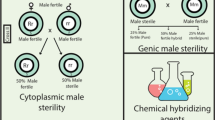
Abstract
The common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a poly(hexa)ploid, derived from an amphi-diploidization process involving the donor species—Triticum urartu, Aegilops speltoides, Triticum turgidum, and Aegilops tauschii. The genetic diversity of the autogamous wheat is narrow, which is a major reason for lesser rate of yield gain in wheat, in contrast to rice and maize. It is desirable to encourage hybrid breeding, i.e., combining different lines into genetically divergent heterotic pools. Thus, hybrid plants are a unique combination of desired alleles produced by crossing between genetically different parental lines. Hybrid seed production in a crop requires male-sterile female parents along with a reliable outcrossing system. The male-sterile female parent prevents pollen shedding and self-fertilization, maintaining the purity of hybrid seeds. An outcrossing system enhances hybrid seed production. This article emphasizes the biological relevance of crossbreeding and self-pollination in wheat, and reviews different male sterility systems which could be utilized for the development of hybrid wheat. Several biotechnological approaches and their practical utility in generating cross-compatible male-sterile female parent lines have been discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adugna A, Nanda GS, Singh K, Bains NS (2004) A comparison of cytoplasmic and chemically-induced male sterility systems for hybrid seed production in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 135(3):297–304
Adugna A, Nanda GS, Bains NS (2006) A comparison of cytoplasmic and chemically-induced male sterility systems for hybrid performance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Acta Agron Hung 54(1):109–120
Barrett SCH (2003) Mating strategies in flowering plants: the outcrossing-selfing paradigm and beyond. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 358:991–1004
Bing-Hua L, Jing-Yang D (1986) A dominant gene for male sterility in wheat. Plant Breeding 97(3):204–209
Block M, Debrouwer D, Moens T (1997) The development of a nuclear male sterility system in wheat. Expression of the barnase gene under the control of tapetum specific promoters. Theor Appl Genet 95(1/2):125–131
Campbell CA, Davidson HR (1979) Effect of temperature, nitrogen fertilization and moisture stress on growth, assimilate distribution and moisture use by manitou spring wheat. Can J Plant Sci 59(3):603–626
Cao W, Somers DJ, Fedak G (2009) A molecular marker closely linked to the region of Rht-D1c and Ms2 genes in common wheat (Triticum aestivum). Genome 52(1):95–99
Chakraborty K, Devakumar C (2005) N-acylanilines, herbicide-CHA chimera, and amino acid analogues as novel chemical hybridizing agents for wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Agric Food Chem 53(20):7899–7907
Chakraborty K, Devakumar C (2006) Evaluation of chemical compounds for induction of male sterility in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 147(3):329–335
Chase CD (2007) Cytoplasmic male sterility: a window to the world of plant mitochondrial-nuclear interactions. Trends Genet 23(2):81–90
Chen X, Sun D, Rong D, Sun G, Peng J (2010) Relationship of genetic distance and hybrid performance in hybrids derived from a new photoperiod-thermo sensitive male sterile wheat line 337S. Euphytica 175(3):365–371
Chen XD, Sun DF, Rong DF, Peng JH, Li CD (2011) A recessive gene controlling male sterility sensitive to short daylength/low temperature in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 12(11):943–950
