Abstract
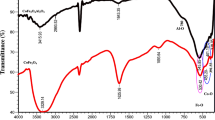
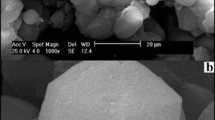
In this study, the synthesis of silver–cobalt ferrite (Ag–CFO) was achieved through a novel approach using Taxus wallichiana leaf extract as a potent reducing agent. By strategically varying the concentrations of silver and cobalt ferrite, Ag–CFO nanocomposites with different ratios were successfully synthesized. Various analytical techniques were used to characterize the adsorbents. XRD confirmed the structure and crystallite sizes were found in the range 40 to 48 nm. The purity of the synthesized material was affirmed through energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis. The impact of pH, concentration, and temperatures on the adsorption of Pb+2 ions from aqueous solutions were performed. The maximum adsorption capacity and binding strength of Pb+2 ions were evaluated by employing different models such as Freundlich, Langmuir, and Temkin. For selectivity, various solutions of divalent metal cations like Zn2+, Ni2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ in the concentration range 5–100 mg/L were used. Delving into the thermodynamics process, the study identified the nature of adsorption as primarily physical. The desorption study was undertaken in the presence of 2-M H2SO4 and 2MNaOH. This study, therefore, provided a successful path to use Ag–CFO NCs as a potential adsorbent for environmental remediation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari P, Pandey A, Agnihotri V, Pande V (2018) Selection of solvent and extraction method for determination of antimicrobial potential of Taxus wallichiana Zucc. Res Pharm 8:1–9
Adhikari P, Joshi K, Singh M, Pandey A (2022) Influence of altitude on secondary metabolites, antioxidants, and antimicrobial activities of Himalayan yew (Taxus wallichiana). Plant Biosyst-Int J Deal All Asp Plant Biol 156:187–195
Adhikari P, Agnihotri V, Suman SK, Pandey A (2023) Deciphering the antimicrobial potential of Taxus wallichiana Zucc: identification and characterization using bioassay-guided fractionation. Chem Biodivers 20:e202200572
Ara A, Usmani JA (2015) Lead toxicity: a review. Interdiscip Toxicol 8:55–64
Arbabi M, Hemati S, Amiri M (2015) Removal of lead ions from industrial wastewater: a review of removal methods. Environment 4:10
Arulmozhi K, Mythili N (2013) Studies on the chemical synthesis and characterization of lead oxide nanoparticles with different organic capping agents. AIP Adv 3:122122
Assi MA, Hezmee MNM, Sabri MYM, Rajion MA (2016) The detrimental effects of lead on human and animal health. Vet World 9:660
Aswathi V, Meera S, Maria CA, Nidhin M (2023) Green synthesis of nanoparticles from biodegradable waste extracts and their applications: a critical review. Nanotechnol Environ Eng 8:377–397
Awual MR, Hasan MM, Islam A, Rahman MM, Asiri AM, Khaleque MA, Sheikh MC (2019) Offering an innovative composited material for effective lead (II) monitoring and removal from polluted water. J Clean Prod 231:214–223
Azizi S, Mahdavi Shahri M, Mohamad R (2017) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for enhanced adsorption of lead ions from aqueous solutions: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Molecules 22:831
Bhatia M, Satish Babu R, Sonawane S, Gogate P, Girdhar A, Reddy E, Pola M (2017) Application of nanoadsorbents for removal of lead from water. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14:1135–1154
Bhuju S, Gauchan DP (2018) Taxus wallichiana (Zucc.), an endangered anti-cancerous plant: a review. Int J Res 5:10–21
Boskabady M, Marefati N, Farkhondeh T, Shakeri F, Farshbaf A, Boskabady MH (2018) The effect of environmental lead exposure on human health and the contribution of inflammatory mechanisms, a review. Environ Int 120:404–420
Debnath B, Singh WS, Manna K (2019) Sources and toxicological effects of lead on human health. Indian J Med Spec 10:66–71
Dissanayake I, Jaye K, Eladwy RAM, Farrukh S, Yasmin S, Bhuyan DJ, Pandohee J (2023) Taxus wallichiana Zucc.: The Himalayan Yew. In: Sharma A, Nayik GA (eds) Immunity boosting medicinal plants of the western himalayas. Springer, Singapore, pp 541–559
