Abstract
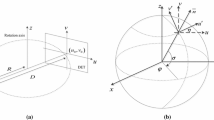
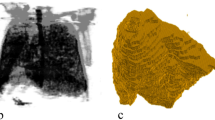
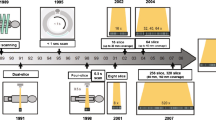
In the clinical research, three-dimensional/volumetric anatomical structure of the human body is very significant for diagnosis, computer-aided surgery, surgical planning, patient follow-up, and biomechanical applications. Medical imaging procedures including MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), CT (Computed Tomography), and CBCT (Cone-beam computed tomography) have certain drawbacks such as radiation exposure, availability, and cost. As a result, 3D reconstruction from 2D X-ray images is an alternative way of achieving 3D models with significantly low radiation exposure to the patient. The purpose of this study is to provide a comprehensive view of 3D image reconstruction methods using X-ray images, and their applicability in the various anatomical sections of the human body. This study provides a critical analysis of the computational methods, requirements and steps for 3D reconstruction. This work includes a comparative critical analysis of the state-of-the-art approaches including the feature selection along with their benefits and drawbacks. This review motivates the researchers to work for 3D reconstruction using X-ray images as only a limited work is available in the area. It may provide a solution for many experts who are looking for techniques to reconstruct 3D models from X-ray images for clinical purposes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta A, Kharbanda OP, Sardana V, Balachandran R, Sardana HK (2015) A knowledge-based algorithm for automatic detection of cephalometric landmarks on cbct images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 10:1737–1752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1173-6
Gupta A, Kharbanda OP, Sardana V, Balachandran R, Sardana HK (2016) Accuracy of 3d cephalometric measurements based on an automatic knowledge-based landmark detection algorithm. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11:1297–1309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1334-7
Henderson R (1995) The potential and limitations of neutrons, electrons and X-rays for atomic resolution microscopy of unstained biological molecules. Q Rev Biophys 28:171–193. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003358350000305X
Gupta A, Kharbanda O, Balachandran R, Sardana V, Kalra S, Chaurasia S, Sardana H (2017) Precision of manual landmark identification between as-received and oriented volume-rendered cone-beam computed tomography images. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 151:118–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.06.027
Gupta A (2020) Challenges for computer aided diagnostics using X-ray and tomographic reconstruction images in craniofacial applications. Int J Comput Vis Robot 10:11. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJCVR.2020.10029170
Ehlke M. 3d reconstruction of anatomical structures from 2d X-ray images. Doctoral Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin
Tomazevic D, Likar B, Pernus F (2006) 3-d/2-d registration by integrating 2-d information in 3-d. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 25:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2005.859715
Neelapu BC, Kharbanda OP, Sardana V, Gupta A, Vasamsetti S, Balachandran R, Rana SS, Sardana HK (2017) A pilot study for segmentation of pharyngeal and sino-nasal airway subregions by automatic contour initialization. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 12:1877–1893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1650-1
Neelapu BC, Kharbanda OP, Sardana V, Gupta A, Vasamsetti S, Balachandran R, Sardana HK (2018) Automatic localization of three-dimensional cephalometric landmarks on cbct images by extracting symmetry features of the skull. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 47:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20170054
Neelapu BC, Kharbanda OP, Sardana HK, Gupta A, Vasamsetti S, Balachandran R, Rana SS, Sardana V (2017) The reliability of different methods of manual volumetric segmentation of pharyngeal and sinonasal subregions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 124:577–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2017.08.020
Tu JY, Inthavong K, Ahmadi G (2013) Computational fluid and particle dynamics in the human respiratory system. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4488-2
(2017) What are the top 5 benefits of advanced medical imaging? https://www.trivitron.com/blog/what-are-the-top-5-benefits-of-advanced-medical-imaging/. Accessed 2 Mar 2017
What is diagnostic imaging? https://www.healthimages.com/what-is-diagnostic-imaging/
