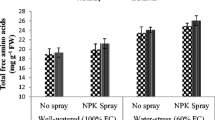
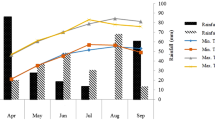
Abstract
Drought stress induced by inconsistency in rainfall lowers the agricultural productivity and necessitates the employment of a drought-tolerance mitigation strategy that involves fertigating plants with a range of biochemicals. The influence of foliar applied exogenous nitrogen (N), potassium (K), and water-soluble fertilizers (NPK) for the reduction of drought stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) was investigated in the current study under field drought stress conditions. The biological yield, yield and yield components, relative water content, chlorophyll content, and leaf osmotic potential of both cultivars were significantly (P ≤ 0.05) reduced by drought stress. In drought treatments, application of K@2% and water-soluble fertilizer NPK@2% significantly (P ≤ 0.05) improved these parameters. In drought-stressed plants, the addition of K and water-soluble NPK increased the accumulation of osmolytes and soluble carbohydrates while lowering malondialdehyde (MDA) levels. Under drought conditions, water-soluble NPK treatments resulted in a considerable increase in yield in GJW 463. Drought stress alleviation and yield increase in wheat cultivars were attributed to better osmotic adjustment, antioxidant activity and favorable water status under stress circumstances, due to K and NPK treatment. Supplemental fertilization with exogenous water-soluble nutrients K and NPK is an effective way to protect and improve drought tolerance and increase wheat grain output in drought-prone locations. Our results demonstrate that application of exogenous water-soluble NPK as a supplemental fertilizer protects wheat and promotes drought tolerance.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Necessary all data used for statistical analysis are available.
References
Abdelaal KAA, Hafez YM, El-Afry MM, Tantawy DS, Alshaal T (2018) Effect of some osmoregulators on photosynthesis, lipid peroxidation, antioxidative capacity, and productivity of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) under water deficit stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:30199–30211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3023-x
Abdel-Motagally FMF, El-Zohri M (2018) Improvement of wheat yield grown under drought stress by boron foliar application at different growth stages. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 17:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2016.03.005
Alam H, Khattak JZK, Ksiksi TS, Saleem MH, Fahad S, Sohail H, Ali Q, Zamin M, El-Esawi MA, Saud S, Jiang X, Alwahibi MS, Alkahtani J (2020) Negative impact of long-term exposure of salinity and drought stress on native Tetraena mandavillei L. Physiol Plant 172:1336–1351. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13273
Alhaithloul HA, Soliman MH, Ameta KL, El-Esawi MA, Elkelish A (2019) Changes in ecophysiology, osmolytes, and secondary metabolites of the medicinal plants of Mentha piperita and Catharanthus roseus subjected to drought and heat stress. Biomolecules 10:43. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010043
Ali A, Hussain M, Habib HS, Kiani TT, Anees MA, Rahman MA (2016) Foliar spray surpasses soil application of potassium for maize production under rainfed conditions. Turkish J Field Crop 21:36–43. https://doi.org/10.17557/tjfc.66054
Ali Q, Javed MT, Noman A, Haider MZ, Waseem M, Iqbal N, Waseem M, Shah MS, Shahzad F, Perveen R (2018) Assessment of drought tolerance in mung bean cultivars/lines as depicted by the activities of germination enzymes, seedling’s antioxidative potential and nutrient acquisition. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:84–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2017.1335393
Anjum SA, Wang CL, Farooq M, Hussain M, Xue LL, Zou MC (2011) Brassinolide application improves the drought tolerance in maize through modulation of enzymatic antioxidants and leaf gas exchange. J Agron Crop Sci 197:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2010.00459.x
Arif M, Chohan MA, Ali S, Gul R, Khan S (2006) Response of wheat to foliar application of nutrients. J Agric Biol Sci 1:30–34
Ashraf M, Harris PJC (2013) Photosynthesis under stressful environments: an overview. Photosynthetica 51:163–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-013-0021-6
Barrs HD, Weatherley PE (1962) A re-examination of relative turgidity of estimating water deficits in leaves. Aust J Biol Sci 15:413–428. https://doi.org/10.1071/BI9620413
Baser I, Sehirali H, Orta AH, Erdem T, Erdem Y, Yorgancilar O (2004) Effect of different water stresses on the yield and yield components of winter wheat. Cereal Res Commun 32:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03543302
Beadle CL (1985) Plant growth analysis. In: Coombs J, Hall DO, Long SP, Scurlock JMO (eds) Techniques in bioproductivity and photosynthesis. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 20–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-031999-5.50012-1
Blum A (1998) Improving wheat grain filling under stress by stem reserve mobilization. Euphytica 100:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018303922482
Bolouri-Moghaddam MR, Le Roy K, Xiang L, Rolland F, Van den Ende W (2010) Sugar signaling and antioxidant network connections in plant cells. FEBS J 277:2022–2037. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07633.x
Crampton CF, Stein WH, Moore S (1957) Comparative studies on chromatographically purified histones. J Biol Chem 225:363–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)64938-5
Demotes-Mainard S, Jeuffroy MH (2004) Effects of nitrogen and radiation on dry matter and nitrogen accumulation in the spike of winter wheat. Field Crop Res 87:221–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2003.11.014
El-Fouly MM, El-Sayed AA (1997) Foliar fertilization: An environmentally friendly application of fertilizers. Dahlia Greidinger International Symposium on “Fertilization and Environment” 24–27 March, Haifa, Israel, John, I. (ed.), p. 346–357.
