Abstract
Over the last decade, there has been a promising increase in market trends toward plant proteins. This trend is expected to persist in coming years due to more sustainability, lower environmental footprints, and health benefits associated with plant proteins along with the recent surge in veganism. To meet market demand, plant-based proteins must compete with or outperform conventional animal proteins in terms of quality and functionality. However, plant proteins possess lower digestibility/solubility, lower water/oil holding capacity, and unfavorable emulsifying/foaming properties, which limit their bioavailability and functionality. The presence of anti-nutrients and non-digestible polysaccharides also results in lower quality, making it necessary to modify these properties through chemical, physical, and enzymatic methods. Food industries prefer physical and biological approaches over chemical approaches due to clean label demand and toxicity issues encountered while applying chemical methods. In this article, we investigate research progress in plant protein modification area using physical approaches comprising ultrasonication, pulse electric field, microwaves, extrusion, gamma irradiation, high-pressure processing, radiofrequency, and cold plasma. This review also highlights associated functionality challenges and summarizes recent studies in an attempt to improve plant protein functionality for obtaining multifunctional proteins.
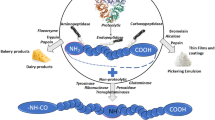
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdelwhab, N. M., Nour, A. M., & Fageer, A. S. M. (2009). The nutritive and functional properties of dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) as affected by gamma irradiation. Pakistan Journal of Nutrition, 8(11), 1739–1742. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2009.1739.1742
Achouri, A., & Boye, J. I. (2013). Thermal processing, salt and high pressure treatment effects on molecular structure and antigenicity of sesame protein isolate. Food Research International, 53(1), 240–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2013.04.016
Adeleye, O. O., Awodiran, S. T., Ajayi, A. O., & Ogunmoyela, T. F. (2020). Effect of high-temperature, short-time cooking conditions on in vitro protein digestibility, enzyme inhibitor activity and amino acid profile of selected legume grains. Heliyon, 6(11), e05419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05419
Afify, A. E. M. M., Rashed, M. M., Mahmoud, E. A., & EL-BELTAGI, H. S. (2011). Effect of gamma radiation on protein profile, protein fraction and solubility’s of three oil seeds: Soybean, peanut and sesame. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca, 39(2), 90–98. https://doi.org/10.15835/nbha3926252
Ahmed, J., Mulla, M., Al-Ruwaih, N., & Arfat, Y. A. (2019). Effect of high-pressure treatment prior to enzymatic hydrolysis on rheological, thermal, and antioxidant properties of lentil protein isolate. Legume Science, 1(1), e10. https://doi.org/10.1002/leg3.10
Ahmed, M. M., Abdalla, I. G., Salih, A. M., & Hassan, A. B. (2018). Effect of gamma radiation on storability and functional properties of sorghum grains (Sorghum bicolor L.). Food Science & Nutrition, 6(7), 1933–1939. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.752
Akharume, F. U., Aluko, R. E., & Adedeji, A. A. (2021). Modification of plant proteins for improved functionality: A review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 20(1), 198–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12688
Alavi, F., Chen, L., & Emam-Djomeh, Z. (2021). Effect of ultrasound-assisted alkaline treatment on functional property modifications of faba bean protein. Food Chemistry, 354, 129494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129494
Alcorta, A., Porta, A., Tárrega, A., Alvarez, M. D., & Vaquero, M. P. (2021). Foods for plant-based diets: Challenges and innovations. Foods, 10(2), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020293
Alonso, R., Aguirre, A., & Marzo, F. (2000a). Effects of extrusion and traditional processing methods on antinutrients and in vitro digestibility of protein and starch in faba and kidney beans. Food Chemistry, 68(2), 159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(99)00169-7
Alonso, R., Orue, E., Zabalza, M. J., Grant, G., & Marzo, F. (2000b). Effect of extrusion cooking on structure and functional properties of pea and kidney bean proteins. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 80(3), 397–403. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0010(200002)80:3%3C397::AID-JSFA542%3E3.0.CO;2-3
Al-Ruwaih, N., Ahmed, J., Mulla, M. F., & Arfat, Y. A. (2019). High-pressure assisted enzymatic proteolysis of kidney beans protein isolates and characterization of hydrolysates by functional, structural, rheological and antioxidant properties. Lwt, 100, 231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.10.074
Amagliani, L., O’Regan, J., Kelly, A. L., & O’Mahony, J. A. (2017). The composition, extraction, functionality and applications of rice proteins: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 64, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.01.008
Aschemann-Witzel, J., Gantriis, R. F., Fraga, P., & Perez-Cueto, F. J. (2021). Plant-based food and protein trend from a business perspective: Markets, consumers, and the challenges and opportunities in the future. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 61(18), 3119–3128. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1793730
Ashraf, Seema & Saeed, Ghufran & Saeed, Syed & And, Sayeed & Ali, Rashida. (2012). Impact of Microwave Treatment on the Functionality of Cereals and Legumes. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology. 14. 356-370.
