Abstract
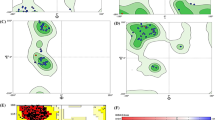
In the present paper, a set of 42 derivatives for 5-oxo-1-thioxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-thiazolo[3,4-a]quinazoline are investigated in silico combining 3D-QSAR study, drug-likeness, ADMET properties, and molecular docking. The study is carried out to elaborate the reliable 3D-QSAR models using the CoMFA and CoMSIA techniques. CoMFA (Q2 = 0.637, R2 = 0.978, SEE = 0.058) and CoMSIA (Q2 = 0.544, R2 = 0.949, SEE = 0.091) models show the two elaborated models have been reliable and statistically significant. The reliability of the obtained models was validated using validation methods such as internal, external, and Y-randomization validation. Based on the contour maps of the CoMFA and CoMSIA models, we obtained information that allows us to propose five new molecules with higher MALT1 inhibitory activity than the 40 compounds. The five compounds were then examined for their drug-like and ADMET properties. Based on the results, two compounds T1 and T2 have very good ADMET properties. The two molecules selected by their ADMET properties T1 and T2 were submitted to the molecular docking test to examine the bindings established between the two newly designed molecules and the MALT1 protein. The obtained results show that the new molecules T1 and T2 have high stability in the active site of MALT1 and more efficient binding affinity compared to the reference compound 26. The two new molecules T1 and T2 may be an interesting proposition for in vitro studies in the treatment of diffuse large B cell lymphoma.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alizadeh AA et al (2000) Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403(6769):503–511
Aouidate A et al (2018) Structural basis of pyrazolopyrimidine derivatives as CAMKIIδ kinase inhibitors: insightsD QSAR, docking studies and in silico ADMET evaluation. Chem Pap 72(11):2833–2847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0510-y
Asaba KN et al (2021) Structure–activity relationship studies of 3-substituted pyrazoles as novel allosteric inhibitors of MALT1 protease. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 41(March):127996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.127996
“Avogadro Download | SourceForge.Net.” https://sourceforge.net/projects/avogadro/ (April 21, 2022).
“Certara Enhances SYBYL-X Drug Design and Discovery Software Suite | Certara.” https://www.certara.com/pressrelease/certara-enhances-sybyl-x-drug-design-and-discovery-software-suite/ (April 21, 2022).
Clark DE (2003) In silico prediction of blood-brain barrier permeation. Drug Discov Today 8(20):927–933
Cramer RD, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110(18):5959–5967
Daina A, Vincent Z (2016) A BOILED-egg to predict gastrointestinal absorption and brain penetration of small molecules. ChemMedChem 11:1117–1121
Daina A, Olivier M, Vincent Z (2014) Approach
Daoui O et al (2021) QSAR, molecular docking and ADMET properties in silico studies of novel 4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[D]-thiazol-2-Yl derivatives derived from dimedone as potent anti-tumor agents through inhibition of C-Met receptor tyrosine kinase. Heliyon 7(7):e07463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07463
Daoui O et al (2022) 3D-QSAR, ADME-Tox, and molecular docking of semisynthetic triterpene derivatives as antibacterial and insecticide agents. Struct Chem 33(4):1063–1084
Download AutoDock4—AutoDock. https://autodock.scripps.edu/download-autodock4/ (April 21, 2022)
Downloads—AutoDock Vina. https://vina.scripps.edu/downloads/ (April 21, 2022).
Egan WJ, Merz KM, Baldwin JJ (2000) Prediction of drug absorption using multivariate statistics. J Med Chem 43(21):3867–3877
Ferch U et al (2009) Inhibition of MALT1 protease activity is selectively toxic for activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J Exp Med 206(11):2313–2320
Fontan L et al (2012) MALT1 small molecule inhibitors specifically suppress ABC-DLBCL in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Cell 22(6):812–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.11.003
Free Download: BIOVIA discovery studio visualizer—dassault systèmes. https://discover.3ds.com/discovery-studio-visualizer-download (April 21, 2022).
