Abstract
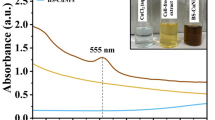
The present experimental survey designed to green synthesis, characterization, as well as in vitro and in vivo anti-Toxplasma gondii activity of silver nanoparticles (SLN) green synthesized by Lupinus arcticus extract. SLN were green synthesized based on the reducing by L. arcticus extract through the precipitation technique. In vitro lethal effects of SLN on T. gondii tachyzoites, infectivity rate, parasites inside of the human macrophage cells (THP-1 cells), nitric oxide (NO) triggering, and iNOS and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) expression genes were evaluated. In vivo, after establishment of toxoplasmosis in BALB/c mice via T. gondii ME49 strain, mice received SLN at 10 and 20 mg/kg/day alone and combined to pyrimethamine at 5 mg/kg for 14 days. SLN exhibited a spherical form with a size ranging from 25 to 90 nm. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of SLN and pyrimethamine against tachyzoites was 29.1 and 25.7 µg/mL, respectively. While, the 50% cytotoxic concentration (CC50) value of SLN and pyrimethamine against THP-1 cells was 412.3 µg/mL and 269.5 µg/mL, respectively. SLN in combined with pyrimethamine obviously (p < 0.05) decreased the number and size of the T. gondii cysts in the infected mice. The level of NO, iNOS and IFN-γ genes was obviously (p < 0.001) upregulated. SLN obviously (p < 0.05) decreased the liver level of oxidative stress and increased the level of antioxidant factors. The findings displayed the promising beneficial effects of SLN mainly in combination with current synthetic drugs against latent T. gondii infection in mice. But we need more experiments to approve these findings, clarifying all possible mechanisms, and its efficiency in clinical phases.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saadatnia G, Golkar M (2012) A review on human toxoplasmosis. Scand J Infect Dis 44(11):805–814. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365548.2012.693197
Molan A, Nosaka K, Hunter M, Wang W (2019) Global status of Toxoplasma gondii infection: systematic review and prevalence snapshots. Trop Biomed 36(4):898–925 PMID 33597463
Martinez VO, de Mendonça Lima FW, De Carvalho CF, Menezes-Filho JA (2018) Toxoplasma gondii infection and behavioral outcomes in humans: a systematic review. Parasitol Res.;117(10):3059-65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-6040-2
Hampton MM (2015) Congenital toxoplasmosis: a review. Neonatal Netw 34(5):274–278. https://doi.org/10.1891/0730-0832.34.5.274
Dubey JP, Tiao N, Gebreyes WA, Jones JL (2012) A review of toxoplasmosis in humans and animals in Ethiopia. Epidemiol Infect 140(11):1935–1938. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268812001392
McCabe RE (2001) Antitoxoplasma chemotherapy. Toxoplasmosis: a comprehensive clinical guide.:319– 59
Montazeri M, Mehrzadi S, Sharif M, Sarvi S, Tanzifi A, Aghayan SA, Daryani A (2018) Drug resistance in Toxoplasma Gondii. Front Microbiol 9:2587. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02587
Jones JL, Lopez A, Wilson M, Schulkin J, Gibbs R (2001) Congenital toxoplasmosis: a review. Obstet Gynecol Surv 56(5):296–305. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006254-200105000-00025
Dunay IR, Gajurel K, Dhakal R, Liesenfeld O, Montoya JG (2018) Treatment of toxoplasmosis: historical perspective, animal models, and current clinical practice. Clin Microbiol Rev 31(4):10–128. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.00057-17
Marra CM (2018) Central nervous system infection with Toxoplasma Gondii. Handbook of clinical neurology. 152:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-63849-6.00009-8
Formoso P, Muzzalupo R, Tavano L, De Filpo G, Pasquale Nicoletta F (2016) Nanotechnology for the environment and medicine. Mini Rev Med Chem 16(8):668–675. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557515666150709105129
Albalawi AE, Alanazi AD, Baharvand P, Sepahvand M, Mahmoudvand H (2020) High potency of organic and inorganic nanoparticles to treat cystic echinococcosis: an evidence-based review. Nanomaterials 10(12):2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122538