Baier, A. K., & Knorr, D. (2015). Influence of high isostatic pressure on structural and functional characteristics of potato protein. Food Research International, 77, 753–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.05.053
Basak, S., & Annapure, U. S. (2022). Recent trends in the application of cold plasma for the modification of plant proteins—A review. Future Foods. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fufo.2022.100119
Beck, S. M., Knoerzer, K., & Arcot, J. (2017). Effect of low moisture extrusion on a pea protein isolate’s expansion, solubility, molecular weight distribution and secondary structure as determined by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). Journal of Food Engineering, 214, 166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.06.037
Boakye, P. G., Okyere, A. Y., & Annor, G. A. (2023). Impact of extrusion processing on the nutritional and physicochemical properties of intermediate wheatgrass (Thinopyrum intermedium). Cereal Chemistry, 100(3), 628–642. https://doi.org/10.1002/cche.10632
Bußler, S., Steins, V., Ehlbeck, J., & Schlüter, O. (2015). Impact of thermal treatment versus cold atmospheric plasma processing on the techno-functional protein properties from Pisum sativum ‘Salamanca.’ Journal of Food Engineering, 167, 166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2015.05.036
Cao, H., Sun, R., Shi, J., Li, M., Guan, X., Liu, J., ... & Zhang, Y. (2021). Effect of ultrasonic on the structure and quality characteristics of quinoa protein oxidation aggregates. Ultrasonics sonochemistry, 77, 105685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105685
Chaple, S., Sarangapani, C., Jones, J., Carey, E., Causeret, L., Genson, A., ... & Bourke, P. (2020). Effect of atmospheric cold plasma on the functional properties of whole wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain and wheat flour. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 66, 102529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2020.102529
Chatur, P., Johnson, S. K., Coorey, R., Bhattarai, R. R., & Bennett, S. J. (2022). The effect of high pressure processing on textural, bioactive and digestibility properties of cooked Kimberley large kabuli chickpeas. Frontiers in Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.847877
Chen, L., Chen, J., Yu, L., Wu, K., & Zhao, M. (2018). Emulsification performance and interfacial properties of enzymically hydrolyzed peanut protein isolate pretreated by extrusion cooking. Food Hydrocolloids, 77, 607–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.11.002
Cheng, C., Yu, X., McClements, D. J., Huang, Q., Tang, H., Yu, K., ... & Deng, Q. (2019). Effect of flaxseed polyphenols on physical stability and oxidative stability of flaxseed oil-in-water nanoemulsions. Food chemistry, 301, 125207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125207
Condés, M. C., Speroni, F., Mauri, A., & Añón, M. C. (2012). Physicochemical and structural properties of amaranth protein isolates treated with high pressure. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 14, 11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2011.12.006
Constantino, A. B. T., & Garcia-Rojas, E. E. (2020). Modifications of physicochemical and functional properties of amaranth protein isolate (Amaranthus cruentus BRS Alegria) treated with high-intensity ultrasound. Journal of Cereal Science, 95, 103076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2020.103076
Dabbour, M., He, R., Mintah, B., Xiang, J., & Ma, H. (2019). Changes in functionalities, conformational characteristics and antioxidative capacities of sunflower protein by controlled enzymolysis and ultrasonication action. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 58, 104625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104625
Dalbhagat, C. G., Mahato, D. K., & Mishra, H. N. (2019). Effect of extrusion processing on physicochemical, functional and nutritional characteristics of rice and rice-based products: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 85, 226–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.01.001
Dan, S., Shujun, L., Laurie, H. M., Fengmin, Z., Lanfang, Z., Xiaopeng, Z., ... & Youfu, C. (2010). Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on in vitro digestion of soy protein. International Agricultural Engineering Journal, 19(1), 49.
