Abstract
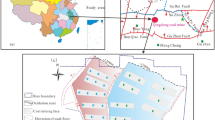
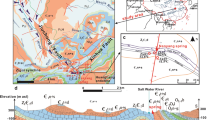
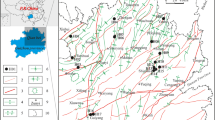
In the Xihu Sag, the reservoirs of the Paleogene Huagang formation have entered the middle diagenetic stage A and the rock physical properties of the water layer are considerably more suitable for the gas migration and storage than those of the present gas layer, indicating the inversion of the physical properties. In this study, core samples were collected from the corresponding reservoir to conduct water-rock reaction experiments in acidic, alkaline, and neutral systems under the specific temperature and pressure. The reasons for the inversion of physical properties were investigated based on the experiment results in reservoir diagenetic environments. The inversion of physical properties can be attributed to the fact that the diagenetic environment around the gas-water interface controls the water-rock reaction effect. With different types of acidic substances, two different situations corresponding to inverted physical properties were analyzed along with the corresponding mechanisms. When the pore fluid is acidic, the physical properties make the overall water layer a better reservoir space than the gas layer, which can be referred to as the overall inversion of physical properties. When the fluid were generally neutral or weakly alkaline and the gas layer was rich in CO2, only the physical properties of the water layer adjacent to the gas-water interface were more favorable for the gas migration than those of the gas layer. This phenomenon can be referred to as the near-interface inversion of physical properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjorlykke, K., Nedkvitne, T., Ramm, M., and Saigal, G. C., 1992. Diagenetic processes in the Brent Group (middle Jurassic) reservoirs of the North Sea: An overview. Geological Society, 61(1): 263–287.
Dai, L. M., Li, S. Z., Lou, D., Liu, X., Suo, Y. H., and Yu, S., 2014. Numerical modeling of late Miocene tectonic inversion in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 86: 25–37.
Giles, M. R., Boer, R. B. D., and Marshall, J. D., 1994. How important are organic acids in generating secondary porosity in the subsurface? In: Organic Acids in Geological Processes. Springer, Berlin, 449–470.
Han, X. Q., Fang, T., Cao, J., Gao, H. L., Zhang, B., Zhang, L. K., et al., 2019. Simulation experiment of gas charging and gasbearing change of tight sandstone reservoir of Shanxi formation in Yan’an gas field, Ordos Basin. Natural Gas Geoscience, 30(12): 1721–1731 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hao, L. L., Wang, Q., Guo, R. L., Tuo, C. G., Ma, D. X., Mou, W. W., et al., 2018. Diagenetic fluids evolution of Oligocene Huagang formation sandstone reservoir in the south of Xihu Sag, the East China Sea Shelf Basin: Constraints from petrology, mineralogy, and isotope geochemistry. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 37(2): 25–34.
He, F. Q., Rao, Y., Wang, W. H., and Wang, Y. H., 2020. Prediction of hydrocarbon reservoirs within coal-bearing formations. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 17(3): 484–492.
Hu, M. Y., Ke, L., and Liang, J. S., 2010. The characteristics and pattern of sedimentary facies of Huagang formation in Xihu Depression. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 32(5): 1–5 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu, W. S., Chai, H. D., Li, R. S., Xu, F., and Ge, H. P., 2010. Application of balanced section technique to the study of positive inversion structure and hydrocarbon accumulation control in Xihu Depression of East China Sea. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 17(1): 15–19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, J. Y., Jiang, B., Qu, Z. H., Shi, Y., Xu, J., and Li, P., 2016. Tectonic evolution and control of coal in Donghai Xihu Sag. Coal Geology & Exploration, 44(5): 22–27 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, S. Q., and Li, C. J., 2003. Analysis on the petroleum resource distribution and exploration potential of the Xihu Depression, the East China Sea. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 25(6): 721–728 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, Y., Chen, S. J., Wu, B. Y., Qiu, D., Lin, R. P., and Li, J. L., 2017. Controlling factors on complex gas-water distribution in Xu-6 tight sandstone gas reservoir in Guang’an area. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 38(2): 198–203 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, R. M., Sun, S. C., and Wang, D. D., 2019. Study on sedimentary system of Huagang formation in Xi Hu Depression. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 4: 133–134 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, Y., 2018. Genetic mechanism of deep high-quality reservoir in the Palaeogene Huagang formation of Xihu Sag in the East China Sea Basin. PhD thesis. Chengdu University of Technology.