Chowdhury AK, Signh G, Tyagi BS, Bhattacharya PM, Roy AKS (2008) Assessment of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars to boron deficiency-induced spike sterility and its impact on grain yield under terai region of West Bengal. Indian J Agric Sci 78(10)
Chrimes D, Rogers HJ, Francis D, Jones HD, Ainsworth C (2005) Expression of fission yeast cdc25 driven by the wheat ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase large subunit promoter reduces pollen viability and prevents transmission of the transgene in wheat. New Phytol 166(1):185–192
Ciha AJ, Ruminski PG (1991) Specificity of pyridine monocarboxylates and benzoic acid analogues as chemical hybridizing agents in wheat. J Agric Food Chem 39:2072–2076
Colombo N, Favret EA (1996) The effect of gibberellic acid on male fertility in bread wheat. Euphytica 91(3):297–303
Dai X-M, Xu Ru-Hong, Lu Jun, Li Fang, Li Jia-Na, Chai You-Rong (2008) Alien chromosome-specific pcr markers for selection of powdery mildew resistance introgressed from Haynaldia villosa in wheat. Genes Genomics 30(5):439–449
Distelfeld A, Pearce SP, Avni R, Scherer B, Uauy C, Piston F, Slade A, Zhao R, Dubcovsky J (2012) Divergent functions of orthologous NAC transcription factors in wheat and rice. Plant Mol Biol 78(4–5):515–524
Dorion S, Lalonde S, Saini HS (1996) Induction of male sterility in wheat by meiotic-stage water deficit is preceded by a decline in invertase activity and changes in carbohydrate metabolism in anthers. Plant Physiol 111(1):137–145
Driscoll CJ (1977) Registration of Cornerstone male-sterile wheat germplasm. Crop Sci 17:190
Driscoll CJ (1978) Induction and use of the “Cornerstone” male-sterility in wheat. In: 5th Int Wheat Genet Symp, pp 499–502
Endo TR, Mukai Y, Yamamoto M, Gill BS (1991) Physical mapping of a male-fertility gene of common wheat. Jpn J Genet 66(3):291–295
Engelke T, Hirsche J, Roitsch T (2010) Anther-specific carbohydrate supply and restoration of metabolically engineered male sterility. J Exp Bot 61(10):2693–2706
Fan P, Cui D, Fan HW (1998) Studies on the male sterility induced by CHA-SC 2053 in common wheat. Acta Agric Univ Henanensis 32(2):149–153
Fossati A, Ingold M (1970) A male sterile mutant in Triticum aestivum. Wheat Information Service 30 (8–10)
Fotiou C, Damialis A, Krigas N, Halley JM, Vokou D (2010) Parietaria judaica flowering phenology, pollen production, viability and atmospheric circulation, and expansive ability in the urban environment: impacts of environmental factors. Int J Biometeorol 55(1):35–50
Gao QR, Sun L, Liu B (1996) Induced male sterility and its effects on growth and development of winter wheat. J Shandong Agric Univ 27:241–248
Gill BS, Appels R, Botha-Oberholster AM, Buell CR, Bennetzen JL, Chalhoub B, Chumley F, Dvorak J, Iwanaga M, Keller B, Li W, McCombie WR, Ogihara Y, Quetier F, Sasaki T (2004) A workshop report on wheat genome sequencing: International Genome Research on Wheat Consortium. Genetics 168(2):1087–1096
Gomez-Casati DF, Busi MV, Gonzalez-Schain N, Mouras A, Zabaleta EJ, Araya A (2002) A mitochondrial dysfunction induces the expression of nuclear-encoded complex I genes in engineered male sterile Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 532(1–2):70–74
Grill LK, Turpen TH, Erwin RL (1990) Male sterility in plants. Patent Application WO1990013654A1, PCT/US1990/002404
Guan RX, Liu DC, Zhang AM (2001) Genetic analysis and identification of RAPD markers of fertility restorer gene Rf6 for the T. timopheevii cytoplasmic Male sterility of wheat. J Agric Biotechnol 9:159–162
Guo RX, Sun DF, Tan ZB, Rong DF, Li CD (2006) Two recessive genes controlling thermophotoperiod-sensitive male sterility in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 112(7):1271–1276
