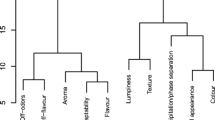
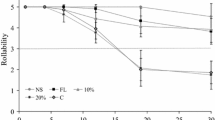
Abstract
The storage shelf life of brews has become progressively important in recent years for the beverage’s manufacturers. The objectives of this study were to investigate the proximate composition and mineral contents of the proposed roasted date seeds powders, to model the kinetic changes in the properties of the brews during storage and to establish a predictive model for forecasting the shelf life by integration of consumer acceptability and quality attributes of the brews. Foremost, the chemical composition and mineral content analysis of both full fat and low-fat powders were investigated using the standard methods. The brews were prepared using hot water and then stored up to 30 days at 4, 25, 38 °C. Samples of brews were taken initially and after 2, 4, 6, 12, 18, 24 and 30 days for conducting pH measurement and sensory evaluation. Kinetic modelling for the properties were conducted by applying the nonlinear regression technique. Besides, the shelf life of the brews was predicted by integration of the acceptability and quality indicators. The results revealed that pH, H3O+ and sensory attributes of the brews were significantly influenced by the storage conditions. Descriptive models have been developed for describing the different properties and the shelf life of brews. In addition, the brews were microbiologically stable during the predicted shelf life period under different storage temperatures and times.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
FAO Data Base. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2016
J.S. Hamada, I.B. Hashim, F.A. Sharif, Preliminary analysis and potential uses of date pits in foods. Food Chem. 76, 135–137 (2002)
M.S. Rahman, S. Kasapis, N.S.Z. Al-Kharusi, I.M. Al-Marhubi, A.J. Khan, Composition characterisation and thermal transition of date pits powders. J. Food Eng. 80, 1–10 (2007)
M. Al-Farsi, C. Alasalvar, M. Al-Abid, K. Al-Shoaily, M. Al-Amry, F. Al-Rawahy, Compositional and functional characteristics of dates, syrups, and their by-products. Food Chem. 104, 943–947 (2007)
E.D.T. Bouhlali, C. Alem, J. Ennassir, M. Benlyas, A.N. Mbark, Y.F. Zegzouti, Phytochemical compositions and antioxidant capacity of three date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) seeds varieties grown in the South East Morocco. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 16, 350–357 (2017)
S. Ghnimi, R. Almansoori, B. Jobe, M. Hassan, K. Afaf, Quality evaluation of Coffee-like beverage from date seeds (Phoenix dactylifera L.). J. Food Process. Technol. 6, 1–6 (2015)
M.S. Baliga, B.R.V. Baliga, S.M. Kandathil, H.P. Bhat, P.K. Vayalil, A review of the chemistry and pharmacology of the date fruits (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Food Res. Int. 44, 1812–1822 (2011)
S. Bahmanpour, T. Talaei, Z. Vojdani, M. Panjehshahin, A. Poostpasand, S. Zareei, M. Ghaeminia, Effect of Phoenix dactylifera pollen on sperm parameters and reproductive system of adult male rats. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 31, 208–212 (2015)
A. Al-Qarawi, H. Abdel-Rahman, H. Mousa, B. Ali, S. El-Mougy, Nephroprotective action of Phoenix dactylifera in gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Pharm. Biol. 46, 227–230 (2008)
D.A. Mohamed, S.Y. Al-Okbi, In vivo evaluation of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of different extracts of date fruits in adjuvant arthritis. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 13, 397–402 (2004)
D.M. El Sheikh, E.A. El-Kholany, S.M. Kamel, Nutritional value, cytotoxicity, anti-carcinogenic and beverage evaluation of roasted date pits. World J. Dairy Food Sci. 9, 308–316 (2014)
N. Sekeroglu, F.S. Senol, I.E. Orhan, A.R. Gulpinar, M. Kartal, B. Sener, In vitro prospective effects of various traditional herbal coffees consumed in Anatolia linked to neurodegeneration. Food Res. Int. 45, 197–203 (2012)
H.M. Habib, W.H. Ibrahim, Effect of date seeds on oxidative damage and antioxidant status in vivo. J. Sci. Food Agric. 91, 1674–1679 (2011)
M.Z. Hossain, M.I. Waly, V. Singh, V. Sequeira, M.S. Rahman, Chemical composition of date-pits and its potential for developing value-added product-a review. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 64, 215–226 (2014)
