Abstract
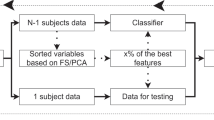
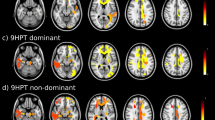
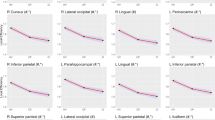
A structural or functional pattern of neuroplasticity that could systematically discriminate between people with impaired and preserved motor performance could help us to understand the brain networks contributing to preservation or compensation of behavior in multiple sclerosis (MS). This study aimed to (1) investigate whether a machine learning-based technique could accurately classify MS participants into groups defined by upper extremity function (i.e. motor function preserved (MP) vs. motor function impaired (MI)) based on their regional grey matter measures (GMM, cortical thickness and deep grey matter volume) and inter-regional functional connection (FC), (2) investigate which features (GMM, FC, or GMM + FC) could classify groups more accurately, and (3) identify the multivariate patterns of GMM and FCs that are most discriminative between MP and MI participants, and between each of these groups and the healthy controls (HCs). With 26 MP, 25 MI, and 21 HCs (age and sex matched) underwent T1-weighted and resting-state functional MRI at 3 T, we applied support vector machine (SVM) based classification to learn discriminant functions indicating regions in which GMM or between which FCs were most discriminative between groups. This study demonstrates that there exist structural and FC patterns sufficient for correct classification of upper limb motor ability of people with MS. The classifier with GMM + FC features yielded the highest accuracy of 85.61 % (p < 0.001) to distinguish between the MS groups using leave-one-out cross-validation. It suggests that a machine-learning approach combining structural and functional features is useful for identifying the specific neural substrates that are necessary and sufficient to preserve motor function among people with MS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand, A., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Wu, J., Gao, S., Bukhari, L., et al. (2005). Activity and connectivity of brain mood regulating circuit in depression: a functional magnetic resonance study. Biological Psychiatry, 57(10), 1079–1088.
Audoin, B., Ibarrola, D., Malikova, I., Soulier, E., Confort-Gouny, S., Duong, M. V. A., et al. (2007). Onset and underpinnings of white matter atrophy at the very early stage of multiple sclerosis–a two-year longitudinal MRI/MRSI study of corpus callosum. Multiple Sclerosis (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England), 13(1), 41–51.
Barkhof, F. (2002). The clinico-radiological paradox in multiple sclerosis revisited. Current Opinion in Neurology, 15(3), 239–245.
Basile, B., Castelli, M., Monteleone, F., Nocentini, U., Caltagirone, C., Centonze, D., et al. (2013). Functional connectivity changes within specific networks parallel the clinical evolution of multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England), 20(8), 1050–1057.
Bendfeldt, K., Klöppel, S., Nichols, T. E., Smieskova, R., Kuster, P., Traud, S., et al. (2012). Multivariate pattern classification of gray matter pathology in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage, 60(1), 400–408.
Brodersen, K. H., Ong, C. S., Stephan, K. E., & Buhmann, J. M. (2010). The balanced accuracy and its posterior distribution. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR ‘10), 3121-3124. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, doi:10.1109/ICPR.2010.764
Calabrese, M., Atzori, M., Bernardi, V., Morra, A., Romualdi, C., Rinaldi, L., et al. (2007). Cortical atrophy is relevant in multiple sclerosis at clinical onset. Journal of Neurology, 254(9), 1212–1220.
Calabrese, M., Rinaldi, F., Grossi, P., Mattisi, I., Bernardi, V., Favaretto, A., et al. (2010). Basal ganglia and frontal/parietal cortical atrophy is associated with fatigue in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England), 16(10), 1220–1228.
Chang, Y.-W., & Lin, C.-J. (2008). Feature ranking using linear svm. Journal of Machine Learning Research: Workshop and Conference Proceedings, 3, 53–64.
Chang, C., & Lin, C. (2011). LIBSVM : a library for support vector machines. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 2, 1–39.
