Abstract
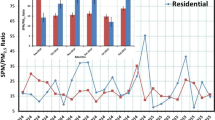
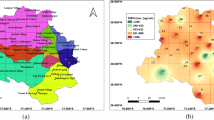
A study of temporal variations of particulate matter in different size fractions (TSP, PM10, PM2.5) was undertaken in the city of San Francisco de Campeche (SFC), in southeast Mexico, in the years 2014 and 2015 in order to assess the contribution of the chemical components. The samples were analyzed using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and ion exchange chromatography (IC) for PM10. XRF identified the presence of Al, Si, P, S, K, Ca, Ti, Cr, Mn, Fe, Cu, and Zn. The results of a cluster analysis (CA) indicates a strong correlation of S and P in the three fractions due to agricultural land use and this may be related to the burning of biomass during the dry season. Also the CA also suggests that the elements Al, Si, K, Ca, Ti, Mn, and Fe can be associated with a geological origin. The results of the IC analysis show high levels of Na+, Cl−, and SO4−2 and the latter must be related to anthropogenic sources. The application of principal components analysis (PCA) suggests that Na+, Cl− and Mg+2 are associated with marine aerosols; NO3− and SO4−2 are from emissions related to fuel combustion due to increase in the number of motor vehicles in the city.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baeza-Squiban A, Bonvallot V, Boland S, Marano F (1999) Airborne particles evoke an inflammatory response in human airway epithelium. Activation of transcription factors. Cell Biol Toxicol 15(6):375–380. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007653900063
Becker S, Dailey LA, Soukup JM, Grambow SC, Devlin RB, Huang Y-CT (2005) Seasonal variations in air pollution particle-induced inflammatory mediator release and oxidative stress. Environ Health Perspect 113(8):1032–1038. 7, 996. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.
Bernasconi G, Tajani A, Kregsamer P (2000) Manual for QXAS/AXIL. Version 3.5. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna
Cope WG (2004) Exposure classes, toxicants in air, water, soil, domestic and occupational settings. Wiley, New Jersey
de Koning HW, Smith KR, Last JM (1985) Biomass fuel combustion and health. Bull H W O 63(1):11 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2536350/
EPA (2009) Index air quality. A guide to air quality and your health. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Espinosa A, Miranda J, Pineda JC (2010) Evaluación de la incertidumbre en cantidades correlacionadas: aplicación al análisis elemental de aerosoles atmosféricos. Rev Mex Fis E 56(1):134–140 http://rmf.smf.mx/pdf/rmf-e/56/1/56_1_134.pdf
Espinosa AA, Reyes-Herrera J, Miranda J, Mercado F, Veytia MA, Cuautle M, Cruz JI (2012) Development of an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer for environmental science applications. Instrum Sci Technol 40(6):603–617. https://doi.org/10.1080/10739149.2012.693560
Flores-Rangel RM, Rodríguez-Espinosa PF, de Oca-Valero JAM, Mugica-Álvarez V, Ortiz-Romero-Vargas ME, Navarrete-López M, Dorantes-Rosales HJ, Morales-García SS (2015) Temporal variation of PM10 and metal concentrations in Tampico, Mexico. Air Qual Atmos Health 8(4):367–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-014-0291-6
Godoy MLD, Godoy JM, Artaxo P (2005) Aerosol source apportionment around a large coal fired power planta Thermoelectric Complex Jorge Lacerda, Santa Catarina, Brazil. Atmos Environ 39(29):5307–5324 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1352231005004899
Gray HA, Cass GR, Huntzicker JJ, Heyerdahl EK, Rau JA (1986) Characteristics of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon particle concentrations in Los Angeles. Environ Sci Technol 20(6):580–589. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00148a006
Gurjar BR, Butler TM, Lawrence MG, Lelieveld J (2008) Evaluation of emissions and air quality in megacities. Atmos Environ 42(7):1593–1606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.10.048
Hautman DP, Munch DJ (1997) Method 300.1 Determination of inorganic anions in drinking water by ion chromatography. EPA, Ohio