Li L, Wu W, Yan G, Liu L, Liu H, Li G, Li J, Liu D (2016) Analogue simulation of pharyngeal airflow response to twin block treatment in growing patients with class ii1 and mandibular retrognathia. Sci Rep 6:26012. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26012
Huang R, Li X, Rong Q (2013) Control mechanism for the upper airway collapse in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a finite element study. Sci China Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-013-4448-6
Stytz MR, Frieder G, Frieder OJACS (1991) Three-dimensional medical imaging: algorithms and computer systems. ACM Comput Surv 23:421–499
Humbert L, De Guise JA, Aubert B, Godbout B, Skalli W (2009) 3d reconstruction of the spine from biplanar X-rays using parametric models based on transversal and longitudinal inferences. Med Eng Phys 31:681–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2009.01.003
Chaibi Y, Cresson T, Benjamin A, Hausselle J, Neyret P, Hauger O, de Guise J, Skalli W (2012) Fast 3d reconstruction of the lower limb using a parametric model and statistical inferences and clinical measurements calculation from biplanar X-rays. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 15:457–466. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2010.540758
Cresson T, Chav R, Branchaud D, Humbert L, Godbout B, Aubert B, Skalli W, De Guise JA (2009) Coupling 2d/3d registration method and statistical model to perform 3d reconstruction from partial X-rays images data. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009:1008–1011. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5333869
Gupta A (2019) Current research opportunities of image processing and computer vision. Comput Sci 20:387–410. https://doi.org/10.7494/csci.2019.20.4.3163
Trivedi M, Gupta A (2022) A lightweight deep learning architecture for the automatic detection of pneumonia using chest X-ray images. Multimed Tools Appl 81:5515–5536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11807-x
Pandey M, Gupta A (2021) A systematic review of the automatic kidney segmentation methods in abdominal images. Biocybern Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2021.10.006
Ashok M, Gupta A (2021) A systematic review of the techniques for the automatic segmentation of organs-at-risk in thoracic computed tomography images. Arch Comput Methods Eng 28:3245–3267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-020-09497-z
Maken P, Gupta A (2021) A method for automatic classification of gender based on text- independent handwriting. Multimed Tools Appl 80:24573–24602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10837-9
Maken P, Gupta A, Gupta MK (2019) A study on various techniques involved in gender prediction system: a comprehensive review. Cybern Inf Technol 19:51–73. https://doi.org/10.2478/cait-2019-0015
Kasten Y, Doktofsky D, Kovler I (2020) End-to-end convolutional neural network for 3d reconstruction of knee bones from bi-planar X-ray images. Machine learning for medical image reconstruction. Springer, Cham, pp 123–133
Dixit S, Pai VG, Rodrigues VC, Agnani K, Priyan SRV (2019) 3d reconstruction of 2d X-ray images. In: 2019 4th International Conference on Computational Systems and Information Technology for Sustainable Solution (CSITSS). pp 1–5
Akkoul S, Hafiane A, Rozenbaum O, Lespessailles E, Jennane R (2017) 3d reconstruction of the proximal femur shape from few pairs of X-ray radiographs. Signal Process 59:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2017.03.014
Kim H, Lee K, Lee D, Baek N (2019) 3d reconstruction of leg bones from X-ray images using cnn-based feature analysis. In: 2019 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC). pp 669–672
Karade V, Ravi B (2015) 3d femur model reconstruction from biplane X-ray images: a novel method based on Laplacian surface deformation. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 10:473–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1097-6
Ehlke M, Ramm H, Lamecker H, Hege HC, Zachow S (2013) Fast generation of virtual X-ray images for reconstruction of 3d anatomy. IEEE Trans Visual Comput Graphics 19:2673–2682. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvcg.2013.159
Zhu Z, Li G (2011) Construction of 3d human distal femoral surface models using a 3d statistical deformable model. J Biomech 44:2362–2368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2011.07.006
Koh K, Kim YH, Kim K, Park WM (2011) Reconstruction of patient-specific femurs using X-ray and sparse ct images. Comput Biol Med 41:421–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2011.03.016
Zheng G (2010) Statistical shape model-based reconstruction of a scaled, patient-specific surface model of the pelvis from a single standard ap X-ray radiograph. Med Phys 37:1424–1439. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3327453