Charil, A., Dagher, A., Lerch, J. P., Zijdenbos, A. P., Worsley, K. J., & Evans, A. C. (2007). Focal cortical atrophy in multiple sclerosis: relation to lesion load and disability. NeuroImage, 34(2), 509–517.
Cifelli, A., Arridge, M., Jezzard, P., Esiri, M. M., Palace, J., & Matthews, P. M. (2002). Thalamic neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Annals of Neurology, 52(5), 650–653.
Cover, K. S., Vrenken, H., Geurts, J. J. G., Van Oosten, B. W., Jelles, B., Polman, C. H., et al. (2006). Multiple sclerosis patients show a highly significant decrease in alpha band interhemispheric synchronization measured using MEG. NeuroImage, 29(3), 783–788.
Crespy, L., Zaaraoui, W., Lemaire, M., Rico, A., Faivre, A., Reuter, F., et al. (2011). Prevalence of grey matter pathology in early multiple sclerosis assessed by magnetization transfer ratio imaging. PloS One, 6(9), 2–7.
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage, 9(2), 179–194.
de Kwaasteniet, B., Ruhe, E., Caan, M., Rive, M., Olabarriaga, S., Groefsema, M., et al. (2013). Relation between structural and functional connectivity in major depressive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 74(1), 40–47.
Desikan, R. S., Ségonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dickerson, B. C., Blacker, D., et al. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage, 31(3), 968–980.
Dogonowski, A. M., Siebner, H. R., Soelberg Sørensen, P., Paulson, O. B., Dyrby, T. B., Blinkenberg, M., & Madsen, K. H. (2013). Resting-state connectivity of pre-motor cortex reflects disability in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 128(5), 328–335.
Dosenbach, N. U. F., Nardos, B., Cohen, A. L., Fair, D. A., Power, D., Church, J. A., et al. (2010). Prediction of Individua brain maturity using fMRI. Science, 329(5997), 1358–1361.
Douaud, G., Behrens, T. E., Poupon, C., Cointepas, Y., Jbabdi, S., Gaura, V., et al. (2009). In vivo evidence for the selective subcortical degeneration in Huntington’s disease. NeuroImage, 46(4), 958–966.
Evangelou, N., Konz, D., Esiri, M. M., Smith, S., Palace, J., & Matthews, P. M. (2000). Regional axonal loss in the corpus callosum correlates with cerebral white matter lesion volume and distribution in multiple sclerosis. Brain, 123(9), 1845–1849.
Faivre, A., Rico, A., Zaaraoui, W., Crespy, L., Reuter, F., Wybrecht, D., et al. (2012). Assessing brain connectivity at rest is clinically relevant in early multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis Journal, 18(9), 1251–1258.
Feis, D. L., Brodersen, K. H., von Cramon, D. Y., Luders, E., & Tittgemeyer, M. (2013). Decoding gender dimorphism of the human brain using multimodal anatomical and diffusion MRI data. NeuroImage, 70, 250–257.
Ferreira, L. K., & Busatto, G. F. (2013). Resting-state functional connectivity in normal brain aging. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 37(3), 384–400.
Filippi, M., & Agosta, F. (2010). Imaging biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 31(4), 770–788.
Filippi, M., Rovaris, M., Inglese, M., Barkhof, F., De Stefano, N., Smith, S., et al. (2004). Interferon beta-1a for brain tissue loss in patients at presentation with syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet, 364(9444), 1489–1496.
Filippi, M., Preziosa, P., & Rocca, M. A. (2014). Magnetic resonance outcome measures in multiple sclerosis trials: time to rethink? Current Opinion in Neurology, 27(3), 290–299.
Filippi, M., Valsasina, P., Vacchi, L., Leavitt, V., Comi, G., Falini, A., & Rocca, M. (2015). Consistent decreased functional connectivity among the main cortical and subcortical functional networks in MS: relationship with disability and cognitive impairment. Neurology, 84(14), Supplement P6.133.
Fischl, B., & Dale, A. M. (2000). Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 97(20), 11050–11055.
