Abstract
Purpose of Review
To compare the prevalence of sensitization in different countries based on specific IgE values and to evaluate the use of isolated native or recombinant allergens for diagnosis.
Recent Findings
Isolated allergens help in the diagnosis of truly sensitized patients avoiding false positives due to cross-reactions. Their use is therefore highly recommended, especially when used as a combination of several relevant allergens.
Summary
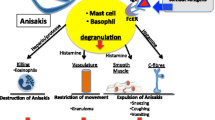
The use of purified allergens allows an accurate diagnosis and this has led to three important findings: (1) in addition to the digestive route of sensitization, occupational and non-digestive exposure seems to be clinically relevant. (2) The parasite appears as an important agent for chronic urticaria. And (3) in endemic countries, the amount of highly sensitized subjects in the general population could be as high as 7%. Adequate information to asymptomatic patients on fish consumption habits would avoid new contacts with parasite allergens and decrease their specific IgE levels and consequently the appearance of acute or chronic episodes induced by the parasite.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
van Thiel PH, van Houten H. The herring worm Anisakis marina as a human parasite outside the wall of the gastrointestinal tract. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1966;110(35):1524–8.
EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Scientific opinion on risk assessment of parasites in fishery products. EFSA J. 2010;8:1543. 91 pp
Lim H, Jung BK, Cho J, Yooyen T, Shin EH, Chai JY. Molecular diagnosis of cause of anisakiasis in humans. South Korea Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21(2):342–4. doi:10.3201/eid2102.140798.
Shimamura Y, Muwanwella N, Chandran S, Kandel G, Marcon N. Common symptoms from an uncommon infection: gastrointestinal anisakiasis. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;2016:5176502. doi:10.1155/2016/5176502.
Kasuya S, Hamano H, Izumi S. Mackerel-induced urticaria and Anisakis. Lancet. 1990;335(8690):665. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(90)90455-E.
Audicana MT, Fernández de Corres L, Muñoz D, Fernández E, Navarro JA, del Pozo MD, et al. Recurrent anaphylaxis caused by Anisakis simplex parasitizing fish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;96(4):558–60. doi:10.1016/S0091-6749(95)70301-2.
Mattiucci S, Fazii P, De Rosa A, Paoletti M, Megna AS, Glielmo A, et al. Anisakiasis and gastroallergic reactions associated with Anisakis pegreffii infection, Italy. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19(3):496–9. doi:10.3201/eid1903.121017.
Daschner A, Pascual CY. Anisakis simplex: sensitization and clinical allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;5(3):281–5.
Arcos SC, Ciordia S, Roberston L, Zapico I, Jiménez-Ruiz Y, Gonzalez-Muñoz M, et al. Proteomic profiling and characterization of differential allergens in the nematodes Anisakis simplex sensu stricto and A. pegreffii. Proteomics. 2014;14(12):1547–68. doi:10.1002/pmic.201300529.
Fæste CK, Jonscher KR, Dooper MM, Egge-Jacobsen W, Moen A, Daschner A, et al. Characterisation of potential novel allergens in the fish parasite Anisakis simplex. EuPA Open Proteom. 2014;4:140–55. doi:10.1016/j.euprot.2014.06.006.
Lorenzo S, Iglesias R, Leiro J, Ubeira FM, Ansotegui I, García M, et al. Usefulness of currently available methods for the diagnosis of Anisakis simplex allergy. Allergy. 2000;55(7):627–33. doi:10.1034/j.1398-9995.2000.00471.x.
Patelis A, Janson C, Borres MP, Nordvall L, Alving K, Malinovschi A. Aeroallergen and food IgE sensitization and local and systemic inflammation in asthma. Allergy. 2014;69(3):380–7. doi:10.1111/all.12345.
Caffarelli C, Garrubba M, Greco C, Mastrorilli C, Povesi DC. Asthma and food allergy in children: is there a connection or interaction? Front Pediatr. 2016;5(4):34. doi:10.3389/fped.2016.00034.
Scala E, Giani M, Pirrotta L, Guerra EC, Cadoni S, Girardelli CR, et al. Occupational generalised urticaria and allergic airborne asthma due to Anisakis simplex. Eur J Dermatol. 2001;11(3):249–50.
Audicana MT, Kennedy MW. Anisakis simplex: from obscure infectious worm to inducer of immune hypersensitivity. Clin Micobiol Re. 2008;21:360–79. doi:10.1128/CMR.00012-07.