He BR (2000) One breeding method of thermo-sensitive male sterile wheat lines that adapt to the wheat production areas of Huanghuai region of China. China Patent CN1316182
He P, Dong P, Song X, Ma L, Hu Y, Jiang T, Wang J, Li H (2003) Study on the thermo-sensitivity of thermo-sensitive male-sterile wheat line A3314. J Triticeae Crops 23(1):1–6
Hernould M, Suharsono S, Litvak S, Araya A, Mouras A (1993) Male-sterility induction in transgenic tobacco plants with an unedited atp9 mitochondrial gene from wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(6):2370–2374
Hoagland AR, Elliott FC, Rasmussen LW (1953) Some histological and morphological effects of maleic hydrazide on a spring wheat. Agron J 45(10):468–472
Ikeguchi S, Hasegawa A, Murai T, Tsunewaki K (1999) Basic studies on hybrid wheat breeding using the 1BL-1RS translocation chromosome/Aegilops kotschyi cytoplasm system 1. Development of male sterile and maintainer lines with discovery of a new fertility-restorer. Euphytica 109(1):33–42
Jauhar PP, Chibbar RN (1999) Chromosome-mediated and direct gene transfers in wheat. Genome 42(4):570–583
Ji X, Shiran B, Wan J, Lewis DC, Jenkins CL, Condon AG, Richards RA, Dolferus R (2010) Importance of pre-anthesis anther sink strength for maintenance of grain number during reproductive stage water stress in wheat. Plant Cell Environ 33(6):926–942
Jiang ML, Wang DQ, Zhang A, Huang C (1998) Male sterile effect of a new pyridazine compound 9403 on wheat. J China Agric Univ 3(5):39–44
Jian-Kui Z, Jing D, Xue-Feng Z, Guo-Dong YU, Xiu-Mei DAI, Ren-Wu R (2009) Fertility alternation of thermo-photo-sensitive genic male sterile (TGMS) Wheat line c412s and its association with adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene expression. Acta Agron Sin 35(4):662–671
Jin F, Ma L, Fan C, Wang A, He B, Li H (2009) Genetic analysis on spike length and spikelet number of 1B/1R and non-1B/1R K type wheat male sterile lines. J Triticeae Crops 29(1):18–23
Kaul MLH (1988) Male sterility in higher plants. Springer, Berlin
Kawanabe T, Ariizumi T, Kawai-Yamada M, Uchimiya H, Toriyama K (2006) Abolition of the tapetum suicide program ruins microsporogenesis. Plant Cell Physiol 47(6):784–787
Kempe K, Gils M (2011) Pollination control technologies for hybrid breeding. Mol Breeding 27(4):417–437
Kempe K, Rubtsova M, Riewe D, Gils M (2013) The production of male-sterile wheat plants through split barnase expression is promoted by the insertion of introns and flexible peptide linkers. Transgenic Res 22(6):1089–1105
Kempe K, Rubtsova M, Gils M (2014) Split-gene system for hybrid wheat seed production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:9097–9102
Kihara H (1951) Substitution of nucleus and its effect on genome manifestation. Cytologia 16:177–193
Kihara H, Tsunewaki K (1964) Some fundamental problems underlying the program for hybrid wheat breeding. Seiken Jiho 16:1–14
Kimatu JN, Bao L (2010) Epigenetic polymorphisms could contribute to the genomic conflicts and gene flow barriers resulting to plant hybrid necrosis. Afr J Biotechnol 9(48):8125–8133
Klindworth DL, Williams ND, Maan SS (2002) Chromosomal location of genetic male sterility genes in four mutants of hexaploid wheat. Crop Sci 42(5):1447–1450
Konagaya K, Ando S, Kamachi S, Tsuda M, Tabei Y (2008) Efficient production of genetically engineered, male-sterile Arabidopsis thaliana using anther-specific promoters and genes derived from Brassica oleracea and B. rapa. Plant Cell Rep 27(11):1741–1754
Kumar J, Singh SP, Kumar J, Tuli R (2012) A novel mastrevirus infecting wheat in India. Arch Virol 157:2031–2034