Fischl, B., Sereno, M. I., & Dale, A. M. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. II: inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage, 9(2), 195–207.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., et al. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355.
Fix, J. D. (2008). Basal Ganglia and the Striatal Motor System. Neuroanatomy (Board Review Series) (4th ed.), Baltimore: Wulters Kluwer & Lippincott Wiliams & Wilkins, 274–281.
Fox, M. D., & Greicius, M. (2010). Clinical applications of resting state functional connectivity. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 19.
Fox, M. D., & Raichle, M. E. (2007). Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 8(9), 700–711.
Francis, S. J. (2004). Automatic lesion identification in MRI of multiple sclerosis patients. Montreal: McGill University.
Gallo, A., Esposito, F., Sacco, R., & Rosa, N. (2012). Visual resting-state network in relapsing- remitting MS with and without previous optic neuritis. Neurology, 79, 1458–1465.
Gean-Marton, A. D., Vezina, L. G., Marton, K. I., Stimac, G. K., Peyster, R. G., Taveras, J. M., & Davis, K. R. (1991). Abnormal corpus callosum: a sensitive and specific indicator of multiple sclerosis. Radiology, 180(1), 215–221.
Geurts, J. J., & Barkhof, F. (2008). Grey matter pathology in multiple sclerosis. The Lancet Neurology, 7(9), 841–851.
Geurts, J. J., Calabrese, M., Fisher, E., & Rudick, R. A. (2012). Measurement and clinical effect of grey matter pathology in multiple sclerosis. The Lancet Neurology, 11(12), 1082–1092.
Giorgio, A., Battaglini, M., Smith, S. M., & De Stefano, N. (2008). Brain atrophy assessment in multiple sclerosis: importance and limitations. Neuroimaging Clinics of North America, 18(4), 675–686.
Gould, I. C., Shepherd, A. M., Laurens, K. R., Cairns, M. J., Carr, V. J., & Green, M. J. (2014). Multivariate neuroanatomical classification of cognitive subtypes in schizophrenia: a support vector machine learning approach. NeuroImage: Clinical, 6, 229–236.
Greve, D. N., & Fischl, B. (2009). Accurate and robust brain image alignment using boundary-based registration. NeuroImage, 48(1), 63–72.
Hayton, T., Furby, J., Smith, K. J., Altmann, D. R., Brenner, R., Chataway, J., et al. (2009). Grey matter magnetization transfer ratio independently correlates with neurological deficit in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, 256, 427–435.
Honey, C. J., & Sporns, O. (2008). Dynamical consequences of lesions in cortical networks. Human Brain Mapping, 29(7), 802–809.
Honey, C. J., Honey, C. J., Kotter, R., Kotter, R., Breakspear, M., Breakspear, M., et al. (2007). Network structure of cerebral cortex shapes functional connectivity on multiple time scales. PNAS, 104(24), 10240–10245.
Honey, C. J., Sporns, O., Cammoun, L., Gigandet, X., Thiran, J. P., Meuli, R., & Hagmann, P. (2009). Predicting human resting-state functional connectivity from structural connectivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(6), 2035–2040.
Iwabuchi, S. J., & Kirk, I. J. (2014). Association between structural and functional connectivity in the verb generation network. Brain Connectivity, 4(3), 221–229.
Janssen, A. L., Boster, A., Patterson, B. A., Abduljalil, A., & Prakash, R. S. (2013). Resting-state functional connectivity in multiple sclerosis: an examination of group differences and individual differences. Neuropsychologia, 51(13), 2918–2929.
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2002). Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage, 17, 825–841.
Johnson, D. E. (1998). Applied multivariate methods for data analysts. Pacific Grove: Duxbury Press.
Kalkers, N. F., Polman, C. H., & Uitdehaag, B. M. J. (2001). Measuring clinical disability: the MS functional composite. Int. MSJ, 8(3), 79–87.
Karagkouni, A., Alevizos, M., & Theoharides, T. C. (2013). Effect of stress on brain inflammation and multiple sclerosis. Autoimmunity Reviews, 12(10), 947–953.