Dar, M. Z., Deepika, K., Jan, K., Swer, T. L., Kumar, P., Verma, R., ... & Bashir, K. (2018). Modification of structure and physicochemical properties of buckwheat and oat starch by γ-irradiation. International journal of biological macromolecules, 108, 1348–1356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.067
Deng, Y., Padilla-Zakour, O., Zhao, Y., & Tao, S. (2015). Influences of high hydrostatic pressure, microwave heating, and boiling on chemical compositions, antinutritional factors, fatty acids, in vitro protein digestibility, and microstructure of buckwheat. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(11), 2235–2245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1578-9
Dhakal, S., Liu, C., Zhang, Y., Roux, K. H., Sathe, S. K., & Balasubramaniam, V. M. (2014). Effect of high pressure processing on the immunoreactivity of almond milk. Food Research International, 62, 215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.02.021
Dilrukshi, H. N., Torrico, D. D., Brennan, M. A., & Brennan, C. S. (2022). Effects of extrusion processing on the bioactive constituents, in vitro digestibility, amino acid composition, and antioxidant potential of novel gluten-free extruded snacks fortified with cowpea and whey protein concentrate. Food Chemistry, 389, 133107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133107
Dong, S., Gao, A., Xu, H., & Chen, Y. (2017a). Effects of dielectric barrier discharges (DBD) cold plasma treatment on physicochemical and structural properties of zein powders. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10, 434–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1814-y
Dong, S., Gao, A., Zhao, Y., Li, Y. T., & Chen, Y. (2017b). Characterization of physicochemical and structural properties of atmospheric cold plasma (ACP) modified zein. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 106, 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2017.05.011
Enujiugha, V. N., Olotu, I. O., Malomo, S. A., & Sanni, T. A. (2012). The effect of [gamma]-irradiation and cooking on the physicochemical properties of African oil bean seed (Pentaclethra macrophylla benth) and its oil extract. Journal of Food Research, 1(2), 189. https://doi.org/10.5539/jfr.v1n2p189
Gao, Y., Sun, Y., Zhang, Y., Sun, Y., & Jin, T. (2022). Extrusion modification: Effect of extrusion on the functional properties and structure of rice protein. Processes, 10(9), 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10091871
Greenebaum, J. (2012). Veganism, identity and the quest for authenticity. Food, Culture & Society, 15(1), 129–144. https://doi.org/10.2752/175174412X13190510222101
Guan, Y. G., Lin, H., Han, Z., Wang, J., Yu, S. J., Zeng, X. A., ... & Sun, W. W. (2010). Effects of pulsed electric field treatment on a bovine serum albumin–dextran model system, a means of promoting the Maillard reaction. Food Chemistry, 123(2), 275–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.04.029
Guan, J. J., Zhang, T. B., Hui, M., Yin, H. C., Qiu, A. Y., & Liu, X. Y. (2011). Mechanism of microwave-accelerated soy protein isolate–saccharide graft reactions. Food Research International, 44(9), 2647–2654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.05.015
Guo, C., Zhang, Z., Chen, J., Fu, H., Subbiah, J., Chen, X., & Wang, Y. (2017). Effects of radio frequency heating treatment on structure changes of soy protein isolate for protein modification. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10(8), 1574–1583. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11947-017-1923-2
Hall, A. E., & Moraru, C. I. (2022). Comparative effects of high pressure processing and heat treatment on in vitro digestibility of pea protein and starch. npj Science of Food, 6(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-021-00116-0
Hall, A. E., & Moraru, C. I. (2021). Structure and function of pea, lentil and faba bean proteins treated by high pressure processing and heat treatment. LWT, 152, 112349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112349
Hassan, A. B., Mahmoud, N. S., Elmamoun, K., Adiamo, O. Q., & Ahmed, I. A. M. (2018). Effects of gamma irradiation on the protein characteristics and functional properties of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) seeds. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 144, 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2017.11.020
Hassan, A. B., Pawelzik, E., & von Hoersten, D. (2016). Effect of radio frequency heating on nutritional quality and protein solubility of corn. Food Science & Nutrition, 4(5), 686–689. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.332
Hassan, A. B., von Hoersten, D., & Ahmed, I. A. M. (2019). Effect of radio frequency heat treatment on protein profile and functional properties of maize grain. Food Chemistry, 271, 142–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.190
He, J., Evans, N. M., Liu, H., & Shao, S. (2020). A review of research on plant-based meat alternatives: Driving forces, history, manufacturing, and consumer attitudes. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 19(5), 2639–2656. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12610
Heydari, M. M., Najib, T., & Meda, V. (2022). Investigating starch and protein structure alterations of the processed lentil by microwave-assisted infrared thermal treatment and their correlation with the modified properties. Food Chemistry Advances. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.focha.2022.100091
