Abstract
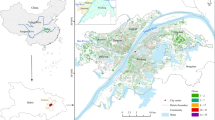
This study applies multi-source datasets (i.e., Baidu Heat Map data, points of interest (POIs) data, and floor area and land use data) and geographically and temporally weighted regression (GTWR) models to elaborate the spatiotemporal relationships between the built environment and urban vibrancy on both weekdays and weekends, using Guangzhou City as a case. First, we verified the spatially and temporally nonstationary nature of the built environment correlates, which have been largely ignored in previous studies based on local regression techniques. The spatially and temporally heterogeneous effects of the built environment on urban vibrancy are then presented and visualized, based on the GTWR results. We found that the elasticity of location (i.e., distance), land use mix (i.e., diversity), building intensity and numbers of POIs with various functions (i.e., density) are different across time (2-h intervals within a day) and space (grids), due to people’s everyday lifestyle, time-space constraints, and geographical context (e.g., spatial structure). The findings highlight the importance of a better understanding of the local geography on the spatiotemporal relationships for urban planners and local governments so as to put forward decision-making support for fostering and maintaining urban vibrancy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrington-Leigh C, Millard-Ball A, 2015. A century of sprawl in the United States. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(27): 8244–8249. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1504033112
Batty M, 2013. Big data, smart cities and city planning. Dialogues in Human Geography, 3(3): 274–279. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/2043820613513390
Brunsdon C, Fotheringham A S, Charlton M E, 1996. Geographically weighted regression: a method for exploring spatial nonstationarity. Geographical Analysis, 28(4): 281–298. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-4632.1996.tb00936.x
Chai Y W, Ta N, Ma J, 2016. The socio-spatial dimension of behavior analysis: frontiers and progress in Chinese behavioral geography. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 26(8): 1243–1260. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-016-1324-x
Chen T T, Hui E C M, Wu J M et al., 2019. Identifying urban spatial structure and urban vibrancy in highly dense cities using georeferenced social media data. Habitat International, 89: 102005. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2019.102005
Delclòs-Alió X, Gutiérrez A, Miralles-Guasch C, 2019. The urban vitality conditions of Jane Jacobs in Barcelona: residential and smartphone-based tracking measurements of the built environment in a Mediterranean metropolis. Cities, 86: 220–228. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2018.09.021
Ewing R, Cervero R, 2010. Travel and the built environment. Journal of the American Planning Association, 76(3): 265–294. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01944361003766766
Gehl J, 1987. Life between Buildings: Using Public Space. Washington: Long Island Press.
Glaeser E, 2011. Triumph of the City: How Our Greatest Invention Makes Us Richer, Smarter, Greener, Healthier, and Happier. New York: The Penguin Press.
Goodchild M F, 2007. Citizens as sensors: the world of volunteered geography. Geojournal, 69(4): 211–221. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-007-9111-y
Graham M, Stephens M, Hale S, 2013. Featured graphic. Mapping the geoweb: a geography of twitter. Environment and Planning A:Economy and Space, 45(1): 100–102. doi: https://doi.org/10.1068/a45349
Hall P, Pfeiffer U, 2000. Urban Future 21: A Global Agenda for Twenty-First Century Cities. New York: Routledge.
Handy S, Cao X Y, Mokhtarian P, 2005. Correlation or causality between the built environment and travel behavior? Evidence from Northern California. Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment, 10(6): 427–444. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2005.05.002
He Q S, He W S, Song Y et al., 2018. The impact of urban growth patterns on urban vitality in newly built-up areas based on an association rules analysis using geographical ‘big data’. Land Use Policy, 78: 726–738. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.07.020
Huang B, Wu B, Barry M, 2010. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatiotemporal variation in house prices. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 24(3): 383–101. doi: https://doi.org/10.1800/36588818002672469
Huang B, Zhou Y L, Li Z G et al., 2020. Evaluating and characterizing urban vibrancy using spatial big data: Shanghai as a case study. Environment and Planning B:Urban Analytics and City Science, 47(9): 1543–1559. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/2399808319828730
Hurvich C M, Simonoff J S, Tsai C L, 1998. Smoothing parameter selection in nonparametric regression using an improved Akaike information criterion. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society:Statistical Methodology Series B, 60(2): 271–293. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9868.00125
Jacobs J, 1961. The Death and Life of Great American Cities. New York: Random House.
Jin X B, Long Y, Sun W et al., 2017. Evaluating cities’ vitality and identifying ghost cities in China with emerging geographical data. Cities, 63: 98–109. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2017.01.002
Kim Y L, 2018. Seoul’s Wi-Fi hotspots: Wi-Fi access points as an indicator of urban vitality. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 72: 13–24. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2018.06.004
Kwan M P, 2012. The uncertain geographic context problem. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 102(5): 958–968. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00045608.2012.687349
Lan F, Gong X Y, Da H L et al., 2020. How do population inflow and social infrastructure affect urban vitality? Evidence from 35 large- and medium-sized cities in China. Cities, 100: 102454. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2019.102454
Landry C, 2012. The Creative City: A Toolkit for Urban Innovators. 2nd ed. London: Routledge.
Li J G, Li J W, Yuan Y Z et al., 2019. Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and mechanism analysis of urban population density: a case of Xi’an, Shaanxi, China. Cities, 86: 62–70. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2018.12.008
Long Y, Huang C C, 2019. Does block size matter? The impact of urban design on economic vitality for Chinese cities. Environment and Planning B:Urban Analytics and City Science, 46(3): 406–422. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/2399808317715640
Loo B P Y, Wang B, 2017. Progress of e-development in China since 1998. Telecommunications Policy, 41(9): 731–742. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2017.03.001
Loo B P Y, Wang B, 2018. Factors associated with home-based e-working and e-shopping in Nanjing, China. Transportation, 45(2): 365–384. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-017-9792-0
Lynch K. 1984. Good City Form. Cambridge: The MIT Press.