Kumar J, Kumar J, Singh SP, Tuli R (2014a) Association of satellites with a mastrevirus in natural infection: complexity of wheat dwarf India virus disease. J Virol 88(12):7093–7104
Kumar J, Kumar J, Singh SP, Tuli R (2014b) βC1 is a pathogenicity determinant: not only for begomovirus but also for mastrevirus. Arch Virol 159(11):3071–3076
Kurek I, Dulberger R, Azem A, Tzvi BB, Sudhakar D, Christou P, Breiman A (2002) Deletion of the C-terminal 138 amino acids of the wheat FKBP73 abrogates calmodulin binding, dimerization and male fertility in transgenic rice. Plant Mol Biol 48(4):369–381
Laurie DA (1989) Factors affecting fertilization frequency in crosses of Triticum aestivum cv. ‘Highbury’ × Zea mays cv. ‘Seneca 60’. Plant Breed 103(2):133–140
Li Y, Zhao C, Zhang F, Sun H, Sun D (2006) Fertility alteration in the photo-thermo-sensitive male sterile line BS20 of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 151(2):207–213
Liu BH, Deng JY (1986) A dominant gene for male sterility in wheat. Plant Breeding 97(3):204–209
Liu CG, Wu YW, Zhang CL, Ren SX, Zhang Y (1997) A preliminary study on the effects of Aegilops crassa cytoplasm on the characters of common wheat. J Genet Genomics 24:241–247
Liu CG, Hou N, Liu GQ, Wu YW, Zhang CL, Zhang Y (2002) Studies on fertility genetic characters in D2-type CMS lines of common wheat. J Genet Genomics 29:638–645
Liu H, Cui P, Zhan K, Lin Q, Zhuo G, Guo X, Ding F, Yang W, Liu D, Hu S, Yu J, Zhang A (2011) Comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes between a wheat K-type cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) line and its maintainer line. BMC Genom 12:163
Longin CFH, Muhleisen J, Maurer HP, Zhang HL, Gowda M, Reif JC (2012) Hybrid breeding in autogamous cereals. Theor Appl Genet 125(6):1087–1096
Luan Y, Wang X, Liu W, Li C, Zhang J, Gao A, Wang Y, Yang X, Li L (2010) Production and identification of wheat-Agropyron cristatum 6P translocation lines. Planta 232(2):501–510
Lucken KA (1987) Hybrid wheat. In: Heyne EG (ed) Wheat and wheat improvement. American Society of Agronomy, Madison
Ma M, Yan Y, Huang L, Chen M, Zhao H (2012) Virus-induced gene-silencing in wheat spikes and grains and its application in functional analysis of HMW-GS-encoding genes. BMC Plant Biol 10(12):141
Maan SS, Kianian SF (2001) Third dominant male sterility gene in common wheat. Wheat Inf Service 93:27–31
Maan SS, Carlson KM, Williams ND, Yang T (1987) Chromosomal arm location and gene-centromere distance of a dominant gene for male sterility in wheat. Crop Sci 27(3):494–500
Manmathan H, Shaner D, Snelling J, Tisserat N, Lapitan N (2013) Virus-induced gene silencing of Arabidopsis thaliana gene homologues in wheat identifies genes conferring improved drought tolerance. J Exp Bot 64(5):1381–1392
Mariani C, Beuckeleer MD, Truettner J, Leemans J, Goldberg RB (1990) Induction of male sterility in plants by a chimaeric ribonuclease gene. Nature 347(6295):737–741
Martin AC, Atienza SG, Ramirez MC, Barro F, Martin A (2008) Male fertility restoration of wheat in Hordeum chilense cytoplasm is associated with 6HchS chromosome addition. Aust J Agric Res 59(3):206–213
Martin A, Atienza S, Ramírez M, Barro F, Martín A (2009) Chromosome engineering in wheat to restore male fertility in the msH1 CMS system. Mol Breed 24(4):397–408
Martin AC, Atienza SG, Ramirez MC, Barro F, Martin A (2010) Molecular and cytological characterization of an extra acrocentric chromosome that restores male fertility of wheat in the msH1 CMS system. Theor Appl Genet 121(6):1093–1101
McIntosh RA, Hart GE, Devos KM, Gale MD, Rogers WJ (1998) Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat. Paper presented at the Internat Wheat Genet Symp, Saskatoon
