synthesized by pressure infiltration echnique. J. Compos. Mater. 40(13), 1163–1174 (2006)
Luo, P., McDonald, D.T., Zhu, S.M., Palanisamy, S., Dargusch, M.S., Xia, K.: Analysis of microstructure and strengthening in pure titanium recycled from machining chips by equal channel angular pressing using electron backscatter diffraction. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 538(January), 252–258 (2012)
Chelliah, N.M., Singh, H., Surappa, M.K.: Microstructural evolution and strengthening behavior in in-situ magnesium matrix composites fabricated by solidification processing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 194(December), 65–76 (2017)
Bhatt, A., Priyadarshini, S., Mohanakrishnan, A.A., Abri, A., Sattler, M., Techapaphawit, S.: Physical, chemical, and geotechnical properties of coal fly ash: A global review. Case Stud. Construct. Mater. 11, e00263 (2019)
Sharma, S.C.: Equation for the density of particle-reinforced metal matrix composites: a new approach. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 12(3), 324–330 (2003)
Peng, H.X., Fan, Z., Evans, J.R.G.: Bi-continuous metal matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 303(1–2), 37–45 (2001)
Singh, A., et al.: Compaction and densification characteristics of iron powder/coal fly ash mixtures processed by powder metallurgy technology. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30(July), 1–14 (2020)
Alhajeri, S.N., Al-Fadhalah, K.J., Almazrouee, A.I., Langdon, T.G.: Microstructure and microhardness of an Al-6061 metal matrix composite processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater. Charact. 118, 270–278 (2016)
Dyachkova, L.N., Feldshtein, E.E., Vityaz, P.A., Mikhalski, M.: Tribological properties of iron-based powder composite materials with addition of graphite, alumina and zirconia nanoparticles. J. Frict. Wear. 41(3), 198–203 (2020)
Saboori, A., Novara, C., Pavese, M., Badini, C., Giorgis, F., Fino, P.: An Investigation on the sinterability and the compaction behavior of aluminum/graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 26(3), 993–999 (2017)
Fu, S.Y., Feng, X.Q., Lauke, B., Mai, Y.W.: Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate-polymer composites. Compos. B Eng. 39(6), 933–961 (2008)
Munday, G., Hogan, J., McDonald, A.: On the microstructure-dependency of mechanical properties and failure of low-pressure cold-sprayed tungsten carbide-nickel metal matrix composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 396, 125947 (2020)
Hongjoo Rhee, C.L., Whittington, W.R., Oppedal, A.L., Sherif, A.R., King, R.L., Kim, H.-J.: Mechanical properties of novel aluminum metal matrix metallic composites: Application to overhead conductors. Mater. Des. 88(Oct), 16–21 (2015)
Samal, P., Vundavilli, P.R., Meher, A., Mahapatra, M.M.: Recent progress in aluminum metal matrix composites: a review on processing, mechanical and wear properties. J. Manuf. Process. 59, 131–152 (2020)
Soorya Prakash, K., Gopal, P.M., Purusothaman, M., Sasikumar, M.: Fabrication and characterization of metal-high entropy alloy composites. Int. J. Metalcasting 14(2), 547–555 (2019)
Pavlina, E.J., Van Tyne, C.J.: Correlation of yield strength and tensile strength with hardness for steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 17(6), 888–893 (2008)
Zhang, P., Li, S.X., Zhang, Z.F.: General relationship between strength and hardness. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 529(1), 62–73 (2011)
Chelliah, N.M., Singh, H., Surappa, M.K.: Microstructural evolution and strengthening behavior in in-situ magnesium matrix composites fabricated by solidification processing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 194(2017), 65–76 (2017)
Sanders, P.G., Youngdahl, C.J., Weertman, J.R.: The strength of nanocrystalline metals with and without flaws. Mater. Sci. Eng., A A234–236(March), 77–82 (1997)
Dixit, S., Stefańska, A., Musiuk, A., Singh, P.: Study of enabling factors affecting the adoption of ICT in the Indian built environment sector. Ain Shams Eng. J. 12(2), 2313–2319 (2021)
Dixit, S.: Impact of management practices on construction productivity in Indian building construction projects: an empirical study. Organ., Technol. Manag. Construct. 13(1), 2383–2390 (2021)
Dixit, S.: Study of factors affecting the performance of construction projects in AEC industry. Organ., Technol. Manag. Construct.: Int. J. 12(1), 2275–2282 (2020)