Gerçel Ö, Gerçel HF (2007) Adsorption of lead(II) ions from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from biomass plant material of Euphorbia rigida. Chem Eng J 132:289–297
Ghaffar N, Lee LS, Khan B, Khan H, Iqbal J, Mian IA, Ihtisham S, Rukhsana IA, Khalid S (2023) Paclitaxel content in various parts of Taxus wallichiana from moist temperate forests of Swat and Hazara, Pakistan. Pak J Bot 55:1851–1856
He G, Ding J, Zhang J, Hao Q, Chen H (2015) One-step ball-milling preparation of highly photocatalytic active CoFe2O4-reduced graphene oxide heterojunctions for organic dye removal. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:2862–2867
Jethva H, Joshi M (2014) FTIR and thermal studies of gel grown lead cobalt mixed levo tartrate crystals. IJIRSET 3:16517–16526
Kanwal Z, Raza MA, Riaz S, Manzoor S, Tayyeb A, Sajid I, Naseem S (2019) Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticle-decorated cobalt nanocomposites (Co@ AgNPs) and their density-dependent antibacterial activity. R Soc Open Sci 6:182135
Khan MAM, Khan W, Ahamed M, Ahmed J, Al-Gawati MA, Alhazaa AN (2020) Silver–decorated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles anchored onto the graphene sheets as electrode materials for electrochemical and photocatalytic applications. ACS Omega 5:31076–31084
Khan F, Shahid A, Zhu H, Wang N, Javed MR, Ahmad N, Xu J, Alam MA, Mehmood MA (2022) Prospects of algae-based green synthesis of nanoparticles for environmental applications. Chemosphere 293:133571
Kombaiah K, Vijaya JJ, Kennedy LJ, Bououdina M, Ramalingam RJ, Al-Lohedan HA (2018) Okra extract-assisted green synthesis of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles and their optical, magnetic, and antimicrobial properties. Mater Chem Phys 204:410–419
Lei N, Li W, Zhao D, Li W, Liu X, Liu L, Yin J, Muddassir M, Wen R, Fan L (2024) A bifunctional luminescence sensor for biomarkers detection in serum and urine based on chemorobust Nickel(II) metal–organic framework. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 306:123585
Li Y-H, Di Z, Ding J, Wu D, Luan Z, Zhu Y (2005) Adsorption thermodynamic, kinetic and desorption studies of Pb2+ on carbon nanotubes. Water Res 39:605–609
Li W, Li W, Liu X, Zhao D, Liu L, Yin J, Li X, Zhang G, Fan L (2023) Two chemorobust cobalt(II) organic frameworks as high sensitivity and selectivity sensors for efficient detection of 3-nitrotyrosine biomarker in serum. Cryst Growth Des 23:7716–7724
Lin Z, Weng X, Owens G, Chen Z (2020) Simultaneous removal of Pb(II) and rifampicin from wastewater by iron nanoparticles synthesized by a tea extract. J Clean Prod 242:118476
Lingamdinne LP, Koduru JR, Rao Karri R (2019) Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles for lead removal from aqueous solutions. Key Eng Mater 805:122–127
Mahmoud AED, Al-Qahtani KM, Alflaij SO, Al-Qahtani SF, Alsamhan FA (2021) Green copper oxide nanoparticles for lead, nickel, and cadmium removal from contaminated water. Sci Rep 11:12547
Merrikhpour H, Jalali M (2012) Waste calcite sludge as an adsorbent for the removal of cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc from aqueous solutions. Clean Technol Environ Policy 14:845–855
Miri A, Najafzadeh H, Darroudi M, Miri MJ, Kouhbanani MAJ, Sarani M (2021) Iron oxide nanoparticles: biosynthesis, magnetic behavior, cytotoxic effect. ChemistryOpen 10:327–333
Mitra S, Chakraborty AJ, Tareq AM, Emran TB, Nainu F, Khusro A, Idris AM, Khandaker MU, Osman H, Alhumaydhi FA (2022) Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J King Saud Univ-Sci 34:101865
Moradi O, Aghaie M, Zare K, Monajjemi M, Aghaie H (2009) The study of adsorption characteristics Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions onto PHEMA and P (MMA–HEMA) surfaces from aqueous single solution. J Hazard Mater 170:673–679
Morosanu I, Teodosiu C, Paduraru C, Ibanescu D, Tofan L (2017) Biosorption of lead ions from aqueous effluents by rapeseed biomass. New Biotechnol 39:110–124
