Abstract
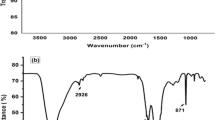
A novel nonenzymatic voltammetric Xanthine biosensor was constructed based on a three-dimensional porous nanocomposite of reduced graphene oxide/polypyrrole/CdO nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE/rGO/PPy/CdO) for measuring of Xanthine. The structure and morphology of rGO/PPy/CdO nanocomposites were characterized by field emission scanning microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, UV–vis spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The GCE/rGO/PPy/CdO based biosensor exhibited excellent electrocatalytic activity and high stability for Xanthine oxidation. Under optimized conditions, the linearity between the current response and the Xanthine concentration was obtained in the range of 1–800 µM with a detection limit of 0.11 μM (S/N = 3). The biosensor was used to determine the Xanthine in fish meat with satisfactory results.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Zhang, J. Dong, X. Qian, Ch Zhao, One-pot synthesis of an RGO/ZnO nanocomposite on zinc foil and its excellent performance for the nonenzymatic sensing of xanthine. Sensors Actuators B 221, 528–536 (2015)
N. Cooper, R. Khosravan, C. Erdmann, J. Fiene, J.W. Lee, Quantification of uricacid, xanthine and hypoxanthine in human serum by HPLC for pharmacody-namic studies. J. Chromatogr. B 837, 1–10 (2006)
R. Parker, W. Snedden, R.W.E. Watts, Mass-spectrometric identification of hypoxanthine and xanthine (oxypurines) in skeletal muscle from two patients with congenital xanthine oxidase deficiency (xanthinuria). Biochem. J. 115, 103–108 (1969)
Z.K. Shihabi, M.E. Hinsdale, A.J. Bleyer, Xanthine analysis in biological fluids by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B 669, 163–169 (1995)
V.K. Gupta, H. Karimi-Maleh, R. Sadegh, Simultaneous determination of hydroxylamine, phenol and sulfite in water and waste water samples using a voltammetric nanosensor. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 10, 303–316 (2015)
G. Kh, S. Bonyadi, An electrochemical sensor based on reducedgraphene oxide decorated with polypyrrolenanofibers and zinc oxide–copper oxide p–n junction heterostructures for the simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, paracetamol, and tryptophan. New J. Chem. 42, 8512–8523 (2018)
M. Raicopol, A. Prună, C. Damian, L. Pilan, Functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes/polypyrrole composites for amperometric glucose biosensors. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 316–323 (2013)
H. Ahmad, A.A. Jasim, M.J. Faruki, M.S. Rahman, K. Thambiratnam, Poly (N-vinylcarbazole)-polypyrrole/graphene oxide nanocomposites based microfiber interferometer for high stability temperature sensor. Sensors Actuators B 263, 44–53 (2017)
K. Naka, H. Itoh, S. Park, Y. Chujo, Synthesis of nanocomposites of metal nanoparticles utilizing miscible polymers. Polym. Bull. 52, 171–176 (2004)
H. Huang, Q. Yuan, X. Yang, Preparation and characterization of metal-chitosan nanocomposites. Colloid Surf. B 39, 31–37 (2004)
C.H. Bhosale, A.V. Kambale, A.V. Kokate, K.Y. Rajpure, Structural, optical and electrical properties of chemically sprayed CdO thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 122, 67–71 (2005)
N. Butwong, L. Zhou, W. Ng-eontae, R. Burakham, E. Moore, S. Srijaranai, J.H.T. Luong, J.D. Glennon, A sensitive nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor using cadmium oxide nanoparticles/multiwall carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 717–718, 41–46 (2014)
K.B. Ravi, R. Gone, P.K. Giri, On the origin and tunability of blue and green photoluminescence from chemically derived graphene: hydrogenation and oxygenation studies. Carbon 95, 228–238 (2015)
Y. Liu, Y. Ma, S. Guang, F. Ke, H. Xu, Polyaniline-graphene composites with a three-dimensional array-based nanostructure for high-performance supercapacitors. Carbon 83, 79–89 (2015)
P. Atri, D.C. Tiwari, R. Sharma, Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide nanoscrolls embedded in polypyrrole matrix for supercapacitor applications. Synth. Met. 227, 21–28 (2017)
Y. Liu, E. Zhu, L. Bian, J. Hai, J. Tang, W. Tang, Robust graphene dispersion with amphiphlic perylene-polyglycidol. Mater Lett. 118, 188–191 (2014)
S. Kumar, A.K. Ojha, B. Walkenfort, Cadmium oxide nanoparticles grown in situ on reduced graphene oxide for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye under ultraviolet irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 159, 111–119 (2016)