Mazzucco W, Lacca G, Cusimano R, Provenzani A, Costa A, Di Noto AM, et al. Prevalence of sensitization to Anisakis simplex among professionally exposed populations in Sicily. Arch Environ Occup Health. 2012;67(2):91–7. doi:10.1080/19338244.2011.578683.
Nieuwenhuizen N, Lopata AL, Jeebhay MF, Herbert DR, Robins TG, Brombacher F. Exposure to the fish parasite Anisakis causes allergic airway hyperreactivity and dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117(5):1098–105. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2005.12.1357.
•• Mladineo I, Poljak V, Martínez-Sernández V, Ubeira FM. Anti-Anisakis IgE seroprevalence in the healthy Croatian coastal population and associated risk factors. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8(2):e2673. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002673. Analysis of IgE seroprevalence to Anisakis spp. in healthy population. A logistic univariate regression analysis confirmed that raw fish intake, daily fish intake, homemade origin of fish dish and occupational exposure were risk factors associated to Anisakis spp. sensitization.
Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO). The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. 2016. http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5555e.pdf.
•• Barbarroja-Escudero J, Sanchez-Gonzalez MJ, Antolin-Amerigo D, Rodriguez-Rodriguez M, Alvarez-Mon M. Nonoccupational airborne-induced anaphylaxis caused by Anisakis simplex. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2016;26(3):196–7. doi:10.18176/jiaci.0055. The first report of non-occupational airborne-induced anaphylaxis caused by Anisakis established by a specific inhalation challenge.
Nieuwenhuizen NE, Lopata AL. Allergic reactions to Anisakis found in fish. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014;14(8):455. doi:10.1007/s11882-014-0455-3.
Carballeda-Sangiao N, Rodríguez-Mahillo AI, Careche M, Navas A, Moneo I, González-Muñoz M. Changes over time in IgE sensitization to allergens of the fish parasite Anisakis spp. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10(7):e0004864. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0004864.
Gracia-Bara MT, Matheu V, Zubeldia JM, Rubio M, Ordoqui E, López-Sáez MP, et al. Anisakis simplex-sensitized patients: should fish be excluded from their diet? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001;86(6):679–85. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62298-3.
Baeza ML, Rodríguez A, Matheu V, Rubio M, Tornero P, de Barrio M, et al. Characterization of allergens secreted by Anisakis simplex parasite: clinical relevance in comparison with somatic allergens. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004;34(2):296–302. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.01883.x.
Alonso-Gómez A, Moreno-Ancillo A, López-Serrano MC, Suarez-de-Parga JM, Daschner A, Caballero MT, et al. Anisakis simplex only provokes allergic symptoms when the worm parasitises the gastrointestinal tract. Parasitol Res. 2004;93(5):378–84. doi:10.1007/s00436-004-1085-9.
Peñalver J, Dolores EM, Muñoz P. Absence of anisakid larvae in farmed European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) and gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) in Southeast Spain. J Food Prot. 2010;73:1332–4.
Trujillo MJ, Rodríguez A, Gracia Bara MT, Matheu V, Herrero T, Rubio M, et al. Dietary recommendations for patients allergic to Anisakis simplex. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2002;30:311–4.
Alonso A, Moreno-Ancillo A, Daschner A, López-Serrano MC. Dietary assessment in five cases of allergic reactions due to gastroallergic anisakiasis. Allergy. 1999;54(5):517–20. doi:10.1034/j.1398-9995.1999.00046.x.
Polimeno L, Loiacono M, Pesetti B, Mallamaci R, Mastrodonato M, Azzarone A, et al. Anisakiasis, an underestimated infection: effect on intestinal permeability of Anisakis simplex-sensitized patients. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010;7(7):809–14. doi:10.1089/fpd.2009.0484.
Saadatnia G, Mohamed Z, Ghaffarifar F, Osman E, Moghadam ZK, Noordin R. Toxoplasma gondii excretory secretory antigenic proteins of diagnostic potential. APMIS. 2012;120(1):47–55. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0463.2011.02810.x.
Gómez-Morales MA, Ludovisi A, Amati M, Pozio E. Validation of an excretory/secretory antigen based-ELISA for the diagnosis of Opisthorchis felineus infection in humans from low trematode endemic areas. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e62267. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062267.
Chung YB, Lee J. Clinical characteristics of gastroallergic anisakiasis and diagnostic implications of immunological tests. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014;6:228–33. doi:10.4168/aair.2014.6.3.228.
