Abstract
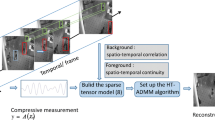
Background subtraction technology is a very important part in the field of video surveillance applications. The common matrix decomposition methods based on robust principal component analysis vectorized video sequences, which destroys the spatial structure and spatio-temporal continuity of videos. Aiming at this problem, a model based on tensor robust principal component analysis was proposed. In the new model, an improved tensor nuclear norm was used to constrain the background, which strengthened the low rank of background and improved the accuracy of foreground background separation. And \(L_{1,1,2}\) norm was applied to constrain foreground and enhanced the tube sparsity and spatio-temporal continuity of foreground, which improved the accuracy of foreground extraction. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms multiple state-of-the-art methods both in qualitative and qualitative aspects, especially, for the videos with the multi-target or in bad weather.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue, Z., Yuan, X., Yang, Y.: Denoising-based turbo message passing for compressed video background subtraction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 2682–2696 (2020)
Kumar, N., Sukavanam, N.: A weakly supervised CNN model for spatial localization of human activities in unconstraint environment. Signal Image Video Process. 14(5), 1009–1016 (2020)
Stauffer, C., Grimson, W.E.L.: Adaptive background mixturemodels for real-time tracking. In: Proceedings. 1999 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Cat. No PR00149), vol. 2, pp. 246C252 (1999)
Zhou, X., Yang, C., Zhao, H., et al.: Low-rank modeling and its applications in image analysis. ACM Comput. Surv. 47(2), 1–33 (2015)
Bouwmans, T., Zahzah, E.: Robust pca via principal component pursuit: a review for a comparative evaluation in video surveillance. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 122(122), 22–34 (2014)
Luo, Q., Han, Z., Chen, X., et al.: Tensor rpca by bayesian cp factorization with complex noise. In: Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 5029–5038 (2017)
Goldfarb, D., Qin, Z.: Models and algorithms. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 35(1), 225–253 (2014)
Rezaei, B., Ostadabbas, S.: Background subtraction via fast robust matrix completion. In: Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1871–1879 (2017)
Cao, W., Wang, Y., Sun, J., et al.: Total variation regularized tensor RPCA for background subtraction from compressive measurements. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(9), 4075–4090 (2016)
Xie, Q., Zhao, Q., Meng, D., et al.: Kronecker-basis-representation based tensor sparsity and its applications to tensor recovery. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(8), 1888–1902 (2018)
Liu, Y., Chen, L., Zhu, C., et al.: Improved robust tensor principal component analysis via low-rank core matrix. IEEE J. Select. Top. Signal Process. 12(6), 1378–1389 (2018)
Lu, C., Feng, J., Chen, W., et al.: Tensor robust principal component analysis with a new tensor nuclear norm. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(2), 925–938 (2020)
Xue, J., Zhao, Y., Liao, W., et al.: Nonconvex tensor rank minimization and its applications to tensor recovery. Inform. Sci. 503, 109–128 (2019)
Ahn, H., Kang, M.: Dynamic background subtraction with masked RPCA. Signal Image Video Process. 15(3), 467–474 (2020)
Yuan, M., Lin, Y.: Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 68(1), 49–67 (2006)
Cao, X., Yang, L., Guo, X., et al.: Total variation regularized RPCA for irregularly moving object detection under dynamic background. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 46(4), 1014–1027 (2016)
Tom, A.J., George, S.N.: Tensor total variation regularized moving object detection for surveillance videos. In: Proceedings of 2018 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications (SPCOM), pp. 327–331 (2018)
Wei, Y., Liu, Y., Jia, L., et al.: Foreground extraction via the tensor-based RPCA with non-convex fused sparsity. In: Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (ICNC-FSKD), pp. 624–630 (2018)
Xu, Y., Wu, Z., Chanussot, J., et al.: Joint reconstruction and anomaly detection from compressive hyperspectral images using mahalanobis distance-regularized tensor RPCA. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 56(5), 2919–2930 (2018)
Zhang, Z., Ely, G., Aeron, S., et al.: Novel methods for multilinear data completion and de-noising based on tensor-SVD. In: Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3842–3849 (2014)
Wang, Y., Yin, W., Zeng, J.: Global convergence of ADMM in nonconvex nonsmooth optimization. J. Sci. Comput. 78(1), 29–63 (2019)
Shahid, N., Kalofolias, V., Bresson, X., et al.: Robust principal component analysis? J. ACM (JACM) 58(3), 1–39 (2011)
Li, L., Huang, W., Gu, I.Y., et al.: Statistical modeling of complex backgrounds for foreground object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(11), 1459–1472 (2004)
Mahadevan, V., Vasconcelos, N.: Spatiotemporal saliency in dynamic scenes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(1), 171–177 (2010)
Wang, Y., Jodoin, P., Porikli, F., et al.: CDNET 2014: An expanded change detection benchmark dataset. In: Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 393–400 (2014)
Liu, Z., He, S., Hu, W., et al.: Moving object detection based on background subtraction for video sequence. J. Comput. Appl. 37(6), 1777–1781 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This project is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11961010, 61661017, 61967005, 61362021), Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2018GXNSFAA138169, 2017GXNSFBA198212), Guangxi Colleges and Universities Key Laboratory project of Data Analysis and Computation (LDAC201704).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Ban, Y. & Wang, X. Background subtraction based on tensor nuclear and \(L_{1,1,2}\) norm. SIViP 16, 1053–1060 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-02054-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-02054-6