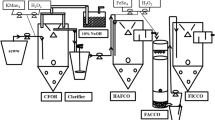
Abstract
Spent caustic can be treated by several treatment methods. Among the advanced techniques, Fenton reagent has many advantages. But since spent caustic contains excessive amounts of sulfide compounds, utilizing this technique in treatment of such wastewaters is not economical. The acid neutralization step, which was applied as the pretreatment process, showed an 84% COD abatement at temperature equal to 80 °C and a pH equal to 4.0. The acid neutralized wastewater was then introduced to the chelate-modified Fenton system and oxidized. Using a ratio of tartrate/Fe2+=1.1, reaction time=50min, temperature=95 °C, Fe2+=110mg/l and a ratio of H2O2/COD=1.2 in the chelate-modified Fenton system at an optimum pH value equal to 1.9, total COD abatement of the wastewater reached over 99.4%. Having tartrate added to the Fenton system, a series of photochemical reactions enhanced Fe2+ and hydroxyl radicals’ generation. This method has proved to be the recommended technique for the contamination abatement of spent caustic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Texas-Technology, What are spent caustics?, http://www.spentcaustic. com (Accessed July 2014).
M.D. LaGrega, P. L. Buckingham and J.C. Evans, Hazardous waste management, McGraw-Hill, Boston, MA (2001).
M. V. Jagushte and V. V. Mahajani, J. Chem. Technol. Biot., 74, 437 (1999).
R. Alnaizy, Environ. Progress, 27, 295 (2008).
I. Ben Hariz, A. Halleb, N. Adhoum and L. Monser, Sep. Purif. Technol., 107, 150 (2013).
M. de Graaff, M.F. Bijmans, B. Abbas, G. J. Euverink, G. Muyzer and A. J. Janssen, Bioresour. Technol., 102, 7257 (2011).
S.-H. Sheu and H.-S. Weng, Water Res., 35, 2017 (2001).
A. Kolhatkar and K. Sublette, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 57-58, 945 (1996).
J. Sipma, A. Svitelskaya, B. van der Mark, L.W. Pol, G. Lettinga, C. J. Buisman and A. J. Janssen, Water Res., 38, 4331 (2004).
Degussa-Corporation, Environmental uses of hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2), Allendale, New Jersey (2009).
R. Venkatadri and R.W. Peters, Hazard. Waste Hazard., 10, 107 (1993).
E. Neyens and J. Baeyens, J. Hazard. Mater., 98, 33 (2003).
P.C. Vandevivere, R. Bianchi and W. Verstraete, J. Chem. Technol. Biot., 72, 289 (1998).
C. P. Huang, C. Dong and Z. Tang, Waste Manage., 13, 361 (1993).
H. J.H. Fenton, J. Chem. Soc. Dalton, 65, 899 (1894).
V. Sarria, S. Parra, M. Invernizzi, P. Peringer and C. Pulgarin, Water. Sci. Technol., 44, 93 (2001).
R. J. Knight and R.N. Sylva, J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem., 37, 779 (1975).
T. E. Graedel, C. J. Weschler and M. L. Mandich, Nature, 317, 240 (1985).
C. J. Weschler, M. L. Mandich and T. E. Graedel, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 91, 5189 (1986).
L. Wang, C. Zhang, F. Wu and N. Deng, J. Coord. Chem., 59, 803 (2006).
Y. Zuo and J. Hoigne, Environ. Sci. Technol., 26, 1014 (1992).
J.M. Joseph, R. Varghese and C.T. Aravindakumar, J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 146, 67 (2001).
R.G. Zepp, J. Hoigne and H. Bader, Environ. Sci. Technol., 21, 443 (1987).
D. Nansheng, W. Feng, L. Fan and X. Mei, Chemosphere, 36, 3101 (1998).
W. Feng, D. Nansheng and Z. Yuegang, Chemosphere, 39, 2079 (1999).
W. Feng and D. Nansheng, Chemosphere, 41, 1137 (2000).
W.W. Eckenfelder, A.R. Bowers and J. A. Roth, Chemical oxidation—technologies for the nineties: Proceedings of the Frst International Symposium, chemical oxidation: Technology for the nineties, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, February 20-22, 1991, Technomic Pub. Co., Lancaster, Pa., U.S.A. (1992).
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association., Water Pollution Control Federation. and Water Environment Federation, “Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater: Including bottom sediments and sludges,” American Public Health Association, New York (1960).
A. Kotronarou and M.R. Hoffmann, Environ. Sci. Technol., 25, 1153 (1991).
B.C. Faust and J. Hoigné, Atmos. Environ. A-Gen., 24, 79 (1990).
E. Casbeer, V. K. Sharma and X.-Z. Li, Sep. Purif. Technol., 87, 1 (2012).
P. Miró, A. Arques, A. M. Amat, M. L. Marin and M.A. Miranda, Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 140-141, 412 (2013).
M. C. Ortega-Liébana, E. Sánchez-López, J. Hidalgo-Carrillo, A. Marinas, J.M. Marinas and F. J. Urbano, Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 127, 316 (2012).
S. Rahim Pouran, A. A. Abdul Raman and W. M. A. Wan Daud, J. Clean. Prod., 64, 24 (2014).
D. Hermosilla, M. Cortijo and C.P. Huang, Sci. Total Environ., 407, 3473 (2009).
I. García-Fernández, M. I. Polo-López, I. Oller and P. Fernández-Ibáñez, Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 121–122, 20 (2012).
P. Karaolia, I. Michael, I. García-Fernández, A. Agüera, S. Malato, P. Fernández-Ibáñez and D. Fatta-Kassinos, Sci. Total Environ., 468-469, 19 (2014).
M. I. Polo-López, I. Oller and P. Fernández-Ibáñez, Catal. Today, 209, 181 (2013).
A. Karci, I. Arslan-Alaton, T. Olmez-Hanci and M. Bekbölet, J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 230, 65 (2012).
V. Kavitha and K. Palanivelu, Water Res., 39, 3062 (2005).
B.G. Kwon, D. S. Lee, N. Kang and J. Yoon, Water Res., 33, 2110 (1999).
S. Parsons, Advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment, IWA, London (2004).
V. Kavitha and K. Palanivelu, J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 170, 83 (2005).
T. E. Furia, Crc handbook of food additives, CRC Press, Cleveland (1972).
X. Xue, K. Hanna, C. Despas, F. Wu and N. Deng, J. Mol. Catal. AChem., 311, 29 (2009).
W. Huang, M. Brigante, F. Wu, K. Hanna and G. Mailhot, J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 239, 17 (2012).
J. An, L. Zhu, Y. Zhang and H. Tang, J. Environ. Sci., 25, 1213 (2013).
N. Klamerth, S. Malato, A. Agüera and A. Fernández-Alba, Water Res., 47, 833 (2013).
D. Panias, M. Taxiarchou, I. Paspaliaris and A. Kontopoulos, Hydrometallurgy, 42, 257 (1996).
S. Navalon, M. Alvaro and H. Garcia, Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 99, 1 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moussavi, M., Matavos-Aramyan, S. Chelate-modified fenton treatment of sulfidic spent caustic. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 33, 2384–2391 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0080-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0080-z