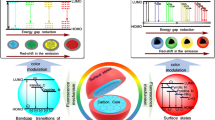
Abstract
In the present work, various capping ligands [thioglycolic acid (TGA), glutathione reduced (L-GSH) and L-cysteine (L-Cyst.)] have been used to modify the surface chemistry of CdTe quantum dots (QDs). Different capped CdTe QDs are prepared by aqueous phase route and characterized by UV–visible, photo-luminescence and FTIR spectrometry. The structural properties of uncapped and capped CdTe QDs were investigated by the scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Optical signal of distinct capped CdTe QDs was observed to be pH, time and temperature dependent. In the presence of most of the metals ions (Xn+), capped CdTe has shown strong “Turn-Off” fluorescence responses due to 1:1 complexation between metal ions and QDs except for Cr3+ and Pb2+metal ions. In the presence of Cr3+ and Pb2+ metal ions “Turn-On” fluorescence response appeared for L-Cyst. + CdTe QDs due to fluorescence resonance energy transfer. The output of Benesi–Hildebrand relation and graphical Job’s plots have established the existence of strong 1:1 complexation (Xn+: TGA + CdTe, L-GSH + CdTe, L-Cyst. + CdTe) between distinctly capped CdTe and metal ions. Further, strong appearance of relative fluorescence intensities (F − F0/F0) established the better sensing capability of L-Cyst. + CdTe and TGA + CdTe QDs for Cr3+, Pb2+ ions. The lower value of limit of detection for TGA + CdTe QDs for Pb2+ and L-Cyst. + CdTe QD for Cr3+ and Pb2+ metals have showed better results towards sensing. The performance of capped CdTe QD in the presence of real sample shows good recovery (66–109%), precision and accuracy(0.2–2%) with a sensitivity of 10–7 M. Our findings have shown a strong possibility of L-Cyst. and TGA capped CdTe QDs to be used as better metal ion sensors for Cr3+ and Pb2+.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF (2018) Selective biosensing of Staphylococcus aureus using chitosan quantum dots. Spectrochim Acta Mol Biomol Spectrosc 188:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.06.047
Ali EM, Zheng Y, Yu HH, Ying JY (2007) Ultrasensitive Pb2+ detection by glutathione-capped quantum dots. Anal Chem 79:9452–9458
Almendral-Parra MJ, Alonso-Mateos A, Boyero-Benito JF, Sanchez-Paradinas S, Rodrıguez-Fernandez E (2014) A novel approach to the fabrication of CdSe quantum dots in aqueous solution: procedures for controlling size, fluorescence intensity, and stability over time. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/397469
Arancibia V, Valderrama M, Silva K, Tapia T (2003) Determination of chromium in urine samples by complexation-supercritical fluid extraction and liquid or gas chromatography. J Chromatogr B 785:303–309
Badawi A, Al-Hosiny N, Abdallah S, Negm S, Talaat H (2013) Tuning photocurrent response through size control of CdTe quantum dots sensitized solar cells. Sol Energy 88:137–143
Baslak C, Kars MD, Karaman M, Kus M, Cengeloglu Y, Ersoz M (2015) Biocompatible multi-walled carbon nanotube–CdTe quantum dot–polymer hybrids for medical applications. J Lumin 160:9–15
Beloglazova NV, Shmelin PS, Speranskaya ES, Lucas B, Helmbrecht C, Knopp D, Niessner R, Saeger SD, Goryacheva IY (2013) Quantum dot loaded liposomes as fluorescent labels for immunoassay. Anal Chem 85:7197–7204
Benesi HA, Hildebrand JH (1949) A spectrophotometric investigation of the interaction of iodine with aromatic hydrocarbons. J Am Chem Soc 71:2703–2707
Chen Y, Chen Z, He Y, Lin H, Sheng P, Liu C, Cai Q (2010) L-cysteine-capped CdTe QD-based sensor for simple and selective detection of trinitrotoluene. Nanotechnology 21(12):125502
Chen Y, Chen Z, He Y, Lin H, Sheng P, Liu C, Cai Q (2010) L-cysteine-capped CdTe QD-based sensor for simple and selective detection of trinitrotoluene. Nanotechnology 21(12):125502
Chin S, Tan S, Pang S, Ng S (2017) Nitrogen doped carbon nanodots as fluorescent probes for selective detection and quantification of Ferric (III) ions. Opt Mater 73:77–82
