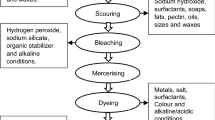
Abstract
In the washing microenvironment, the shedding of reactive dyes from cotton fabrics dyed in highly saturated color (CFSCs) causes pollution of the water environment and the staining of light-colored fabrics (LCFs) washed together, which have gradually attracted the attention of researchers in the washing machine industry and environmental field. Therefore, inspired by the application of electrochemical technology in dyeing wastewater of the textile dyeing and finishing industry, electrochemical technology was successfully applied to a washing machine to degrade reactive dyes shed from fabric, thus effectively controlling potential environmental pollution problems. First, electrochemical equipment for the washing machine was built with Ti/IrO2 as the anode and stainless steel as the cathode. Second, in the simulated washing-electrochemical degradation experiment, the electrochemical degradation parameters were selected by analyzing a single factor. The experiments show that the voltage (X1), electrolyte concentration (X2), and initial shed dye concentration (X3) had significant effects on the degradation of shed dyes from CFSCs and staining of LCF in the simulated washing system. The Box‒Behnken experimental design method was used to optimize the electrochemical degradation parameters corresponding to the simulated washing-electrochemical degradation experiment. Finally, the electrochemical equipment was installed in a real washing machine, and the washing experiment verified that the electrochemical technology could effectively inhibit the water pollution and staining problems of LCFs caused by dye desorption in the washing microenvironment, which provides technical support for the research and development of new washing machines.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akula LK, Gaddam VB, Damaraju M et al (2021) Domestic wastewater treatment in a coupled sequential batch reactor-electrochemical reactor process. Water Environ Res 93: 953–967.https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1488
Ahmad Q, Ziad AG (2020) Regression modeling for rapid prediction of wastewater BOD5. Desalin Water Treat 201:165–172. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.26043
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl Catal B-Environ 166/167: 603–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.11.016
Forgacs E, Cserhati T, Oros G (2004) Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ Int 30:953–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.001
Guzmán-Duque FL, Palma-Goyes RE, González I et al (2014) Relationship between anode material, supporting electrolyte and current density during electrochemical degradation of organic compounds in water. J Hazard Mater 278:221–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.076
Hang CY, He JX (2013) Study of the desorption of hydrolysed reactive dyes from cotton fabrics in anethanol–water solvent system. Color Technol 130: 81–85.https://doi.org/10.1111/cote.12066
Hu B, Wang YM, Hu CL et al (2016) Design, fabrication and high efficient visible-light assisted photoelectric-synergistic performance of 3-D mesoporous DSA electrodes. Mater Design 91:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.11.105
Hu JM, Zhang JQ, Meng HM et al (2005) Electrochemical activity, stability and degradation characteristics of IrO2-based electrodes in aqueous solutions containing C1 compounds. Electrochim Acta 50: 5370–5378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.03.016
Hu J, Bian XZ, Xia Y et al (2020) Application of response surface methodology in electrochemical degradation of amoxicillin with Cu-PbO2 electrode: Optimization and mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 250: 117109–1–117109–7.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117109
Kapoor RT, Danish M, Singh RS et al (2021) Exploiting microbial biomass in treating azo dyes contaminated wastewater: Mechanism of degradation and factors affecting microbial efficiency. J Water Process Eng 43:102–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102255
Khandegar V, Saroha AK (2013) Electrocoagulation for the treatment of textile industry effluent - a review. J Environ Manage 128: 949–963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.06.043
Kumar T, Mohasin R, Majid ZA et al (2020) Wash Experimental study of the anti-knock efficiency of high-octane fuels in spark-ignited aircraft engine using response surface methodology. Appl Energy 259: 114150–1–114150–23.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.114150
Körbahti BK, Taşyürek S (2015) Electrochemical oxidation of ampicillin antibiotic at boron-doped diamond electrodes and process optimization using response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:3265–3278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3101-7
Lewis DM (2014) Developments in the chemistry of reactive dyes and their application processes. Color Technol 130:382–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/cote.12114
Li J, Li YJ, Xiong ZK et al (2019) The electrochemical advanced oxidation processes coupling of oxidants for organic pollutants degradation: A mini-review. Chinese Chem Let 30:2139–2146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.04.057
Marshall AT, Herritsch A (2018) Understanding how the oxygen evolution reaction kinetics influences electrochemical wastewater oxidation. Electrochim Acta 282:448–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.06.065
Minoo B, Ali RM, Behnam M (2014) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of congo red by solvothermally synthesized CuInSe2–ZnO nanocomposites. Rsc Adv 4:21757–21764. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra01753f
Nazari L, Yuan ZS, Ray MB et al (2017) Co-conversion of waste activated sludge and sawdust through hydrothermal liquefaction: Optimization of reaction parameters using response surface methodology. Appl Energ 203: 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.06.009
Nizar K, Davide C, Carpanese MP et al (2019) Electrochemical oxidation of crystal violet using a BDD anode with a solid polymer electrolyte. Sep Purif Technol 208: 178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.03.042.
