Abstract
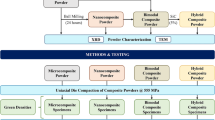
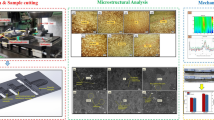
Metal matrix composites with superior mechanical and fatigue properties are in great industrial demand. In the present study, a two-step stir casting method and T6 heat treatment were implemented to fabricate Al7075-SiC composites. SiC particles of varying content and size (nano, submicron, and micron) were added to the Al7075 matrix. Tensile strength and fatigue properties of the fabricated composites were then evaluated. Results showed that addition of SiC particles into the matrix increased tensile and fatigue strength. In contrast, the elongation of samples decreased. Samples reinforced with nanoparticles showed better tensile and fatigue properties compared with the other composites (submicron and micron reinforcement). It was observed that Al7075 reinforced with 1% weight percentage of SiC nanoparticles improved the ultimate tensile strength and fatigue strength of pure Al7075 samples by 21.33% and 66%, respectively. However, further addition of reinforcing particles above a certain limit resulted in a decrease in tensile strength.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Bhaduri, Mechanical Properties and Working of Metals and Alloys (Springer Singapore, Singapore, 2018), pp 317–371.
K.R. Kashyzadeh, S.S. Rahimian Koloor, M. Omidi Bidgoli, M. Petrů, and A. Amiri Asfarjani, Polymers 13, 483 (2021).
S. Setia and S.R. Chauhan, Silicon 13, 4681–4701 (2021).
T. Feister, H. Kim, A. Gwinn, T. Schiller, and M. Austin, In: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, (IOP Publishing, 2018), p. 012024.
J. Xia, J.J. Lewandowski, and M.A. Willard, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 770, 138518 (2020).
M. Karthik, C. Honnaiah, S.A. Prasad and M. Srinath, In: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, (IOP Publishing, 2018), p. 012068.
D. Davidson, Eng. Fract. Mech. 33, 965 (1989).
N. Chawla, J. Jones, C. Andres, and J. Allison, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 29, 2843 (1998).
J.N. Hall, J.W. Jones, and A.K. Sachdev, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 183, 69 (1994).
Z. Chen, and K. Tokaji, Mater. Lett. 58, 2314 (2004).
S. Shin, and D. Bae, Compos. B Eng. 134, 61 (2018).
C. Kaynak, and S. Boylu, Mater. Des. 27, 776 (2006).
G. Majzoobi, H. Bakhtiari, A. Atrian, M. Pipelzadeh, and S. Hardy, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 230, 375 (2016).
A. Mamoon and A. Al-Jaafari, In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, (IOP Publishing: 2020), p. 012159.
P.R.M. Raju, S. Rajesh, K.S.R. Raju, and V.R. Raju, Mater. Today Proc. 4, 3188 (2017).
J. Schijve, Fatigue of Structures and Materials (Springer Science & Business Media, New York, 2001).
S. Beden, S. Abdullah, and A. Ariffin, Eur. J. Sci. Res. 28, 364 (2009).
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Sect. Three Met. Test Methods Anal. Proced 3, 628 (2002).
J.O. Almen, and P.H. Black, Residual Stresses and Fatigue in Metals (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1963).
O.J. Horger and J. Maulbetsch, J. Appl. Mech. 3(4), A147–A148 (1936).
A. Sanaty-Zadeh, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 531, 112 (2012).
T. Sritharan, L. Chan, L. Tan, and N. Hung, Mater. Charact. 47, 75 (2001).
M. Malaki, A.F. Tehrani, and B. Niroumand, Ceram. Int. 46(15), 23326–23336 (2020).
C. Goh, J. Wei, L. Lee, and M. Gupta, Acta Mater. 55, 5115 (2007).
C. Goh, J. Wei, L. Lee, and M. Gupta, Compos. Sci. Technol. 68, 1432 (2008).
S.K. Soni, and B. Thomas, Mater. Res. Express 6, 1265f3 (2020).
S.K. Soni, D. Ganatra, P. Mendiratta, C. Reddy, and B. Thomas, Met. Mater. Int. 1 (2021).
P. Agarwal, A. Kishore, V. Kumar, S.K. Soni, and B. Thomas, Eng Res Express 1, 015004 (2019).
M. Sijo, and K. Jayadevan, Procedia Technol. 24, 379 (2016).
J. Hashim, L. Looney, and M. Hashmi, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 119, 324 (2001).
J. Hashim, L. Looney, and M.S.J. Hashmi, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 119, 329 (2001).
M. Singla, D.D. Dwivedi, L. Singh, and V. Chawla, J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 8, 455 (2009).
P.K. Jain, P. Baredar, and S. Soni, Mater. Today Proc. 26, 2740 (2020).
(ASM).
J. LLorca, Progress Mater. Sci. 47, 283–353 (2002).
S.H. Anand and N. Venkateshwaran, Biomass Convers. Biorefinery, 1 (2021).
V.K. Dwivedi, S.P. Dwivedi, and R. Yadav, Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2020.1829955
A. Standard, West Conshohocken: ASTM International (2016).
P. Raghuvaran, J. Baskaran, C. Aagash, A. Ganesh, and S.G. Krishna, Mater. Today Proc. 45, 1914 (2021).
A. Atrian, G. Majzoobi, M. Enayati, and H. Bakhtiari, Adv. Powder Technol. 26, 73 (2015).
A. Slipenyuk, V. Kuprin, Y. Milman, V. Goncharuk, and J. Eckert, Acta Mater. 54, 157 (2006).
J. Hashim, L. Looney, and M. Hashmi, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 92, 1 (1999).
Funding
The authors declare that this research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Bakhtiari, H., Zhou, J. et al. Investigating the Effect of Reinforcing Particles Size and Content on Tensile and Fatigue Properties of Heat-Treated Al7075-SiC Composites Fabricated by the Stir Casting Method. JOM 74, 1859–1869 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05248-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05248-6