Abstract
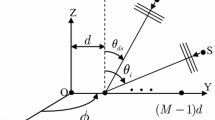
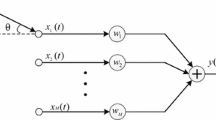
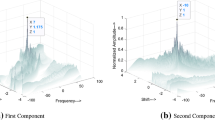
Essentially, the observed signal of interest is buried under the clutter due to high backscatters in radar or sonar applications. The presence of colored-Gaussian stationary noise (clutter) degrades the traditional beamformers, significantly. A new adaptive beamforming technique is presented here based on the numerical selection of the fractional order. The new method maximizes the fractional domain spectral kurtosis and optimum fractional Fourier domain cyclostationarity of the non-stationary linear chirp signal. This concentrates the desired chirp signal in the optimum time–frequency domain, rejects the clutter, and improves the minimization and convergence of the adaptive mean-squared error beamformer, greatly. Simulation results show that the new method performs well under low signal-to-noise ratio.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schleher, D.C.: Electronic Warfare in the Information Age. Artech House Inc, Norwood (1999)
Ahmad, M.I., Sardar, M.U., Ahmad, I.: Blind beamforming using fractional Fourier transform domain cyclostationarity. Signal Image Video Process. 12(2), 379–383 (2018)
Krim, H., Viberg, M.: Two decades of array signal processing research: the parametric approach. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 13(4), 67–94 (1996)
Applebaum, S., Chapman, D.: Adaptive arrays with main beam constraints. IEEE Trans. Ant. Propag. 24(5), 650–662 (1976)
Widrow, B., Mantey, P.E., Griffiths, L.J., Goode, B.B.: Adaptive antenna systems. IEEE Proc. 55(12), 2143–2159 (1967)
Frost, O.L.: An algorithm for linearly constrained adaptive array processing. IEEE Proc. 60(8), 926–935 (1972)
Capon, J.: High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis. IEEE Proc. 57(8), 1408–1418 (1969)
Yetik, I.S., Nehorai, A.: Beamforming using the fractional Fourier transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 51(6), 1663–1668 (2003)
Ahmad, M.I., Liu, Z., Xu, Y.: Order selection in fractional Fourier transform based beamforming. J. Syst. Eng. Electr. 21(3), 361–369 (2010)
Benesty, J., Chen, J., Huang, Y., Dmochowski, J.: On microphone-array beamforming from a MIMO acoustic signal processing perspective. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 15(3), 1053–1065 (2007)
Scott, L., Mulgrew, B.: Sparse LCMV beamformer design for suppression of ground clutter in airborne radar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43(12), 2843–2851 (1995)
Limpiti, T., Van Veen, B.D., Wakai, R.T.: Cortical patch basis model for spatially extended neural activity. IEEE Trans. Biomed Eng. 53(9), 1740–1754 (2006)
Chen, R., Wang, Y.: Efficient detection of chirp signals based on the fourth-order origin moment of fractional spectrum. Circuit Syst. Signal Process. 33(5), 1585–1596 (2014)
Guan, J., Chen, X.L., Huang, Y., He, Y.: Adaptive fractional Fourier transform-based detection algorithm for moving target in heavy sea clutter. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 6(5), 389–401 (2012)
Shamsunder, S., Giannakis, G.B., Friedlander, B.: Estimating random amplitude polynomial phase signals: a cyclostationary approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43(2), 492–505 (1995)
Gini, F., Montanari, M., Verrazzani, L.: Estimation of chirp radar signals in compound-Gaussian clutter: a cyclostationary approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 48(4), 1029–1039 (2000)
Kutay, A., Ozaktas, H.M., Ankan, O., Onural, L.: Optimal filtering in fractional Fourier domains. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(5), 1129–1143 (1997)
Wei, D., Ran, Q.: Multiplicative filtering in the fractional Fourier domain. Signal Image Video Process. 7(3), 575–580 (2013)
Ting, L.K., Cowan, C.F., Woods, R.F.: LMS coefficient filtering for time-varying chirped signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52(11), 3160–3169 (2004)
Antoni, J.: The spectral kurtosis: a useful tool for characterising nonstationary signals. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 20(2), 282–307 (2006)
Alieva, T., Bastiaans, M.J.: On fractional Fourier transform moments. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 7(11), 320–323 (2000)
Markhi, H.E., Haibala, O.M.M., Mrabti, F., Chargé, P., Zouak, M.: An improved cyclic beamforming method for signal DOA estimation. Signal Image Video Process. 1(3), 267–272 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank the editor and the anonymous referee for their valuable comments and suggestions that improved the clarity and quality of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, M.I. Optimum FrFT domain cyclostationarity based adaptive beamforming. SIViP 13, 551–556 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1381-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1381-y