Abstract
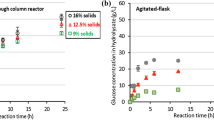
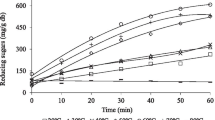
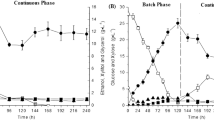
Cellulases are enzymes required for the production of second-generation ethanol (E2G) via biochemical route. The current paper reports the development of an apparatus for solid-liquid extraction of cellulases from solid-state fermentation (SSF) carried out in a packed bed bioreactor (PBB), operated as batch and as semicontinuous. The case study was the cultivation of Myceliophthora thermophila I-1D3b on sugarcane bagasse (SCB) and wheat bran (WB) (7: 3 w/w). The current work integrates the PBB to the first downstream step for recovering the enzymes produced by SSF. The substrate was inoculated and packed into the modules that composed the PBB. The fermentation occurred at 45 °C and air was supplied with flow rate of 350 L/h. At the end of the cultivations, each module was placed in an extraction column, a dynamic closed system in which distilled water was circulated and made to percolate the cultivated material. Variables tested were volume of water per mass of substrate, water flow rate and time of percolation. Higher contact time (120 min) and higher flow rate (2.4m3/h) allowed us to recover up to 85% of total enzyme activity by percolation. Lower volume (20mL/g) provides higher titer extract. The apparatus showed to be promising for SSF downstream, mainly for semicontinuous operation of PPBs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Travaini, M. D. M. Otero, M. Coca, R. Da Silva and S. Bolado, Bioresour. Technol., 133, 332 (2013).
C. Florencio, A. C. Badino and C. S. Farinas, Quím. Nova, 40, 1082 (2017).
A. Pandey, C. R. Soccol, P. Nigam and V. T. Soccol, Bioresour. Technol., 74, 69 (2000).
D. Mishima, M. Tateda, M. Ike and M. Fujita, Bioresour. Technol., 97, 2166 (2006).
C. S. Farinas, C. Florencio and A. C. Badino, in Cellulases. Methods in molecular biology, M. Lübeck Ed., Humana Press, New York (2018).
M. S. Chandra, B. Viswanath and B. R. Reddy, Indian J. Microbiol., 47, 323 (2007).
D. A. Mitchell, N. Krieger and M. Berovic, Solid-state fermentation bioreactors: fundamentals, design and operation, Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2006).
R. da Silva, E. S. Lago, C. W. Merheb, M. M. Macchione and Y. K. Park, Braz. J. Microbiol., 36, 235 (2005).
F. P. Casciatori, A. Bück, J. C. Thoméo and E. Tsotsas, Chem. Eng. J., 287, 103 (2016).
F. P. Casciatori and J. C. Thoméo, in Topics in waste treatment and environment, F. B. Freire, F. B. Freire and J. T. Freire Eds., Novas Edições Acadêmicas, Saarbrücken (2015).
D. A. Mitchell, L. E. N. Cunha, A. V. L. Machado, L. F. L. Luz Jr. and N. Krieger, Biochem. Eng. J., 48, 195 (2010).
R. D. P. B. Pirota, L. S. Miotto, P. S. Delabona and C. S. Farinas, Braz. J. Chem. Eng., 30, 177 (2013).
A. I. Zanelato, V. M. Shiota, E. Gomes and J. C. Thoméo, Braz. J. Microbiol., 43, 1536 (2012).
C. L. Perez, F. P. Casciatori and J. C. Thoméo, Chem. Eng. J., 361, 1142 (2019).
M. M. Bradford, Anal. Biochem., 72, 248 (1976).
T. K. Ghose, Pure Appl. Chem., 59, 257 (1987).
G. L. Miller, Anal. Chem., 31, 426 (1959).
L. O. Calixto, UFSCar (2019).
F. P. Casciatori, C. L. Laurentino, K. C. M. Lopes, A. G. Souza and J. C. Thoméo, Int. J. Food Prop., 16, 1578 (2013).
F. P. Casciatori, C. L. Laurentino, S. R. Taboga, P. A. Casciatori and J. C. Thoméo, Chem. Eng. J., 255, 214 (2014).
I. T. Ichiba, UFSCar (2019).
F. Fenila and Y. Shastri, Resource-Efficient Technol., 2, S96 (2016).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support of the Säo Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) (grant number 2018/009962, 2018/26097-4 and 2018/16689-1), of Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES — Finance Code 001) and of Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq, grant number 430786/2018-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
No conflict of interest declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, S.P., Alvarez Rodrigues, N., Casciatori-Frassatto, P.A. et al. Solid-liquid extraction of cellulases from fungal solid-state cultivation in a packed bed bioreactor. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 37, 1530–1540 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-020-0579-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-020-0579-1