Abstract
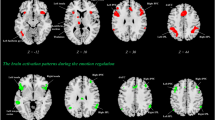
Individual differences in self-monitoring, which are the capability to adjust behavior to adapt to social situations, influence a wide range of social behaviors. However, understanding of focal differences in brain structures related to individual self-monitoring is minimal, particularly when micro and macro structures are considered simultaneously. The present study investigates the relationship between self-monitoring and brain structure in a relatively large sample of young adults. Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) revealed a significant positive correlation between self-monitoring and gray matter volume in the dorsal cingulate anterior cortex (dACC), dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), and bilateral ventral striatum (VS). Further analysis revealed a significant negative correlation between self-monitoring and white matter (WM) integrity, as indexed by fractional anisotropy (FA) in the anterior cingulum (ACG) bundle. Moreover, there was a significant positive correlation between self-monitoring and mean radius diffusion (RD). These results shed light on the structural neural basis of variation in self-monitoring.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113.
Baumeister, R. F., & Twenge, J. M. (2003). The social self. Handbook of psychology.
Beaulieu, C., & Allen, P. S. (1994). Determinants of anisotropic water diffusion in nerves. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 31(4), 394–400.
Bechara, A., Damasio, H., Tranel, D., & Anderson, S. W. (1998). Dissociation of working memory from decision making within the human prefrontal cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 18(1), 428–437.
Beer, J. S., John, O. P., Scabini, D., & Knight, R. T. (2006). Orbitofrontal cortex and social behavior: integrating self-monitoring and emotion-cognition interactions. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 18(6), 871–879.
Bland, J. M., & Altman, D. G. (1995). Multiple significance tests: the Bonferroni method. BMJ, 310(6973), 170.
Bono, J. E., & Vey, M. A. (2007). Personality and emotional performance: extraversion, neuroticism, and self-monitoring. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 12(2), 177.
Botvinick, M. M., Braver, T. S., Barch, D. M., Carter, C. S., & Cohen, J. D. (2001). Conflict monitoring and cognitive control. Psychological Review, 108(3), 624.
Brown, J. D., Collins, R. L., & Schmidt, G. W. (1988). Self-esteem and direct versus indirect forms of self-enhancement. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55(3), 445.
Cabeza, R., Grady, C. L., Nyberg, L., McIntosh, A. R., Tulving, E., Kapur, S., & Craik, F. I. (1997). Age-related differences in neural activity during memory encoding and retrieval: a positron emission tomography study. The Journal of Neuroscience, 17(1), 391–400.
Caldwell, D. F., & O’Reilly, C. A. (1982). Boundary spanning and individual performance: the impact of self-monitoring. Journal of Applied Psychology, 67(1), 124.
Carter, C. S., Macdonald, A. M., Botvinick, M., Ross, L. L., Stenger, V. A., Noll, D., & Cohen, J. D. (2000). Parsing executive processes: strategic vs. evaluative functions of the anterior cingulate cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 97(4), 1944–1948.
Carter, C. S., MacDonald, A. W., Ross, L. L., & Stenger, V. A. (2001). Anterior cingulate cortex activity and impaired self-monitoring of performance in patients with schizophrenia: an event-related fMRI study. American Journal of Psychiatry, 158(9), 1423–1428.
Catani, M., & Thiebaut de Schotten, M. (2008). A diffusion tensor imaging tractography atlas for virtual in vivo dissections. Cortex, 44(8), 1105–1132.
Cohen, J. D., Botvinick, M., & Carter, C. S. (2000). Anterior cingulate and prefrontal cortex: who’s in control? Nature Neuroscience, 3, 421–423.
Colzato, L. S., Bajo, M. T., van den Wildenberg, W., Paolieri, D., Nieuwenhuis, S., la Heij, W., & Hommel, B. (2008). How does bilingualism improve executive control? A comparison of active and reactive inhibition mechanisms. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 34(2), 302.
Croxson, P. L., Johansen-Berg, H., Behrens, T. E., Robson, M. D., Pinsk, M. A., Gross, C. G., & Rushworth, M. F. (2005). Quantitative investigation of connections of the prefrontal cortex in the human and macaque using probabilistic diffusion tractography. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25(39), 8854–8866.
Cui, Z., Zhong, S., Xu, P., He, Y., & Gong, G. (2013). PANDA: a pipeline toolbox for analyzing brain diffusion images. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 7.
D’Argembeau, A., Collette, F., van der Linden, M., Laureys, S., del Fiore, G., Degueldre, C., & Salmon, E. (2005). Self-referential reflective activity and its relationship with rest: a PET study. NeuroImage, 25(2), 616–624.