M. Amany, M.A. Shaker, A. Abeer, Antioxidant activities of date pits in a model meat system. Int. Food Res. J. 19, 223–227 (2012)
C. Platat, H.M. Habib, I.B. Hashim, H. Kamal, F. AlMaqbali, U. Souka, W.H. Ibrahim, Production of functional pita bread using date seed powder. J. Food Sci. Technol. 52, 6375–6384 (2015)
M.A. Bouaziz, F. Abbes, A. Mokni, C. Blecker, H. Attia, S. Besbes, The addition effect of Tunisian date seed fibers on the quality of chocolate spreads. J. Texture Stud. 48, 143–150 (2017)
C.D. Venkatachalam, M. Sengottian, Study on roasted date seed non caffeinated Coffee powder as a promising alternative. Humanities 6, 1387–1394 (2016)
C. Delgado-Andrade, F.J. Morales, Unraveling the contribution of melanoidins to the antioxidant activity of coffee brews. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 1403–1407 (2005)
T.H. Parliment, C.-T. Ho, P. Schieberle, Caffeinated Beverages: Health Benefits, Physiological Effects, and Chemistry (ACS Publications, Washington, DC, 2000)
A.L. Kristjansson, I.D. Sigfusdottir, S.S. Frost, J.E. James, Adolescent caffeine consumption and self-reported violence and conduct disorder. J. Youth Adolesc. 42, 1053–1062 (2013)
E.B. Saafi-Ben Salah, G. Flamini, A. ElArem, M. Issaoui, S. Dabbou, L. Benyahia, A. Ferchichi, M. Hammami, L. Achour, Compositional characteristics and aromatic profile of date palm seeds from seven varieties grown in Tunisia. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 47, 1903–1908 (2012)
C. Somporn, A. Kamtuo, P. Theerakulpisut, S. Siriamornpun, Effects of roasting degree on radical scavenging activity, phenolics and volatile compounds of Arabica coffee beans (Coffea arabica L. cv. Catimor). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 46, 2287–2296 (2011)
T. Labuza, B. Altunakar, Water Activity in Foods: Fundamentals and Applications (Blackwell Publishing, Iwoa, 2007)
S. Jena, H. Das, Shelf life prediction of aluminum foil laminated polyethylene packed vacuum dried coconut milk powder. J. Food Eng. 108, 135–142 (2012)
M. Achour, A new method to assess the quality degradation of food products during storage. J. Food Eng. 75, 560–564 (2006)
L. Manzocco, C. Lagazio, Coffee brew shelf life modelling by integration of acceptability and quality data. Food Qual. Prefer. 20, 24–29 (2009)
I.Y. Rustom, M. Lopez-Leiva, B.M. Nair, UHT-sterilized peanut beverages: Kinetics of physicochemical changes during storage and shelf-life prediction modeling. J. Food Sci. 61, 198–203 (1996)
M. Fikry, Y.A. Yusof, A.M. Al-Awaadh, R.A. Rahman, H.M. Ghazali, Antioxidative and quality properties of full-fat date seeds brew as influenced by the roasting conditions. Antioxidants 8, 226 (2019)
M. Fikry, Y.A. Yusof, A.M. Al-Awaadh, R.A. Rahman, N.L. Chin, E. Mousa, L.S. Chang, Effect of the roasting conditions on the physicochemical, quality and sensory attributes of coffee-like powder and brew from defatted palm date seeds. Foods 8, 61 (2019)
M. Fikry, Y.A. Yusof, A.M. Al-Awaadh, R.A. Rahman, N.L. Chin, E. Mousa, L.S. Chang, Kinetics modelling of the color, hardness, grinding energy consumption and oil yield changes during the conventional roasting of palm date seeds. Food Science and Technology Research 25, 351–362 (2019)
M. Akbari, R. Razavizadeh, G. Mohebbi, A. Barmak, Oil characteristics and fatty acid profile of seeds from three varieties of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) cultivars in Bushehr-Iran. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 11, 12088–12093 (2012)
M. Nicoli, M. Anese, L. Manzocco, C. Lerici, Antioxidant properties of coffee brews in relation to the roasting degree. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 30, 292–297 (1997)
AOAC, Official methods of analysis, 18th edn. (Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, 2005)
H. Egan, R.S. Kirk, R. Sawyer, Pearson’s Chemical Analysis of Foods Edinburgh, London (Churchill Livingstone, Melbourne and New York, 1981)
G.D. Sadler, P.A. Murphy, pH and titratable acidity, in Food Analysis, ed. by S. Suzanne Nielsen (Springer, Boston, 2010), pp. 219–238
M.D. Rosa, D. Barbanti, C.R. Lerici, Changes in coffee brews in relation to storage temperature. J. Sci. Food Agric. 50, 227–235 (1990)
G.L. Robertson, Food Packaging and Shelf Life: A Practical Guide (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2009)