Meng, Q., Wang, Z.: Prediction of interfacial strength and failure mechanisms in particle-reinforced metal-matrix composites based on a micromechanical model. Eng. Fract. Mech. 142(June), 170–183 (2015)
Biswas, P., Mandal, D., Mondal, M.K.: Micromechanical response of Al-Mg2Si composites using approximated representative volume elements (RVEs) model. Mater. Res. Exp. 6(11), 1–38 (2019)
Kennedy, A.R., Wyatt, S.M.: The effect of processing on the mechanical properties and interfacial strength of aluminium/TiC MMCs. Compos. Sci. Technol. 60(2), 307–314 (2000)
Guo, Q., Han, Y., Zhang, D.: Interface-dominated mechanical behavior in advanced metal matrix composites. Nano Mater. Sci. 2(1), 66–71 (2020)
Geilen, M.B., Schönherr, J.A., Klein, M., Leininger, D.S., Giertler, A., Krupp, U., Oechsner, M.: On the influence of control type and strain rate on the lifetime of 50CrMo4. Metals 10(11), 1458 (2020)
James, L.A.: Ramberg-Osgood strain- hardening characterization. J. Press. Vessel Technol. 1, 1–5 (2017)
Kasar, A.K., Gupta, N., Rohatgi, P.K., Menezes, P.L.: A brief review of fly ash as reinforcement for composites with improved mechanical and tribological properties. Jom. 72(6), 2340–2351 (2020)
Surappa, M.K.: Synthesis of fly ash particle reinforced A356 Al composites and their characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 480(1–2), 117–124 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.06.068
Dixit, S., Mandal, S.N., Thanikal, J.V., Saurabh, K.: Evolution of studies in construction productivity: a systematic literature review (2006–2017). Ain Shams Eng. J. 10(3), 555–564 (2019)
Dixit, S., Sharma, K.: An empirical study of major factors affecting productivity of construction projects. In: Emerging trends in civil engineering, pp. 121-129. Springer, Singapore (2020).
Dixit, S., Mandal, S. N., Thanikal, J. V., & Saurabh, K.: Study of significant factors affecting construction productivity using relative importance index in Indian construction industry. In: E3S Web of Conferences, vol. 140, pp. 09010. EDP Sciences (2019).
Singh, A., Singh, J., Sinha, M.K., Kumar, R., Verma, V.: Investigations on microstructural and microhardness developments in sintered iron–coal fly ash composites. Sādhanā 45(1), 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-020-01408-z
Kanth, U.R., Rao, P.S., Krishna, M.G.: Mechanical behaviour of fly ash/SiC particles reinforced Al-Zn alloy-based metal matrix composites fabricated by stir casting method. J. Market. Res. 8(1), 737–744 (2019)
Jahani, B., Salimi Jazi, M., Azarmi, F., Croll, A.: Effect of volume fraction of reinforcement phase on mechanical behavior of ultra-high-temperature composite consisting of iron matrix and TiB2 particulates. J. Compos. Mater. 52(5), 609–620 (2017)
Perugu, C. S.: Effect of SiC Reinforcement on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Aluminum Metal Matrix Composite Effect of SiC Reinforcement on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Aluminum Metal Matrix Composite (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/376/1/012057.
Bacciarini, C., Mathier, V.: Aluminium aa6061 matrix composite reinforced with spherical alumina particles produced by infiltration: perspective on aerospace applications. J. Metall. 1–10, 2014 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/248542
Dixit, S.: Analysing the impact of productivity in indian transport infra projects. In: IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng, vol. 1218, pp. 12059 (2022).
Singh, P., Dixit, S., Sammanit, D., Krishnan, P.: The automated farmlands of tomorrow: an IoT integration with farmlands. In: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 1218, No. 1, pp. 012048. IOP Publishing (2022).
Rai, R. K., Gosain, A. K., Singh, P., Dixit, S.: Farm advisory services for farmers using SWAT and APEX Model. In: International Conference Sustainable Energy Systems: innovative perspectives, pp. 444-458. Springer, Cham (2020).
Shah, M.N., Dixit, S., Kumar, R., Jain, R., Anand, K.: Causes of delays in slum reconstruction projects in India. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 21(5), 452–467 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dixit, S., Singh, A., Singh, J. et al. Comparison of theoretical and experimental physio-mechanical properties of coal-fly ash (CFA) reinforced iron matrix composites. Int J Interact Des Manuf 17, 2429–2444 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-01022-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-01022-9