P. Moozarm, N.W. PeiMeng, F. Lorestani, M.R. Mahmoudian, Y.Alias, Electrodeposition of copper oxide/polypyrrole/reduced graphene oxide as a nonenzymatic glucose biosensor. Sensors Actuators B 209, 100–108 (2015)
H. Mirzazadeh, M. Lashanizadegan, Improving the catalytic activity of magnetic Fe3O4/ZnO–CdO/reduced graphene oxide for ultrasonic degradation of the organic pollutants and the green oxidation of olefins. Solid State Sci. 79, 48–57 (2018)
S. Pourhashem, E. Ghasemy, A. Rashidi, M.R. Vaezi, Corrosion protection properties of novel epoxy nanocomposite coatings containing silane functionalized graphene quantum dots. J. Alloys Compd. 731, 1112–1118 (2018)
K.N. Kudin, B. Ozbas, H.C. Schniepp, R.K. Prud’homme, I.A. Aksay, R. Car, Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 8, 36–41 (2008)
J. Li, G. Xiao, C. Chen, R. Li, D. Yan, Superior dispersions of reduced graphene oxide synthesized by gallic acid as a reductant and stabilizer. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 1481–1487 (2013)
S. Stankovich, D.A. Dikin, R.D. Piner, K.A. Kohlhaas, A. Kleinhammes, Y. Jia, Y. Wu, S.T. Nguyen, R.S. Ruoff, Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 45, 1558–1565 (2007)
X. Fan, Zh Yang, N. He, Hierarchical nanostructured polypyrrole/graphene composites as supercapacitor electrode. RSC Adv. 5, 15096–15102 (2015)
G. Murugadoss, R. Jayavel, R. Thangamuthu, M.R. Kumar, PbO/CdO/ZnO and PbS/CdS/ZnS nanocomposites: studies on optical, electrochemical and thermal properties. J. Lumin. 170, 78–89 (2016)
X. Niu, W. Yang, J. Ren, H. Guo, S. Long, J. Chen, J. Gao, Electrochemical behaviors and simultaneous determination of guanine and adenine based on graphene–ionic liquid–chitosan composite film modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim. Acta 80, 346–353 (2012)
M. Dekker, in Laboratory Techniques in Electroanalytical Chemistry, ed. by P.T. Kissinger, W.R. Heineman (New York: Marcel Dekker, 1984), p. 82
N.F. Atta, M.F. El-Kady, A. Galal, Palladium nanoclusters-coated polyfuran as a novel sensor for catecholamine neurotransmitters and paracetamol. Sensors Actuators B 141, 566–574 (2009)
J.J. Gooding, V.G. Praig, E.A. Hall, Platinum-catalyzed enzyme electrodes immobilized on gold using self-assembled layers. Anal. Chem. 70, 2396–2402 (1998)
V. Vamvakaki, K. Tsagaraki, N. Chaniotakis, Carbon nanofiber-based glucose biosensor. Anal. Chem. 78, 5538–5542 (2006)
R. Devi, B. Batra, S. Lata, S. Yadav, C.S. Pundir, A method for determination of xanthine in meat by amperometric biosensor based on silver nanoparticles/cysteine modified Au electrode. Process. Biochem. 48, 242–249 (2013)
B. Dalkiran, C. Kacar, P.E. Erden, E. Kilic, Amperometric xanthine biosensors based on chitosan Co3O4 multiwalled carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode. Sensors Actuators B 200, 83–91 (2014)
N. Dimcheva, E. Horozova, Z. Jordanova, An amperometric xanthine oxidase enzyme electrode based on hydrogen peroxide electroreduction. Z. Naturforsch C. 57, 883–889 (2002)
S. Sadeghi, E. Fooladi, M. Malekaneh, A nanocomposite/crude extract enzyme-based xanthine biosensor. Anal. Biochem. 464, 51–59 (2014)
F. Öztürk, P.E. Erden, C. Kaçar, E. Kiliç, Amperometric biosensor for xanthine determination based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Acta Chim. Slov. 61, 19–26 (2014)
R. Devi, M. Thakur, C.S. Pundir, Construction and application of an amperometric xanthine biosensor based on zinc oxide nanoparticles–polypyrrole composite film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 3420–3426 (2011)
S. Çevik, Xanthine biosensor based on XO/AuNP/PtNP/MWCNT hybrid nanocomposite modified GCPE. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 21, 314–320 (2016)
M. Dervisevic, E. Custiuc, E. Çevik, Z. Durmus, M. Şenel, A. Durmus, Electrochemical biosensor based on REGO/Fe3O4 bionanocomposite interface for xanthine detection in fish sample. Food Control 57, 402–410 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge partial financial support from the Research Council of Alzahra University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghanbari, K., Nejabati, F. Construction of novel nonenzymatic Xanthine biosensor based on reduced graphene oxide/polypyrrole/CdO nanocomposite for fish meat freshness detection. Food Measure 13, 1411–1422 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00057-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00057-z