Hernández-Mena L, Saldarriaga-Noreña H, Carbajal-Romero P, Cosío-Ramírez R, Esquivel-Hernández B (2007) Ionic species associated with PM2.5 in the City of Guadalajara, México during 2007. Environ Monit Assess 161(1):281–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0745-0
INECC. (2012). Reporte final. Estudio de emisiones y actividad vehicular en Campeche, Campeche. Instituto Nacional de Ecología y Cambio Climático. INECC. Ciudad de México. https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/195212/2012_CGCSA_RSD_Campeche.pdf
INEGI. (2015). Anuario Estadístico y Geográfico por entidad federativa, 2015. vol. 1, ISBN: 978–607–739-8. Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. INEGI. Aguascualientes, México
Jaina. (2008). Boletín Informativo.. Universidad Autónoma de Campeche 19(1): 4–10. https://epomex.uacam.mx/view/paginas/13
Karson MJ (1982) Multivariate statistical methods: an introduction. Iowa State University Press, Ames
Kreidenweis SM, Remer LA, Bruintjes R, Dubovik O (2001) Smoke aerosol from biomass burning in Mexico: hygroscopic smoke optical model. J Geophys Res Atmos 106(D5):4831–4844. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD900488
Kumar R, Elizabeth A, Gawane AG (2006) Air quality profile of inorganic ionic composition of fine aerosols at two sites in Mumbai City. Aerosol Sci Technol 40(7):477–489. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786820600672726
Lê S, Josse J, Husson F et al (2008) FactoMineR: an R package for multivariate analysis. J Stat Softw 25(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v025.i01
Liu Y, Villalba G, Ayres RU, Schroder H (2008) Global phosphorus flows and environmental impacts from a consumption perspective. J Ind Ecol 12(2):229–247. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9290.2008.00025.x
Maechler M, Rousseeuw P, Struyf A, Hubert M, Hornik K (2012) Cluster: cluster analysis basics and extensions. R package. Version 2.0. 1. 1, 56
Mancilla Y, Herckes P, Fraser MP, Mendoza A (2015) Secondary organic aerosol contributions to PM2.5 in Monterrey, Mexico: temporal and seasonal variation. Atmos Res 153:348–359 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169809514003664
Martínez MA, Caballero P, Carrillo O, Mendoza A, Mejia GM (2012) Chemical characterization and factor analysis of PM2.5 in two sites of Monterrey, Mexico. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 62(7):817–827. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2012.681421
Minguillón MC, Campos AA, Cárdenas B, Blanco S, Molina LT, Querol X (2014) Mass concentration, composition and sources of fine and coarse particulate matter in Tijuana, Mexico, during Cal-Mex campaign. Atmos Environ 88:320–329 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/ S1352231013007206
Miranda J, Barrera VA, Espinosa AA, Galindo OS, Núñez-Orosco A, Montesinos RC, Leal-Castro A, Meinguer J (2004) PIXE analysis of atmospheric aerosols from three sites in Mexico City. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect B 219-220:157–160 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/ S0168583X04000734
Miranda J, Barrera VA, Espinosa AA, Galindo OS, Meinguer J (2005) PIXE analysis of atmospheric aerosols in Mexico City. X-Ray Spectrom 34(4):315–319 https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/ d oi/abs/10.1002/xrs.823
Moyers JL, Ranweiler LE, Hopf SB, Korte NE (1977) Evaluation of particulate trace species in southwest desert atmosphere. Environ Sci Technol 11(8):789–795. https://doi.org/10.1021/es60131a002
Pope CA III, Burnett RT, Thun MJ (2002) Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 287(9):1132–1141. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.287.9.1132
Reyes J, Bartolo-Pérez P, Cauich W, Huerta Quintanilla DA, Hermośın B, Pérez T (2009) Análisis morfológico y qúımico de costras de deterioro de edificios históricos mediante SEM/EDX. Acta Microsc 18(2):185–194 http://digital.csic.es/bitstream/10261/47227/1/An%c3%a1lisis%20morfol%c3%b3gico%20y%20qu%c3%admico%20de%20costras%20de%20deterioro.pdf