Chullasat K, Nurerk P, Kanatharana P, Davis F, Bunkoed O (2018) A facile optosensing protocol based on molecularly imprinted polymer coated on CdTe quantum dots for highly sensitive and selective amoxicillin detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 254:255–263
Cliff N (1998) The eigenvalues-greater-than-one rule and the reliability of components. Psychol Bull 103:276–279
Ding Y, Shen SZ, Sun H, Sun K, Liu F (2014) Synthesis of L-glutathione-capped-ZnSe quantum dots for the sensitive and selective determination of copper ion in aqueous solutions. Sens Actuators b Chem 203:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.06.054
Diwan P, Bharadwaj A (2006) Nanoelectronics. Pentagon Press New Delhi
Elmizadeh H, Soleimani M, Faridbod F, Bardajee GR (2017) Ligand-capped CdTe quantum dots as a fluorescent nanosensor for detection of copper ions in environmental water sample. J Fluoresc 27(6):2323–2333
EychmüllerA RAL (2000) Chemistry and photophysics of thiol-stabilized II-VI semiconductor nanocrystals. Pure Appl Chem 72(1–2):179–188
Feng Y, Liu L, Hu S, Zou P, Zhang J, Huang C, Zhang X (2016) Efficient fluorescence energy transfer system between fluorescein isothiocyanate and CdTe quantum dots for the detection of silver ions. Luminescence 31(2):356–363
Gao M, Kirstein S, Möhwald H, Rogach AL, Kornowski A, Eychmüller A, Weller H (1998) Strongly photo luminescent CdTe nanocrystals by proper surface modification. J Phys Chem B 102:8360–8363
Genger UR, Grabolle M, Jaricot SC, Nitschke R, Nann T (2008) Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat Methods 5:763–775
Green M (2010) The nature of quantum dot capping ligands. J Mater Chem 20:5797. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm00007h
Guerrini L, Alvarez-Puebla R, Pazos-Perez N (2018) Surface modifications of nanoparticles for stability in biological fluids. Materials 11:1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071154
Hu Z, Xia R, Kais S (2020) A quantum algorithm for evolving open quantum dynamics on quantum computing devices. Sci Rep 10:3301
Huang CY (1982) Determination of binding stoichiometry by the continuous variation method: the job plot. Methods Enzymol 87:509–525
Husseini HBA, Abdalah SF, Khursan AHA, Naimee KAMA, Meucci R, Arecchi FT (2020) Encrypted chaos in quantum dot light emitting diode. J Phys 65:398–404
Ishikawa M, Biju V (2010) Luminescent quantum dots, making invisibles visible in bioimaging. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 104:53–99
Jocelin G, Arivarasan A, Ganesan M, Prasad NR, Sasikala G (2016) Synthesis of colloidal quantum dots coated with mercaptosuccinic acid for early detection and therapeutics of oral cancers. Int J Nanosci 15:1650015. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219581x16500150
Kagan CR, Lifshitz E, Sargent EH, Talapin DV (2016) Building devices from colloidal quantum dots. Science 353:6302
Kamyabi MA, Hajari N, Moharramnezhad MA (2021) promising sensitive electrochemiluminescence hydrogen peroxide sensor based on incorporated CuO nanostructures on 3-D Ni foam. Chem Pap. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01584-0
Kang Z, Zhang Y, Menkara H, Wagner BK, Summers CJ, Lawrence W, Nagarkar V (2011) CdTe quantum dots and polymer nanocomposites for x-ray scintillation and imaging. Appl Phys Lett 98(18):181914
Kroupa DM, Vörös M, Brawand NP, McNichols BW, Miller EM, Gu J, Beard MC (2017) Tuning colloidal quantum dot band edge positions through solution-phase surface chemistry modification. Nat Commun 8(1):1–8
Labeb M, Sakr AH, Soliman M, Abdel-Fettah TM, Ebrahim S (2018) Effect of capping agent on selectivity and sensitivity of CdTe quantum dots optical sensor for detection of mercury ions. Opt Mater 79:331–335
Litvin AP, Martynenko IV, Purcell-Milton F, Baranov AV, Fedorov AV, Gun’Ko YK (2017) Colloidal quantum dots for optoelectronics. J Mater Chem A 5(26):13252–13275