Generalized TO (1984) The Partial. 5(3):735–43
Golbraikh A, Tropsha A (2002) Beware of Q2! J Mol Graph Model 20(4):269–276
Hailfinger S et al (2009) Essential role of MALT1 protease activity in activated B cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(47):19946–19951
HalimZaheer-Ul-Ha SA (2015) Structure based 3D-QSAR studies of interleukin-2 inhibitors: comparing the quality and predictivity of 3D-QSAR models obtained from different alignment methods and charge calculations. Chem Biol Interact 238:9–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2015.05.018
Han Y et al (2019) In silico ADME and toxicity prediction of ceftazidime and its impurities. Front Pharmacol 10:1–12
Jia CY, Li JY, Hao GF, Yang GF (2020) A drug-likeness toolbox facilitates ADMET study in drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 25(1):248–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2019.10.014
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) Molecular similarity indices in a comparative analysis (CoMSIA) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological activity. J Med Chem 37(24):4130–4146
T Klein et al. (2015) The paracaspase MALT1 cleaves HOIL1 reducing linear ubiquitination by LUBAC to dampen lymphocyte NF-κ B signalling. Nat Commun 6
Lambrinidis G, Vallianatou T, Tsantili-Kakoulidou A (2015) In vitro, in silico and integrated strategies for the estimation of plasma protein binding. a review. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 86:27–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.03.011
Lenz G et al (2008) Oncogenic CARD11 mutations in human diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Science 319(5870):1676–1679
Liang X, Sun C et al (2021a) Identification of novel fused heteroaromatics-based MALT1 inhibitors by high-throughput screening to treat B cell lymphoma. J Med Chem 64(13):9217–9237
Liang X, Cao YC et al (2021b) MALT1 as a promising target to treat lymphoma and other diseases related to MALT1 anomalies. Med Res Rev 41(4):2388–2422
Lim SM et al (2015) Identification of β-lapachone analogs as novel MALT1 inhibitors to treat an aggressive subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Med Chem 58(21):8491–8502
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (2012) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:4–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.019
Lu T et al (2019) Discovery and optimization of a series of small-molecule allosteric inhibitors of MALT1 protease. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29(23):126743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.126743
Maréchal JD et al (2006) In silico and in vitro screening for inhibition of cytochrome P450 CYP3A4 by comedications commonly used by patients with cancer. Drug Metab Dispos 34(4):534–538
Martin YC (2005) A bioavailability score. J Med Chem 48(9):3164–3170
Martin F, Kearney JF (2002) Marginal-zone B cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2(5):323–335
Morris GM et al (1998) Automated docking using a lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19(14):1639–1662
Nagel D et al (2012) Pharmacologic Inhibition of MALT1 protease by phenothiazines as a therapeutic approach for the treatment of aggressive ABC-DLBCL. Cancer Cell 22(6):825–837
Pai S, Thomas R (2008) Immune deficiency or hyperactivity-Nf-Κb Illuminates autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 31(3):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2008.04.012
Pal G, Dasgupta S, Banerjee U (2021) Immunohistochemical subtypes of non-hodgkin lymphomas with special emphasis on diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: an epidemiological study in a tertiary care center of Eastern India. Biomed Biotechnol Res J 5(2):149–154
Pires DEV, Blundell TL, Ascher DB (2015) PkCSM: predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties using graph-based signatures. J Med Chem 58(9):4066–4072
Purcell WP, Singer JA (1967) A brief review and table of semiempirical parameters used in the hueckel molecular orbital method. J Chem Eng Data 12(2):235–246
RCSB PDB- 41R: Human MALT1 (Caspase-IG3) in complex with thioridazine. https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4I1R (April 21, 2022)
Rodrigues-Junior VS et al (2020) Nonclinical evaluation of IQG-607, an anti-tuberculosis candidate with potential use in combination drug therapy. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 111:104553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2019.104553