Merezhko AF (1998) Impact of plant genetic resources on wheat breeding. Euphytica 100(1):295–303
Mizumoto K, Hatano H, Hirabayashi C, Murai K, Takumi S (2011) Characterization of wheat Bell1-type homeobox genes in floral organs of alloplasmic lines with Aegilops crassa cytoplasm. BMC Plant Biol 11:2
Morgan JM (1980) Possible role of abscisic acid in reducing seed set in water-stressed wheat plants. Nature 285(5767):655–657
Mukai Y, Tsunewaki K (1979) Basic studies on hybrid wheat breeding. Theor Appl Genet 54(4):153–160
Mukasa Y, Suzuki T, Honda Y (2007) Emasculation of Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn.) using hot water. Euphytica 156(3):319–326
Murai K (1998) F1 seed production efficiency by using photoperiod-sensitive cytoplasmic male sterility and performance of F1 hybrid lines in wheat. Breed Sci 48:35–40
Murai K (2001) Factors responsible for levels of male sterility in photoperiod-sensitive cytoplasmic male sterile (PCMS) wheat lines. Euphytica 117(2):111–116
Murai K, Tsunewaki K (1993) Photoperiod-sensitive cytoplasmic male sterility in wheat with Aegilops crassa cytoplasm. Euphytica 67(1):41–48
Murai K, Takumi S, Koga H, Ogihara Y (2002) Pistillody, homeotic transformation of stamens into pistil-like structures, caused by nuclear-cytoplasm interaction in wheat. Plant J 29(2):169–181
Murai K, Tsutui I, Kawanishi Y, Ikeguchi S, Yanaka M, Ishikawa N (2008) Development of photoperiod-sensitive cytoplasmic male sterile (PCMS) wheat lines showing high male sterility under long-day conditions and high seed fertility under short-day conditions. Euphytica 159(3):315–323
Niu N, Zhang G, Cao Y, Zhang Y, Wei F (2008) Directional transduction of male sterile gene rfv 1 of NIAN type in wheat. Front Agric China 2(4):386–390
Nonaka S, Toriyama K, Tsunewaki K, Shimada T (1993) Breeding of male-sterile lines and their maintainer lines by backcross method for hybrid wheat production using an Sv type cytoplasm and a 1BL-1RS chromosome. Japan J Breed 43:567–574
Oehler E, Ingold M (1966) New cases of male sterility and new restorer source in T. aestivum. Wheat Inf Service 22:1–3
Ohtsuka I, Konzak CF (2002) Cytoplasmic male sterility-based system for hybrid wheat plant and seed production
Otsuka J, Yamaguchi S, Chigira O, Kato K (2010) Application of hot water emasculation to Acacia auriculiformis for controlled pollination. J Forest Res 15(3):210–216
Panayotov I, Gotsova DK, Gotsov K (1986) Male fertility restoration against alien cytoplasm. I. Comparison between the restoration abilities of three groups of lines. Wheat Inf Service 63:7–10
Parodi P, Gaju M (2009a) Male sterility induced by the chemical hybridizing agent clofencet on wheat, Triticum aestivum and T. turgidum var. durum. Cien Inv Agr 36(2):267–276
Parodi PC, Gaju MA (2009b) Male sterility induced by the chemical hybridizing agent clofencet on wheat, Triticum aestivum and T. turgidum var. durum. Ciencia e Investigación Agraria 36:267–276
Perez-Prat E, van Lookeren Campagne MM (2002) Hybrid seed production and the challenge of propagating male-sterile plants. Trends Plant Sci 7(5):199–203
Phan HA, Li SF, Parish RW (2012) MYB80, a regulator of tapetal and pollen development, is functionally conserved in crops. Plant Mol Biol 78(1–2):171–183
Pickett AA (1993) Cereals: seed shedding, dormancy and longevity. Aspects Appl Biol/Assoc Appl Biol 35:17–28
Rao MK, Devi KU, Arundhati A (1990) Applications of genie male sterility in plant breeding. Plant Breed 105(1):1–25
Reynolds M, Foulkes J, Furbank R, Griffiths S, King J, Murchie E, Parry M, Slafer G (2012) Achieving yield gains in wheat. Plant Cell Environ 35:1799–1823
