Abstract
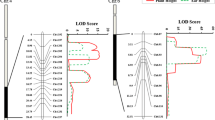
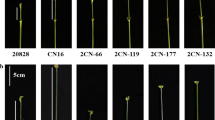
The low ratio of ear-to-plant heights (EPR) contributes to the balance and stability of maize plant’s center of gravity, resulting in reduced lodging for high grain yield. Previous studies on EPR of maize plants in response to ethylene mainly focused on phenotypic correlations with grain yield or stalk trait. In this study, QTL mapping by SNPs marker for EPR of maize plants was analyzed under ethylene treatment (ET) and non-ET control. The results indicated that ET significantly decreased phenotypic performance of EPR. High variance of EPR among RIL population showed a normal distribution. Five QTLs associated with EPR were identified under the two treatments using composition–interval mapping. The phenotypic variance observed by an individual QTL ranged from 5.69 to 10.02%. Two QTLs (qEPR1, qEPR2-2) were identified in ET treatment. One QTL (qEPR2-2) was simultaneously detected in both treatments at two geographic locations. These stable and consistent QTLs were important spots for EPR. Our findings provided important information for the fine mapping of quantitative trait genes and would help to reveal the molecular mechanisms of how EPR response to the application of ethylene.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abendroth LJ, Elmore R, Boyer M, Marlay S (2011) Corn growth and development. Iowa State University, University Extension, Ames
Bai W, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Teng F, Wang L, Tao Y, Zheng Y (2010) The evidence for non-additive effect as the main genetic component of plant height and ear height in maize using introgression line populations. Plant Breed 129:376–384
Bian D, Jia G, Cai L, Ma Z, Eneji AE, Cui Y (2016) Effects of tillage practices on root characteristics and root lodging resistance of maize. Field Crops Res 185:89–96
Chen X, Chen F, Chen Y, Gao Q, Yang X, Yuan L, Zhang F, Mi G (2013) Modern maize hybrids in Northeast China exhibit increased yield potential and resource use efficiency despite adverse climate change. Glob Change Biol 19:923–936
Chen G, Wang X, Long S, Jaqueth J, Li B, Yan J, Ding J (2016) Mapping of QTL conferring resistance to northern corn leaf blight using high-density SNPs in maize. Mol Breed 36:1–9
Clark R, Fedak G (1977) Effects of chlormequat on plant height, disease development and chemical constituents of cultivars of barley, oats, and wheat. Can J Plant Sci 57:31–36
Dong Z, Jiang C, Chen X, Zhang T, Ding L, Song W, Luo H, Lai J, Chen H, Liu R (2013) Maize LAZY1 mediates shoot gravitropism and inflorescence development through regulating auxin transport, auxin signaling, and light response. Plant Physiol 163:1306–1322
Flint-Garcia SA, Jampatong C, Darrah LL, McMullen MD (2003) Quantitative trait locus analysis of stalk strength in four maize populations. Crop Sci 43:13–22
Foster T, Yamaguchi J, Wong BC, Veit B, Hake S (1999) Gnarley1 is a dominant mutation in the knox4 homeobox gene affecting cell shape and identity. Plant Cell 11:1239–1252
Fu Z, Li W, Zhang Q, Wang L, Zhang X, Song G, Fu Z, Ding D, Liu Z, Tang J (2014) Quantitative trait loci for mercury accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) identified using a RIL population. PLoS One 9:e107243
Fu Z, Li W, Xing X, Xu M, Liu X, Li H, Xue Y, Liu Z, Tang J (2016) Genetic analysis of arsenic accumulation in maize using QTL mapping. Sci Rep 21292:1–8
Guo J, Chen Z, Liu Z, Wang B, Song W, Li W, Chen J, Dai J, Lai J (2011) Identification of genetic factors affecting plant density response through QTL mapping of yield component traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Euphytica 182:409–412