Zheng G (2009) Statistical deformable model-based reconstruction of a patient-specific surface model from single standard X-ray radiograph. Springer, Berlin, pp 672–679
Zheng G (2009) Statistically deformable 2d/3d registration for accurate determination of post-operative cup orientation from single standard X-ray radiograph. Springer, Berlin, pp 820–827
Gamage P, Xie SQ, Delmas P, Xu P (2009) 3d reconstruction of patient specific bone models from 2d radiographs for image guided orthopedic surgery. In: 2009 digital image computing: techniques and applications. pp 212–216
Gunay M, Shim MB, Shimada K (2007) Cost- and time-effective three-dimensional bone-shape reconstruction from X-ray images. Int J Med Robot. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.162
Mahfouz M, Badawi A, Abdel Fatah E, Kuhn M, Merkl B (2006) Reconstruction of 3d patient-specific bone models from biplanar X-ray images utilizing morphometric measurements. In: Proceedings of the 2006 international conference on image processing, computer vision, & pattern recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, pp 26–29
Lamecker H, Wenckebach T, Hege H-C (2006) Atlas-based 3d-shape reconstruction from X-ray images. In: Proc Int Conf of Pattern Recognition (ICPR2006). IEEE Computer Society, pp 371–374
Mitton D, Deschênes S, Laporte S, Godbout B, Bertrand S, de Guise JA, Skalli W (2006) 3d reconstruction of the pelvis from bi-planar radiography. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 9:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255840500521786
Laporte A, Mitulescu D, Mitton J, Dubousset JAdG, W. Skalli (2001) 3d personalized geometric modeling of the pelvis using stereo x rays. In: VIIIth Congr Biomech. pp 186
Zheng G (2010) Statistically deformable 2d/3d registration for estimating post-operative cup orientation from a single standard ap X-ray radiograph. Ann Biomed Eng 38:2910–2927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-010-0060-0
Novosad J, Cheriet F, Petit Y, Labelle H (2004) Three-dimensional (3-d) reconstruction of the spine from a single X-ray image and prior vertebra models. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51:1628–1639. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2004.827537
Kabaliuk N, Nejati A, Loch C, Schwass D, Cater JE, Jermy MC (2017) Strategies for segmenting the upper airway in cone-beam computed tomography (cbct) data. Open J Med Imaging 07:196–219. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojmi.2017.74019
Jena M, Mishra S, Mishra D (2018) A survey on applications of machine learning techniques for medical image segmentation. Int J Eng Technol 7:4489–4495. https://doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v7i4.19005
Wang X, Wong BS, Guan TC (2005) Image enhancement for radiography inspection. SPIE
Koonsanit K, Thongvigitmanee SS, Pongnapang N, Thajchayapong PJtBEIC (2017) Image enhancement on digital X-ray images using n-clahe. In: 10th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON). pp 1–4
Ahmad SAB, Taib MN, Khalid NEA, Taib H (2012) Analysis of image quality based on dentists' perception cognitive analysis and statistical measurements of intra-oral dental radiographs. In: 2012 International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICoBE). pp 379–384
Zeng M, Li Y, Meng Q, Yang T, Liu J (2012) Improving histogram-based image contrast enhancement using gray-level information histogram with application to X-ray images. Optik 123:511–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2011.05.017
Öktem H, Egiazarian K, Niittylahti J, Lemmetti J (2003) An approach to adaptive enhancement of diagnostic X-ray images. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2003:635640. https://doi.org/10.1155/S1110865703211069
Sezn MI, Teklap AM, Schaetzing R (1989) Automatic anatomically selective image enhancement in digital chest radiography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 8:154–162. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.24863
Deng G (2011) A generalized unsharp masking algorithm. IEEE Trans Image Process 20:1249–1261. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2092441
Huang R-Y, Dung L-R, Chu C-F, Wu Y-Y (2016) Noise removal and contrast enhancement for X-ray images. Br J Healthcare Med Res 3:56. https://doi.org/10.14738/jbemi.31.1893
Dah-Chung C, Wen-Rong W (1998) Image contrast enhancement based on a histogram transformation of local standard deviation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17:518–531. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.730397
Zheng G, Schumann S, Akcoltekin A, Jaramaz B, Nolte L (2016) Patient-specific 3d reconstruction of a complete lower extremity from 2d X-rays. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-43775-0_37