• Fitzsimmons CM, Falcone FH, Dunne DW. Helminth allergens, parasite-specific IgE, and its protective role in human immunity. Front Immunol. 2014;14(5):61. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00061. This review describes the modulation of the human immune responses by helminth parasites and compares dominant IgE-antigens in worms with clinically important environmental allergens.
Pérez-Pérez J, Fernández-Caldas E, Marañón F, Sastre J, Bernal ML, Rodríguez J, et al. Molecular cloning of paramyosin, a new allergen of Anisakis simplex. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000;123(2):120–9. doi:10.1159/000024442.
Asturias JA, Eraso E, Moneo I, Martínez A. Is tropomyosin an allergen in Anisakis? Allergy. 2000;55(9):898–9. doi:10.1034/j.1398-9995.2000.00734.x.
Rodriguez-Mahillo AI, Gonzalez-Muñoz M, Gomez-Aguado F, Rodriguez-Perez R, Corcuera MT, Caballero ML, et al. Cloning and characterisation of the Anisakis simplex allergen Ani s 4 as a cysteine-protease inhibitor. Int J Parasitol. 2007;37(8–9):907–17. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2007.01.007.
Kobayashi Y, Ishizaki S, Shimakura K, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K. Molecular cloning and expression of two new allergens from Anisakis simplex. Parasitol Res. 2007;100(6):1233–41. doi:10.1007/s00436-006-0396-4.
Kobayashi Y, Shimakura K, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K. Purification and cDNA cloning of a new heat-stable allergen from Anisakis simplex. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2007;155(2):138–45. doi:10.1016/j.molbiopara.2007.06.012.
Rodriguez-Perez R, Moneo I, Rodriguez-Mahillo A, Caballero ML. Cloning and expression of Ani s 9, a new Anisakis simplex allergen. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2008;159(2):92–7. doi:10.1016/j.molbiopara.2008.02.008.
Caballero ML, Umpierrez A, Moneo I, Rodriguez-Perez R. Ani s 10, a new Anisakis simplex allergen: cloning and heterologous expression. Parasitol Int. 2011;60(2):209–12. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2011.01.003.
Kobayashi Y, Ohsaki K, Ikeda K, Kakemoto S, Ishizaki S, Shimakura K, et al. Identification of novel three allergens from Anisakis simplex by chemiluminescent immunoscreening of an expression cDNA library. Parasitol Int. 2011;60(2):144–50. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2011.01.004.
González-Fernández J, Daschner A, Nieuwenhuizen NE, Lopata AL, Frutos CD, Valls A, et al. Haemoglobin, a new major allergen of Anisakis simplex. Int J Parasitol. 2015;45(6):399–407. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2015.01.002.
Kobayashi Y, Kakemoto S, Shimakura K, Shiomi K. Molecular cloning and expression of a new major allergen, Ani s 14, from Anisakis simplex. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2015;56(5):194–9. doi:10.3358/shokueishi.56.194.
Moneo I, Caballero ML, Rodriguez-Perez R, Rodriguez-Mahillo AI, Gonzalez-Muñoz M. Sensitization to the fish parasite Anisakis simplex: clinical and laboratory aspects. Parasitol Res. 2007;101(4):1051–5. doi:10.1007/s00436-007-0587-7.
Rodero M, Cuéllar C, Chivato T, Mateos JM, Laguna R. Western blot antibody determination in sera from patients diagnosed with Anisakis sensitization with different antigenic fractions of Anisakis simplex purified by affinity chromatography. J Helminthol. 2007;81(3):307–10. doi:10.1017/S0022149X07820220.
Shimakura K, Miura H, Ikeda K, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Shirai T, et al. Purification and molecular cloning of a major allergen from Anisakis simplex. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2004;135(1):69–75. doi:10.1016/j.molbiopara.2004.01.007.
Kobayashi Y, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K. Ani s 1, the major allergen of Anisakis simplex: purification by affinity chromatography and functional expression in Escherichia coli. Parasitol Int. 2008;57(3):314–9. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2008.01.005.
Ibarrola I, Arilla MC, Herrero MD, Esteban MI, Martínez A, Asturias JA. Expression of a recombinant protein immunochemically equivalent to the major Anisakis simplex allergen Ani s 1. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2008;18:78–83.