Hu, H., Wu, J., Li-Chan, E. C., Zhu, L., Zhang, F., Xu, X., ... & Pan, S. (2013). Effects of ultrasound on structural and physical properties of soy protein isolate (SPI) dispersions. Food hydrocolloids, 30(2), 647–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.08.001
Huang, L., Ding, X., Li, Y., & Ma, H. (2019). The aggregation, structures and emulsifying properties of soybean protein isolate induced by ultrasound and acid. Food Chemistry, 279, 114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.147
Jambrak, A. R., Lelas, V., Mason, T. J., Krešić, G., & Badanjak, M. (2009). Physical properties of ultrasound treated soy proteins. Journal of Food Engineering, 93(4), 386–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2009.02.001
Ji, H., Dong, S., Han, F., Li, Y., Chen, G., Li, L., & Chen, Y. (2018). Effects of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) cold plasma treatment on physicochemical and functional properties of peanut protein. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(2), 344–354. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11947-017-2015-z
Jiang, L., Wang, J., Li, Y., Wang, Z., Liang, J., Wang, R., ... & Zhang, M. (2014). Effects of ultrasound on the structure and physical properties of black bean protein isolates. Food Research International, 62, 595–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.04.022
Jiang, Z. Q., Pulkkinen, M., Wang, Y. J., Lampi, A. M., Stoddard, F. L., Salovaara, H., ... & Sontag-Strohm, T. (2016). Faba bean flavour and technological property improvement by thermal pre-treatments. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 68, 295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.12.015
Jiang, Y., Wang, S., He, F., Fan, Q., Ma, Y., Yan, W., ... & Zhao, W. (2018). Inactivation of lipoxygenase in soybean by radio frequency treatment. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 53(12), 2738–2747. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13885
Jiang, Y., Zhou, X., Zheng, Y., Wang, D., Deng, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2021). Impact of ultrasonication/shear emulsifying/microwave-assisted enzymatic extraction on rheological, structural, and functional properties of Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. seed protein isolates. Food Hydrocolloids, 112, 106355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106355
Jin, J., Okagu, O. D., Yagoub, A. E. A., & Udenigwe, C. C. (2021). Effects of sonication on the in vitro digestibility and structural properties of buckwheat protein isolates. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 70, 105348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105348
Kalu, R. E., & Etim, K. D. (2018). Factors associated with malnutrition among underfive children in developing countries: A review. Global Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 24(1), 69–74. https://doi.org/10.4314/gjpas.v24i1.8
Kamble, D. B., Singh, R., Pal Kaur, B., Rani, S., & Upadhyay, A. (2020). Effect of microwave processing on physicothermal properties, antioxidant potential, in vitro protein digestibility and microstructure of durum wheat semolina. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 14(2), 761–769. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11694-019-00324-z
Karabulut, G., & Yemiş, O. (2022). Modification of hemp seed protein isolate (Cannabis sativa L.) by high-intensity ultrasound treatment. Part 1: Functional properties. Food Chemistry, 375, 131843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131843
Kausar, T., Hanan, E., Ayob, O., Praween, B., & Azad, Z. R. A. A. (2019). A review on functional ingredients in red meat products. Bioinformation, 15(5), 358. https://doi.org/10.6026/97320630015358
Khan, N. M., Mu, T. H., Sun, H. N., Zhang, M., & Chen, J. W. (2015). Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on secondary structure and emulsifying behavior of sweet potato protein. High Pressure Research, 35(2), 189–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/08957959.2015.1005013
Khan, N. M., Mu, T. H., Zhang, M., & Arogundade, L. A. (2014). The effects of pH and high hydrostatic pressure on the physicochemical properties of a sweet potato protein emulsion. Food Hydrocolloids, 35, 209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.05.011
Kowalski, R. J., Medina-Meza, I. G., Thapa, B. B., Murphy, K. M., & Ganjyal, G. M. (2016). Extrusion processing characteristics of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) var. Cherry Vanilla. Journal of Cereal Science, 70, 91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2016.05.024
Lee, H., Ha, M. J., Shahbaz, H. M., Kim, J. U., Jang, H., & Park, J. (2018). High hydrostatic pressure treatment for manufacturing of red bean powder: A comparison with the thermal treatment. Journal of Food Engineering, 238, 141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.06.016
Leonard, W., Zhang, P., Ying, D., & Fang, Z. (2020). Application of extrusion technology in plant food processing byproducts: An overview. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 19(1), 218–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12514