Laporte S, Skalli W, de Guise JA, Lavaste F, Mitton D (2003) A biplanar reconstruction method based on 2d and 3d contours: application to the distal femur. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 6:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/1025584031000065956
Le Bras A, Laporte S, Bousson V, Mitton D, De Guise JA, Laredo JD, Skalli W (2004) 3d reconstruction of the proximal femur with low-dose digital stereoradiography. Comput Aid Surg 9:51–57. https://doi.org/10.3109/10929080400018122
Yu W, Zheng G (2015) 2d-3d regularized deformable b-spline registration: Application to the proximal femur. In: 2015 IEEE 12th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI). pp 829–832
Baka N, Kaptein B, de Bruijne M, Walsum T, Giphart J, Niessen WJ, Lelieveldt B (2011) 2d–3d shape reconstruction of the distal femur from stereo X-ray imaging using statistical shape models. Med Image Anal 15:840–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2011.04.001
Ahmad O, Ramamurthi K, Wilson KE, Engelke K, Prince RL, Taylor RH (2010) Volumetric dxa (vxa): a new method to extract 3d information from multiple in vivo dxa images. J Bone Mineral Res 25:2744–2751. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.140
Fleute M, Lavallée S (1999) Nonrigid 3-d/2-d registration of images using statistical models. Springer, Berlin, pp 138–147
Benameur S, Mignotte M, Parent S, Labelle H, Skalli W, de Guise J (2003) 3d/2d registration and segmentation of scoliotic vertebrae using statistical models. Comput Med Imaging Graph 27:321–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0895-6111(03)00019-3
Sadowsky O, Chintalapani G, Taylor RH (2007) Deformable 2d–3d registration of the pelvis with a limited field of view, using shape statistics. Springer, Berlin, pp 519–526
Schumann S, Liu L, Tannast M, Bergmann M, Nolte LP, Zheng G (2013) An integrated system for 3d hip joint reconstruction from 2d X-rays: a preliminary validation study. Ann Biomed Eng 41:2077–2087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0822-6
Zheng G, Gollmer S, Schumann S, Dong X, Feilkas T, González Ballester MA (2009) A 2d/3d correspondence building method for reconstruction of a patient-specific 3d bone surface model using point distribution models and calibrated X-ray images. Med Image Anal 13:883–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2008.12.003
Çallı E, Sogancioglu E, van Ginneken B, van Leeuwen KG, Murphy K (2021) Deep learning for chest X-ray analysis: a survey. Med Image Anal 72:102125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2021.102125
Munawar F, Azmat S, Iqbal T, Grönlund C, Ali H (2020) Segmentation of lungs in chest X-ray image using generative adversarial networks. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3017915
Cao F, Zhao H (2021) Automatic lung segmentation algorithm on chest X-ray images based on fusion variational auto-encoder and three-terminal attention mechanism. In: JÄNTSCHI DBL (ed), p 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050814
Chen H-J, Ruan S-J, Huang S-W, Peng Y-T (2020) Lung X-ray segmentation using deep convolutional neural networks on contrast-enhanced binarized images. Mathematics 8:545. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8040545
Xie L, Siqi C, Xie L, Chen G, Zhou H (2017) Development of a computer-aided design and finite-element analysis combined method for customized nuss bar in pectus excavatum surgery. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03622-y
Ozanian TO, Phillips R (2000) Image analysis for computer-assisted internal fixation of hip fractures. Med Image Anal 4:137–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1361-8415(00)00010-4
Behiels G, Maes F, Vandermeulen D, Suetens P (2002) Evaluation of image features and search strategies for segmentation of bone structures in radiographs using active shape models. Med Image Anal 6:47–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1361-8415(01)00051-2
Ferrarini L, Olofsen H, Palm WM, van Buchem MA, Reiber JH, Admiraal-Behloul F (2007) Games: growing and adaptive meshes for fully automatic shape modeling and analysis. Med Image Anal 11:302–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2007.03.006
Selim M, Koomullil R (2016) Mesh deformation approaches – a survey. J Phys Math. https://doi.org/10.4172/2090-0902.1000181
Burg C (2006) Analytic study of 2d and 3d grid motion using modified Laplacian. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 52:163–197. https://doi.org/10.1002/fld.1173
Farhat C, Degand C, Koobus B, Lesoinne M (1998) Torsional springs for two-dimensional dynamic unstructured fluid meshes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 163:231–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7825(98)00016-4