Saini HS, Aspinall D (1982) Sterility in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) induced by water deficit or high temperature: possible mediation by abscisic acid. Funct Plant Biol 9(5):529–537
Sakata T, Oshino T, Miura S, Tomabechi M, Tsunaga Y, Higashitani N, Miyazawa Y, Takahashi H, Watanabe M, Higashitani A (2010) Auxins reverse plant male sterility caused by high temperatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(19):8569–8574
Sasakuma T, Ohtsuka I (1979) Cytoplasmic effects of Aegilops species having D genome in wheat. I. Cytoplasmic differentiation among five species regarding pistilody induction. Seiken Ziho 27:59–65
Sasakuma T, Maan SS, Williams ND (1978) EMS-induced male-sterile mutants in euplasmic and alloplasmic common wheat. Crop Sci 18(5):850–853
Scofield SR, Huang L, Brandt AS, Gill BS (2005) Development of a virus-induced gene-silencing system for hexaploid wheat and its use in functional analysis of the Lr21-mediated leaf rust resistance pathway. Plant Physiol 138(4):2165–2173
Shaowen Y, Shan R (1980) Studies on the ve-type male sterility of wheat. Acta Genet Sin 7(1):26–35
Shewry PR (2009) Wheat. J Exp Bot 60(6):1537–1553
Singh SK, Chatrath R, Mishra B (2010a) Perspective of hybrid wheat research: a review. Indian J Agric Sci 80
Singh SP, Pandey T, Srivastava R, Verma PC, Singh PK, Tuli R, Sawant SV (2010b) BECLIN1 from Arabidopsis thaliana under the generic control of regulated expression systems, a strategy for developing male sterile plants. Plant Biotechnol J 8(9):1005–1022
Singh SP, Vogel-Mikuš K, Arčon I, Vavpetič P, Jeromel L, Pelicon P, Kumar J, Tuli R (2013) Pattern of iron distribution in maternal and filial tissues in wheat grains with contrasting levels of iron. J Exp Bot 64(11):3249–3260
Singh SP, Vogel-Mikuš K, Vavpetič P, Jeromel L, Pelicon P, Kumar J, Tuli R (2014a) Spatial X-ray fluorescence micro-imaging of minerals in grain tissues of wheat and related genotypes. Planta 240(2):277–289
Singh SP, Jeet R, Kumar J, Shukla V, Srivastava R, Mantri SS, Tuli R (2014b) Comparative transcriptional profiling of two wheat genotypes, with contrasting levels of minerals in grains, shows expression differences during grain filling. PLoS One doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111718
Snape J, Pánková K (2006) Triticum aestivum (wheat). Encyclopedia of life sciences. Wiley, New York
Suneson CA (1962) Use of Pugsley’s sterile wheat in cross breeding. Crop Sci 2(6):534–535
Takada K, Ishimaru K, Minamisawa K, Kamada H, Ezura H (2005) Expression of a mutated melon ethylene receptor gene Cm-ETR1/H69A affects stamen development in Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Sci 169(5):935–942
Tan CH, Yu GD, Yang PF, Zhang ZH, Pan Y, Zheng J (1992) Preliminary study on sterility of thermo-photo-sensitive genic male sterile wheat in Chongqing. Southwest China J Agric Sci 5:31–35
Tang Z, Zhang L, Yang D, Zhao C, Zheng Y (2011) Cold stress contributes to aberrant cytokinesis during male meiosis I in a wheat thermosensitive genic male sterile line. Plant Cell Environ 34(3):389–405
Tang Z, Zhang L, Xu C, Yuan S, Zhang F, Zheng Y, Zhao C (2012) Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to cold stress in a wheat thermosensitive genic male-sterile line by deep sequencing. Plant Physiol 159(2):721–738
Tepliakov BI, Maksimenko VP, Chekurov VM (1974) The influence of decreased temperatures on meiotic disorders in spring wheat. Tsitol Genet 8(5):406–408
Trottet M, Deffains D, Jahier J (2010) A novel partial male sterility resource in bread wheat. Breed Sci 60(4):454–457