Leonard, W., Zhang, P., Ying, D., Xiong, Y., & Fang, Z. (2021). Effect of extrusion technology on hempseed (Cannabis sativa L.) oil cake: Polyphenol profile and biological activities. Journal of Food Science, 86(7), 3159–3175. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15813
Li, H., Zhu, K., Zhou, H., & Peng, W. (2012). Effects of high hydrostatic pressure treatment on allergenicity and structural properties of soybean protein isolate for infant formula. Food Chemistry, 132(2), 808–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.11.040
Li, R., & Xiong, Y. L. (2021). Ultrasound-induced structural modification and thermal properties of oat protein. LWT, 149, 111861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111861
Li, T., Wang, L., Chen, Z., Sun, D., & Li, Y. (2019). Electron beam irradiation induced aggregation behaviour, structural and functional properties changes of rice proteins and hydrolysates. Food Hydrocolloids, 97, 105192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105192
Li, Y. Q. (2012). Structure changes of soybean protein isolates by pulsed electric fields. Physics Procedia, 33, 132–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.05.040
Li, Y., Chen, Z., & Mo, H. (2007). Effects of pulsed electric fields on physicochemical properties of soybean protein isolates. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 40(7), 1167–1175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2006.08.015
Li, Z., Chu, S., Wang, P., Gao, S., Li, S., & Yu, X. (2020). Effects of irradiation treatment on protein structure and digestion characteristics of seed-watermelon (Citrullus lanatus var.) kernel protein. Food Science and Biotechnology, 29(9), 1201–1211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-020-00777-9
Liang, R., Cheng, S., & Wang, X. (2018). Secondary structure changes induced by pulsed electric field affect antioxidant activity of pentapeptides from pine nut (Pinus koraiensis) protein. Food Chemistry, 254, 170–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.090
Ling, B., Ouyang, S., & Wang, S. (2019). Effect of radio frequency treatment on functional, structural and thermal behaviors of protein isolates in rice bran. Food Chemistry, 289, 537–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.072
Linsberger-Martin, G., Weiglhofer, K., Phuong, T. P. T., & Berghofer, E. (2013). High hydrostatic pressure influences antinutritional factors and in vitro protein digestibility of split peas and whole white beans. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 51(1), 331–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2012.11.008
Liu, C., & Ma, X. (2016). Study on the mechanism of microwave modified wheat protein fiber to improve its mechanical properties. Journal of Cereal Science, 70, 99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2016.05.018
Liu, Y. Y., Zhang, Y., Zeng, X. A., El-Mashad, H., Pan, Z. L., & Wang, Q. J. (2014). Effect of pulsed electric field on microstructure of some amino acid group of soy protein isolates. International Journal of Food Engineering, 10(1), 113–120. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijfe-2013-0033
Lu, Z. X., He, J. F., Zhang, Y. C., & Bing, D. J. (2020). Composition, physicochemical properties of pea protein and its application in functional foods. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 60(15), 2593–2605. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1651248
Ma, W., Qi, B., Sami, R., Jiang, L., Li, Y., & Wang, H. (2018). Conformational and functional properties of soybean proteins produced by extrusion-hydrolysis approach. International Journal of Analytical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9182508
Malik, M. A., & Saini, C. S. (2017). Gamma irradiation of alkali extracted protein isolate from dephenolized sunflower meal. LWT, 84, 204–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.05.067
Malik, M. A., Sharma, H. K., & Saini, C. S. (2017). High intensity ultrasound treatment of protein isolate extracted from dephenolized sunflower meal: Effect on physicochemical and functional properties. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 39, 511–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.05.026
Mao, C., Wu, J., Zhang, X., Ma, F., & Cheng, Y. (2020). Improving the solubility and digestibility of potato protein with an online ultrasound-assisted pH shifting treatment at medium temperature. Foods, 9(12), 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121908
Martínez-Velasco, A., Lobato-Calleros, C., Hernández-Rodríguez, B. E., Román-Guerrero, A., Alvarez-Ramirez, J., & Vernon-Carter, E. J. (2018). High intensity ultrasound treatment of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) protein: Effect on surface properties, foaming ability and structural changes. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 44, 97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.02.007
Mehr, H. M., & Koocheki, A. (2020). Effect of atmospheric cold plasma on structure, interfacial and emulsifying properties of Grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) protein isolate. Food Hydrocolloids, 106, 105899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105899