Kister, I., Bacon, T. E., Chamot, E., Salter, A. R., Cutter, G. R., Kalina, J. T., & Herbert, J. (2013). Natural history of multiple sclerosis symptoms. International Journal of MS Care, 15(3), 146–158.
Kriegeskorte, N., Simmons, W. K., Bellgowan, P. S., & Baker, C. I. (2009). Circular analysis in systems neuroscience: the dangers of double dipping. Nature Neuroscience, 12(5), 535–540.
LaConte, S., Strother, S., Cherkassky, V., Anderson, J., & Hu, X. (2005). Support vector machines for temporal classification of block design fMRI data. NeuroImage, 26(2), 317–329.
Llufriu, S., Blanco, Y., Martinez-Heras, E., Casanova-Molla, J., Gabilondo, I., Sepulveda, M., et al. (2012). Influence of corpus callosum damage on cognition and physical disability in multiple sclerosis: a multimodal study. PloS One, 7(5), 1–7.
Mahmoudi, A., Takerkart, S., Regragui, F., Boussaoud, D., & Brovelli, A. (2012). Multivoxel pattern analysis for fMRI data: A review. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2012, Article ID 961257.
Makris N, Kennedy DN, Meyer J, Worth A, Caviness VS, Jr., Seidman L, Goldstein J, Goodman J, Hoge E, Macpherson C, Tourville J, Klaveness S, Hodge SM, Melrose R, Rauch S, Kim H, Harris G, Boehland A, Glode B, Koch J, Segal E, Sonricker A, Dieterich M, Papadimitriou G, Normandin JJ, Cullen N, Boriel D, Sanders H (2004). Segmentation manual. Center for Morphometric Analysis (CMA), Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), http://www.cma.mgh.harvard.edu/manuals/segmentation/.
Mallucci, G., Peruzzotti-Jametti, L., Bernstock, J. D., & Pluchino, S. (2015). The role of immune cells, glia and neurons in white and gray matter pathology in multiple sclerosis. Progress in Neurobiology, 127, 1–22.
Marzelli, M. J., Hoeft, F., Hong, D. S., & Reiss, A. L. (2011). Neuroanatomical spatial patterns in turner syndrome. NeuroImage, 55(2), 439–447.
McDonald, I., & Compston, A. (2006). The symptoms and signs of multiple sclerosis. In A. Compston, G. Ebers, & H. Lassmann (Eds.), McAlpine’s Multiple Sclerosis (4th ed., pp. 287–346). London: Churchill Livingstone.
McNemar, Q. (1947). Note on the sampling error of the difference between correlated proportions or percentages. Psychometrika, 12(2), 153–157.
Minagar, A., Sheremata, W. A., & Weiner, W. J. (2002). Transient movement disorders and multiple sclerosis. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders, 9(2), 111–113.
Mink, J. W. (1996). The basal ganglia: focused selection and inhibition of competing motor programs. Progress in Neurobiology, 50(4), 381–425.
Mitchell, A. S., Sherman, S. M., Sommer, M. A., Mair, R. G., Vertes, R. P., & Chudasama, Y. (2014). Advances in understanding mechanisms of thalamic relays in cognition and behavior. The Journal of Neuroscience, 34(46), 15340–15346.
Mourão-Miranda, J., Bokde, A. L. W., Born, C., Hampel, H., & Stetter, M. (2005). Classifying brain states and determining the discriminating activation patterns: support vector machine on functional MRI data. NeuroImage, 28(4), 980–995.
Mourão-Miranda, J., Reinders, A., Rocha-Rego, V., Lappin, J., Rondina, J., Morgan, C., et al. (2012). Individualized prediction of illness course at the first psychotic episode: a support vector machine MRI study. Psychological Medicine, 42, 1037–1047.
Müller, K.-R., Krauledat, M., Dornhege, G., Curio, G., & Blankertz, B. (2004). Machine learning techniques for brain-computer interfaces. Biomedizinische Technik, 49, 11–22.