Tsunewaki K (1993) Genome-plasmon interaction in wheat. Jpn J Genet 68(1):1–34
Virmani SS, Donald LS (1996) Hybrid rice. In: Advances in agronomy, vol 57. Academic Press, pp 377–462
Wei L, Yan Z-X, Ding Y (2008) Mitochondrial RNA editing of F0-ATPase subunit 9 gene (atp9) transcripts of Yunnan purple rice cytoplasmic male sterile line and its maintainer line. Acta Physiol Plant 30(5):657–662
Wells DG, Caffey HR (1956) Scissor emasculation of wheat and barley. Agron J 48(11):496–499
Wilson P, Driscoll CJ (1983) Hybrid wheat. In: Frankel R (ed) Monographs on theoretical and applied genetics, vol 6, Heterosis edn. Springer, Berlin
Wilson JA, Ross WM (1962) Male sterility interaction of the Triticum aestivum nucleus and Triticum timopheevi cytoplasm. Wheat Inf Service 14 (29–30)
Wu YW, Zhang CL, Zhang Y (1995) Breeding of wheat male sterile line with Aegilops crassa 6x cytoplasm and research of its characters. Chin Sci Bull 3:243–247
Xi Y-J, Ma X-F, Zhong H, Liu S-D, Wang Z-L, Song Y-Y, Zhao C-H (2011) Characterization of a male sterile mutant from progeny of a transgenic plant containing a leaf senescence-inhibition gene in wheat. Euphytica 177(2):241–251
Xing QH, Ru ZG, Zhou CJ, Xue X, Liang CY, Yang DE, Jin DM, Wang B (2003) Genetic analysis, molecular tagging and mapping of the thermo-sensitive genic male-sterile gene (wtms1) in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 107(8):1500–1504
Xu C, Liu Z, Zhang L, Zhao C, Yuan S, Zhang F (2013) Organization of actin cytoskeleton during meiosis I in a wheat thermo-sensitive genic male sterile line. Protoplasma 250:415–422
Yang M, Gu J, Liu K, Li S, Tian Y, Yang H, Zhou J, Liu D, Chen P (2006) Ecological adaptability of thermo–photo–sensitive genic male sterile wheat K78S in Yunnan Province. Zuo wu xue bao 32:1618–1624
Yang L, Liu BH, Zhai HQ, Wang SH, Liu HW et al (2009) Dwarf male-sterile wheat: a revolutionary breeding approach to wheat. Vienna, Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture, International Atomic Energy Agency
Yuan A-P, Hou A-B, Zhang F-Y, Guo Y-D (2008) Inheritance and effects of the photoperiod sensitivity in foxtail millet (Setaria italica P. Beauv). Hereditas 145:147–153
Zhang GS (1992) Breeding of wheat male sterile line having Aegilops uniaristata cytoplasm. Chin Sci Bull 7:641–645
Zhang J, Feng L, He L, Yu G (2003) Thermo-sensitive period and critical temperature of fertility transition of thermo-photo-sensitive genic male sterile wheat. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 14(1):57–60
Zhou KJ, Wang SH, Feng YQ, Liu ZX, Wang GX (2006) The 4E-ms system of producing hybrid wheat. Crop Sci 46:250–255
Zhou K, Wang S, Feng Y, Ji W, Wang G (2008) A new male sterile mutant LZ in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 159(3):403–410
Zhou L, Song G, He B, Hu YG (2011) A ras GTPase-activating protein-binding protein, TaG3BP, associated with the modulation of male fertility in a thermo-sensitive cytoplasmic male sterile wheat line. Mol Genet Genomics 286(5–6):417–431
Zhu Y, Saraike T, Yamamoto Y, Hagita H, Takumi S, Murai K (2008) orf260cra, a novel mitochondrial gene, is associated with the homeotic transformation of stamens into pistil-like structures (pistillody) in alloplasmic wheat. Plant Cell Physiol 49(11):1723–1733
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A.K. Kononowicz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.P., Srivastava, R. & Kumar, J. Male sterility systems in wheat and opportunities for hybrid wheat development. Acta Physiol Plant 37, 1713 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1713-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1713-7