Guo S, Ku L, Qi J, Tian Z, Han T, Zhang L, Su H, Ren Z, Chen Y (2015) Genetic analysis and major quantitative trait locus mapping of leaf widths at different positions in multiple populations. PLoS One 10:e0119095
Hao Z, Li X, Xie C, Weng J, Li M, Zhang D, Liang X, Liu L, Liu S, Zhang S (2011) Identification of functional genetic variations underlying drought tolerance in maize using SNP markers. J Integr Plant Biol 53:641–652
He K, Chang L, Cui T, Qu J, Guo D, Xu S, Zhang X, Zhang R, Xue J, Liu J (2016) Mapping QTL for plant height and ear height in maize under multi-environments. Sci Agric Sin 49:1443–1452
Hu H, Liu W, Fu Z, Homann L, Technow F, Wang H, Song C, Li S, Melchinger AE, Chen S (2013) QTL mapping of stalk bending strength in a recombinant inbred line maize population. Theor Appl Genet 126:2257–2266
Hund A, Fracheboud Y, Soldati A, Frascaroli E, Salvi S, Stamp P (2004) QTL controlling root and shoot traits of maize seedlings under cold stress. Theor Appl Genet 109:618–629
Ku LX, Zhao WM, Zhang J, Wu LC, Wang CL, Wang PA, Zhang WQ, Chen YH (2010) Quantitative trait loci mapping of leaf angle and leaf orientation value in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 121:951–959
Ku L, Zhang L, Tian Z, Guo S, Su H, Ren Z, Wang Z, Li G, Wang X, Zhu Y (2015) Dissection of the genetic architecture underlying the plant density response by mapping plant height-related traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Mol Genet Genomics 290:1223–1233
Li Q, Li Y, Yang Z, Liu C, Liu Z, Li C, Peng B, Zhang Y, Wang D, Tan W (2013) QTL mapping for plant height and ear height by using multiple related RIL populations in maize. Acta Agron Sin 39:1521–1529
Li Y, Li Y, Ma X, Liu C, Shi Y, Song Y, Zhang D, Smith S, Wang T (2016) Genetically mediated changes in the grain quality of single-cross maize hybrids grown in China. Crop Sci 56:132
Lv H, Zheng J, Wang T, Fu J, Huai J, Min H, Zhang X, Tian B, Shi Y, Wang G (2014) The maize d2003, a novel allele of VP8, is required for maize internode elongation. Plant Mol Biol 84:243–257
Ma D, Xie R, Niu X, Li S, Long H, Liu Y (2014) Changes in the morphological traits of maize genotypes in China between the 1950s and 2000s. Eur J Agron 58:1–10
Messmer R, Fracheboud Y, Banziger M, Vargas M, Stamp P, Ribaut JM (2009) Drought stress and tropical maize: QTL-by-environment interactions and stability of QTLs across environments for yield components and secondary traits. Theor Appl Genet 119:913–930
Norberg O, Mason S, Lowry S (1988) Ethephon influence on harvestable yield, grain quality, and lodging of corn. Agron J 80:768–772
Osman KA, Tang B, Wang Y, Chen J, Yu F, Li L, Han X, Zhang Z, Yan J, Zheng Y, Yue B, Qiu F (2013) Dynamic QTL analysis and candidate gene mapping for waterlogging tolerance at maize seedling stage. PLoS One 8:e79305
Pan Q, Li L, Yang X, Tong H, Xu S, Li Z, Li W, Muehlbauer GJ, Li J, Yan J (2015) Genome-wide recombination dynamics are associated with phenotypic variation in maize. New Phytol 210:1083–1094
Peiffer JA, Flint-Garcia SA, De Leon N, McMullen MD, Kaeppler SM, Buckler ES (2013) The genetic architecture of maize stalk strength. PLoS One 8:e67066
Qin X, Feng F, Li Y, Xu S, Siddique KHM, Liao Y, Lübberstedt T (2016) Maize yield improvements in China: past trends and future directions. Plant Breed 135:166–176
Rajala A (2004) Plant growth regulators to manipulate oat stands. Agric Food Sci 13:186–197
Rajala A, Peltonen-Sainio P (2002) Timing applications of growth regulators to alter spring cereal development at high latitudes. Agric Food Sci 11:233–244
Rajala A, Peltonen-Sainio P (2008) Timing applications of growth regulators to alter spring cereal development at high latitudes. Agric Food Sci 11:233–244