Nadaroglu H, Güngör AA, Selvi İ (2017) Synthesis of nanoparticles by green synthesis method. Int J Innov Res Rev 1:6–9
Naseem T, Baig MM, Warsi MF, Hussain R, Agboola PO, Waseem M (2020) Mesoporous silica prepared via a green route: a comparative study for the removal of crystal violet from wastewater. Mater Res Express 8:015005
Negi S, Singh V, Rawat J (2021) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using microalgal extract and its application in metal ion removal from aqueous solution. J Exp Biol Agric Sci 9:214–230
Niu Z, Feng W, Huang H, Wang B, Chen L, Miao Y, Su S (2020) Green synthesis of a novel Mn–Zn ferrite/biochar composite from waste batteries and pine sawdust for Pb2+ removal. Chemosphere 252:126529
Qasem NA, Mohammed RH, Lawal DU (2021) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: a comprehensive and critical review. Npj Clean Water 4:36
Rathore P, Roy A, Karnatak H (2019) Modelling the vulnerability of Taxus wallichiana to climate change scenarios in South East Asia. Ecol Ind 102:199–207
Samuel MS, Ravikumar M, John J A, Selvarajan E, Patel H, Chander PS, Soundarya J, Vuppala S, Balaji R, Chandrasekar N (2022) A review on green synthesis of nanoparticles and their diverse biomedical and environmental applications. Catalysts 12:459
Satheeshkumar M, Kumar ER, Srinivas C, Suriyanarayanan N, Deepty M, Prajapat C, Rao TC, Sastry D (2019) Study of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Ag substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by honey assisted combustion method and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. J Magn Magn Mater 469:691–697
Sethy NK, Arif Z, Mishra PK, Kumar P (2020) Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles from Syzygium cumini extract for photo-catalytic removal of lead (Pb) in explosive industrial wastewater. Green Process Synth 9:171–181
Sharma H, Garg M (2015) A review of traditional use, phytoconstituents and biological activities of Himalayan yew Taxus Wallichiana. J Integr Med 13:80–90
Venkateswarlu S, Kumar BN, Prathima B, SubbaRao Y, Jyothi NVV (2019) A novel green synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanorods using Punica Granatum rind extract and its application for removal of Pb(II) from aqueous environment. Arab J Chem 12:588–596
Wu Z, Cheng Z, Ma W (2012) Adsorption of Pb (II) from glucose solution on thiol-functionalized cellulosic biomass. Biores Technol 104:807–809
Yang X, Xu G, Yu H (2019) Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by ferric activated sludge-based adsorbent derived from biological sludge. Arab J Chem 12:4142–4149
Yin J, Li W, Li W, Liu L, Zhao D, Liu X, Hu T, Fan L (2023) Heterometallic ZnHoMOF as a dual-responsive luminescence sensor for efficient detection of hippuric acid biomarker and nitrofuran antibiotics. Molecules 28:6274
Ying S, Guan Z, Ofoegbu PC, Clubb P, Rico C, He F, Hong J (2022) Green synthesis of nanoparticles: current developments and limitations. Environ Technol Innov 26:102336
Yousaf A, Waseem M, Javed A, Baig S, Ismail B, Baig A, Shahzadi I, Nawazish S, Zaman I (2022) Augmented anticancer effect and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by using Taxus wallichiana leaf extract. PeerJ 10:e14391
Zhang X, Wang H, He L, Lu K, Sarmah A, Li J, Bolan NS, Pei J, Huang H (2013) Using biochar for remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals and organic pollutants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8472–8483
Zhao T, Yao Y, Wang M, Chen R, Yu Y, Wu F, Zhang C (2017) Preparation of MnO2-modified graphite sorbents from spent Li-ion batteries for the treatment of water contaminated by lead, cadmium, and silver. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:25369–25376
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tasqeen, H., Waseem, M., Hussain, S. et al. Green synthesis of Ag–CoFe2O4 nanocomposites by Taxus wallichiana leaf extract for adsorption of Pb+2 ions from aqueous solution. Chem. Pap. 78, 4517–4528 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-024-03415-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-024-03415-4