Lorenzo S, Romarís F, Iglesias R, Audicana MT, Alonso JM, Leiro J, et al. O-glycans as a source of cross-reactivity in determinations of human serum antibodies to Anisakis simplex antigens. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000;30(4):551–9. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2222.2000.00758.x.
Carballeda-Sangiao N, Olivares F, Rodriguez-Mahillo AI, Careche M, Tejada M, Moneo I, et al. Identification of autoclave-resistant Anisakis simplex allergens. J Food Prot. 2014;77(4):605–9. doi:10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-13-278.
Gonzalez-Muñoz M, Rodriguez-Mahillo AI, Moneo I. Different Th1/Th2 responses to Anisakis simplex are related to distinct clinical manifestations in sensitized patients. Parasite Immunol. 2010;32(1):67–73. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3024.2009.01162.x.
Rodriguez-Mahillo AI, Gonzalez-Muñoz M, Moneo I. Identification and allergenic characterisation of a new isoform of the A. simplex allergen Ani s 4. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2008;160(2):152–6. doi:10.1016/j.molbiopara.2008.04.007.
Anadón AM, Rodríguez E, Gárate MT, Cuéllar C, Romarís F, Chivato T, et al. Diagnosing human anisakiasis: recombinant Ani s 1 and Ani s 7 allergens versus the UniCAP 100 fluorescence enzyme immunoassay. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010;17:496–502. doi:10.1128/CVI.00443-09.
Martínez-Aranguren RM, Gamboa PM, García-Lirio E, Asturias J, Goikoetxea MJ, Sanz ML. In vivo and in vitro testing with rAni s 1 can facilitate diagnosis of Anisakis simplex allergy. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2014;24(6):431–8.
Lin AH, Nepstad I, Florvaag E, Egaas E, Van Do T. An extended study of seroprevalence of anti-Anisakis simplex IgE antibodies in Norwegian blood donors. Scand J Immunol. 2014;79(1):61–7. doi:10.1111/sji.12130.
Iijima S, Moriyama T, Ichikawa H, Kobayashi Y, Shiomi K. A case of an allergic reaction due to Anisakis simplex possibly after the ingestion of squid—successful detection of four A. simplex allergens, Ani s 1, Ani s 2, Ani s 12 and troponin C-like protein. Arerugi. 2012;61(8):1104–10.
Caballero ML, Umpierrez A, Perez-Piñar T, Moneo I, de Burgos C, Asturias JA, et al. Anisakis simplex recombinant allergens increase diagnosis specificity preserving high sensitivity. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012;158(3):232–40. doi:10.1159/000331581.
Carballeda-Sangiao N, Rodríguez-Mahillo AI, Careche M, Navas A, Caballero T, Dominguez-Ortega J, et al. Ani s 11-like protein is a pepsin-and heat-resistant major allergen of Anisakis spp. and a valuable tool for Anisakis allergy component-resolved diagnosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2016;169(2):108–12. doi:10.1159/000444981.
Gamboa PM, Asturias J, Martínez R, Antépara I, Jáuregui I, Urrutia I, et al. Diagnostic utility of components in allergy to Anisakis simplex. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2012;22:13–9.
Moneo I, Caballero ML, Gómez F, Ortega E, Alonso MJ. Isolation and characterization of a major allergen from the fish parasite Anisakis simplex. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;106(1Pt1):177–82. doi:10.1067/mai.2000.106732.
Cuéllar C, Daschner A, Valls A, De Frutos C, Fernández-Fígares V, Anadón AM, et al. Ani s 1 and Ani s 7 recombinant allergens are able to differentiate distinct Anisakis simplex-associated allergic clinical disorders. Arch Dermatol Res. 2012;304(4):283–8. doi:10.1007/s00403-012-1206-8.
Daschner A, Fernández-Fígares V, Rodero M, Valls A, De Frutos C, Ubeira FM, et al. Specific IgG4: possible role in the pathogenesis and a new marker in the diagnosis of Anisakis-associated allergic disease. Scand J Immunol. 2014;79(2):120–6. doi:10.1111/sji.12129.
López-Sáez MP, Zubeldia JM, Caloto M, Olalde S, Pelta R, et al. Is Anisakis simplex responsible for chronic urticaria? Allergy Asthma Proc. 2003;24(5):339–45.
Fernández-Fígares V, Rodero M, Valls A, De Frutos C, Daschner A, Cuéllar C. Positive associations between infections of Toxoplasma gondii and seropositivity with Anisakis simplex in human patients suffering from chronic urticaria. J Helminthol. 2015;89(6):707–13. doi:10.1017/S0022149X14000480.