Garg BK, Burman U, Kathju S (2004) The influence of phosphorus nutrition on the physiological response of moth bean genotypes to drought. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 167:503–508. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200320368
Gautam P, Lal B, Tripathi R, Shahid M, Baig MJ, Maharan S, Puree C, Nayak AK (2016) Beneficial effects of potassium application in improving submergence tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Exp Bot 128:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.04.005
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. Wiley and Sons, New York (ISBN: 978-0-471-87092-0)
Guellim A, Hirel B, Chabrerie O, Catterou M, Tetu T, Dubois F, Ahmed HB, Kichey T (2020) Screening for durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) cultivar resistance to drought stress using an integrated physiological approach. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 23:355–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-020-00043-8
Hussain HA, Men S, Hussain S, Chen Y, Ali S, Zhang S, Zhang K, Li Y, Xu Q, Liao C, Wang L (2019) Interactive effects of drought and heat stresses on morpho-physiological attributes, yield, nutrient uptake and oxidative status in maize hybrids. Sci Rep 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40362-7
Ihsan MZ, Shahzad N, Kanwal S, Naeem M, Khaliq A, El-Nakhlawy FS, Matloob A (2013) Potassium as foliar supplementation mitigates moisture induced stresses in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) as revealed by growth, photosynthesis, gas exchange capacity and Zn analysis of shoot. Int J Agron Plant Prod 4:3828–3835
Javed IUH, Akhtar S, Akram M, Arfanm M, Yasmin S (2003) Differential yield responses of barley genotypes to NaCl salinity. Int J Agric Biol 5:1560–8530
Kelaleche H, Guendouz A, Hafsi M (2018) The effect of water stress on some physiological and biochemical traits in five durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) genotypes. Int J Biosci 12:90–97
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0110591
Liu F, Jensena C, Andersen M (2004) Drought stress effect on carbohydrate concentration in soybean leaves and pods during early reproductive development: its implication in altering pod set. Field Crops Res 86:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(03)00165-5
Lv X, Ding Y, Long M, Liang W, Gu X, Liu Y, Wen X (2021) Effect of foliar application of various nitrogen forms on starch accumulation and grain filling of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under drought stress. Front Plant Sci 12:645379. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.645379
Maghsoudi K, Emam Y, Niazi A, Pessarakli M, Arvin MJ (2018) P5CS expression level and proline accumulation in the sensitive and tolerant wheat cultivars under control and drought stress conditions in the presence/absence of silicon and salicylic acid. J Plant Interact 13:461–471. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2018.1506516
Manomani V, Srimathi P (2009) Influence of mother crop nutrition on seed and quality of blackgram. Madras Agric J 96:125–128
Martineau E, Domec JC, Bosc A, Denoroy P, Fandino VA, Lavres J, Jordan-Meille L (2017) The effects of potassium nutrition on water use in field-grown maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Exp Bot 134:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.11.004
Mikiciuk G, Mikiciuk M, Ptak P (2015) The effects of anitranspirant Di-1-P-menthenephysiological traits of strawberry. J Ecol Eng. 16:161–167. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/59366
Mohammadi M, Tavakoli A, Pouryousef M, Fard EM (2020) Study the effect of 24-epibrassinolide application on the Cu/Zn-SOD expression and tolerance to drought stress in common bean. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00757-7
Naveenaa M, Amaregouda A, Meena MK, Suma TC, Kuchanur PH (2018) Influence of foliar nutrition at different growth stages on physiological and biochemical parameters of maize (Zea mays L.). J Pharmacogn Phytochem 7:256–262