Rajala A, Peltonen-Sainio P, Onnela M, Jackson M (2002) Effects of applying stem-shortening plant growth regulators to leaves on root elongation by seedlings of wheat, oat and barley: mediation by ethylene. Plant Growth Regul 38:51–59
Revilla P, Rodriguez VM, Ordas A, Rincent R, Charcosset A, Giauffret C, Melchinger AE, Schon CC, Bauer E, Altmann T, Brunel D, Moreno-Gonzalez J, Campo L, Ouzunova M, Alvarez A, Ruiz de Galarreta JI, Laborde J, Malvar RA (2016) Association mapping for cold tolerance in two large maize inbred panels. BMC Plant Biol 16:127
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard R (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Sari-Gorla M, Krajewski P, Di Fonzo N, Villa M, Frova C (1999) Genetic analysis of drought tolerance in maize by molecular markers. II. Plant height and flowering. Theor Appl Genet 99:289–295
Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush GS (2002) Green revolution: a mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice. Nature 416:701–702
Shekoofa A, Emam Y (2008) Plant growth regulator (ethephon) alters maize (Zea mays L.) growth, water use and grain yield under water stress. J Agron 7:41–48
Teng F, Zhai L, Liu R, Bai W, Wang L, Huo D, Tao Y, Zheng Y, Zhang Z (2013) ZmGA3ox2, a candidate gene for a major QTL, qPH3.1, for plant height in maize. Plant J 73:405–416
Van Der Straeten D, Zhou Z, Prinsen E, Van Onckelen HA, Van Montagu MC (2001) A comparative molecular-physiological study of submergence response in lowland and deepwater rice. Plant Physiol 125:955–968
Van Ooijen J (2006) JoinMap 4: Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen
Wang S, Basten C, Zeng Z (2007) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh
Wei X (2011) Study on regulation mechanism of ethephon on internode elongation in maize. PhD Dissertation of China Agricultural University, pp 14–19
Xing A, Gao Y, Ye L, Zhang W, Cai L, Ching A, Llaca V, Johnson B, Liu L, Yang X, Kang D, Yan J, Li J (2015) A rare SNP mutation in Brachytic2 moderately reduces plant height and increases yield potential in maize. J Exp Bot 66:3791–3802
Yang Q, Zhang D, Xu M (2012) A sequential quantitative trait locus fine-mapping strategy using recombinant-derived progeny. J Integr Plant Biol 54:228–237
Ye DL, Zhang YS, Al-Kaisi MM, Duan LS, Zhang MC, Li ZH (2015) Ethephon improved stalk strength associated with summer maize adaptations to environments differing in nitrogen availability in the North China Plain. J Agric Sci 6:960–977
Zhang X, Tang B, Yu F, Li L, Wang M, Xue Y, Zhang Z, Yan J, Yue B, Zheng Y, Qiu F (2013) Identification of major QTL for waterlogging tolerance using genome-wide association and linkage mapping of maize seedlings. Plant Mol Biol Rep 31:594–606
Zhang Q, Zhang L, Evers J, van der Werf W, Zhang W, Duan L (2014) Maize yield and quality in response to plant density and application of a novel plant growth regulator. Field Crops Res 164:82–89
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The China National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant 31425017 to L.D.). The authors are grateful to Professor Xiaohong Yang, China Agricultural University, who developed the populations and contributed materials. The authors thank Professor Lizhen Zhang, China Agricultural University, for language improvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by W. Wang.
Appendix
Appendix
See Table 7.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zhang, M., Li, Z. et al. Dissection of the molecular genetic architecture of the ratio of ear to plant heights in response to ethylene by a RIL population with SNPs marker in maize. Acta Physiol Plant 39, 142 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2438-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2438-1