Degand C, Farhat C (2002) A three-dimensional torsional spring analogy method for unstructured dynamic meshes. Comput Struct 80:305–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7949(02)00002-0
Yao J, Taylor R (2000). Tetrahedral mesh modeling of density data for anatomical atlases and intensity-based registration. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-40899-4_54
Tang TS, Ellis RE (2005) 2d/3d deformable registration using a hybrid atlas. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Intervent 8:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/11566489_28
Fleute M, Lavallée S (1999) Nonrigid 3-d/2-d registration of images using statistical models. In: Proceedings of the second international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, pp 138–147
Cootes TF, Taylor CJ, Cooper DH, Graham J (1992) Training models of shape from sets of examples. In: Hogg D, Boyle R (eds) BMVC92. Springer, London, pp 9–18
Heap T, Hogg DC (1995) Extending the point distribution model using polar coordinates. In: CAIP
Kainmueller D, Lamecker H, Zachow S, Hege HC (2009) An articulated statistical shape model for accurate hip joint segmentation. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009:6345–6351. https://doi.org/10.1109/iembs.2009.5333269
Jack D, Pontes JK, Sridharan S, Fookes C, Shirazi S, Maire F, Eriksson A (2019) Learning free-form deformations for 3d object reconstruction. Springer International Publishing, Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20890-5_21
Bézier PJCAGD (1974) Mathematical and practical possibilities of unisurf. pp 127–152
Böhm W, Farin G, Kahmann J (1984) A survey of curve and surface methods in cagd. Comput Aid Geometr Des 1:1–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-8396(84)90003-7
Yu W, Tannast M, Zheng G (2017) Non-rigid free-form 2d–3d registration using a b-spline-based statistical deformation model. Pattern Recogn 63:689–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.09.036
Zheng G, Yu W (2017) Chapter 12 - statistical shape and deformation models based 2d–3d reconstruction. In: Zheng G, Li S, Székely G (eds) Statistical shape and deformation analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp 329–349
Mohd Ali M, Jaafar NN, Abdul Aziz F, Nooraizedfiza Z (2014) Review on non uniform rational b-spline (nurbs): concept and optimization. Adv Mater Res 903:338–343. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.903.338
Sanchez-Reyes J (1997) A simple technique for nurbs shape modification. IEEE Comput Graphics Appl 17:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1109/38.576858
Shimer C. Free form deformation and extended free form deformation. https://web.cs.wpi.edu/~matt/courses/cs563/talks/freeform/free_form.html
Redmon J, Farhadi A (2018) Yolov3: an incremental improvement. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. ArXiv Prepr. arXiv:1804.02767v1
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R (2017) Mask r-cnn. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). pp 2980–2988
Siddique MT, Zakaria MN (2010) 3d reconstruction of geometry from 2d image using genetic algorithm. In: 2010 international symposium on information technology. pp 1–5
Kabolizade M, Ebadi H, Mohammadzadeh A (2012) Design and implementation of an algorithm for automatic 3d reconstruction of building models using genetic algorithm. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 19:104–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2012.05.006
Kadoury S, Cheriet F, Labelle H (2009) Personalized X-ray 3-d reconstruction of the scoliotic spine from hybrid statistical and image-based models. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28:1422–1435. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2009.2016756
Aubin CE, Dansereau J, Parent F, Labelle H, de Guise JA (1997) Morphometric evaluations of personalised 3d reconstructions and geometric models of the human spine. Med Biol Eng Comput 35:611–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02510968
Pearcy MJ (1985) Stereo radiography of lumbar spine motion. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 212:1–45. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453678509154154
Keaomanee Y, Heednacram A, Youngkong P (2020) Implementation of four kriging models for depth inpainting. ICT Express 6:209–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2020.05.004
Mitton D, Landry C, Véron S, Skalli W, Lavaste F, De Guise JA (2000) 3d reconstruction method from biplanar radiography using non-stereocorresponding points and elastic deformable meshes. Med Biol Eng Compu 38:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344767
Quijano S, Serrurier A, Aubert B, Laporte S, Thoreux P, Skalli W (2013) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the lower limb from biplanar calibrated radiographs. Med Eng Phys 35:1703–1712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2013.07.002
