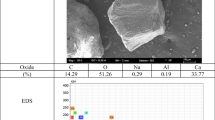
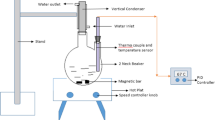
Abstract
Titanomagnetite concentrate is known for the difficulty of its sintering by traditional sintering process (TSP) because of a high content of TiO2. In this study, the feasibility study of blast furnace burden preparation was carried out by composite agglomeration process (CAP). The work in this study focuses on the effects of titanomagnetite concentrate ratio, composite basicity, and coke breeze dosage on agglomeration indexes of CAP. The calculation results of the pneumatics of sintered bed show that CAP optimizes the particle size distribution of the mixed feed and increases the voidage of the material layer, which improves the permeability index. Under the following experimental conditions (coke breeze dosage of 3.8 wt.%, pelletized feed proportion of 25%, and composite basicity of 1.76), a sintering yield of 73.60%, productivity of 1.58t·(m2 h), and RDI+3.15 of 76.76% have been achieved by CAP, which were 12.10%, 49.06%, and 16.71% higher than those by TSP, respectively. Under same conditions of composite basicity, agglomeration technical indexes of CAP are obviously better than those of TSP. CAP is an effective method to produce low-basicity sinter, which can reduce the proportion of acid pellets that cost more in blast furnace burden.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Naito, K. Takeda, and Y. Matsui, ISIJ Int. 55, 7 (2015).
X. Lv, Z. Lun, J. Yin, and C. Bai, ISIJ Int. 53, 1115 (2013).
P.R. Taylor, S.A. Shuey, E.E. Vidal, and J.C. Gomez, Min. Metall. Explor. 23, 80 (2006).
S. Samanta, M.C. Goswami, T.K. Baidya, S. Mukherjee, and R. Dey, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 20, 917 (2013).
Z. Yu, G. Li, T. Jiang, Y. Zhang, F. Zhou, and Z. Peng, ISIJ Int. 55, 907 (2015).
A. Dehghanmanshadi, J. Manuel, S. Hapugoda, and N. Ware, ISIJ Int. 54, 2189 (2014).
N.J. Bristow, and C.E. Loo, ISIJ Int. 32, 819 (1992).
S. Ren, J. Zhang, L. Wu, B. Su, X. Xing, and G. Zhu, Ironmak. Steelmak. 41, 132 (2014).
M. Zhou, T. Jiang, S. Yang, and X. Xue, Int. J. Miner. Process. 142, 125 (2015).
M. Zhou, S. Yang, T. Jiang, and X. Xue, Ironmak. Steelmak. 42, 217 (2015).
J. Tang, M. Chu, and X. Xue, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 22, 371 (2015).
X. Chen, Y. Huang, X. Fan, and M. Gan, J. Cent. South Univ. Sci. Technol. 47, 359 (2016).
J. Zhang, G. Yang, H. Guo, Y. Shao, J. Li, and Y. Wen, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 35, 41 (2013).
T. Jiang, G. Li, H. Wang, K. Zhang, and Y. Zhang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 37, 1 (2010).
F. Gu, Y. Zhang, G. Li, Q. Zhong, J. Luo, Z. Su, M. Rao, Z. Peng, and T. Jiang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27, 1363 (2020).
G. Li, C. Liu, Z. Yu, M. Rao, Q. Zhong, Y. Zhang, and T. Jiang, Energies 11, 2382 (2018).
G. Li, J. Zeng, T. Jiang, Q. Li, Y. Yang, R. Wang, and H. Wu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 16, 149 (2009).
Y. Zhang, B. Liu, L. Xiong, G. Li, and T. Jiang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 44, 532 (2017).
Y. Zhang, M. Du, Z. Su, G. Li, and T. Jiang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 45, 566 (2018).
Y. Lu, S. Wu, H. Zhou, L. Ma, Z. Liu, and Y. Wang, ISIJ Int. 61, 2211 (2021).
Y. Lu, S. Wu, L. Niu, Z. Liu, H. Zhou, Z. Hong, and S. Song, Ironmak. Steelmak. 48, 477 (2020).
Z. Yuan, L. Li, Y. Han, L. Liu, and T. Liu, J. Cent. South Univ. 23, 2838 (2016).
S. Wu, L. Wang, Y. Lu, and K. Gu, Steel Res. Int. 89, 1800041 (2018).
S. AI-Jaroudi, A. UI-Hamid, A. Mohammed, and S. Saner, Powder Technol. 175, 115 (2007).
F.H. Chung, J. Appl. Cryst. 7, 519 (1974).
N.A. Webster, M.I. Pownceby, I.C. Madsen, A.J. Studer, J.R. Manuel, and J.A. Kimpton, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45, 2097 (2014).
X. Zhang, Q. Zhong, C. Liu, M. Rao, Z. Peng, G. Li, and T. Jiang, Sci. Rep. 11, 1 (2021).
S. Ergun, Chem. Eng. Prog. 48, 89 (1952).
T. Jiang, Technical manual of sintering and pelletizing production (Metallurgical Industry Press, 2014), p65.
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to express their thanks to National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 22021YFC2902301) for the financial support for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Zhou, H., Yuan, F. et al. Study on Feasibility and Superiority of Preparing TiO2-Rich Burdens by Composite Agglomeration Process. JOM 75, 3424–3434 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05998-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05998-x