Abstract
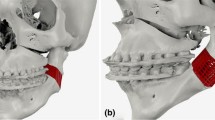
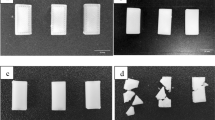
The aim of this work was to manufacture 70/30 poly-l-dl-lactic acid (PLDLLA) filaments for three-dimensional (3D) printers by using the extrusion technique and to study the properties of filaments and printed plates for surgical fracture stabilization. Different extrusion methodologies were tested and filaments were analyzed in terms of homogeneity, accuracy diameter, finishing surface morphology, and chemical degradation. X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry showed that the filaments have less crystallinity than does the raw material. Infrared and thermogravimetric analysis showed no evidence of chemical degradation. Surgical plates made with the filaments revealed small changes in the material properties after the printing process. PLDLLA filament extrusion and 3D printing are a promising way to satisfy the demand of implantable bioabsorbable products.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Pruitt and J. Furmanski, JOM 61, 14 (2009).
D. Garlotta, J. Pol. Environ. 9, 63 (2002).
P.I.J.M. Wuisman and T.H. Smit, Eur. Spine J. 15, 133 (2006).
T.H. Smit, T.A.P. Engels, P.I.J.M. Wuisman, and L.E. Govaert, Spine 33, 14 (2008).
M.S. Park, H.E. Aryan, B.M. Ozgur, R. Jandial, and W.R. Taylor, Neurosurgery 54, 631 (2004).
M.R. Krijnen, M.G. Mullender, T.H. Smit, V. Everts, and P.I.J.M. Wuisman, Spine 31, 1559 (2006).
K.A. Thomas, J.M. Toth, N.R. Crawford, H.B. Seim, L.L. Shi, M.B. Harris, and A.S. Turner, Spine 33, 734 (2008).
M.J. Kaab, B.A. Rahn, A. Weiler, R. Curtis, S.M. Perren, and E. Schneider, Int. J. Care Inj. 33, 37 (2002).
L.R. Holmes and J.C. Riddick, JOM 66, 270 (2014).
H. Xu, D. Han, J.-S. Dong, G.-X. Shen, G. Chai, Z.-Y. Yu, and W.-J. Lang, Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 6, 66 (2010).
S. Shaffer, K. Yang, J. Vargas, M.A. Di Prima, and W. Voit, Polymer 55, 5969 (2014).
J.J. Cooper-White and M.E. Mackay, J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 37, 1803 (1999).
T. Villmow, B. Kretzschmar, and P. Potschke, Compos. Sci. Technol. 70, 2045 (2010).
S. Zepnik, S. Kabasci, R. Kopitsky, H.-J. Radusch, and T. Wodke, Polymer 5, 873 (2013).
A.D. Messias, K.F. Martins, A.C. Motta, and E.A.R. Duek, Int. J. Biomater. 2014, 1 (2014).
T. Miyata and T. Masuko, Polymer 39, 5515 (1998).
F. Signori, M.-B. Coltelli, and S. Bronco, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 94, 74 (2009).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor Ronaldo de Biasi for reading and considerably improving the manuscript and the Carlos Chagas Foundation for Research Support from the Rio de Janeiro State (FAPERJ) and the National Council of Technological and Scientific Development from Brazilian Government (CNPq) for supporting this study via the following grants: E-26/201.759/2015, E-26/201.828/2015, E-26/010.001.262/2015, and 449472-2014-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, D.J., Vidal, R., da Silva, L.P. et al. Development of 70/30 Poly-l-dl-Lactic Acid Filaments for 3D Printers (Part 1): Filament Manufacturing and Characterization of Printed Samples for Use as Bioabsorbable Products. JOM 69, 71–77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-2168-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-2168-7