Pomero V, Mitton D, Laporte S, de Guise JA, Skalli W (2004) Fast accurate stereoradiographic 3d-reconstruction of the spine using a combined geometric and statistic model. Clin Biomech 19:240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2003.11.014
Zeng X, Wang C, Zhou H, Wei S, Chen X (2014) Low-dose three-dimensional reconstruction of the femur with unit free-form deformation. Med Phys 41:081911. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4887816
Dworzak J, Lamecker H, von Berg J, Klinder T, Lorenz C, Kainmüller D, Seim H, Hege HC, Zachow S (2010) 3d reconstruction of the human rib cage from 2d projection images using a statistical shape model. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 5:111–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-009-0390-2
Sharma S, Kumar V (2022) 3d face reconstruction in deep learning era: a survey. Arch Comput Methods Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09705-4
Yuniarti A, Suciati N (2019) A review of deep learning techniques for 3d reconstruction of 2d images. In: 2019 12th International Conference on Information & Communication Technology and System (ICTS). pp 327–331
Mulayim AY, Yılmaz U, Atalay MV (2003) Silhouette-based 3-d model reconstruction from multiple images. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B 33:582–591. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2003.814303
Hosseinian S, Arefi H (2015) 3d reconstruction from multi-view medical X-ray images – review and evaluation of existing methods. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences XL-1/W5: 319-326. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsarchives-XL-1-W5-319-2015
Cresson T, Branchaud D, Chav R, Godbout B, de Guise J (2010) 3d shape reconstruction of bone from two X-ray images using 2d/3d non-rigid registration based on moving least-squares deformation. Progr Biomed Opt Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.844098
McKenna C, Wade R, Faria R, Yang H, Stirk L, Gummerson N, Sculpher M, Woolacott N (2012) Eos 2d/3d X-ray imaging system: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 16:1–188. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta16140
Kalifa G, Charpak Y, Maccia C, Fery-Lemonnier E, Bloch J, Boussard JM, Attal M, Dubousset J, Adamsbaum C (1998) Evaluation of a new low-dose digital X-ray device: first dosimetric and clinical results in children. Pediatr Radiol 28:557–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002470050413
Gajic D, Mihic S, Dragan D, Petrovic V, Anisic Z (2019) Simulation of photogrammetry-based 3d data acquisition. Int J Simulat Model 18:59–71. https://doi.org/10.2507/IJSIMM18(1)460
Zhang X, Li L, Chen G, Lytton R (2015) A photogrammetry-based method to measure total and local volume changes of unsaturated soils during triaxial testing. Acta Geotech 10:55–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-014-0346-8
Gesslein T, Scherer D, Grubert J (2017) Bodydigitizer: an open source photogrammetry-based 3d body scanner
Hufnagel H (2011) Current methods in statistical shape analysis. A probabilistic framework for point-based shape modeling in medical image analysis. Vieweg+Teubner, Wiesbaden, pp 7–25
Frysz M, Gregory JS, Aspden RM, Paternoster L, Tobias JH (2019) Describing the application of statistical shape modelling to dxa images to quantify the shape of the proximal femur at ages 14 and 18 years in the avon longitudinal study of parents and children. Wellcome Open Res 4:24–24. https://doi.org/10.12688/wellcomeopenres.15092.2
Malekzadeh M, Gul M, Kwon I-B, Catbas N (2014) An integrated approach for structural health monitoring using an in-house built fiber optic system and non-parametric data analysis. Smart Struct Syst 14:917–942. https://doi.org/10.12989/sss.2014.14.5.917
Oswald M, Toeppe E, Nieuwenhuis C, Cremers D (2013) A survey on geometry recovery from a single image with focus on curved object reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the 2011 conference on innovations for shape analysis: models and algorithms. pp 343–378
Prasad M, Fitzgibbon AW, Zisserman A (2005) Fast and controllable 3d modelling from silhouettes. In: Eurographics
Sintini I. Statistical shape and intensity modeling of the shoulder. University of Denver
Ourselin S, Roche A, Prima S, Ayache N (2000) Block matching: A general framework to improve robustness of rigid registration of medical images. Springer, Berlin, pp 557–566
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maken, P., Gupta, A. 2D-to-3D: A Review for Computational 3D Image Reconstruction from X-ray Images. Arch Computat Methods Eng 30, 85–114 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-022-09790-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-022-09790-z