Davis, S. W., Dennis, N. A., Buchler, N. G., White, L. E., Madden, D. J., & Cabeza, R. (2009). Assessing the effects of age on long white matter tracts using diffusion tensor tractography. NeuroImage, 46(2), 530–541.
Delgado, M., Stenger, V., & Fiez, J. (2004). Motivation-dependent responses in the human caudate nucleus. Cerebral Cortex, 14(9), 1022–1030.
Devinsky, O., Morrell, M. J., & Vogt, B. A. (1995). REVIEW ARTICLE Contributions of anterior cingulate cortex to behaviour. Brain, 118(1), 279–306.
Dubois, J., Dehaene‐Lambertz, G., Perrin, M., Mangin, J. F., Cointepas, Y., Duchesnay, E., & Hertz Pannier, L. (2008). Asynchrony of the early maturation of white matter bundles in healthy infants: quantitative landmarks revealed noninvasively by diffusion tensor imaging. Human Brain Mapping, 29(1), 14–27.
Egner, T., & Hirsch, J. (2005). Cognitive control mechanisms resolve conflict through cortical amplification of task-relevant information. Nature Neuroscience, 8(12), 1784–1790.
Elliott, R., Friston, K. J., & Dolan, R. J. (2000). Dissociable neural responses in human reward systems. The Journal of Neuroscience, 20(16), 6159–6165.
Fellows, L. K., & Farah, M. J. (2005). Is anterior cingulate cortex necessary for cognitive control? Brain, 128(4), 788–796.
Fornito, A. (2004). Individual differences in anterior cingulate/paracingulate morphology are related to executive functions in healthy males. Cerebral Cortex, 14(4), 424–431. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhh004.
Fornito, A., Whittle, S., Wood, S. J., Velakoulis, D., Pantelis, C., & Yucel, M. (2006). The influence of sulcal variability on morphometry of the human anterior cingulate and paracingulate cortex. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. NeuroImage, 33(3), 843–854. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.06.061.
Gangestad, S., & Snyder, M. (1985). “ To carve nature at its joints”: on the existence of discrete classes in personality. Psychological Review, 92(3), 317.
Gangestad, S. W., & Snyder, M. (1991). Taxonomic analysis redux: some statistical considerations for testing a latent class model.
Gangestad, S. W., & Snyder, M. (2000). Self-monitoring: appraisal and reappraisal. Psychological Bulletin, 126(4), 530.
Glenn, O. A., Henry, R. G., Berman, J. I., Chang, P. C., Miller, S. P., Vigneron, D. B., & Barkovich, A. J. (2003). DTI‐based three‐dimensional tractography detects differences in the pyramidal tracts of infants and children with congenital hemiparesis. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 18(6), 641–648.
Goffman, E. (1956). Embarrassment and social organization. American Journal of Sociology, 264–271.
Good, C. D., Johnsrude, I. S., Ashburner, J., Henson, R. N., Fristen, K., & Frackowiak, R. S. (2002). A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Paper presented at the Biomedical Imaging, 2002. 5th IEEE EMBS International Summer School on.
Gusnard, D. A., & Raichle, M. E. (2001). Searching for a baseline: functional imaging and the resting human brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2(10), 685–694.
Haruno, M., Kuroda, T., Doya, K., Toyama, K., Kimura, M., Samejima, K., & Kawato, M. (2004). A neural correlate of reward-based behavioral learning in caudate nucleus: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study of a stochastic decision task. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24(7), 1660–1665.
Hayasaka, S., Phan, K. L., Liberzon, I., Worsley, K. J., & Nichols, T. E. (2004). Nonstationary cluster-size inference with random field and permutation methods. NeuroImage, 22(2), 676–687.
Heatherton, T. F. (2011a). Building a social brain. Social neuroscience: toward understanding the underpinnings of the social mind, 274-283.
Heatherton, T. F. (2011b). Neuroscience of self and self-regulation. Annual Review of Psychology, 62, 363.
Heatherton, T., & Krendi, A. (2009). Social emotion: neuroimaging. Encyclopedia of Neuroscience, 9, 35–39.
Hiscock, M., Inch, R., Jacek, C., Hiscock-Kalil, C., & Kalil, K. M. (1994). Is there a sex difference in human laterality? I. An exhaustive survey of auditory laterality studies from six neuropsychology journals. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 16(3), 423–435.
Huster, R. J., Westerhausen, R., Kreuder, F., Schweiger, E., & Wittling, W. (2007). Morphologic asymmetry of the human anterior cingulate cortex. NeuroImage, 34(3), 888–895.