Keyhani A, Ziaali N, Shakibaie M, Kareshk AT, Shojaee S, Asadi-Shekaari M, Sepahvand M, Mahmoudvand H (2020) Biogenic selenium nanoparticles target chronic toxoplasmosis with minimal cytotoxicity in a mouse model. J Med Microbiol 69(1):104–110. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.001111
Marin S, Mihail Vlasceanu G, Elena Tiplea R, Raluca Bucur I, Lemnaru M, Minodora Marin M, Mihai Grumezescu A (2015) Applications and toxicity of silver nanoparticles: a recent review. Curr Top Med Chem 15(16):1596–1604. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026615666150414142209
Saravanan A, Kumar PS, Karishma S, Vo DV, Jeevanantham S, Yaashikaa PR, George CS (2021) A review on biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles and its environmental applications. Chemosphere 264:128580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128580
Huq MA, Ashrafudoulla M, Rahman MM, Balusamy SR, Akter S (2022) Green synthesis and potential antibacterial applications of bioactive silver nanoparticles: a review. Polymers 14(4):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040742
Costa IN, Ribeiro M, Silva Franco P, da Silva RJ, de Araújo TE, Milián IC, Luz LC, Guirelli PM, Nakazato G, Mineo JR, Mineo TW (2021) Biogenic silver nanoparticles can control toxoplasma gondii infection in both human trophoblast cells and villous explants. Front Microbiol 11:623947. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.623947
da Silva Sanfelice RA, Silva TF, Tomiotto-Pellissier F, da Silva Bortoleti BT, Lazarin-Bidóia D, Scandorieiro S, Nakazato G, de Barros LD, Garcia JL, Verri WA, Conchon-Costa I (2022) Biogenic silver nanoparticles reduce Toxoplasma Gondii infection and proliferation in RAW 264.7 macrophages by inducing tumor necrosis factor-alpha and reactive oxygen species production in the cells. Microbes Infect 24(5):104971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2022.104971
Saadatmand M, Al-Awsi GR, Alanazi AD, Sepahvand A, Shakibaie M, Shojaee S, Mohammadi R, Mahmoudvand H (2021) Green synthesis of zinc nanoparticles using Lavandula angustifolia Vera. Extract by microwave method and its prophylactic effects on Toxoplasma Gondii infection. Saudi J Biol Sci 28(11):6454–6460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.07.007
Mahmoudvand H, Kheirandish F, Ghasemi Kia M, Tavakoli Kareshk A, Yarahmadi M (2016) Chemical composition, protoscolicidal effects and acute toxicity of Pistacia atlantica Desf. Fruit extract. Nat Prod Res 30(10):1208–1211. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2015.1046868
Ezzatkhah F, Khalaf AK, Mahmoudvand H (2021) Copper nanoparticles: biosynthesis, characterization, and protoscolicidal effects alone and combined with albendazole against hydatid cyst protoscoleces. Biomed Pharmacother 136:111257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111257
Albalawi AE, Abdel-Shafy S, Khudair Khalaf A, Alanazi AD, Baharvand P, Ebrahimi K, Mahmoudvand H (2021) Therapeutic potential of green synthesized copper nanoparticles alone or combined with meglumine antimoniate (glucantime®) in cutaneous leishmaniasis. Nanomaterials 11(4):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040891
Albalawi AE, Khalaf AK, Alyousif MS, Alanazi AD, Baharvand P, Shakibaie M, Mahmoudvand H (2021) Fe3O4@ piroctone olamine magnetic nanoparticles: synthesize and therapeutic potential in cutaneous leishmaniasis. Biomed Pharmacother 139:111566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111566
Alanazi AD, Majeed QA, Alnomasy SF, Almohammed HI (2023) Potent in Vitro and in vivo effects of Stachys Lavandulifolia Methanolic Extract against Toxoplasma gondii infection. Trop Med Infect Disease 8(7):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8070355
Almohammed HI, Alanazi AD (2022) In vitro/in vivo Assessment and Cellular mechanisms of Astragalus Spinosus Extract against Leishmania major. Pharmacognosy Magazine 18(80):830–835. https://doi.org/10.4103/pm.pm_53_22
Albalawi AE, Alanazi AD, Alyousif MS, Sepahvand A, Ebrahimi K, Niazi M, Mahmoudvand H (2021) The high potency of green synthesized copper nanoparticles to prevent the Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. Acta Parasitol 66(4):1472–1479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-021-00421-4