Qin Xiao, Zhen Feng, Zhu Shoujia et al., 2014. Spatial pattern of catering industry in Nanjing urban area based on the degree of public praise from Internet: a case study of Dianping. com. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 34(7): 810–817. (in Chinese)
Schwanen T, Kwan M P, 2008. The Internet, mobile phone and space-time constraints. Geoforum, 39(3): 1362–1377. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoforum.2007.11.005
Song Y, Merlin L, Rodriguez D, 2013. Comparing measures of urban land use mix. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 42: 1–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2013.08.001
Sun C, Zheng S Q, Wang J H et al., 2019. Does clean air increase the demand for the consumer city? Evidence from Beijing. Journal of Regional Science, 59(3): 409–434. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jors.12443
Ta Na, Zeng Yutian, Zhu Qiuyu et al., 2020. Relationship between built environment and urban vitality in Shanghai downtown area based on big data. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 40(1): 60–68. (in Chinese)
Tan Xin, Huang Daquan, Zhao Xingshuo et al., 2016. Jobs housing balance based on Baidu thermodynamic diagram. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 52(5): 622–627 (in Chinese)
Timmermans H, Arentze T, Joh C H, 2002. Analysing space-time behaviour: new approaches to old problems. Progress in Human Geography, 26(2): 175–190. doi: https://doi.org/10.1191/0309132502ph363ra
Tu W, Zhu T T, Xia J Z et al., 2020. Portraying the spatial dynamics of urban vibrancy using multisource urban big data. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 80: 101428. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2019.101428
Wang Bo, Zhen Feng, Wei Zongcai et al., 2015a. A theoretical framework and methodology for urban activity spatial structure in e-society: empirical evidence for Nanjing City, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 25(6): 672–683. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-015-0751-4
Wang Bo, Zhen Feng, Zhang Hao, 2015b. The dynamic changes of urban space-time activity and activity zoning based on check-in data in Sina Web. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 35(2): 151–160. (in Chinese)
Wang B, Loo B P Y, 2019. The hierarchy of cities in Internet news media and Internet search: some insights from China. Cities, 84: 121–133. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2018.07.013
Wang B, Loo B P Y, Zhen F et al., 2020a. Urban resilience from the lens of social media data: responses to urban flooding in Nanjing, China. Cities, 106: 102884. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2020.102884
Wang Bo, Zhen Feng, Zhang Shanqi et al., 2020b. The impact of air pollution on urban vibrancy and its built environment heterogeneity: An empirical analysis based on big data. Geographical Research, 40(7): 1935–1948. (in Chinese)
Wang Lucang, Chang Fei, 2020. The study of job-housing relationship of citybased on multisource big data-taking central urban area of Lanzhou as an examplemain city area. Human Geography, 35(3): 65–75. (in Chinese)
Wang M S, 2021. Polycentric urban development and urban amenities: evidence from Chinese cities. Environment and Planning B:Urban Analytics and City Science, 48(3): 400–416. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/2399808320951205
Wei Z C, Zhen F, Mo H T et al., 2021. Travel behaviours of sharing bicycles in the central urban area based on geographically weighted regression: the case of Guangzhou, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 31(1): 54–69. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-020-1159-3
Wu C, Ye X Y, Ren F et al., 2018. Check-in behaviour and spatiotemporal vibrancy: an exploratory analysis in Shenzhen, China. Cities, 77: 104–116. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2018.01.017
Wu Zhiqiang, Ye Zhongnan, 2016. Research on urban spatial structure based on Baidu Heat Map: a case study on the central city of Shanghai. City Planning Review, 40(4): 33–40. (in Chinese)
Xia C, Yeh A G O, Zhang A Q, 2020. Analyzing spatial relationships between urban land use intensity and urban vitality at street block level: a case study of five Chinese megacities. Landscape and Urban Planning, 193: 103669. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2019.103669
Xu J, Yeh A G O, 2003. City profile: Guangzhou. Cities, 20(5): 361–374. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-2751(03)00056-8
Yang J W, Cao J, Zhou Y F, 2021. Elaborating non-linear associations and synergies of subway access and land uses with urban vitality in Shenzhen. Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice, 144: 74–88. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2020.11.014
Yang L C, Wang B, Zhou J P et al., 2018. Walking accessibility and property prices. Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment, 62: 551–562. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2018.04.001
Ye Y, Li D, Liu X J, 2018. How block density and typology affect urban vitality: an exploratory analysis in Shenzhen, China. Urban Geography, 39(4): 631–652. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/02723638.2017.1381536
Yue Y, Zhuang Y, Yeh A G O et al., 2017. Measurements of POI-based mixed use and their relationships with neighbourhood vibrancy. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 31(4): 658–675. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2016.1220561
Zeng C, Song Y, He Q S et al., 2018. Spatially explicit assessment on urban vitality: case studies in Chicago and Wuhan. Sustainable Cities and Society, 40: 296–306. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2018.04.021
Zhen F, Cao Y, Qin X et al., 2017. Delineation of an urban agglomeration boundary based on Sina Weibo microblog ‘check-in’ data: a case study of the Yangtze River Delta. Cities, 60: 180–191. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2016.08.014
Zheng Z, Zhou S H, 2017. Scaling laws of spatial visitation frequency: applications for trip frequency prediction. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 64: 332–343. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2017.04.004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41901191, 41930646), Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai) (No. 311020017)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Lei, Y., Xue, D. et al. Elaborating Spatiotemporal Associations Between the Built Environment and Urban Vibrancy: A Case of Guangzhou City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 32, 480–492 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-022-1272-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-022-1272-6