Nazar Z, Akram NA, Saleem MH, Ashraf M, Ahmed S, Ali S, Abdullah Alsahli A, Alyemeni MN (2020) Glycine betaine-induced alteration in gaseous exchange capacity and osmoprotective phenomena in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius l.) under water deficit conditions. Sustainability 12:10649. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410649
Noctor G, Foyer CH (1998) Ascorbate and glutathione: Keeping active oxygen under control. Ann Rev Plant Biol 49:249–279. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.249
Oosterhuis DM (1998) Foliar fertilization of cotton with potassium in the USA. Proc. Symp. “Foliar Fertilization: A Technique to Improve Production and Decrease Pollution” 10–14 Dec. 1995, Cairo, Eds. El-Fouly, p. 49–64.
Plaut Z, Butow JBS, Blumenthal C, Wrigley WC (2004) Transport of dry matter into developing wheat kernels and its contribution to grain yield under post- anthesis water deficit and evaluated temperature. Field Crops Res 86:185–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2003.08.005
Ratzmann G, Zakharova L, Tietjen B (2019) Optimal leaf water status regulation of plants in drylands. Sci Rep 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40448-2
Raza MAS, Saleem MF, Shah GM, Jamil M, Khan IH (2013) Potassium applied under drought improves physiological and nutrient uptake performances of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 13:175–185. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162013005000016
Sairam RK, Deshmukh PS, Shukla DS (1997) Increased antioxidant enzyme activity in response to drought and temperature stress related with stress tolerance in wheat genotypes, Abstract: National Seminar (ISSP). IARI, New Delhi. p. 69
Saud S, Fahad S, Chen YJ, Ihsan MZ, Hammad HM, Nasim W, Amanullah Jr, Arif M, Alharby H (2017) Effects of nitrogen supply on water stress and recovery mechanisms in Kentucky bluegrass plants. Front Plant Sci 8:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00983
Shabbir RN, Ashraf MY, Waraich EA, Ahmad R, Shahbaz M (2015) Combined effects of drought stress and NPK foliar spray on growth, physiological processes and nutrient uptake in wheat. Pak J Bot 47:1207–1216
Shabbir RN, Waraich EA, Ali H, Nawaz F, Ashraf MY, Ahmad R, Awan MI, Ahmad S, Irfan M, Hussain S, Ahmad Z (2016) Supplemental exogenous NPK application alters biochemical processes to improve yield and drought tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:2651–2662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5452-0
Weldearegay DF, Yan F, Jiang D, Liu F (2012) Independent and combined effects of soil warming and drought stress during anthesis on seed set and grain yield in two spring wheat varieties. J Agron Crop Sci 198:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2012.00507.x
Yadav VK, Singh AK, Singh P, Kumar R, Srivastav SK, Yadav V, Yadav RK (2019) Effect on foliar application of potassium nitrate on physiological, biochemical and yield potential in different wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars under drought and irrigated conditions. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 8:254–257
Zheng YH, Xu XB, Wang MY, Zheng XH, Li ZJ, Jiang GM (2009) Responses of salt-tolerant and intolerant wheat genotypes to sodium chloride: photosynthesis, antioxidants activities, and yield. Photosynthetica 47:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-009-0014-7
Acknowledgements
We sincerely acknowledge the Research Scientist, Wheat Research Station and Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh, Gujarat for providing necessary experimental filed and laboratory facilities for conduction and execution of this study. We would like to thank Dr. Rajkumar B.K., for improving the manuscript through the use of English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Srivastava.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pandya, Y., Singh, C., Godha, U. et al. Interactive responses of water-soluble fertilizers to mitigate drought stress effects on wheat (T. aestivum). Acta Physiol Plant 45, 62 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-023-03550-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-023-03550-7