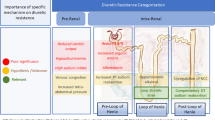
Abstract
Purpose of Review
To review the most recent data on the development of endothelin receptor antagonists (ERAs) for the treatment of hypertension and the management of diabetic nephropathy
Recent Findings
Recent reviews and meta-analyses of experimental and clinical data obtained with ERAs confirmed that endothelin receptor blockade is associated with significant decreases in blood pressure in essential hypertension but also in resistant hypertension. In addition, in patients with diabetic nephropathy, ERAs induce significant 30–40% decreases in albuminuria when administered on top of blockers of the renin-angiotensin system. Yet, the benefits of ERAs have often been limited by their tolerability profile, essentially fluid retention and the development of edema and liver toxicity. Hence, several programs have been interrupted. Today, only one ERA, aprocitentan, is still under development for the treatment of resistant hypertension. Regarding the place of ERAs in the management of diabetic nephropathy, the results of the SONAR trial with atrasentan are eagerly awaited but the recent interruption of this trial because of insufficient events is worrisome, as one might not obtain all the expected information for this major trial.
Summary
Blockade of endothelin receptor have a high potential in the treatment of hypertension and the prevention of the progression of renal diseases such as diabetic nephropathy. Today, the number of clinical programs investigating the potential benefits of ERAs is limited and more data must be obtained to define the real place of ERAs in these indications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S, Tomobe Y, Kobayashi M, Mitsui Y, et al. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988;332:411–5.
•• Davenport AP, Hyndman KA, Dhaun N, Southan C, Kohan DE, Pollock JS, et al. Endothelin. Pharmacol Rev. 2016;68:357–418. Excellent updated review on the endopthelin system.
Davenport AP. International Union of Pharmacology. XXIX. Update on endothelin receptor nomenclature. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:219–26.
Kiowski W, Luscher TF, Linder L, Buhler FR. Endothelin-1-induced vasoconstriction in humans. Reversal by calcium channel blockade but not by nitrovasodilators or endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Circulation. 1991;83:469–75.
Iglarz M, Steiner P, Wanner D, Rey M, Hess P, Clozel M. Vascular effects of endothelin receptor antagonists depends on their selectivity for ETA versus ETB receptors and on the functionality of endothelial ETB receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2015;66:332–7.
Lu YP, Tsuprykov O, Vignon-Zellweger N, Heiden S, Hocher B. Global overexpression of ET-1 decreases blood pressure—a systematic review and meta-analysis of ET-1 transgenic mice. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016;41:770–80.
Amiri F, Virdis A, Neves MF, Iglarz M, Seidah NG, Touyz RM, et al. Endothelium-restricted overexpression of human endothelin-1 causes vascular remodeling and endothelial dysfunction. Circulation. 2004;110:2233–40.
Hathaway CK, Grant R, Hagaman JR, Hiller S, Li F, Xu L, et al. Endothelin-1 critically influences cardiac function via superoxide-MMP9 cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:5141–6.
Schiffrin EL. Vascular endothelin in hypertension. Vasc Pharmacol. 2005;43:19–29.
Ergul S, Parish DC, Puett D, Ergul A. Racial differences in plasma endothelin-1 concentrations in individuals with essential hypertension. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex: 1979). 1996;28:652–5.
• Dhaun N, Moorhouse R, MacIntyre IM, Melville V, Oosthuyzen W, Kimmitt RA, et al. Diurnal variation in blood pressure and arterial stiffness in chronic kidney disease: the role of endothelin-1. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex: 1979). 2014;64:296–304. Interesting paper investigating the impact of ERA on circadian rhythm of blood pressure.
•• Yuan W, Cheng G, Li B, Li Y, Lu S, Liu D, et al. Endothelin-receptor antagonist can reduce blood pressure in patients with hypertension: a meta-analysis. Blood Press. 2017;26:139–49. First meta-analysis on the impact of ERA on blood pressure.