T.P. Labuza, Shelf-life Dating of Foods (Food & Nutrition Press Inc.: Westport, 1982)
R. Singh, in Shelf Life Evaluation of Foods. Scientific principles of shelf life evaluation (Springer, Berlin, 1994), pp. 3–26
M. Nicoli, S. Calligaris, L. Manzocco, Shelf-life testing of coffee and related products: uncertainties, pitfalls, and perspectives. Food Eng. Rev. 1, 159–168 (2009)
BIS Handbook of food analysis, Dairy products. Bur. Indian Stand. SP 18, 129 (1981)
A.K. Chauhan, V. Patil, Effect of packaging material on storage ability of mango milk powder and the quality of reconstituted mango milk drink. Powder Technol. 239, 86–93 (2013)
J. Floros, M. Chinnan, Computer graphics-assisted optimization for product and process development. Food Technol. 42, 72–78 (1988)
M. Fikry, A.M. Al-Awaadh, Characteristics of dynamics sorption isotherms of Date flesh powder rich in fiber. Int. J. Food Eng. 12, 469–480 (2016)
D. Choudhury, J.K. Sahu, G. Sharma, Moisture sorption isotherms, heat of sorption and properties of sorbed water of raw bamboo (Dendrocalamus longispathus) shoots. Ind Crops Prod 33, 211–216 (2011)
C. Lomauro, A. Bakshi, T. Labuza, Evaluation of food moisture sorption isotherm equations. Part I: Fruit, vegetable and meat products. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und Technologie 18, 111–117 (1985)
A. Talla, Y. Jannot, G.E. Nkeng, J.-R. Puiggali, Experimental determination and modeling of sorption isotherms of tropical fruits: banana, mango, and pineapple. Dry. Technol. 23, 1477–1498 (2005)
A. Vega-Gálvez, R. Lemus-Mondaca, P. Fito, A. Andrés, Note: moisture sorption isotherms and isosteric heat of red bell pepper (var. Lamuyo). Revista de Agaroquimica y Tecnologia de Alimentos 13, 309–316 (2007)
K. Prasad, N. Nath, Comparison of sugarcane juice based beverage optimisation using response surface methodology with Fuzzy method. Sugar Tech 4, 109–115 (2002)
IBM statistical package for the social sciences IBM, 2012
A.E. Bender, Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2016)
F.A.L. Juhaimi, K. Ghafoor, M.M. Özcan, Physical and chemical properties, antioxidant activity, total phenol and mineral profile of seeds of seven different date fruit (Phoenix dactylifera L.) varieties. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 63, 84–89 (2012)
S. Suresh, N. Guizani, M. Al-Ruzeiki, A. Al-Hadhrami, H. Al-Dohani, I. Al-Kindi, M.S. Rahman, Thermal characteristics, chemical composition and polyphenol contents of date-pits powder. J. Food Eng. 119, 668–679 (2013)
S. Niazi, S. Rasheed, I.M. Khan, Chemical, mineral and phytochemical screening assay of date palm seeds for the development of date palm seed coffee. Int. J. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2, 6–12 (2017)
F. Barron, Acid, Acidified and Low-Acid Foods (Clemson University, South Carolina, 2000)
A.M. Muñoz, V.G. Civille, B.T. Carr, Sensory Evaluation in Quality Control (Reinhold, van Mostrand, 1992)
C. Wong, W. Lim, Storage stability of spray-dried papaya (Carica papaya L.) powder packaged in aluminium laminated polyethylene (ALP) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Int. Food Res. J. 23, 1887–1894 (2016)
N.F. Authority, Microbiological quality guide for ready-to-eat foods: a guide to interpreting microbiological results. NSW/FA/CP028/0906, 1–9 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Universiti Putra Malaysia, IPS Grant with Vote Number: 9634800. The authors acknowledge the efforts done by the Research Centre in the faculty of food science and agriculture, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia and the Supercritical Fluid Centre, UPM for their technical support. The authors would like to take this opportunity to say warm thanks to Dr. Esraa Mousa from Food Technology Research Institute, Agricultural research centre, Giza, Egypt and Mr. Abdul Afiq from Halal Products Research Institute at UPM for their appreciated supporting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fikry, M., Yusof, Y.A., Al-Awaadh, A.M. et al. Prediction of the shelf-life of date seeds brew by integration of acceptability and quality indices. Food Measure 14, 1158–1171 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00365-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00365-4