Shaapan RM, Al-Abodi HR, Alanazi AD, Abdel-Shafy S, Rashidipour M, Shater AF, Mahmoudvand H (2021) Myrtus communis essential oil; anti-parasitic effects and induction of the innate immune system in mice with Toxoplasma Gondii infection. Molecules 26(4):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040819
Alanazi AD, Almohammed HI (2022) Therapeutic potential and safety of the Cinnamomum zeylanicum Methanolic Extract against Chronic Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in mice. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:900046. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.900046
Alday PH, Doggett JS (2017) Drugs in development for toxoplasmosis: advances, challenges, and current status. Drug Des Devel Ther 273–293. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.s60973
KarimiPourSaryazdi A, Tavakoli P, Barati M, Ghaffarifar F, Ghaffari D (2019) Anti-toxoplasma effects of Silver nanoparticles based on Ginger Extract: an in Vitro Study. J Arch Mil Med 7(4):e104248. https://doi.org/10.5812/jamm.104248
Hematizadeh A, Ebrahimzadeh MA, Sarvi S, Sadeghi M, Daryani A, Gholami S, Nayeri T, Hosseini SA (2023) In Vitro and in vivo anti-parasitic activity of Sambucus ebulus and Feijoa sellowiana extracts silver nanoparticles on Toxoplasma Gondii tachyzoites. Acta Parasitol 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-023-00689-8
Saleh M, Nagaty I, Zalat R, Yaseen D, Abdelhameed R, Kishik S (2021) Assessment of Nitazoxanide loaded on silver nanoparticles efficacy on treatment of Murine Model of Chronic Toxoplasmosis. Benha Med J 38(Academic issue):186–199. https://doi.org/10.21608/bmfj.2021.58655.1372
Gaafar MR, Mady RF, Diab RG, Shalaby TI (2014) Chitosan and silver nanoparticles: promising anti-toxoplasma agents. Exp Parasitol 143:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2014.05.005
Alajmi RA, Al-Megrin WA, Metwally D, Al-Subaie H, Altamrah N, Barakat AM, Abdel Moneim AE, Al-Otaibi TT, El-Khadragy M (2019) Anti-toxoplasma activity of silver nanoparticles green synthesized with Phoenix dactylifera and Ziziphus spina-christi extracts which inhibits inflammation through liver regulation of cytokines in Balb/c mice. Biosci Rep 39(5):BSR20190379. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20190379
James SL (1995) Role of nitric oxide in parasitic infections. Microbiological reviews. 1995; 59(4), 533–547. https://doi.org/10.1128/mr.59.4.533-547.1995
Gazzinelli RT, Brezin A, Li QI, Nussenblatt RB, Chan CC (1994) Toxoplasma Gondii: acquired ocular toxoplasmosis in the murine model, protective role of TNF-α and IFN-γ. Exp Parasitol 78(2):217–229. https://doi.org/10.1006/expr.1994.1022
Nazarlu ZH, Matini M, Bahmanzadeh M, Foroughi-Parvar F (2020) Toxoplasma Gondii: a possible inducer of oxidative stress in reproductive system of male rats. Iran J Parasitol 15(4):521. https://doi.org/10.18502/ijpa.v15i4.4857
Szewczyk-Golec K, Pawłowska M, Wesołowski R, Wróblewski M, Mila-Kierzenkowska C (2021) Oxidative stress as a possible target in the treatment of Toxoplasmosis: perspectives and ambiguities. Int J Mol Sci 22(11):5705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115705
Selseleh M, Modarressi MH, Mohebali M, Shojaee S, Eshragian MR, Selseleh M, Azizi E, Keshavarz H (2012) Real-time RT-PCR on SAG1 and BAG1 gene expression during stage conversion in immunosuppressed mice infected with Toxoplasma Gondii Tehran strain. Korean J Parasitol 50(3):199–205. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2012.50.3.199
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the deanship of scientific research at Shaqra University for funding this research work through the project number (SU-ANN-2023020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Majeed, Q.A., Alnomasy, S.F., Shater, A.F. et al. High Efficacy of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles for Treatment of Toxoplasma Gondii Infection Through Their Immunomodulatory, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antioxidant Potency. Acta Parasit. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-024-00845-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-024-00845-8