Huster, R. J., Westerhausen, R., Kreuder, F., Schweiger, E., & Wittling, W. (2009). Hemispheric and gender related differences in the midcingulum bundle: a DTI study. Human Brain Mapping, 30(2), 383–391.
Huster, R. J., Enriquez-Geppert, S., Pantev, C., & Bruchmann, M. (2014). Variations in midcingulate morphology are related to ERP indices of cognitive control. Brain Structure and Function, 219(1), 49–60.
Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Woolrich, M. W., & Smith, S. M. (2012). Fsl. NeuroImage, 62(2), 782–790.
Kanai, R., & Rees, G. (2011). The structural basis of inter-individual differences in human behaviour and cognition. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(4), 231–242.
Kerns, J. G., Cohen, J. D., MacDonald, A. W., Cho, R. Y., Stenger, V. A., & Carter, C. S. (2004). Anterior cingulate conflict monitoring and adjustments in control. Science, 303(5660), 1023–1026.
Konishi, S., Nakajima, K., Uchida, I., Kikyo, H., Kameyama, M., & Miyashita, Y. (1999). Common inhibitory mechanism in human inferior prefrontal cortex revealed by event-related functional MRI. Brain, 122(5), 981–991.
Krendl, A. C., & Heatherton, T. F. (2009). Self versus Others/Self‐Regulation. Handbook of Neuroscience for the Behavioral Sciences.
Lhermitte, F. (1986). Human autonomy and the frontal lobes. Part II: patient behavior in complex and social situations: the “environmental dependency syndrome”. Annals of Neurology, 19(4), 335–343.
Li, H., Li, W., Wei, D., Chen, Q., Jackson, T., Zhang, Q., & Qiu, J. (2014). Examining brain structures associated with perceived stress in a large sample of young adults via voxel-based morphometry. NeuroImage, 92, 1–7.
MacDonald, A. W., Cohen, J. D., Stenger, V. A., & Carter, C. S. (2000). Dissociating the role of the dorsolateral prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex in cognitive control. Science, 288(5472), 1835–1838.
Mathalon, D. H., Jorgensen, K. W., Roach, B. J., & Ford, J. M. (2009). Error detection failures in schizophrenia: ERPs and FMRI. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 73(2), 109–117.
Miller, R. S., & Leary, M. R. (1992). Social sources and interactive functions of emotion: The case of embarrassment.
Moran, J. M., Lee, S. M., & Gabrieli, J. D. (2011). Dissociable neural systems supporting knowledge about human character and appearance in ourselves and others. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 23(9), 2222–2230.
Mori, S., Oishi, K., Jiang, H., Jiang, L., Li, X., Akhter, K., & Woods, R. (2008). Stereotaxic white matter atlas based on diffusion tensor imaging in an ICBM template. NeuroImage, 40(2), 570–582.
Naccache, L., Dehaene, S., Cohen, L., Habert, M.-O., Guichart-Gomez, E., Galanaud, D., & Willer, J.-C. (2005). Effortless control: executive attention and conscious feeling of mental effort are dissociable. Neuropsychologia, 43(9), 1318–1328.
Northoff, G., & Bermpohl, F. (2004). Cortical midline structures and the self. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8(3), 102–107.
Northoff, G., Heinzel, A., de Greck, M., Bermpohl, F., Dobrowolny, H., & Panksepp, J. (2006). Self-referential processing in our brain—a meta-analysis of imaging studies on the self. NeuroImage, 31(1), 440–457.
Perrine, N. E., & Aloise-Young, P. A. (2004). The role of self-monitoring in adolescents’ susceptibility to passive peer pressure. Personality and Individual Differences, 37(8), 1701–1716.
Posner, M. I., & DiGirolamo, G. J. (1998). Executive attention: conflict, target detection, and cognitive control.
Prigatano, G. P. (1991). Disturbances of self-awareness of deficit after traumatic brain injury. Awareness of deficit after brain injury: Clinical and theoretical issues, 111–126.
Ridgway, G. R., Omar, R., Ourselin, S., Hill, D. L., Warren, J. D., & Fox, N. C. (2009). Issues with threshold masking in voxel-based morphometry of atrophied brains. NeuroImage, 44(1), 99–111.
Rushworth, M., Behrens, T., Rudebeck, P., & Walton, M. (2007). Contrasting roles for cingulate and orbitofrontal cortex in decisions and social behaviour. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11(4), 168–176.
Schlenker, B. R., & Leary, M. R. (1982). Audiences’ reactions to self-enhancing, self-denigrating, and accurate self-presentations. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 18(1), 89–104.
Schmaal, L., Joos, L., Koeleman, M., Veltman, D. J., van den Brink, W., & Goudriaan, A. E. (2013). Effects of modafinil on neural correlates of response inhibition in alcohol-dependent patients. Biological Psychiatry, 73(3), 211–218.