Daschner A, Vega de la Osada F, Pascual CY. Allergy and parasites reevaluated: wide-scale induction of chronic urticaria by the ubiquitous fish-nematode Anisakis simplex in an endemic region. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2005;33:31–7.
Frezzolini A, Cadoni S, De Pitá O. Usefulness of the CD63 basophil activation test in detecting Anisakis hypersensivity in patients with chronic urticaria: diagnosis and follow-up. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:765–70. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2009.03694.x.
• Ventura MT, Napolitano S, Menga R, Cecere R, Asero R. Anisakis simplex hypersensitivity is associated with chronic urticaria in endemic areas. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013;160(3):297–300. doi:10.1159/000339869. Analysis of the association of chronic urticaria with Anisakis spp. sensitization in Italy and the beneficial effect of a 6-month diet regimen.
del Pozo MD. Estudio de la sensibilización a Anisakis simplex y su relevancia clínica como causa de urticaria o angioedema. 1998. Ph.D. thesis. University of Zaragoza, Spain.
Lopez-Saez MP, Zubeldia JM, Matheu V, Gracia MT, De Barrio M, Tornero P, et al. Sensibilización al Anisakis simplex: prevalencia en una consulta de Alergia hospitalaria de Madrid. Rev Esp Alergol Inmunol Clin. 1999;14:23–9.
Buendia E. Anisakis, anisakidosis and allergy to Anisakis. Allergy. 1997;52(5):481–2. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.1997.tb02590.x.
Kimura S, Takagi Y, Gomi K. IgE response to Anisakis simplex compared to seafood. Allergy. 1999;54:1225–6. doi:10.1034/j.1398-9995-1999.00329.x.
Abattouy N, Valero A, Martín-Sánchez J, Peñalver MC, Lozano J. Sensitization to Anisakis simplex species in the population of northern Morocco. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2012;22(7):514–9.
• Carballeda-Sangiao N, Rodríguez-Mahillo AI, Puente S, Gutiérrez MT, Moneo I, González-Muñoz M. Anisakis/Ascaris IgE ratio improves specificity for the diagnosis of Anisakis simplex sensitization in travellers and immigrants. Acta Trop. 2014;138:1–4. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2014.05.020. ROC curve analysis providing cut-off values for the specific IgE to Anisakis spp. that increase the specificity of routine tests.
Rodero I, García L, Moneo I, Caballero ML, Sanz JC, Ordobás M, et al. Seroprevalencia frente a Anisakis simplex en población adulta de la Comunidad de Madrid. Gac Sant. 2005;19(Supl 1):49.
Nieuwenhuizen NE. Anisakis—immunology of a foodborne parasitosis. Parasite Immunol. 2016;38:5548–57. doi:10.1111/plm12349.
•• Bao M, Pierce GJ, Pascual S, González-Muñoz M, Mattiucci S, Mladineo I, et al. Assessing the risk of an emerging zoonosis of worldwide concern: anisakiasis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:43699. doi:10.1038/srep43699. Development of a quantitative risk assessment for predicting the number of annual anisakiasis cases in Spain. It was elaborated using data on fishery landings, fish infection rates and consumption habits from questionnaires.
Mattiucci S, D’Amelio S. Anisakiasis. In: Bruschi F, editor. Helminth infections and their impact on global public health. Springer; 2014.
Carrascosa MF, Mones JC, Salcines-Caviedes JR, Román JG. A man with unsuspected marine eosinophilic gastritis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15(2):248. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70892-8.
Toro C, Caballero ML, Baquero M, García-Samaniego J, Casado I, Rubio M, et al. High prevalence of seropositivity to a major allergen of Anisakis simplex, Ani s 1, in dyspeptic patients. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004;11(1):115–8. doi:10.1128/CDLI.11.1.115-118.2004.
Acknowledgements
This work has been co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund and a grant from the Ministry of Economy, Industry, and Competitiveness (AGL2015-68248-C2-2-R, MINECO/FEDER).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Drs. Moneo, Carballeda-Sangiao, and González-Muñoz declare no conflicts of interest relevant to this manuscript.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Immunologic/Diagnostic Tests in Allergy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moneo, I., Carballeda-Sangiao, N. & González-Muñoz, M. New Perspectives on the Diagnosis of Allergy to Anisakis spp.. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 17, 27 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-017-0698-x
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-017-0698-x