Nantes, J. C., Zhong, J., Holmes, S. A., Whatley, B., Narayanan, S., Lapierre, Y., & Koski, L. M. (2015). Intracortical inhibition abnormality during the remission phase of multiple sclerosis is related to upper limb dexterity and lesions. Clinical Neurophysiology. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2015.08.011.
Norman, K. A., Polyn, S. M., Detre, G. J., & Haxby, J. V. (2006). Beyond mind-reading: multi-voxel pattern analysis of fMRI data. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 10(9), 424–430.
Nygaard, G. O., Walhovd, K. B., Sowa, P., Chepkoech, J. L., Bjørnerud, A., Due-Tønnessen, P., et al. (2015). Cortical thickness and surface area relate to specific symptoms in early relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis Journal, 21(4), 402–414.
Oxford Grice, K., Vogel, K. A., Le, V., Mitchell, A., Muniz, S., & Vollmer, M. A. (2003). Adult norms for a commercially available nine hole peg test for finger dexterity. American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 57(5), 570–573.
Ozturk, A., Smith, S. A., Gordon-Lipkin, E. M., Harrison, D. M., Shiee, N., Pham, D. L., et al. (2010). MRI of the corpus callosum in multiple sclerosis: association with disability. Multiple Sclerosis (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England), 16(2), 166–177.
Pagani, E., Rocca, M. A., Gallo, A., Rovaris, M., Martinelli, V., Comi, G., & Filippi, M. (2005). Regional brain atrophy evolves differently in patients with multiple sclerosis according to clinical phenotype. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 26(2), 341–346.
Parent, A., & Hazrati, L. N. (1995). Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. I. The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Brain Research Reviews, 20(1), 91–127.
Pariyadath, V., Stein, E. A., & Ross, T. J. (2014). Machine learning classification of resting state functional connectivity predicts smoking status. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 1–10.
Ponten, S. C., Daffertshofer, A., Hillebrand, A., & Stam, C. J. (2010). The relationship between structural and functional connectivity: graph theoretical analysis of an EEG neural mass model. NeuroImage, 52(3), 985–994.
Rehme, A. K., Volz, L. J., Feis, D.-L., Bomilcar-Focke, I., Liebig, T., Eickhoff, S. B., et al. (2015). Identifying neuroimaging markers of motor disability in acute stroke by machine learning techniques. Cerebral Cortex, 25(9), 3046–3056.
Richiardi, J., Gschwind, M., Simioni, S., Annoni, J.-M., Greco, B., Hagmann, P., et al. (2012). Classifying minimally disabled multiple sclerosis patients from resting state functional connectivity. NeuroImage, 62(3), 2021–2033.
Rocca, M. A., Valsasina, P., Martinelli, V., Misci, P., Falini, A., Comi, G., & Filippi, M. (2012). Large-scale neuronal network dysfunction in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 79(14), 1449–1457.
Saeys, Y., Inza, I., & Larrañaga, P. (2007). A review of feature selection techniques in bioinformatics. Bioinformatics, 23(19), 2507–2517.
Schmierer, K., Niehaus, L., Röricht, S., & Meyer, B. U. (2000). Conduction deficits of callosal fibres in early multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 68(5), 633–638.
Schmierer, K., Irlbacher, K., Grosse, P., Röricht, S., & Meyer, B. U. (2002). Correlates of disability in multiple sclerosis detected by transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology, 59(8), 1218–1224.
Seiss, E., & Praamstra, P. (2004). The basal ganglia and inhibitory mechanisms in response selection: evidence from subliminal priming of motor responses in Parkinson’s disease. Brain, 127(2), 330–339.
Siegle, G. J., Thompson, W., Carter, C. S., Steinhauer, S. R., & Thase, M. E. (2007). Increased amygdala and decreased dorsolateral prefrontal BOLD responses in unipolar depression: related and independent features. Biological Psychiatry, 61(2), 198–209.