Segerstrom, S. C., Tsao, J. C., Alden, L. E., & Craske, M. G. (2000). Worry and rumination: repetitive thought as a concomitant and predictor of negative mood. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 24(6), 671–688.
Sekiguchi, A., Sugiura, M., Taki, Y., Kotozaki, Y., Nouchi, R., Takeuchi, H., & Miyauchi, C. M. (2014). White matter microstructural changes as vulnerability factors and acquired signs of post-earthquake distress. PloS One, 9(1), e83967.
Sharp, M. J., & Getz, J. G. (1996). Substance use as impression management. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 22(1), 60–67.
Smith, E. E., & Jonides, J. (1999). Storage and executive processes in the frontal lobes. Science, 283(5408), 1657–1661.
Snyder, M. (1974). Self-monitoring of expressive behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 30(4), 526.
Snyder, M. (1979). Self-monitoring processes 1. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 12, 85.
Snyder, M. (1987). Public appearances, private realities: The psychology of self-monitoring. WH Freeman/Times Books/Henry Holt & Co.
Song, S.-K., Sun, S.-W., Ramsbottom, M. J., Chang, C., Russell, J., & Cross, A. H. (2002). Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. NeuroImage, 17(3), 1429–1436.
Song, S.-K., Sun, S.-W., Ju, W.-K., Lin, S.-J., Cross, A. H., & Neufeld, A. H. (2003). Diffusion tensor imaging detects and differentiates axon and myelin degeneration in mouse optic nerve after retinal ischemia. NeuroImage, 20(3), 1714–1722.
Song, S.-K., Yoshino, J., Le, T. Q., Lin, S.-J., Sun, S.-W., Cross, A. H., & Armstrong, R. C. (2005). Demyelination increases radial diffusivity in corpus callosum of mouse brain. NeuroImage, 26(1), 132–140.
Sporns, O., Tononi, G., & Kötter, R. (2005). The human connectome: a structural description of the human brain. PLoS Computational Biology, 1(4), e42.
Takei, K., Yamasue, H., Abe, O., Yamada, H., Inoue, H., Suga, M., & Kasai, K. (2009). Structural disruption of the dorsal cingulum bundle is associated with impaired Stroop performance in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 114(1), 119–127.
Takeuchi, H., Taki, Y., Sekiguchi, A., Hashizume, H., Nouchi, R., Sassa, Y., Iizuka, K. (2015). Mean diffusivity of globus pallidus associated with verbal creativity measured by divergent thinking and creativity‐related temperaments in young healthy adults. Human brain mapping.
Wei, D., Yang, J., Li, W., Wang, K., Zhang, Q., & Qiu, J. (2014). Increased resting functional connectivity of the medial prefrontal cortex in creativity by means of cognitive stimulation. Cortex, 51, 92–102.
Weissman, D., Giesbrecht, B., Song, A., Mangun, G., & Woldorff, M. (2003). Conflict monitoring in the human anterior cingulate cortex during selective attention to global and local object features. NeuroImage, 19(4), 1361–1368.
Whittle, S., Allen, N. B., Fornito, A., Lubman, D. I., Simmons, J. G., Pantelis, C., & Yucel, M. (2009). Variations in cortical folding patterns are related to individual differences in temperament. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. Psychiatry Research, 172(1), 68–74. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2008.06.005.
Zhu, X., Wang, X., Xiao, J., Liao, J., Zhong, M., Wang, W., & Yao, S. (2012). Evidence of a dissociation pattern in resting-state default mode network connectivity in first-episode, treatment-naive major depression patients. Biological psychiatry, 71, 611–617.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31070900; 30800293; 30970892; 31170983), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (2011) by the Ministry of Education, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SWU1209101), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (2012 M510098), the Research Funds for Southwest University (SWU09103), the Key Discipline Fund of National 211 Project (NSKD11007), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (swu1209101), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (2011) by the Ministry of Education, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (2012 M510098), and the postgraduate Innovation Foundation of Science and Technology of Southwest University(kb2011002).
Conflict of Interest
Junyi Yang, Xue Tian, Dongtao Wei, Huijuan Liu, Qinglin Zhang, KangchengWang, Qunlin Chen, and Jiang Qiu declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of theresponsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the HelsinkiDeclaration of 1975, and the applicable revisions at the time of the investigation. Informed consentwas obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Junyi Yang and Xue Tian contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Tian, X., Wei, D. et al. Macro and micro structures in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex contribute to individual differences in self-monitoring. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 477–485 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9398-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9398-0