Abstract
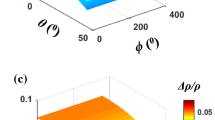
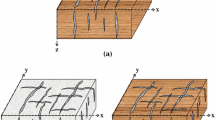
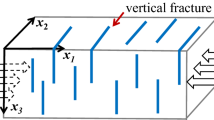
The existence of aligned fractures in fluid-saturated rocks leads to obvious attenuation anisotropy and velocity anisotropy. Attenuation anisotropy analysis can be applied to estimate fracture density and scale, which provide important information for reservoir identification. This paper derives P-wave attenuation anisotropy in the ATI media where the symmetry axis is in the arbitrary direction theoretically and modifies the spectral ratio method to measure attenuation anisotropy in the ATI media, thus avoiding a large measurement error when applied to wide azimuth or full azimuth data. Fracture dip and azimuth can be estimated through attenuation anisotropy analysis. For small-scale fractures, fracture scale and fracture density can be determined with enhanced convergence if velocity and attenuation information are both used. We also apply the modified spectralratio method to microseismic field data from an oilfield in East China and extract the fracture dip through attenuation anisotropy analysis. The result agrees with the microseismic monitoring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carcione, J. M., 2000, A model for seismic velocity and attenuation in petroleum source rocks: Geophysics, 65, 1080–1092.
Chapman, M., 2003, Frequency-dependent anisotropy due to meso-scale fractures in the presence of equant porosity: Geophysical Prospecting, 51, 369–379.
Chichinina, T., Obolentseva, I., Gik, L., et a., 2009, Attenuation anisotropy in the linear–slip model: Interpretation of physical modeling data: Geophysics, 74(5), 165–176.
Dasgupta, R., and Clark, R. A., 1998, Estimation of Q from surface seismic reflection data: Geophysics, 63, 2120–2128.
Dasios, A., Astin, T., and McCann, C., 2001, Compressional wave Q estimation from full-waveform sonic data: Geophysical Prospecting, 49, 353–373.
Draper, N., and Smith, H., 1981, Applied Regression Analysis: John Wiley and Sons, Second Edition, 83–135.
Hackert, C. L., Parra, J. O., Brown, R. L., and Collier, H. A., 2001, Characterization of dispersion, attenuation and anisotropy at the Buena Vista Hills field, California: Geophysics, 66, 90–96.
Hauge, P. S., 1981, Measurements of attenuation from vertical seismic profiles: Geophysics, 46, 1548–1558.
Maultzsch, S., Chapman, M., Liu, E., and Li, X. Y., 2007, Modelling and analysis of attenuation anisotropy in multi-azimuth VSP data from the Clair field: Geophysical Prospecting, 55, 627–642.
Pujol, J., and Smithson, S., 1991, Seismic wave attenuation in volcanic rocks from VSP experiments: Geophysics, 56, 1441–1455.
Quan, Y., and Harris, J. M., 1997, Seismic attenuation tomography using the frequency shift method: Geophysics, 62, 895–905.
Shekar, B., and Tsvankin, I., 2012, Anisotropic attenuation analysis of crosshole data generated during hydraulic fracturing: The Leading Edge, Special section: Seismic inversion for Reservoir Properties, 588–593.
Vavrycuk, V., 2006, Calculation of the slowness vector from the ray vector in anisotropic media: Proc. R. Soc. A, 462, 883–896.
Vavrycuk, V., 2007, Asymptotic Green’s function in homogeneous anisotropic viscoelastic media: Proc. R. Soc. A, 463, 2689–2707.
Wang, Z. J., Cao, S. Y., Zhang, H. R., Qu, Y. M., Yuan, D., Yang, J. H., and Shao, G. M., 2015, Estimation of quality factors by energy ratio method: Applied Geophysics, 12(1), 86–92.
Zhu, Y., and Tsvankin, I., 2007, Plane-wave attenuation anisotropy in orthorhombic media, Geophysics, 72(1), D9–D19.
Zhu, Y., Tsvankin, I., Dewangan, P., and Wijk, K. V., 2007, Physical modeling and analysis of P-wave attenuation anisotropy in transversely isotropic media: Geophysics, 72(1), D1–D7.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Prof. Jerry M. Harris of the Stanford Wave Physics Lab for his suggestions on the characteristics of attenuation anisotropy in a fractured media. We are also grateful to the reviewers Wang Runqiu and Yang Kai for their helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research is supported by 973 Program of China (No. 2013CB228602), National Science and Technology Major Project of China (No. 2016ZX05004003-002) and 863 Program of China (No. 2013AA064202).
He Yi-Yuan received her B.Sc. from Peking University in 2007 and obtained her Ph.D.in Geophysics in Peking University in 2016. Her research work focuses on seismic attenuation anisotropy and fracture prediction. Currently, she works at the China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Land and Resources. Email: heyiyuan_0321@126.com
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, YY., Hu, TY., He, C. et al. P-wave attenuation anisotropy in TI media and its application in fracture parameters inversion. Appl. Geophys. 13, 649–657 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-016-0592-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-016-0592-7