Abstract
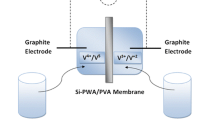
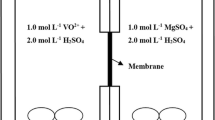
Vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) have been researched as large energy storage systems due to their long cycle life, high energy efficiency, low cost, and flexible design. However, cation exchange membranes are permeable to the vanadium ions in aqueous acidic electrolyte, and vanadium ions crossover reduces the efficiency and capacity of VRFBs. To improve membrane selectivity, proton conducting inorganic materials are proposed for the modification of conventional membranes, e.g., Nafion. Clusters inside Nafion membrane are filled with inorganic materials using in situ sol-gel processes, and this results in homogeneous distribution of inorganic materials. Hybrid membranes with Nafion 115 (coded as HN115) exhibit comparable ionic conductivity and a 70% reduced permeability to vanadium ions compared with pristine Nafion 115 (coded as N115). The columbic and energy efficiencies of VRFBs with HN115 at 20mA·cm−2 exhibit higher values of 95% and 80% in their columbic and energy efficiencies, respectively; VRFBs with N115 exhibit 78% and 70%, respectively. The capacity performance is also improved when HN115 is used in VRFBs. The VRFBs with hybrid membranes (lower permeable membrane) show higher columbic efficiency than the VRFB with N115. HN115 exhibit similar columbic efficiency values of 95% over entire current ranges, which are almost unrelated to the current density. However, N115 shows a fluctuating and lower columbic efficiency of 75%, 88%, 93% at 20mA·cm−2, 40mA·cm−2, 80mA·cm−2, respectively. VRFB with N115 (high conductive membrane) exhibits lower voltage drops for discharging and higher energy efficiency at high current ranges. With these results, it is proposed that the energy efficiencies of VRFBs are compromised with membrane conductivity and permeability. The columbic efficiencies are more contributed by membrane permeability. The permeability properties are more dominant in low current density and the ionic conductivity is more effective in high current ranges. To obtain higher performance of VRFBs, the membrane design for selectivity should be considered according to the operation conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Menictas and M. Skyllas-Kazacos, J. Appl. Electrochem., 41, 1223 (2011).
C. Ponce de Leon, A. Frias-Ferrer, J. Gonzalez, D. A. Szanto and F. C. Walsh, J. Power Sources, 160, 716 (2006).
Z. Yang, J. Zhang, M. C. W. Kintner-Meyer, X. Lu, D. Choi, J. P. Lemmon and J. Liu, Chem. Rev., 111, 3577 (2011).
N. Armaroli and V. Balzani, Energy Environ. Sci., 4, 3193 (2011).
G. Kear, A. A. Shah and F. C. Walsh, Int. J. Energy Res., 36, 1105 (2012).
A. Parasuraman, T. M. Lim, C. Menictas and M. Skyllas-Kazacos, Electrochim. Acta, 101, 27 (2013).
X. Luo, Z. Lu, J. Xi, Z. Wu, W. Zhu, L. Chen and X. Qiu, J. Phys. Chem. B, 109, 20310 (2005).
C. Yao, H. Zhang, T. Liu, X. Li and Z. Liu, J. Power Sources, 237, 19 (2013).
N. Wang, S. Peng, Y. Li, H. Wang, S. Liu and Y. Liu, J. Solid State Electrochem., 16, 2169 (2012).
S. Kim, J. Yan, B. Schwenzer, J. Zhang, L. Li, J. Liu, Z. Yang and M. Hickner, Electrochem. Commun., 12, 1650 (2010).
S. Kim, T. B. Tighe, B. Schwenzer, J. Yan, J. Zhang, J. Liu, Z. Yang and M. A. Hickner, J. Appl. Electrochem., 41, 1201 (2011).
X. Ling, C. Jia, J. Liu and C. Yan, J. Membr. Sci., 415-416, 306 (2012).
D. Chen, S. Kim, L. Li, G. Yang and M. A. Hickner, RSC Adv., 2, 8087 (2012).
J. Pan, S. Wang, M. Xiao, M. Hickner and Y. Meng, J. Membr. Sci., 443, 19 (2013).
N. Wang, J. Yu, Z. Zhou, D. Fang, S. Liu and Y. Liu, J. Membr. Sci., 437, 114 (2013).
C. Fujimoto, S. Kim, R. Stains, X. Wei, L. Li and Z. Yang, Electrochem. Commun., 20, 48 (2012).
M. J. Jung, J. Parrondo, C. G. Arges and V. Ramani, J. Mater. Chem. A, 1, 10458 (2013).
S. Zhang, B. Zhang, D. Xing and X. Jian, J. Mater. Chem. A, 1, 12246 (2013).
Z. Mai, H. Zhang, H. Zhang, W. Xu, W. Wei, H. Na and X. Li, ChemSusChem, 6, 328 (2013).
D. Chen, M. A. Hickner, E. Agar and E. C. Kumbur, Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 5, 7559 (2013).
J. Xi, Z. Wu, X. Teng, Y. Zhao, L. Chen and X. Qiu, J. Mater. Chem., 18, 1232 (2008).
X. Teng, Y. Zhao, J. Xi, Z. Wu, X. Qiu and L. Chen, J. Membr. Sci., 341, 149 (2009).
X. Teng, Y. Zhao, J. Xi, Z. Wu, X. Qiu and L. Chen, J. Power Sources, 189, 1240 (2009).
Z. Mai, H. Zhang, X. Li, S. Xiao and H. Zhang, J. Power Sources, 196, 5737 (2011).
N. Wang, S. Peng, D. Lu, S. Liu, Y. Liu and K. Huang, J. Solid State Electrochem., 16, 1577 (2012).
X. Teng, J. Dai, J. Su, Y. Zhu, H. Liu and Z. Song, J. Power Sources, 240, 131 (2013).
X. Teng, C. Sun, J. Dai, H. Liu, J. Su and F. Li, Electrochim. Acta, 88, 725 (2013).
Z. Li, J. Xi, H. Zhou, L. Liu, Z. Wu, X. Qiu and L. Chen, J. Power Sources, 237, 132 (2013).
H. Kim and H. Chang, J. Membr. Sci., 288, 188 (2007).
L. Yang, B. Tang and P. Wu, J. Membr. Sci., 467, 236 (2014).
P. Alotto, M. Guarnieri and F. Moro, Renw. Sust. Energy Rev., 29, 325 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.M., Kim, H. Hybrid membranes with low permeability for vanadium redox flow batteries using in situ sol-gel process. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 32, 2434–2442 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-015-0077-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-015-0077-z