Liu Y, Hou W, Sun H, Cui C, Zhang L, Jiang Y, Tan W (2017) Thiol–ene click chemistry: a biocompatible way for orthogonal bioconjugation of colloidal nanoparticles. Chem Sci 8(9):6182–6187
Mahmoud WE, Al-Amri AM, Yaghmour SJ (2012) Low temperature synthesis of CdSe capped 2-mercaptoethanol quantum dots. Opt Mater 34(7):1082–1086
Malik MA, O’Brien P, Revaprasadu NA (2002) Simple route to the synthesis of core/ shell nanoparticles of chalcogenides. Chem Mater 14:2004–2010
Mandal A, Tamai N (2008) Influence of acid on luminescence properties of thioglycolic acid-capped CdTe quantum dots. J Phys Chem C 112(22):8244–8250
Murase N, Gao M (2004) Preparation and photoluminescence of water-dispersible ZnSe nanocrystals. Mater Lett 58:3898–3902
Ngamdee K, Chaiendoo K, Saiyasombat C, Busayaporn W, Ittisanronnachai S, Promarak V, Ngeontae W (2019) Highly selective circular dichroism sensor based on D-penicillamine/cysteamine cadmium sulfide quantum dots for copper (II) ion detection. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 211:313–321
Nideep TK, Ramya M, Kailasnath M (2019) The influence of ZnS buffer layer on the size dependent efficiency of CdTe quantum dot sensitized solar cell. Superlattices Microstruct 130:175–181
Oh E, Liu R, Nel A, Gemill KB, Bilal M, Cohen Y, Medintz IL (2016) Meta-analysis of cellular toxicity for cadmium-containing quantum dots. Nat Nanotechnol 11:49–486
Pal M, Mathews NR, Santiago P, Mathew X (2012) A facile one-pot synthesis of highly luminescent CdS nanoparticles using thioglycerol as capping agent. J Nanopart Res 14:916
Paul D (2017) Research on heavy metal pollution of river Ganga: a review. Ann Agrar Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aasci.2017.04.001
Pei J, Zhu H, Wang X, Zhang H, Yang X (2012) Synthesis of cysteamine-coated CdTe quantum dots and its application in mercury (II) detection. Anal Chim Acta 757:63–68
Petrovic M, Fernández-Alba AR, Borrull F, Marce RM, Mazo EG, Barceló D (2002) Occurrence and distribution of nonionic surfactants, their degradation products, and linear alkylbenzene sulfonates in coastal waters and sediments in Spain. Environ Toxicol Chem Int J 21(1):37–46
Pooja, Chowdhury P (2021) Functionalized CdTe fluorescence nanosensor for the sensitive detection of water borne environmentally hazardous metal ions. Opt Mater 111:110584
Pooja, Rana M, Chowdhury P (2021) Modern applications of quantum dots: environmentally hazardous metal ion sensing and medical imaging. Elsevier, pp 465–505
Pu Y, Cai F, Wang D, Wang JX, Chen JF (2018) Colloidal synthesis of semiconductor quantum dots toward large-scale production: a review. Ind Eng Chem Res 57(6):1790–1802
Rana M, Chowdhury P (2019) Studies on size dependent structures and optical properties of CdSeS clusters. J Cluster Sci 31:1111
Rana M, Chowdhury P (2019b) L-glutathione capped CdSeS/ZnS quantum dot sensor for the detection of environmentally hazardous metal ions. J Lumin 206:105–112
Rana M, Jain A, Rani V, Chowdhury P (2020) Glutathione capped core/shell CdSeS/ZnS quantum dots as a medical imaging tool for cancer cells. Inorg Chem Commun 112:107723
Reiss P, Bleuse J, Pron A (2002) Highly luminescent CdSe/ZnSe core/shell nanocrystals of low size dispersion. Nano Lett 2:781–784
Ribeiro DSM, Castro RC, Pascoa RNMJ, Soares JX, Rodrigues SSM, Santos JLM (2019) Tuning CdTe quantum dots reactivity for multipoint detection of mercury(II), silver(I) and copper(II). J Lumin 207:386–396
Riedinger A, Zhang F, Dommershausen F, Röcker C, Brandholt S, Nienhaus GU, Koert U, Parak WJ (2010) Ratiometric optical sensing of chloride ions with organic fluorophore-gold nanoparticle hybrids: a systematic study of design parameters and surface charge effects. Small 22:2590–2597
Rodas DS, Corns WT, Chenbm B, Stockwel PB (2010) Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry: a suitable detection technique in speciation studies for arsenic, selenium, antimony and mercury. J Anal at Spectrom 25:933–946