Melchior, S., Calligaris, S., Bisson, G., & Manzocco, L. (2020). Understanding the impact of moderate-intensity pulsed electric fields (MIPEF) on structural and functional characteristics of pea, rice and gluten concentrates. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(12), 2145–2155. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11947-020-02554-2
Mir, N. A., Riar, C. S., & Singh, S. (2019). Structural modification of quinoa seed protein isolates (QPIs) by variable time sonification for improving its physicochemical and functional characteristics. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 58, 104700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104700
Motoki, K., Park, J., Spence, C., & Velasco, C. (2022). Contextual acceptance of novel and unfamiliar foods: Insects, cultured meat, plant-based meat alternatives, and 3D printed foods. Food Quality and Preference, 96, 104368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2021.104368
Nasrabadi, M. N., Doost, A. S., & Mezzenga, R. (2021). Modification approaches of plant-based proteins to improve their techno-functionality and use in food products. Food Hydrocolloids, 118, 106789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106789
Nazari, B., Mohammadifar, M. A., Shojaee-Aliabadi, S., Feizollahi, E., & Mirmoghtadaie, L. (2018). Effect of ultrasound treatments on functional properties and structure of millet protein concentrate. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 41, 382–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.10.002
North, M., Kothe, E., Klas, A., & Ling, M. (2021). How to define “Vegan”: An exploratory study of definition preferences among omnivores, vegetarians, and vegans. Food Quality and Preference, 93, 104246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2021.104246
Pednekar, M., Das, A. K., Rajalakshmi, V., & Sharma, A. (2010). Radiation processing and functional properties of soybean (Glycine max). Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 79(4), 490–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2009.10.009
Peyrano, F., Speroni, F., & Avanza, M. V. (2016). Physicochemical and functional properties of cowpea protein isolates treated with temperature or high hydrostatic pressure. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 33, 38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2015.10.014
Qin, Z., Guo, X., Lin, Y., Chen, J., Liao, X., Hu, X., & Wu, J. (2013). Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on physicochemical and functional properties of walnut (Juglans regia L.) protein isolate. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 93(5), 1105–1111. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.5857
Rahman, M. M., Byanju, B., Grewell, D., & Lamsal, B. P. (2020). High-power sonication of soy proteins: Hydroxyl radicals and their effects on protein structure. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 64, 105019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105019
Rathod, R. P., & Annapure, U. S. (2016). Effect of extrusion process on antinutritional factors and protein and starch digestibility of lentil splits. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 66, 114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.10.028
Resendiz-Vazquez, J. A., Ulloa, J. A., Urías-Silvas, J. E., Bautista-Rosales, P. U., Ramírez-Ramírez, J. C., Rosas-Ulloa, P., & González-Torres, L. (2017). Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the technofunctional properties and structure of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) seed protein isolate. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 37, 436–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.01.042
Saricaoglu, F. T. (2020). Application of high-pressure homogenization (HPH) to modify functional, structural and rheological properties of lentil (Lens culinaris) proteins. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 144, 760–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.034
Saricaoglu, F. T., Gul, O., Besir, A., & Atalar, I. (2018). Effect of high pressure homogenization (HPH) on functional and rheological properties of hazelnut meal proteins obtained from hazelnut oil industry by-products. Journal of Food Engineering, 233, 98–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.04.003
Sethi, S., Tyagi, S. K., & Anurag, R. K. (2016). Plant-based milk alternatives an emerging segment of functional beverages: a review. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 53(9), 3408–3423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2328-3
Sharafodin, H., & Soltanizadeh, N. (2022). Potential application of DBD Plasma Technique for modifying structural and physicochemical properties of Soy Protein Isolate. Food Hydrocolloids, 122, 107077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107077
Sim, S. Y. J., Srv, A., Chiang, J. H., & Henry, C. J. (2021). Plant proteins for future foods: A roadmap. Foods, 10(8), 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10081967
Sofi, B. A., Wani, I. A., Masoodi, F. A., Saba, I., & Muzaffar, S. (2013). Effect of gamma irradiation on physicochemical properties of broad bean (Vicia faba L.) starch. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 54(1), 63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2013.05.021
Yarrakula, S. A. S., Rehaman, A., & Saravanan, S. (2022). Effect of hot air assisted radio frequency technology on physical and functional properties of pearl millet. Pharma Innov J, 11(5), 633-637.