Roschewski M, Staudt LM, Wilson WH (2014) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma–treatment approaches in the molecular era. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 11(1):12–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.197
Roy K (2007) On some aspects of validation of predictive quantitative structure-activity relationship models. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2(12):1567–1577
Roy K, Mitra I (2011) On various metrics used for validation of predictive QSAR models with applications in virtual screening and focused library design. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 14(6):450–474
Roy K, Ambure P, Aher RB (2017) How important is to detect systematic error in predictions and understand statistical applicability domain of QSAR models? Chemom Intell Lab Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2017.01.010
Roy K, Kar S, Das RN (2015) SAR and QSAR in drug discovery and chemical design—some examples. In: Understanding the basics of QSAR for applications in pharmaceutical sciences and risk assessment pp 427–53
Rücker C, Rücker G, Meringer M (2007) Y-Randomization and its variants in QSPR/QSAR. J Chem Inf Model 47(6):2345–2357
Ruefli-Brasse AA, French DM, Dixit VM (2003) Regulation of NF-ΚB-dependent lymphocyte activation and development by paracaspase. Science 302(5650):1581–1584
Sarvagalla S, Syed SB, Coumar MS (2019) An overview of computational methods, tools, servers, and databases for drug repurposing. In: Silico drug design, Elsevier. http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-816125-8.00025-0.
Schlauderer F et al (2013) Structural analysis of phenothiazine derivatives as allosteric inhibitors of the MALT1 paracaspase. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(39):10384–10387
Staal J, Bekaert T, Beyaert R (2011) Regulation of NF-ΚB signaling by caspases and MALT1 paracaspase. Cell Res 21(1):40–54
Ståhle L, Wold S (1988) 6 multivariate data analysis and experimental design in biomedical research. Prog Med Chem 25(C):291–338
Stead AG, Hasselblad V, Creason JP, Claxton L (1981) Modeling the ames test. Mutat Res Environ Mutagen Relat Subj 85(1):13–27
Sun SC, Chang JH, Jin J (2013) Regulation of nuclear factor-ΚB in autoimmunity. Trends Immunol 34(6):282–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2013.01.004
Tong JB, Feng Yi, Luo D, Wang TH (2021) 6-Amide-2-Aryl benzoxazole/benzimidazole derivatives as VEFGR-2 inhibitors in two-and three-dimensional QSAR studies: topomer CoMFA and HQSAR. Chem Pap 75(7):3551–3562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01588-w
Tropsha A, Gramatica P, Gombar VK (2003) The importance of being earnest: validation is the absolute essential for successful application and interpretation of QSPR models. QSAR Comb Sci 22(1):69–77
Veber DF et al (2002) Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J Med Chem 45(12):2615–2623
Yadav MR (2013) New drug discovery: where are we heading to? J Adv Pharm Technol Res 4(1):2–3
Young RM, Staudt LM (2012) A new ‘brew’ of MALT1 inhibitors. Cancer Cell 22(6):706–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.11.011
Zanger UM, Schwab M (2013) Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism: regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities, and impact of genetic variation. Pharmacol Ther 138(1):103–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.12.007
Zheng J et al (2011) Exploring QSARs for 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) inhibitory activity of 2-substituted 5-hydroxyindole-3-carboxylates by CoMFA and CoMSIA. Chem Biol Drug Des 78(2):314–321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest, or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors declare that the article is original work, not published previously, without consideration for publication in another journal, approve the submission and have no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Haloui, R., Daoui, O., Mkhayar, K. et al. 3D-QSAR, drug-likeness, ADMET prediction, and molecular docking studies in silico of novel 5-oxo-1-thioxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-thiazolo[3,4-a]quinazoline derivatives as MALT1 protease inhibitors for the treatment of B cell lymphoma. Chem. Pap. 77, 2255–2274 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02627-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02627-w