Smith, S. M., Zhang, Y., Jenkinson, M., Chen, J., Matthews, P. M., Federico, A., & De Stefano, N. (2002). Accurate, robust, and automated longitudinal and cross-sectional brain change analysis. NeuroImage, 17(1), 479–489.
Sripada, R. K., King, A. P., Garfinkel, S. N., Wang, X., Sripada, C. S., Welsh, R. C., & Liberzon, I. (2012). Altered resting-state amygdala functional connectivity in men with posttraumatic stress disorder. Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience, 37(4), 241–249.
Stevens, J. S., Jovanovic, T., Fani, N., Ely, T. D., Glover, E. M., Bradley, B., & Ressler, K. J. (2013). Disrupted amygdala-prefrontal functional connectivity in civilian women with posttraumatic stress disorder. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 47(10), 1469–1478.
Vapnik, V. N. (2000). The nature of statistical learning theory (2nd ed.). New York: Springer-Verlag.
Vercellino, M., Masera, S., Lorenzatti, M., Condello, C., Merola, A., Mattioda, A., et al. (2009). Demyelination, inflammation, and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis deep gray matter. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 68(5), 489–502.
Wang, X., & Tian, J. (2012). Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2012, 586246.
Wang, F., Kalmar, J. H., He, Y., Jackowski, M., Chepenik, L. G., Edmiston, E. E., et al. (2009). Functional and structural connectivity between the Perigenual anterior cingulate and amygdala in bipolar disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 66(5), 516–521.
Warren, S., Greenhill, S., & Warren, K. G. (1982). Emotional stress and the development of multiple sclerosis: case-control evidence of a relationship. Journal of Chronic Disease, 35(11), 821–831.
Xia, M., Wang, J., & He, Y. (2013). BrainNet viewer: a network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PloS One, 8(7), e68910.
Yaldizli, Ö., Glassl, S., Sturm, D., Papadopoulou, A., Gass, A., Tettenborn, B., & Putzki, N. (2011). Fatigue and progression of corpus callosum atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, 258(12), 2199–2205.
Yozbatiran, N., Baskurt, F., Baskurt, Z., Ozakbas, S., & Idiman, E. (2006). Motor assessment of upper extremity function and its relation with fatigue, cognitive function and quality of life in multiple sclerosis patients. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 246(1–2), 117–122.
Zar, J. H. (2010). Biostatistical analysis. New Jersey USA: Prentice Hall.
Zeng, L.-L., Shen, H., Liu, L., & Hu, D. (2014). Unsupervised classification of major depression using functional connectivity MRI. Human Brain Mapping, 35(4), 1630–1641.
Zito, G., Luders, E., Tomasevic, L., Lupoi, D., Toga, A. W., Thompson, P. M., et al. (2014). Inter-hemispheric functional connectivity changes with corpus callosum morphology in multiple sclerosis. Neuroscience, 266, 47–55.
Zivadinov, R., Reder, A. T., Filippi, M., Minagar, A., Stüve, O., Lassmann, H., et al. (2008). Mechanisms of action of disease-modifying agents and brain volume changes in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 71(2), 136–144.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Douglas Arnold, Dr. David Araujo, Serge Gallant, Dr. Elena Lebedeva, Afiqua Yusef, Ben Whatley, Rebecca Sussex, Haz-Edine Assemlal, Dr. Kunio Nakamura and Stanley Hum for their contributions to data collection and processing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (grant number: MOP119428), and by the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre.
Conflict of interest
Author Jidan Zhong, Author David Qixiang Chen, Author Julia C. Nantes, Author Scott A. Holmes, Author Mojgan Hodaie and Author Lisa Koski declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Board of the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital. All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig S1
(DOCX 259 kb)
Supplementary Table S1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Supplementary Table S2
(DOCX 28 kb)
Supplementary Table S3
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, J., Chen, D.Q., Nantes, J.C. et al. Combined structural and functional patterns discriminating upper limb motor disability in multiple sclerosis using multivariate approaches. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 754–768 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9551-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9551-4