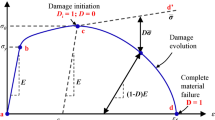
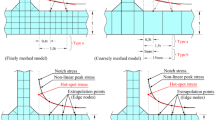
Abstract
We used the split Hopkinson dynamic impact test and ABAQUS finite element simulation to study the damage mechanism of dynamic impacts on the 7055-T4 aluminum alloy. The results show that the energy absorption phenomenon occurs when the dynamic impact temperature is 220°C. There is a clear positive correlation between the size of the precipitated phase and the dynamic impact temperature. The regression effect of the 7055-T4 aluminum alloy is most obvious when the dynamic impact temperature is 320°C. The adiabatic temperature rise model in the dynamic impact shear zone and the damage model considering the adiabatic temperature increase are established. Moreover, the above model has high accuracy and is verified by projectile impact simulation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Yang, X. Li, C. Xu, L. Zhang, Q. Zhang, and X. Tong, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 21, 197 (2012).
Y. Yang, Z. Zhang, X. Li, Q. Wang, and Y. Zhang, Mater. Des. 51, 592 (2013).
M. Tajally, Z. Huda, and H.H. Masjuki, Int. J. Impact Eng. 37, 425 (2010).
Y. Cao, A. Feng, and G. Hua, J. Appl. Phys. 116, 775 (2014).
P. Zhang and Y. Wang, Vacuum 152, 150 (2018).
A.S. Mahdi, M.S. Mustapa, A.L.M. Tobi, and I. Zaman, Mater. Sci. Forum 887, 74 (2017).
K. Labisz, T. Tański, D. Janicki, W. Borek, K. Lukaszkowicz, and L. Dobrzański, Arch. Metall. Mater. 61, 741 (2016).
K.K. Babu, K. Panneerselvam, P. Sathiya, A.N. Haq, S. Sundarrajan, P. Mastanaiah, and C.V. Srinivasa Murthy, Mater. Today Proc. 4, 285 (2017).
P. Zhang and Y. Wang, Vacuum 151, 243 (2018).
J. Konieczny, K. Labisz, M. Polokrubiniec, and A. Włodarczykfligier, Arch. Metall. Mater. 61, 1337 (2016).
M. Qi, C. Luo, H. He, Y. Wang, D. Fan, and S. Yan, J. Appl. Phys. 111, 043506 (2012).
J.Z. Lu, K.Y. Luo, Y.K. Zhang, J.Z. Zhou, X.G. Cui, L. Zhang, and J.W. Zhong, Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 528, 730 (2010).
L. Oger, E. Andrieu, G. Odemer, L. Peguet, and C. Blanc, Mater. Sci. Forum 877, 1107 (2017).
Z. Zhan, W. Hu, Q. Meng, and S. Shi, Int. J. Damage Mech. 25, 342 (2016).
C. Su, J. Zhou, X. Meng, and S. Huang, Materials 9, 799 (2016).
B. Çevik, Y. Özçatalbaş, and B. Gülenç, Prakt. Metallogr-PR M 53, 6 (2016).
R. Singh, R.K. Khatirkar, R.N. Chouhan, and S.G. Sapate, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 69, 1 (2016).
M. Sharma, G.K. Gupta, R. Dasgupta, M. Kumar, and P. Kumar, Trans. Indian Inst. Met 36, 1 (2018).
J.M. Liang, C. Kong, M.Z. Quadir, Y.F. Zheng, X. Yao, P. Munroe, and D.L. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 658, 192 (2016).
A. Kumar, A. Patnaik, and I.K. Bhat, Powder Metall. 125, 1 (2017).
D. Bolibruchová, L. Richtárech, S.M. Dobosz, and K. Majorgabryś, Arch. Metall. Mater. 62, 339 (2017).
W.S. Lee, W.C. Sue, C.F. Lin, and C.J. Wu, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 100, 116 (2000).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of the China Youth Fund and the First Project (No. 51705270), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51575289), Shandong Natural Science Foundation Doctoral Fund (No. ZR2016EEP03) and A Project of the Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (No. J17KA0031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Wang, Y., Luo, H. et al. Research on the Large Plastic Deformation Damage and Shock Resistance of 7055 Aluminum Alloy. JOM 71, 2380–2387 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03477-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03477-w