Su, J., & Cavaco-Paulo, A. (2021). Effect of ultrasound on protein functionality. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 76, 105653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105653
Subaşı, B. G., Jahromi, M., Casanova, F., Capanoglu, E., Ajalloueian, F., & Mohammadifar, M. A. (2021). Effect of moderate electric field on structural and thermo-physical properties of sunflower protein and sodium caseinate. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 67, 102593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2020.102593
Subasi, B. G., Yildirim-Elikoğlu, S., Altay, İ, Jafarpour, A., Casanova, F., Mohammadifar, M. A., & Capanoglu, E. (2022). Influence of non-thermal microwave radiation on emulsifying properties of sunflower protein. Food Chemistry, 372, 131275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131275
Sullivan, A. C., Pangloli, P., & Dia, V. P. (2018). Impact of ultrasonication on the physicochemical properties of sorghum kafirin and in vitro pepsin-pancreatin digestibility of sorghum gluten-like flour. Food Chemistry, 240, 1121–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.046
Sun, M., Mu, T., Sun, H., & Zhang, M. (2014). Digestibility and structural properties of thermal and high hydrostatic pressure treated sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) protein. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 69(3), 270–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-014-0426-9
Sun, X., Ohanenye, I. C., Ahmed, T., & Udenigwe, C. C. (2020). Microwave treatment increased protein digestibility of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) flour: Elucidation of underlying mechanisms. Food Chemistry, 329, 127196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127196
Thakur, R., Yadav, B. K., & Goyal, N. (2023). An insight into recent advancement in plant-and algae-based functional ingredients in 3D food printing ink formulations. Food and Bioprocess Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03040-1
Urbizo-Reyes, U., San Martin-González, M. F., Garcia-Bravo, J., Vigil, A. L. M., & Liceaga, A. M. (2019). Physicochemical characteristics of chia seed (Salvia hispanica) protein hydrolysates produced using ultrasonication followed by microwave-assisted hydrolysis. Food Hydrocolloids, 97, 105187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105187
Vanga, S. K., Wang, J., & Raghavan, V. (2020). Effect of ultrasound and microwave processing on the structure, in-vitro digestibility and trypsin inhibitor activity of soymilk proteins. LWT, 131, 109708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109708
Venkateswara Rao, M., CK, S., Rawson, A., & DV, C. (2021). Modifying the plant proteins techno-functionalities by novel physical processing technologies: a review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1997907
Wang, C., Yin, H., Zhao, Y., Zheng, Y., Xu, X., & Yue, J. (2021a). Optimization of high hydrostatic pressure treatments on soybean protein isolate to improve its functionality and evaluation of its application in yogurt. Foods, 10(3), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030667
Wang, L., Dong, J. L., Zhu, Y. Y., Shen, R. L., Wu, L. G., & Zhang, K. Y. (2021b). Effects of microwave heating, steaming, boiling and baking on the structure and functional properties of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) protein isolates. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 56(2), 709–720. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14706
Wang, S., Xu, X., Wang, S., Wang, J., & Peng, W. (2022a). Effects of microwave treatment on structure, functional properties and antioxidant activities of germinated Tartary buckwheat protein. Foods, 11(10), 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11101373
Wang, T., Wang, N., Li, N., Ji, X., Zhang, H., Yu, D., & Wang, L. (2022b). Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the physicochemical properties, microstructure, and stability of soy protein isolate-pectin emulsion. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 82, 105871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105871
Wang, X. S., Tang, C. H., Li, B. S., Yang, X. Q., Li, L., & Ma, C. Y. (2008). Effects of high-pressure treatment on some physicochemical and functional properties of soy protein isolates. Food Hydrocolloids, 22(4), 560–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2007.01.027
Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Li, K., Bai, Y., Li, B., & Xu, W. (2020). Effect of high intensity ultrasound on physicochemical, interfacial and gel properties of chickpea protein isolate. Lwt, 129, 109563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109563
Wani, H. M., Sharma, P., Gul, K., Bishnoi, J. P., Wani, I. A., Kothari, S. L., & Wani, A. A. (2022). Influence of Ƴ-irradiation and genotype on the structural and techno-functional properties and microbial quality of Millet flour. Applied Food Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.afres.2022.100181
Wen, C., Zhang, J., Yao, H., Zhou, J., Duan, Y., Zhang, H., & Ma, H. (2019). Advances in renewable plant-derived protein source: The structure, physicochemical properties affected by ultrasonication. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 53, 83–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.12.036
Whitnall, T., & Pitts, N. (2019). Global trends in meat consumption. Agricultural Commodities, 9(1), 96–99.