• Boss C, Bolli MH, Gatfield J. From bosentan (Tracleer(R)) to macitentan (Opsumit(R)): the medicinal chemistry perspective. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016;26:3381–94. Fantastic description of the chemical development of ERA.
Komers R, Gipson DS, Nelson P, Adler S, Srivastava T, Derebail VK, et al. Efficacy and safety of sparsentan compared with irbesartan in patients with primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: randomized, controlled trial design (DUET). Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2:654–64.
Krum H, Viskoper RJ, Lacourciere Y, Budde M, Charlon V. The effect of an endothelin-receptor antagonist, bosentan, on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. Bosentan hypertension investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:784–90.
Nakov R, Pfarr E, Eberle S. Darusentan: an effective endothelinA receptor antagonist for treatment of hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2002;15:583–9.
Weber MA, Black H, Bakris G, Krum H, Linas S, Weiss R, et al. A selective endothelin-receptor antagonist to reduce blood pressure in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (London, England). 2009;374:1423–31.
Bakris GL, Lindholm LH, Black HR, Krum H, Linas S, Linseman JV, Arterburn S, Sager P and Weber M. Divergent results using clinic and ambulatory blood pressures: report of a darusentan-resistant hypertension trial. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex: 1979). 2010;56:824–830.
Webb DJ. DORADO: opportunity postponed: lessons from studies of endothelin receptor antagonists in treatment-resistant hypertension. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex: 1979). 2010;56:806–7.
Sidharta PN, van Giersbergen PL, Halabi A, Dingemanse J. Macitentan: entry-into-humans study with a new endothelin receptor antagonist. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;67:977–84.
Boesen EI. Endothelin receptors, renal effects and blood pressure. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015;21:25–34.
Kohan DE, Barton M. Endothelin and endothelin antagonists in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2014;86:896–904.
Wilck N, Matus MG, Kearney SM, Olesen SW, Forslund K, Bartolomaeus H, et al. Salt-responsive gut commensal modulates TH17 axis and disease. Nature. 2017;551:585–9.
Anguiano L, Riera M, Pascual J, Soler MJ. Endothelin blockade in diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Med. 2015;4:1171–92.
Wenzel RR, Littke T, Kuranoff S, Jurgens C, Bruck H, Ritz E, et al. Avosentan reduces albumin excretion in diabetics with macroalbuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:655–64.
Mann JF, Green D, Jamerson K, Ruilope LM, Kuranoff SJ, Littke T, et al. Avosentan for overt diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:527–35.
Kohan DE, Pritchett Y, Molitch M, Wen S, Garimella T, Audhya P, et al. Addition of atrasentan to renin-angiotensin system blockade reduces albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:763–72.
Andress DL, Coll B, Pritchett Y, Brennan J, Molitch M, Kohan DE. Clinical efficacy of the selective endothelin a receptor antagonist, atrasentan, in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Life Sci. 2012;91:739–42.
de Zeeuw D, Coll B, Andress D, Brennan JJ, Tang H, Houser M, et al. The endothelin antagonist atrasentan lowers residual albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:1083–93.
Heerspink HJL, Andress DL, Bakris G, Brennan JJ, Correa-Rotter R, Dey J, et al. Rationale and protocol of the study of diabetic nephropathy with AtRasentan (SONAR) trial: a clinical trial design novel to diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;
•• Wei A, Gu Z, Li J, Liu X, Wu X, Han Y, et al. Clinical adverse effects of endothelin receptor antagonists: insights from the meta-analysis of 4894 patients from 24 randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016;5 Meta-analysis of adverse effects induced by ERAs in trials.
Macias Saint-Gerons D, de la Fuente Honrubia C, Montero Corominas D, Catala-Lopez F. Hepatotoxicity in patients treated with endothelin receptor antagonists: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Med Clin (Barc). 2014;142:333–42.
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:311–22.
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2117–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
MB has received research grants from Actelion AG, Switzerland, and Speedel AG, Switzerland.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Antihypertensive Agents: Mechanisms of Drug Action
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burnier, M. Update on Endothelin Receptor Antagonists in Hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 20, 51 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-018-0848-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-018-0848-0