Reyes J, Silva I, Pérez T, Corvo F, Mart́ınez W, Alonso-Guzmán EM, Quintana P (2012) El deterioro del Baluarte de San Pedro, un estudio de caso. Revista ALCONPAT 2(3):161–173. https://doi.org/10.21041/ra.v2i3.35
Rodríguez-Espinosa PF, Flores-Rangel RM, Múgica-Alvárez V, Morales-García SS (2017) Sources of trace metals in PM10 from a petrochemical industrial complex in Northern Mexico. Air Qual Atmos Health 10(1):69–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-016-0409-0
Samoli E, Peng R, Ramsay T, Pipikou M, Touloumi G, Dominici F, Burnett R, Cohen A, Krewski D, Samet J, Katsouyanni K (2008) Acute effects of ambient particulate matter on mortality in Europe and North America: results from the APHENA study. Environ Health Perspect 116(11):1480–1486. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.11345
SEMARNAT (1993) Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-035-SEMARNAT-1993. Que establece los métodos de medición para determinar la concentración de partículas suspendidas totales en el aire ambiente y el procedimiento para la calibración de los equipos de medición. Secretaría del Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales. Diario Oficial de la Federación. 18 de octubre de 1993, Ciudad de México. http://www.aire.cdmx.gob.mx/descargas/monitoreo/normatividad/NOM-035-SEMARNAT-1993.pdf
Spurny KR (1999) Analytical chemistry of aerosols: science and technology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
SSA (2014) Secretaría de Salud Ambiental. NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-025-SSA1–2014, Salud ambiental. Valores ĺımite permisibles para la concentración de part́ıculas suspendidas PM10 y PM2. 5 en el aire ambiente y criterios para su evaluación. Al margen un sello con el Escudo Nacional, que dice: Estados Unidos Mexicanos. Secretaría de Salud. Diario Oficial de la Federación. 3 de abril de 2014. Ciudad de México
Vega E, Reyes E, Ruiz H, García J, Sánchez G, Martínez-Villa G, González U, Chow JC, Watson JG (2004) Analysis of PM2.5 and PM10 in the atmosphere of Mexico City during 2000-2002. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 54(7):786–798. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2004.10470952
Wang X, Bi X, Sheng G, Fu J (2006) Chemical composition and sources of PM10 and PM2.5 aerosols in Guangzhou, China. Environ Monit Assess 119(1):425–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9034-3
WHO (2006) Air quality guidelines. Global update 2005. Particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide. World Health Organization, Copenhagen
Yokelson RJ, Crounse JD, DeCarlo PF, Karl T, Urbanski SP, Atlas E, Weinheimer A (2009) Emissions from biomass burning in the Yucatan. Atmos Chem Phys 9(15):5785–5812. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-5785-2009
Yongming H, Peixuan D, Junji C, Posmentier ES (2006) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci Total Environ 355(1):176–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.02.026
Acknowledgments
The support from CONACyT Mexico under the program of CATEDRAS for “Jóvenes Investigadores” is acknowledged. The authors thank J.C. Pineda for X-ray spectrometer operation, DGAPA-UNAM IN-102615, and the CONACyT-279740-LANCIC project. The author acknowledges Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales of Campeche (SEMARNATCAM) for lending the devices for the sampling.
Funding
This work was supported by the “Cátedras-CONACYT” program (project no. 1854). and at Dirección General de Asuntos del Personal Académico (DGAPA), Universidad Nacional Autónoma de Mexico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Espinosa, A.A., Miranda, J., Hernández, E. et al. Temporal variation of suspended particles (TSP, PM10, and PM2.5) and chemical composition of PM10 in a site at the coast of the Gulf of Mexico. Air Qual Atmos Health 12, 1267–1277 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-019-00730-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-019-00730-8