Su, A., Chen, H. H., Cao, L. S., Li, C. H., Lei, M. Z., and Zhao, Y. T., 2014. Distribution and genesis of the secondary pore of Paleogene reservoir in Xihu Depression, Eastern Sea Basin. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 32(5): 949–956 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Su, A., Chen, H. H., Wang, C. W., Li, P. J., Zhang, H., Xiong, W. L., et al., 2013. Genesis and maturity identification of oil and gas in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(5): 558–565.
Surdam, R. C., Boese, S. W., and Grossey, L. J., 1984. The chemistry of secondary porosity: Part 2. Aspects of porosity modification. AAPG Memoir, 37: 127–149.
Surdam, R. C., Crossey, L. J., Sven Hagen, E., and Heasler, H. P., 1989. Organic-inorganic interactions and sandstone diagenesis. AAPG Bulletin, 73(1): 1–23.
Tang, X. P., Huang, W. H., Li, M., Dong, G. G., Wu, G., Wang, W. Y., et al., 2013. Diagenetic environment evolution of deep sandstones in the upper Es4 of the Palaeogene in Lijin Sag. Earth Science — Journal of China University of Geosciences, 38(4): 843–852 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Taylor, T. R., Giles, M. R., Hathon, L. A., Diggs, T. N., Braunsdorf, N. R., Birbiglia, G. V., et al., 2010. Sandstone diagenesis and reservoir quality prediction: Models, myths, and reality. AAPG Bulletin, 94(8): 1032–1093.
Wang, Q., Li, S. Z., Guo, L. L., Suo, Y. H., and Dai, L. M., 2017. Analogue modelling and mechanism of tectonic inversion of the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 139: 129–141.
Xie, G. L., Shen, Y. L., Liu, S. G., and Hao, W. D., 2018. Trace and rare earth element (REE) characteristics of mudstones from Eocene Pinghu formation and Oligocene Huagang formation in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin: Implications for provenance, depositional conditions and paleoclimate. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 92: 20–36.
Yang, F. L., Yu, H. X., Zhang, Q. L., and Li, Q. Y., 2009. Correlations between shortening rate, uplift rate, and inversion rate in central inversion zone of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin. Journal of Earth Science, 20(4): 699–708.
Yang, S. C., Hu, S. B., Cai, D. S., Feng, X. J., Chen, L. L., and Gao, L., 2004. Present-day heat flow, thermal history and tectonic subsidence of the East China Sea Basin. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 21(9): 1095–1105.
Zeng, J. H., and Wang, H. Y., 2000. Experimental study on oil migration and accumulation in the heterogeneous sand beds of different porosity and permeability. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 24(4): 108–112 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, S. L., Zhang, J. P., Tang, X. J., and Zhang, T., 2014. Geometry characteristic of the fault system in Xihu Sag in East China Sea and its formation mechanism. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 34(1): 87–94 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou, R. Q., Fu, H., Xu, G. S., Miao, Q., and Fu, Z. Q., 2018. Eocene Pinghu formation-Oligocene Huagang formation sequence stratigraphy and depositional model of Xihu Sag in East China Sea Basin. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 36(1): 132–141 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Acknowledgement
This research was supported financially by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China during the ‘13th Five-Year Plan’ (No. 2016ZX0502 7-002-006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Xu, F., Xu, G. et al. Studies on the Inversion Phenomenon of Physical Properties Observed in the Huagang Formation Reservoir in the Xihu Sag Based on the Water-Rock Reaction Experiments. J. Ocean Univ. China 20, 755–764 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4565-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4565-y