Sadek MS, Kumar R, Babu MS (2009) Optical properties of thiol-stabilised CdTe nanoparticles. Int J Nanoparticles 2(1–6):20–29
Shrivastava A, Gupta VB (2011) Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron Young Sci 2:21–25
Snyder RG, Hsu SL, Krimm S (1978) Vibrational spectra in the C H stretching region and the structure of the polymethylene chain. Spectrochim Acta Part A 34(4):395–406
Spanhel L, Haase M, Weller H, Henglein A (1987) Photochemistry of colloidal semiconductors surface modification and stability of strong luminescing CdS particles. J Am Chem Soc 109:5649–5655
Subramanian S, Ganapathy S, Rajaram M, Ayyaswamy A (2020) Tuning the optical properties of colloidal quantum dots using thiol group capping agents and its comparison. Mater Chem Phys 249:123127
Suoa B, Sub X, Wub J, Chena D, Guo Z (2010) Poly (vinyl alcohol) thin film filled with CdSe–ZnS quantum dots: fabrication, characterization and optical properties. Mater Chem Phys 119:237–242
Takagahara T, Takeda K (1992) Theory of the quantum confinement effect on excitons in quantum dots of indirect-gap materials. Phys Rev B 46:578–581
Talmage SS (1994) Environmental and human safety of major surfactants: alcohol ethoxylates and alkylphenol ethoxylates. CRC Press
Tang J, Marcus RA (2006) Determination of energetics and kinetics from single-particle intermittency and ensemble-averaged fluorescence intensity decay of quantum dots. J Chem Phys 125:044703
Vaishnavi E, Renganathan R (2013) CdTe quantum dot as a fluorescence probe for vitamin B(12) in dosage form. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 115:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.06.068
Wei X, Meng M, Song Z, Gao L, Li H, Dai J, Yan Y (2014) Synthesis of molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres embedded mercaptosuccinic acid-coated CdTe quantum dots for selective recognition of λ-cyhalothrin. J Lumin 153:326–332
Willard DM (2003) Nanoparticles in bioanalytics. Anal Bioanal Chem 376:84–286
Wu HF, Gopal J, Abdelhamid HN, Hasan N (2012) Quantum dot applications endowing novelty to analytical proteomics. Proteomics 12:2949–2961. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201200295
Zare H, Ghalkhani M, Akhavan O, Taghavinia N, Marandi M (2017) Highly sensitive selective sensing of nickel ions using repeatable fluorescence quenching-emerging of the CdTe quantum dots. Mater Res Bull 95:532–538
Zeeb M, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P (2012) Pre concentration and trace determination of chromium using modified ionic liquid cold-induced aggregation dispersive liquid-liquid micro extraction: application to different water and food samples. Food Anal Methods 6:1398–1406
Zhang Y, Guo X, Si W, Jia L, Qian X (2008) Ratiometric and water-soluble fluorescent zinc sensor of carboxamidoquinoline with an alkoxy ethyl amino chain as receptor. Org Lett 10:473–476
Zheng Y, Gao S, Ying JY (2007) Synthesis and cell-imaging applications of glutathione-capped CdTe quantum dots. Adv Mater 19(3):376–380
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PY was involved in data curation, writing—original draft preparation, visualization, investigation, software, validation, writing—reviewing and editing. PC was involved in conceptualization, methodology, writing—reviewing and editing and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors Dr. Papia Chowdhury and Pooja Yadav declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Data availability
Authors can confirm that all relevant data are included in the article and/or its supplementary information files.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, P., Chowdhury, P. Optical efficiency of CdTe QDs for metal ion sensing in the presence of different thiol-based capping agents. Chem. Pap. 76, 1833–1850 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01991-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01991-3