Abstract
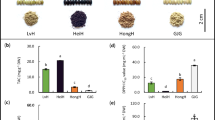
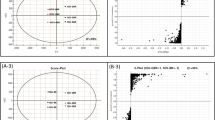
In the present study, polar metabolites including primary metabolites were analysed from red, black and white rice grains using gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC–MS). Quantitative as well as qualitative differences in metabolite profiles of red, black and white rice were observed. Principal component analysis (PCA) of the data obtained from semi-targeted metabolite profiling showed a clear separation of grains with different pericarp colour. In the PCA scores plot, PC1 separated pigmented rice and non-pigmented rice. While, PC2 separated red rice and black rice. Biplot generated from metabolite profile of the rice grains indicated that vanillic acid, protocatechuic acid and glycerol-3-phosphate differentiate black rice from red and white rice. Erythritol and ribonic acid are present only in red rice causing its separation from black and white rice. Additionally, total phenolic content (TPC), 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), 2,2′-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonicacid) (ABTS) and the reducing potential of extracts in terms of ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) were carried out. DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activities of pigmented rice are higher than that of white rice, possibly due to the presence of high TPC in their grains. However, reducing power in terms of FRAP is highest in black rice and is comparable in red and white rice. Furthermore, correlation analysis of antioxidant activities with the metabolites was done to identify the possible primary metabolites contributing to antioxidant capacities of pigmented and non-pigmented rice. This study provides a premise for integration of pigmented rice in our daily diet owing to the potential health benefits of the compositional metabolites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.F. Deng, X.R. Xu, Y.J. Guo, E.Q. Xia, S. Li, S. Wu, F. Chen, W.H. Ling, H.B. Li, J. Funct. Foods 4, 906 (2012)
G.F. Deng, X.R. Xu, Y. Zhang, D. Li, R.Y. Gan, H.B. Li, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 53, 296 (2013)
G. Pereira-Caro, G. Cros, T. Yokota, A. Crozier, J. Agric. Food Chem. 61, 7976 (2013)
I.L. Massaretto, M.F.M Alves, N.V.M de Mira, A.K. Carmona, U.M.L. Marquez. J. Cereal Sci. 54, 236 (2011)
Y. Shao, J. Bao, Food Chem. 180, 86 (2015)
S. Jang, Z. Xu, J. Agric. Food. Chem. 57, 858 (2009)
T. Oki, M. Masuda, M. Kobayashi, Y. Nishiba, S. Furuta, I. Suda, J. Agric. Food. Chem. 50, 7524 (2002)
B. Min, A.M. McClung, M.H. Chen, J. Food Sci. 76, 117 (2011)
W.H. Ling, Q.X. Cheng, J. Ma, T. Wang, J. Nutr. 131, 1421 (2001)
R. Valarmathi, M. Raveendran, S. Robin, N. Senthil, J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-014-0274-6
Q. Wang, P. Han, M. Zhang, M. Xia, H. Zhu, J. Ma, M. Hou, Z. Tang, W. Ling, Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 16, 295 (2007)
J. Shipp, E.S. Abdel-Aal, Open Food Sci. J. 4, 7 (2010)
F.J. Francis, Cereal Food. World 45, 208 (2000)
C. Chotimarkorn, S. Benjakul, N. Silalai, Food Res. Int. 41, 616 (2008)
D.K. Lim, C. Mo, J.H. Lee, N.P. Long, Z. Dong, J. Li, J. Lim, S.W. Kwon, J. Food Drug Anal. 26, 769 (2018)
S.K. Biswas, D.E. Kim, Y.S. Keum, R.K. Saini, J. Food Meas. Charact. 12, 2484 (2018)
T. Frank, B. Reichardt, Q. Shu, K.H. Engel, J. Cereal Sci. 55, 112 (2012)
J.K. Kim, S.Y. Park, S.H. Lim, Y. Yeo, H.S. Cho, S.H. Ha, J. Cereal Sci. 57, 14 (2013)
J. Taylor, R.D. King, T. Altmann, O. Fiehn, Bioinformatics 18, 241 (2002)
Y. Shao, Z. Hu, Y. Yu, R. Mou, Z. Zhu, Food Chem. 239, 733 (2018)
P. Pramai, N.A.A. Hamid, A. Mediani, M. Maulidiani, F. Abasb, S. Jiamyangyuen, J. Food Drug Anal. 26, 47 (2018)
G.R. Kim, E.S. Jung, S. Lee, S.H. Lim, S.H. Ha, C.H. Lee, Molecules 219, 15673 (2014)
B. Min, L. Gu, A.M. McClung, C.J. Bergman, M.H. Chen, Food Chem. 133, 715 (2012)
M.Y. Kang, C.W. Rico, H.J. Bae, S.C. Lee, Cereal Chem. 90, 497 (2013)
U.R. Moon, S.K. Sen, A. Mitra, J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants. 20, 115 (2014)
B. De, G. Nag, C. R. Biol. 337, 283 (2014)
J. Xia, I. Sinelnikov, B. Han, D.S. Wishart, Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 251 (2015)
R. Sompong, S. Siebenhandl-Ehn, G. Linsberger-Martin, E. Berghofer, Food Chem. 124, 132 (2011)
Y. Shen, L. Jin, P. Xiao, Y. Lu, J. Bao, J. Cereal Sci. 49, 106 (2009)
Y.P. Huang, H.M. Lai, J. Food Drug Anal. 24, 564 (2016)
W. Pongsuwan, E. Fukusaki, T. Bamba, T. Yonetani, T. Yamahara, A. Kobayashi, J. Agric. Food. Chem. 55, 231 (2007)
P. Goufo, H, Trindade. Food Sci Nutr. 2, 75 (2014)
C.L. Dittgen, J.F. Hoffmann, F.C. Chaves, C.V. Rombaldi, J.M.C. Filho, N.L. Vanier, Food Chem. 288, 297 (2019)
L. Tarpley, A.L. Duran, T.H. Kebrom, L.W. Sumner, BMC Plant Biol. 5, 8 (2005)
M. Goto, Y. Murakami, H. Yamanaka, Koshihikari and Minenishiki. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. 43, 821 (1996)
H. Du, Y. Huo, H. Liu, G.M. Kamal, J. Yang, Y. Zeng, S. Zhao, Y. Liu, CYTA J. Food 17, 128 (2019)
D. Camacho, A. de la Fuente, P. Mendes, Metabolomics 1, 53 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was a part of a mega project on Sustainable Food Security (File No: 4–25/2013/TS-I) funded by Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India. JNRK was a recipient of a doctoral fellowship from the institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotamreddy, J.N.R., Hansda, C. & Mitra, A. Semi-targeted metabolomic analysis provides the basis for enhanced antioxidant capacities in pigmented rice grains. Food Measure 14, 1183–1191 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00367-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00367-2