Palanisamy G, Bhuvaneswari K, Pazhanivel T et al (2022a) Biowaste derived hydroxyapatite embedded on two‑dimensional g‑C3N4 nanosheets for degradation of hazardous dye and pharmacological drug via Z‑scheme charge transfer. Sci Rep 12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-15799-y
Paz EC, Aveir LR, Pinheiro VS et al (2018) Evaluation of H2O2 electrogeneration and decolorization of Orange II azo dye using tungsten oxide nanoparticle-modified carbon. Appl Catal B- Environ 232:436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.082
Palanisamy G, Venkatesh G, Srinivasan M (2022b) et al α-Bi2O3 nanoparticle and multiwall carbon nanotube hybrid with protonated g-C3N4 nanosheets for superior photocatalytic performance towards the mixed organic contaminants. J Alloy Compd 922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022b.166147
Schneider J, Matsuoka M, Takeuchi M et al (2014) Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: mechanisms and materials. Chem Rev 114:9919–9986. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr5001892
Stephen MB, Liu KS (2019) The wash-off of dyeings using interstitial water Part 5: Residual dyebath and wash-off liquor generated during the application of disperse dyes and reactive dyes to polyester/cotton fabric, Dyes Pigments 171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2017.11.021
Tang YN, He DL, Guo YN et al (2022) Improved Electrochemical oxidative degradation of reactive red 24 dye by BDD anodes coupled with nitrate. J Electrochem Soc 169. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ ac5b35
Wang SJ, Kong FG, Fatehi P et al (2018) Cationic High molecular weight lignin polymer: a flocculant for the removal of anionic azo-dyes from simulated wastewater. Molecules 23:8. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082005
Wang LL, Ding XM, Huang R et al (2014) Choices and using of washing machines in Chinese households. Int J Consum Stud 38: 104–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12070
Wei N, Zhang Y, Zhang H et al (2022) The effect of modifying group on the acid properties and catalytic performance of sulfonated mesoporous polydivinylbenzene solid acid in the Bisphenol-A synthesis reaction. React Funct Polym 171:105–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2021.105156
Xu HH, Deng Y (2018) dependent evidence combination based on shearman coefficient and pearson coefficient. IEEE Access 6:11634–11640. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2783320
Yang WL, Zhou MH, Mai L et al (2021) Generation of hydroxyl radicals by metal-free bifunctional electrocatalysts for enhanced organics removal. Sci Total Environ 791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148107
Yu YK, Zhang YJ (2013) Roles of Novel Reactive Cationic Copolymers of 3-Chloro-2-hydroxypropylmethyldiallylammonium Chloride and Dimethyldiallylammonium Chloride in Fixing Anionic Dyes on Cotton Fabric. J Chem 7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/365103
Zghida H, Baouab MHV, Gauthier R (2002) Adsorption of Oleate Anions on to Cationized Lignocelluloses. Adsorpt Sci Technol 20: 555–563. https://doi.org/10.1260/026361702321039483
Zhao R, Zhang X, Chen FL et al (2019) Study on electrochemical degradation of nicosulfuron by IrO2-based DSA electrodes: performance, kinetics, and degradation mechanism. Ann Am Thorac Soc 16:343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030343
Zhong CL, Tabrez AK, AzharulIslam Md et al (2022) A review on the treatment of dyes in printing and dyeing wastewater by plant biomass carbon. Bioresource Technol 354:127–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127168
Zhou MH, Dai QZ, Lei LC et al (2005) Long Life Modified lead dioxide anode for organic wastewater treatment: electrochemical characteristics and degradation mechanism. Environ Sci Technol 39:363–370. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049313a
Zhu XP, Tong MP, Shi SY (2008) Essential explanation of the strong mineralization performance of boron-doped diamond electrodes. Environ Sci Technol 42:4914–4920. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800298p
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers and the associate editor for their insightful comments.
Funding
This research was funded by the Industry-University-Research Project of Jiangnan University (191186).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ is responsible for the conception of the whole study, the design, and implementation of the experiment, the collection and analysis of data, and the drafting of the first draft, CYZ, ZHR, and BXW are responsible for the planning of the paper, QBY is responsible for coordinating the research tasks and data analysis, and LHA and JLL are responsible for data analysis and the revision of the first draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Human and animal rights
Research does not involve any human participants and/or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Zhang, C., Ren, Z. et al. Application of electrochemistry technology to effectively inhibit dye pollution and unfixed dye transfer in a washing microenvironment. Chem. Pap. 77, 1951–1970 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02597-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02597-z