Xiang, S., Zou, H., Liu, Y., & Ruan, R. (2020). Effects of microwave heating on the protein structure, digestion properties and Maillard products of gluten. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 57(6), 2139–2149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04249-0
Xiong, T., Xiong, W., Ge, M., Xia, J., Li, B., & Chen, Y. (2018). Effect of high intensity ultrasound on structure and foaming properties of pea protein isolate. Food Research International, 109, 260–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.04.044
Yalcin, E., Sakiyan, O., Sumnu, G., Celik, S., & Koksel, H. (2008). Functional properties of microwave-treated wheat gluten. European Food Research and Technology, 227(5), 1411–1417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-008-0860-8
Yan, G., Cui, Y., Lia, D., Ding, Y., Han, J., Wang, S., ... & Zheng, H. (2022). The characteristics of soybean protein isolate obtained by synergistic modification of high hydrostatic pressure and phospholipids as a promising replacement of milk in ice cream. LWT, 160, 113223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113223
Yan, S., Xu, J., Zhang, S., & Li, Y. (2021). Effects of flexibility and surface hydrophobicity on emulsifying properties: Ultrasound-treated soybean protein isolate. Lwt, 142, 110881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.110881
Yang, J., Liu, G., Zeng, H., & Chen, L. (2018). Effects of high pressure homogenization on faba bean protein aggregation in relation to solubility and interfacial properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 83, 275–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.05.020
Yao, G., Guo, Y., Cheng, T., Wang, Z., Li, B., Xia, C., ... & Zhao, H. (2022). Effect of γ-irradiation on the physicochemical and functional properties of rice protein. Food Science and Technology, 42, e12422. https://doi.org/10.1590/fst.12422
Yin, H., Jiang, Y., Zhou, X., Zhong, Y., Wang, D., Deng, Y., & Xue, H. (2022). Effect of radio frequency, ultrasound, microwave-assisted papain, and alcalase hydrolysis on the structure, antioxidant activity, and peptidomic profile of Rosa roxburghii Tratt. seed protein. Journal of Food Science, 87(9), 4040–4055. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.16266
Yin, S. W., Tang, C. H., Wen, Q. B., Yang, X. Q., & Li, L. (2008). Functional properties and in vitro trypsin digestibility of red kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) protein isolate: Effect of high-pressure treatment. Food Chemistry, 110(4), 938–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.090
Yu, X., Huang, S., Nie, C., Deng, Q., Zhai, Y., & Shen, R. (2020). Effects of atmospheric pressure plasma jet on the physicochemical, functional, and antioxidant properties of flaxseed protein. Journal of Food Science, 85(7), 2010–2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15184
Yuanqing, H., Min, C., Lingling, S., Quancai, S., Pengyao, Y., Rui, G., ... & Haile, M. (2020). Ultrasound pretreatment increases the bioavailability of dietary proteins by dissociating protein structure and composition. Food Biophysics, 15, 409–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-020-09634-y
Zare, L., Mollakhalili-Meybodi, N., Fallahzadeh, H., & Arab, M. (2022). Effect of atmospheric pressure cold plasma (ACP) treatment on the technological characteristics of quinoa flour. LWT, 155, 112898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112898
Zhang, H., Claver, I. P., Zhu, K. X., & Zhou, H. (2011). The effect of ultrasound on the functional properties of wheat gluten. Molecules, 16(5), 4231–4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16054231
Zhang, J., Liu, L., Liu, H., Yoon, A., Rizvi, S. S., & Wang, Q. (2019). Changes in conformation and quality of vegetable protein during texturization process by extrusion. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 59(20), 3267–3280. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1487383
Zhang, L., Wang, L. J., Jiang, W., & Qian, J. Y. (2017). Effect of pulsed electric field on functional and structural properties of canola protein by pretreating seeds to elevate oil yield. LWT, 84, 73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.05.048
Zhang, Q., Cheng, Z., Zhang, J., Nasiru, M. M., Wang, Y., & Fu, L. (2021). Atmospheric cold plasma treatment of soybean protein isolate: Insights into the structural, physicochemical, and allergenic characteristics. Journal of Food Science, 86(1), 68–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15556
Zhao, G., Liu, Y., Zhao, M., Ren, J., & Yang, B. (2011). Enzymatic hydrolysis and their effects on conformational and functional properties of peanut protein isolate. Food Chemistry, 127(4), 1438–1443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.01.046
Zheng, Y., Li, Z., Zhang, C., Zheng, B., & Tian, Y. (2020). Effects of microwave-vacuum pre-treatment with different power levels on the structural and emulsifying properties of lotus seed protein isolates. Food Chemistry, 311, 125932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125932
Zhou, H., Wang, C., Ye, J., Chen, H., Tao, R., & Cao, F. (2016). Effects of high hydrostatic pressure treatment on structural, allergenicity, and functional properties of proteins from ginkgo seeds. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 34, 187–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2016.02.001
Zhu, Z., Zhu, W., Yi, J., Liu, N., Cao, Y., Lu, J., ... & McClements, D. J. (2018). Effects of sonication on the physicochemical and functional properties of walnut protein isolate. Food Research International, 106, 853–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.01.060
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Neha Goyal: writing—original draft preparation and data collection; Rishabh Thakur: writing—original draft, review, and editing; Binod Kumar Yadav: project administration, supervision, review, and final editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
We confirm that the research has been conducted ethically and responsibly. This manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by any other journal. All authors have approved the manuscript and agreed with its submission to the journal. The manuscript has been prepared according to the journal’s format as provided in the instructions for authors. There is no conflict of interest among authors regarding this article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, N., Thakur, R. & Yadav, B.K. Physical Approaches for Modification of Vegan Protein Sources: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-024-03368-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-024-03368-2